Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Lien
Încărcat de
IZZAH ZAHIN100%(3)100% au considerat acest document util (3 voturi)
932 vizualizări7 paginiLien
Drepturi de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
DOC, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentLien
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOC, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
100%(3)100% au considerat acest document util (3 voturi)
932 vizualizări7 paginiLien
Încărcat de
IZZAH ZAHINLien
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOC, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 7
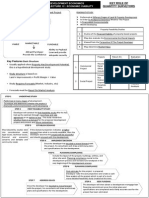
SECURITY DEALING LIENS ( S.
281 of NLC 1965)
Definition:
Lien is the act of depositing something valuable to the amount owed to the
person who holds the property. There must be an intention to pledge that
property. The person who holds the property has the right to that property
until payment is settled.
Lien occurs where there is no formal instrument of charge but the IDT has
been deposited as security for the loan.
Halsbury Laws of England (Vol.19 at p.2) defines liens as:
Lien in its primary sense is a right in one man to retain that, which is in his
possession belonging to another man until certain demands on the person in
possession are satisfied
In Palaniappa Chetty v Dupire Brothers & Anor. [1919] 1 FMSLR 370,
Earnshaw, J.C., FMS Court of Appeal had said that the meaning of lien is
said to have been derived through French from Latin that is ligo, ligamen is
that of binding or tying or securing something. A lien is one and a special
form of security. In fact security is the genus of which lien is a specie.
Osborn D!"on#r$% The right to hold the property of another as security for
the performance of an obligation
Thus a lien is a dealing, which gives rise to a non-registrable interest in land,
lease or undivided share
S. 281 provides that:
Any proprietor or lessee for the time being may deposit with any other
person or body as security for a loan, his issue document or title or duplicate
lease
Types of Lien
1
st
: E&'"#b() L)n when IDT or duplicate lease has been deposited to the
bank/lender
1
2
nd
: S"#"'"or$ L)n Bank/lender, as a lien-holder enters a LH under !" ##$ usin%
&or' 1(D
R)*)+$ f (o#n s no" ,#+-
!" 2)1 *2+ : 1" ,btain -ud%e'ent b. ci/il action *pro/e the debt+, then
2" 0ppl. to court 1or an order 1or sale *like 1oreclosure+
Note : !ee connection between !s" 2)1 and ##$ *1+" an an. person who has the IDT
lod%e a LH2
./o !#n !r)#") # ()n-
!" 2)1 *1+ : 30n. proprietor or lessee4
5e%istered 6roprietor or Lessee or o-6roprietor
7: How i1 the proprietor deposit the IDT to the lender as securit. 1or a loan2 0 loan does
not 'ean the proprietor8s loan" It could be so'e one else loan"
9ote: wordin% o1 s" 2)1 4:an. person:4
In Peter PChient v Ramasamy Chetty (9) 3 FMSLR 220 :;atson <: proprietor onl.
since he is the onl. person that entitled to ha/e the custod. o1 the IDT
!ee Perwira Hai !an" (M) !h#$ % Loo & Sons Rea'ty S$ !$ (No$ () )(99*+ 3 ML,
-09. (No$2) )(99*+ 3 ML, -2(
./o !#n b) "/) L)n 0o(+)r-
!" 2)1 *1+ : 30n. other person or bod.4
6ersons listed in !s"=# > 2$? *#+ "
onsider also !"=##B
S'b1)!" *#"")r of ()n
;hat can be the sub-ect 'atter o1 lien would be alienated land or lease o1 land" 0 lien
'a. be e11ected o/er an undi/ided share" This 'eans that a co-proprietor in an undi/ided
share 'a. e11ect lien o/er his share in land as 'entioned in !" #=# *@+ o1 9L 1(@?"
./$ ()n-
2
The concept o1 lien is an eAception 1ro' the %eneral principles o1 re%istration o1 title"
This is because a lien is a dealin% which %i/es rise to a non-re%istrable interest *0s
hi%hli%hted in !" 2$@ *2+ *b++
9on-5e%istrable Interest 9o special instru'ent *&or'+ 1or a lien"
Howe/er, as 'entioned b. !B Cok such unre%istrable interest co/ered b. a lien are
reco%niDed b. the 9L as bein% entitled to protection /ia the ca/eat s.ste'
In order 1or a lien to be reco%niDed under the 9L, the lien-holder 'ust under !"2)1 *1+
*a+ *b+ enter a lien-holder8s ca/eat, which will restrain other dealin%s on the land"
0 lien is an eAception especiall. 'ade 1or the purpose o1 enablin% business 'en to raise
'one. on loan speedil." This is because a lien can be created 1aster than a re%istered
char%e"
o'parin% with the creation o1 char%e
&"1@0 si%ned b. both parties > 'ust be attested b. law.ers properl. eAecuted
Eust be sta'ped with the appropriate sta'p dut. *01ter ,ct 1(F), propert. 'ust
be /alued 1
st
be1ore instru'ent can be sta'ped" It takes about # 'onths+
Gnlike Lien, to create it is /er. eas., where a lien-holder -ust needs to 1ill in &or' 1(D >
lod%e LH"
In practice : Lien is created while pendin% the ad-udication > sta'pin% o1 the 'e'o" o1
trans1er
!ee: N/an 0hon/ v !amah t Pa"eh )(931+ ML, (*
6rinciple % 5i%ht to enter ca/eat passed on the trans1eree
!ee : Stan#ar# Chartere# !an" v 2a3 Sin/ 2o"e & 4rs )(959+2 ML, -9
6rinciple : 6lainti11 who deposited the IDT acHuire an eHuitable interest" It is not been
a11ected in the absence o1 a ca/eat" He has a better clai'"
Dff)r)n!) b)"2))n # !/#r3) 4 # ()n
1" To create a char%e" 9eed to use &or' 1@0
To create lien" 9o special 1or'" But Lien Holder 'ust lod%e ca/eat in &or' 1(D
2" 5e'ed." &or char%e !ale and/or takin% possession
#
&or Lien-Holder 6ro/e debt b. ci/il action, then %et re'ed. o1 sale
#" har%e 'ore co'plicated
Lien - si'ple/easier *!i'pler 1or' o1 securit.+
=" De1ault: char%e: ,,! > possession" De1ault: Lien: ,,! onl.
ase : In 0)#, 0'#" R'bb)r Co S+n 5/+. 6 U.O.5#n7 L"+.8 9's"!) LC 6o/r#/
acknowled%ed that there is a distinction between a lien > a char%e
!ee !B Cok8s article on the ad/anta%es o1 a lien o/er char%es" 0t pa%e l/i
C/#r#!")rs"!s of ()n
a" Borrower and lender
b"Deposit o1 IDT/duplicate lease
c"Intention to create lien
d"!ecurit. 1or a loan
Paramoo v 6eno Lt# )(9*5+ 2 ML, 230
Principle: The Plaintiffs lien has a priority over the 2
nd
defendants claim
because there was an intention to create a lien from the fact
gathered by the court & as the IDT has been deposited to the lender
as security for loan & not for any other purposes.
However : The element of intention is not satisfied if possession of the iDT
was obtained through fraud or misrepresentation & the deposit of
title as security was never authorised by the registered proprietor
Other case: Nallamal & Anor. V Karrupannan & Anor. [1993] 3 MLJ
476
In Mercantile Bank v The Official Assignee of the Property of How
Han The [1969] 2 MLJ 196
Raja Azlan Shah J. : You can apply for LHC at anytime as long as you have
the title of the property
There is no specific duration as soon as possible
=
However failure to enter a LHC will not necessarily deprive the lender of a
right to a lien in equity so long as the prerequisite intention to create a lien is
complied with & deposit of the title to the land are present.
S. 206 (3) of NLC recognize the existence of a right to an equitable interest
under the contract in question
Held : Though registration of a LHC is essential for a valid statutory lien, the
court can still gives effect to equitable rights existing between the parties.
Mercantile Bank had an equitable right to a lien.
At p. 197 Raja Azlan Shah J : As the interest is equitable & non-statutory
in case of two conflicting equities, the 1
st
in time prevails.
General view : This retention of the IDT gives priority to LHC.
Raja Azlan Shah : The registration of the caveat does not confer priority nor
does it create new right. It temporarily protects such rights in anticipation of
legal proceeding
In case of conflicting between 2 equities; a lender who is prior in time & with
whom the title has been deposited will not lose his priority merely on account
of his failure to enter a LHC
In Standard Chartered Bank v Yap Sin Yoke & Ors [1987] 2 MLJ 49
This case dealt with an unregistered charge which the High Court accepted
as a lien in equity. According to Justice Lamin, an equitable lien is not
affected by the absence of a caveat
The learned judge followed Raja Azlan Shahs decision in Mercantile Bank
Ltds case, where he held: The registration of a caveat does not confer
priority nor does it create new rights
The court also held in this case that an equitable lien holder has priority over
a judgment creditor who had subsequently lodged a Prohibitory Order (PO)
As a lien holder, the chargee may lodge a caveat to protect his interest. As
held in Standard Chartered Bank v Yap Seng Yoke & Ors (1989) 2 MLJ
?
49, a lien holder may enter a caveat to perfect the security at any time. Thus
protected, the lien holder may seek remedy under the NLC as his interest is a
security interest within cognizance of the NLC and does not depend on
contractual relief.
In another case :
Heap Huat Rubber Co. Sdn. Bhd. V United Overseas Bank Ltd [1992]
3 CLJ 1589
Held : Until LHC is entered, no lien was created or could arise & at the time
the lien created there were no restriction on the creation of a lien on non-
citizen. A valid lien had come into existence
Principle: The entry of LHC need not be made contemporaneously with the
deposit of the IDT
However in more recent case:
Perwira Habib Bank Msia Bhd. V Tin Siang Sdn Bhd & Ors [1992] 4
CLJ 1875; [1995] 4 CLJ 619
This case dealt with the application to remove a LHC on the ground that the
IDT was deposited merely for safe keeping.
The application was dismissed by Justice LC Vohrah because evidence
showed that the title was deposited to secure a loan.
Held : The Plaintiff was a lien holder & entitled to a lien once the title be
deposited though the application to sell the land was opposed because no
agreement between lender & borrower that LHC be entered
High Court : LHC declared invalid by the High Court & ordered the
Appellant return the IDT
Determination of lien: S 331
a. withdrawal of the caveat by the lender
b. Upon payment of the sum due
c. Upon order of sale by the court under s. 281(2)
@
d. Upon order of court because it had wrongfully been entered
F
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Discharge of ContractDocument37 paginiDischarge of ContractSunita VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Secured Transactions OutlineDocument31 paginiSecured Transactions Outlinekurt100% (1)
- California High Tech Trusts Attornys Can Barely UnderstandDocument129 paginiCalifornia High Tech Trusts Attornys Can Barely Understandtraderash1020Încă nu există evaluări
- EFA Agreement Early TerminationDocument2 paginiEFA Agreement Early TerminationKhoa PhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Estate Planning Basics732Document7 paginiEstate Planning Basics732anon_909251819Încă nu există evaluări
- Mechanic's Liens: (Reprinted With Permission From NACM's Manual of Credit and Commercial Laws, 104 Edition)Document95 paginiMechanic's Liens: (Reprinted With Permission From NACM's Manual of Credit and Commercial Laws, 104 Edition)Lenza McelrathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Probate A Practical GuideDocument16 paginiProbate A Practical GuideAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Latin Legal Phrases, Terms and Maxims as Applied by the Malaysian CourtsDe la EverandLatin Legal Phrases, Terms and Maxims as Applied by the Malaysian CourtsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notice of Human Rights Violations - 20170607 - 0001Document4 paginiNotice of Human Rights Violations - 20170607 - 0001PriyaSiranELÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Real Property Interests and DeedsDocument9 paginiUnderstanding Real Property Interests and DeedsLisa Stinocher OHanlon100% (1)
- Distinguishing private and public nuisance in a construction disputeDocument21 paginiDistinguishing private and public nuisance in a construction disputeChinYeeTuck100% (1)
- Deed of Assignment Transfer RightsDocument2 paginiDeed of Assignment Transfer RightsRowenaYbanezMercado67% (9)
- Essay On MortgagesDocument2 paginiEssay On MortgagesViorel Mihai Mitrana100% (1)
- Trust Financial ManagementDocument26 paginiTrust Financial ManagementCalvince Ouma100% (1)
- North Carolina Mortgages and Deed of Trust Statutes - Chapter 45Document61 paginiNorth Carolina Mortgages and Deed of Trust Statutes - Chapter 45ForeclosureGate.org LibraryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Private CaveatDocument1 paginăPrivate CaveatIZZAH ZAHIN100% (2)
- Security Interest AppendixDocument17 paginiSecurity Interest Appendixobama mammaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanic LienDocument7 paginiMechanic LienGenovieveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Security Agreement ReviewDocument3 paginiSecurity Agreement ReviewStephen MonaghanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bank of New York Mellon V. DeaneDocument15 paginiBank of New York Mellon V. DeaneMortgage Compliance Investigators100% (1)
- Land Development As InvestmentDocument2 paginiLand Development As InvestmentIZZAH ZAHIN100% (1)
- Notes Land Titles and DeedsDocument5 paginiNotes Land Titles and DeedsMaria Fiona Duran MerquitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Letter of InstructionDocument3 paginiLetter of InstructionKenneth Vercammen, Esq.Încă nu există evaluări
- Assignment of Action, Chose in ActionDocument10 paginiAssignment of Action, Chose in ActionMalcolm WalkerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steel Structures Design and Behavior 5th Edition Salmon Solutions ManualDocument17 paginiSteel Structures Design and Behavior 5th Edition Salmon Solutions Manualbrianpottsmdodcibnwmxr100% (11)
- 59 CJS MortgagesDocument1 pagină59 CJS MortgagesrdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adverse PossessionDocument34 paginiAdverse Possessionkorkor hammondÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 3 - Lien ProceduresDocument12 paginiAssignment 3 - Lien Proceduresrajnishatpec100% (2)
- Chapter 7 Vs Chapter 13 BankruptcyDocument2 paginiChapter 7 Vs Chapter 13 BankruptcyInternalJoy100% (1)
- Adverse PosessionDocument6 paginiAdverse Posessionhifsa waheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Remove Trustees Who Have Lost CapacityDocument11 paginiHow To Remove Trustees Who Have Lost Capacityweast3047100% (4)
- Methods and Modes of Terminating ContractsDocument83 paginiMethods and Modes of Terminating ContractsNusrat ShatyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Negotiable InstrumentsDocument26 paginiNegotiable InstrumentsChabudi100% (3)
- Understanding Cause of ActionDocument22 paginiUnderstanding Cause of Actionazreeariffin100% (1)
- Washington D.C. Commercial Lease Agreement: Page 1 of 10Document10 paginiWashington D.C. Commercial Lease Agreement: Page 1 of 10Jose KempÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Uniform Bonding Code - (UBC)Document45 paginiThe Uniform Bonding Code - (UBC)honsoloÎncă nu există evaluări
- DEED OF ASSUMPTION OF CHATTEL MORTGAGE BlankDocument2 paginiDEED OF ASSUMPTION OF CHATTEL MORTGAGE Blankmarc marc100% (1)
- Land Titles and Deeds ReviewerDocument26 paginiLand Titles and Deeds ReviewerAd Altiora TendoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Checklist and Steps For Land Title TransferDocument3 paginiChecklist and Steps For Land Title TransferBeth de Vera100% (1)
- Super Injunction Report 20052011Document112 paginiSuper Injunction Report 20052011IndexOnCensorshipÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER 1 - 3 Q Flashcards - QuizletDocument17 paginiCHAPTER 1 - 3 Q Flashcards - Quizletrochacold100% (1)
- Doctrines on property rights and land ownershipDocument11 paginiDoctrines on property rights and land ownershipmaica_prudenteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bases Del Entrenamiento Deportivo Zhelyazkov Tsvetan (2018)Document543 paginiBases Del Entrenamiento Deportivo Zhelyazkov Tsvetan (2018)Tifany QuinteroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subject 15.1 Due Diligence & Role of The Office of The Assessor (Tax Mapping / Tax Declaration)Document8 paginiSubject 15.1 Due Diligence & Role of The Office of The Assessor (Tax Mapping / Tax Declaration)Junjie TebreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deed of Extrajudicial Settlement of The Estate Waiver of RightsDocument2 paginiDeed of Extrajudicial Settlement of The Estate Waiver of RightsBabylen BahalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Repair and Maintenance Agreement DAR1Document2 paginiRepair and Maintenance Agreement DAR1michael ሚካኤል adinew አድነው100% (1)
- Vizconde Vs CADocument1 paginăVizconde Vs CAKristine JoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Landti Bar QsDocument5 paginiLandti Bar QsMikkaEllaAnclaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agency EssentialsDocument31 paginiAgency EssentialsMaryam MalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Clog On The Equity of RedemptDocument27 paginiA Clog On The Equity of Redemptamit dipankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deed of Donation - AdvancedDocument3 paginiDeed of Donation - AdvancedErin GamerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Judgment Debtor Summons (JDS)Document9 paginiJudgment Debtor Summons (JDS)IZZAH ZAHIN100% (27)
- Tenancy Aggrement Taska (No.2-4R) 2011Document13 paginiTenancy Aggrement Taska (No.2-4R) 2011wadi8450% (2)
- PCI Leasing not barred from collecting unpaid balanceDocument2 paginiPCI Leasing not barred from collecting unpaid balancePaolo Brillantes0% (1)
- I Concurrent Estates Attack SheetDocument14 paginiI Concurrent Estates Attack SheetDrew RymerÎncă nu există evaluări
- ESTATE ADMINISTRATOR ACTION BEFORE PROBATEDocument1 paginăESTATE ADMINISTRATOR ACTION BEFORE PROBATEKhairun NisaazwaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Bankruptcy Proof of Claim Rules Now in Effect (b10) Dec 2011Document7 paginiNew Bankruptcy Proof of Claim Rules Now in Effect (b10) Dec 201183jjmackÎncă nu există evaluări
- Letter To Lender TemplateDocument1 paginăLetter To Lender TemplateCarrieonic100% (1)
- RESPADocument55 paginiRESPACarrieonicÎncă nu există evaluări
- William H. Brine, JR., Administrator DBN of The Estate of Francis H. Swift v. Paine Webber, Jackson & Curtis, Incorporated, 745 F.2d 100, 1st Cir. (1984)Document8 paginiWilliam H. Brine, JR., Administrator DBN of The Estate of Francis H. Swift v. Paine Webber, Jackson & Curtis, Incorporated, 745 F.2d 100, 1st Cir. (1984)Scribd Government DocsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Void, Voidable and Enforceable Contracts by SYAFINAZ IDRUSDocument39 paginiVoid, Voidable and Enforceable Contracts by SYAFINAZ IDRUSInaz IdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Affidavit of Fact: AffiantDocument1 paginăAffidavit of Fact: Affiantc4382543rÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contracts and Lease On 310 GarfieldDocument144 paginiContracts and Lease On 310 GarfieldMegan BantaÎncă nu există evaluări
- American Court Structure and Jurisdiction OverviewDocument67 paginiAmerican Court Structure and Jurisdiction Overviewmjwyatt01Încă nu există evaluări
- Surety BondDocument3 paginiSurety BondRenz Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Law of Contract - II GuaranteeDocument36 paginiLaw of Contract - II GuaranteePayal ShuklaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Municipal Bond Risk DisclosureDocument2 paginiMunicipal Bond Risk Disclosuretonyw87dÎncă nu există evaluări
- Breach of Contract CasesDocument2 paginiBreach of Contract CasesshfulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standardized Compromise and Write-Off ProceduresDocument3 paginiStandardized Compromise and Write-Off ProceduresscarsunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contracts Notes. 2.27.2013Document14 paginiContracts Notes. 2.27.2013Jairus AntonyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mortgage Loan Origination AgreementDocument3 paginiMortgage Loan Origination Agreementnolandpark100% (1)
- Spousal Unity DoctrineDocument2 paginiSpousal Unity DoctrineRESEARCHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Remedies On Rejection of GoodsDocument14 paginiRemedies On Rejection of GoodsArasan ArasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notice of LevyDocument2 paginiNotice of LevyEliot Houman100% (1)
- Holton v. Reed, 193 F.2d 390, 10th Cir. (1951)Document7 paginiHolton v. Reed, 193 F.2d 390, 10th Cir. (1951)Scribd Government DocsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drafting Dispute Resolution Clauses - A Practical GuideDocument134 paginiDrafting Dispute Resolution Clauses - A Practical GuidepeucelleÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Terms Lien of SharesDocument6 paginiThe Terms Lien of SharesAmit MakwanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contract To Purchase Agricultural LandDocument18 paginiContract To Purchase Agricultural LandavsharikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Credit TransDocument34 paginiCredit TransBasil IskÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1st Lec DigestDocument3 pagini1st Lec DigestKrissaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Outline-Law of Evidence IDocument72 paginiCourse Outline-Law of Evidence IIZZAH ZAHIN100% (1)
- Course Outline: International Islamic University MalaysiaDocument7 paginiCourse Outline: International Islamic University MalaysiaJose Abraham HadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evidence - Tips Sample QA 5Document3 paginiEvidence - Tips Sample QA 5IZZAH ZAHINÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jurisprudence - JusticeDocument11 paginiJurisprudence - JusticeIZZAH ZAHIN100% (2)
- Land LawDocument16 paginiLand LawIZZAH ZAHINÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economic ViabilityDocument3 paginiEconomic ViabilityIZZAH ZAHINÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evidence & Procedure in Shariah Court - TrialDocument2 paginiEvidence & Procedure in Shariah Court - TrialIZZAH ZAHINÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evidence-Tips Sample QA 4Document3 paginiEvidence-Tips Sample QA 4IZZAH ZAHIN100% (2)
- Evidence Law 2Document9 paginiEvidence Law 2IZZAH ZAHIN100% (1)
- Development ControlDocument1 paginăDevelopment ControlIZZAH ZAHINÎncă nu există evaluări
- Company LawDocument13 paginiCompany LawIZZAH ZAHINÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bay' At-Tawarruq Vs Bay' Al-InahDocument3 paginiBay' At-Tawarruq Vs Bay' Al-InahIZZAH ZAHINÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shariah Governance FrameworkDocument2 paginiShariah Governance FrameworkIZZAH ZAHINÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shariah LawyerDocument29 paginiShariah LawyerMuhammad Farid Ariffin100% (2)
- Land Law II - Course OutlineDocument30 paginiLand Law II - Course OutlineIZZAH ZAHINÎncă nu există evaluări
- Commercial LawDocument9 paginiCommercial LawIZZAH ZAHINÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management CorporationDocument2 paginiManagement CorporationIZZAH ZAHINÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial Questions 2012Document11 paginiTutorial Questions 2012IZZAH ZAHINÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jurisprudence - JusticeDocument11 paginiJurisprudence - JusticeIZZAH ZAHIN100% (2)
- LL II - Caveats Compare & ContrastDocument3 paginiLL II - Caveats Compare & ContrastIZZAH ZAHINÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strata TitlesDocument1 paginăStrata TitlesIZZAH ZAHINÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adverse PossessionDocument3 paginiAdverse PossessionIZZAH ZAHINÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chart:Remedies of ChargeDocument1 paginăChart:Remedies of ChargeIZZAH ZAHINÎncă nu există evaluări
- LL II - Chart - Remedies of Charge OOSDocument1 paginăLL II - Chart - Remedies of Charge OOSIZZAH ZAHINÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jual JanjiDocument11 paginiJual JanjiIZZAH ZAHIN100% (7)
- Restraints of DealingsDocument1 paginăRestraints of DealingsIZZAH ZAHIN100% (1)
- Prohibitory OrderDocument1 paginăProhibitory OrderIZZAH ZAHIN100% (1)
- EASEMENT Acquisition and EstablishmentDocument16 paginiEASEMENT Acquisition and EstablishmentElbert TramsÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Mexican Trust (fideicomiso) ExplainedDocument6 paginiThe Mexican Trust (fideicomiso) Explainedartsan3Încă nu există evaluări
- Deed of SaleDocument5 paginiDeed of SaleCha VergaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deed of Partition Agreement FormatDocument2 paginiDeed of Partition Agreement FormatAnonymous DzdOFkÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1Document5 pagini1Ammar MustaqimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edpm LeaseDocument2 paginiEdpm LeaseKALI LAWRENCEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agreement For Letting Furnished Dwelling House or Flat On Short Period TenancyDocument3 paginiAgreement For Letting Furnished Dwelling House or Flat On Short Period TenancySiddharth ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Special Power of Attorney: Day of - at Quezon CityDocument2 paginiSpecial Power of Attorney: Day of - at Quezon CityPLO Printing 2Încă nu există evaluări
- Deed of Sale of A Real PropertyDocument6 paginiDeed of Sale of A Real Propertyoshin saysonÎncă nu există evaluări
- GazzeteDocument48 paginiGazzetepawatamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 25 OvesDocument5 paginiAssignment 25 OvesfaarehaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DPC ReportDocument3 paginiDPC ReportSanskruti AwareÎncă nu există evaluări