Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
(Culture) Tribals of India - Classification, Geographical Spread - For GS Mains Paper I (Culture + Human Geography) Mrunal
Încărcat de
Bhaiya KamalenduDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
(Culture) Tribals of India - Classification, Geographical Spread - For GS Mains Paper I (Culture + Human Geography) Mrunal
Încărcat de
Bhaiya KamalenduDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
3/7/13
[Culture] Tribals of India: Classification, Geographical Spread For GS Mains Paper I (Culture + Human Geography) Mrunal
[Culture] Tribals of India: Classification, Geographical Spread For GS Mains Paper I (Culture + Human Geography)
This article is important for GS (Mains) Paper I : Culture + Human Geography This article contains truckload of 2 markers, although it is not possible to prepare all of them but do as many as you can. This article wont help you, unless you keep looking at a Map of india while reading it. This article is created using content from IGNOUs Tourism studies course. Some data is outdated- new states have been created. Keep the map ready and make corrections accordingly.
Classification A: Based on Ethnicity Group I: Negritos Group II: The Mongoloid Group III: Mediterranean (Dravidians) Classification B: Based on Location Zone 1: Northern and North-Eastern Himachal Pradesh Uttar Pradesh Zone II: Central Bihar Rajasthan Gujarat and Maharashtra Madhya Pradesh West Bengal Orissa Zone III: South-Western Zone IV: Scattered Tribes of Andaman and Nicobar
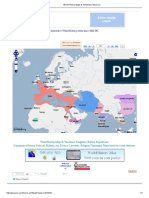
First See this Diagram
mrunal.org/2012/07/culture-tribalsp1.html
1/7
3/7/13
[Culture] Tribals of India: Classification, Geographical Spread For GS Mains Paper I (Culture + Human Geography) Mrunal
Classification A: Based on Ethnicity Group I: Negritos
are believed to be the earliest inhabitants of the Indian peninsula who were unable to defend themselves and were gradually forced to recede before the invading hordes of Indo-Aryans, Mongoloids, etc. coming from the North-West and North-East. These tribes were not only superior to them in numerical strength but also in mechanical equipment. These tribals took shelter in the mountains and thick forests where a considerable number of them are still found and have been estimated to be about ten million. Those who were left behind in the plains gradually disappeared either by absorption or by acculturation. Some tracts of them are still found among the tribals of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands known as the Onne, the Great Andamanese, the Sentinelese and the Jarwas also in Kerala among the Kadars, the Irulars and the Paniyans. identifying features are dark skin, curly hair, broad nose and medium height.
Group II: The Mongoloid
represented by the tribal people of sub- Himalayan region. They may be divided into two categories Mongoloid Subcategories 1. Palaeo Mongoloids represented by the tribes living in Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland and Manipur. Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh. They are believed to have migrated from Tibet. They have typical eyes and facial features. They speak Mon-Khmer and Tibeto-Burmese dialects.
2. Tibeto -Mongoloids
Group III: Mediterranean (Dravidians)
They form bulk of the tribal population and are generally known as the Dravidians. Dravidian is, however, the name of the language group spoken by these people and has no ethnic significance. Location The tribes believed to be belonging to the Dravidian race are found in the Chhotanagpur Plateau, Rajmahal Hills region, Aravalli ranges, Central Vindhyachal, Deccan Plateau region and Nilgiri Hills. Dravidian language still survives not only in Southern India where Tamil, Telugu, Malayalam and Kannada are its leading representatives, but also in Central India where its traces are found in the dialects spoken by the Oraons, Gonds, Mundas, Malers, Khonds and other tribes. The Dravidians are presumed to be of two stocks, Dravidian Sub-Categories Characteristics Kolarians speak a dialect called Mundari examples: Mundas, Santhals, Oraons and other tribes inhabiting Chhotanagpur Plateau region Speak dailects of Tamil, Telugu, Malayalam and Kannada Gonds, Kondhs, and other tribes found in Central Vindhyachal and the Deccan Plateau regions.
Dravidian proper
Classification B: Based on Location
Tribal population of India is spread all over the country. However, in Haryana, Punjab, Chandigarh, Delhi, Goa and Pondicherry there exist very little tribal population. The rest of the states and union territories possess fairly good number of tribal population Madhya Pradesh registers the largest number of tribes (73) followed by Arunachal Pradesh (62), Orissa (56), Maharashtra (52), Andhra Pradesh (43). In India there is almost a continuous belt of high tribal concentration starting from the Western coast from Thane district in
mrunal.org/2012/07/culture-tribalsp1.html 2/7
3/7/13
In India there is almost a continuous belt of high tribal concentration starting from the Western coast from Thane district in Maharashtra passing through Surat and Dang districts in Gujarat to Mayurbhanj in Orissa on the Eastern coast and Bihar. The chief concentration is in Dhulia in Maharashtra; West Nimar, Betul, Chhindwara, Seeni, Mandla, Shandol and Sarguja in Madhya Pradesh; and Ranchi, Santhal Parganas_ and Singhbhum district in Bihar. Another long range of tribal belt is found in the North-East spreading over Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Meghalaya, Mizo Hills, United Mikir and North Cachar Hills of Assam and hilly regions of Manipur and Tripura. These belts are also linked up by a chain of pockets of tribal concentration at Taluk or sub-divisional levels. Tribal concentrations are also found in Bastar district of Madhya Pradesh, Korapur, Bauch- Khandenals, and Agency tracts of Orissa and Andhra Pradesh which are linked up with the Central belt by a chain of small pockets of tribal concentration. The scheduled tribes live in exclusive pockets of the territory, upon which they have traditional ownership rights.
[Culture] Tribals of India: Classification, Geographical Spread For GS Mains Paper I (Culture + Human Geography) Mrunal
Zone 1: Northern and North-Eastern
In the mountain valleys and other areas of North-East, Indian tribes largely belong to Mongolian social stock. The tribal people are distributed all over the sub-Himalayan region and the mountain valleys in the North-East from Simla in the West to the Lushai hills and the Mishmi track in the East which merge imperceptibly with those of Burma in the South-East. It covers Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Meghalaya, Nagaland, Tripura, Manipur and Mizoram, Eastern Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Tarai areas of Uttar Pradesh and the mountaineous West Bengal. Tribal Cultures paro-Barokachari is numerically the strongest tribe in Assam then comes Miri and Mizo. The hill districts, i.e., Mikir Hills and North Cachar Hills are predominantly inhabited by scheduled tribes. In the plains Goalpara, Lakhimpur, Darrang and Kamrup districts possess fairly large number of scheduled tribes. In Manipur, the highest distribution of scheduled tribes is found in Manipur west districts followed by Manipur east districts. The third highest position goes to Manipur south districts. North Manipur contains the lowest number of scheduled tribe population.. The major tribes inhabiting the region are Anal, Kabui, Gangte, Zarao, Moyan-Mansang, etc. In Meghalaya the most important tribes are the Khasis, Garos and Jaintias. Mizos, Pawis_and Lakhers are of importance in Mizoram. Nagaland basically a tribal state, is inhabited by Nagas.
Himachal Pradesh
Following tribes are important. 1. Gaddi 2. Kinner reside exclusively on the snowy range which divides Chamba from Kangra settled in the frontier district of Kinnaur in Himachal Pradesh.
3. Pangwal the Pangi region of the Chamba district in Himachal Pradesh 4. Lahuli Lahul-Spiti region of Himachal Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh
declared scheduled areas are hills, Tarai Bhabar, and Southern U.P. The hill zone is represented by the Jaunsari, Bhotia, and Raji tribes. Bhotias are a late introduction in the scheduled tribes following the set back they suffered after Indo-China war. The eastern and northern parts of Tarai Bhabar tract are inhabited by Tharu and Buxa tribes.
Zone II: Central
In the Chhotanagpur Plateau, along the dividing line between peninsular India and Indo-Gangetic basin, live many tribal communities like the Bhumij, Gond, Ho, Oraon, Munda, Santhal, Bhil, etc. They belong to Proto-Australoid group. This group occupy the mountain belt between Narbada and the Godavari the central barrier that divides the north from the Peninsular India has provided a shelter for these tribes from very ancient times. It includes West Bengal, Southern Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Orissa and Maharashtra. This region further extends to the Santhal Pargana (Bihar) in the east, Hyderabad in the South and Rajasthan and Gujarat with a strong Bhil population in the West.
Bihar
mrunal.org/2012/07/culture-tribalsp1.html 3/7
3/7/13
[Culture] Tribals of India: Classification, Geographical Spread For GS Mains Paper I (Culture + Human Geography) Mrunal
Oraon, Munda, Chero, Parchaiya, Santhal_and Asuras are very dominant.
Rajasthan
Banjaras, Moghias and Sathiyas are important tribes of Rajasthan. They mostly inhabit the Thar desert.
Gujarat and Maharashtra
Bhil is the most important tribe in Gujarat. Anal, Chiru_and Konkanas_are important tribes inhabiting Maharashtra.
Madhya Pradesh
1. Muria The word Muria is used in Bastar for a tribesman. Murias reside in the Muria Hill and Abujhmar mountains. 2. Dorla 3. Bhil a tribe of south Bastar in Madhya Pradesh. The word Dorla, appears to have been derived from the Telugu word Dora meaning Lord.
West Bengal
Mala and Savara tribes
Orissa
out ofthe 62 Scheduled tribes, Bhuiya, Baiga, Dharua, Gaaro, Ho, Koli, Lodha, etc. are more populous. The Baiga appears to be a branch of the great Bhuiya tribe of Madhya Pradesh. Baiga means a sorcerer or medicine man. The name Baiga also applies to anyone who serves as a village priest in the Central Provinces.
Zone III: South-Western
In the hills and converging line of the Western Ghats live the Chenchus, Irulas, Kadars, Ketas, Kurumbas, Jedas, etc. having Negrito, Caucasoid, and proto-Australoid features. This group is chiefly concentrated in the southern-most parts of the Western Ghats stretching from Vindhyas to Cape Comorin. From the fact that they occupy the marginal areas and also from the records in the oldest Tamil literature of the Sangam period, they appear to be one of the most ancient and primitive inhabitants of present day India. Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamilnadu fall within this zone. State AP Kerala Important tribes Chenchus_and Lambadi Koragas
Karnataka Koragas, Kuruba
Zone IV: Scattered Tribes of Andaman and Nicobar
There are various scattered tribal groups like the Andamanese and such other tribes of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, and other Union territories. The aborigines of the Andaman Islands may be described as a race by themselves, and can be divided into two groups, i.e., Subgroups Andamanese, the Onges and the Sentinelese. This group is found in the Andaman group of Islands. has an affinity with the Semangos and Sakais of Malaya, the Vedas of Sri Lanka and other Negrito groups of South-East Asia It is believed that these aborigines migrated from the lower regions of Burma. On their arrival at these islands, they moved to different part of the islands and very likelyon account of the different types of physical environment they developed different traits.
Negrito
Mongoloid inhabitants of Nicobar group of islands, i.e., the Shorn Pens and the Nicobarese.
mrunal.org/2012/07/culture-tribalsp1.html
Tribals of Andaman Nicobar
4/7
3/7/13
[Culture] Tribals of India: Classification, Geographical Spread For GS Mains Paper I (Culture + Human Geography) Mrunal
Tribals of Andaman Nicobar
Jarawa Onge Sentinelese Shorn Pens Nicobarese (Holchu)
confined to the western part of the south, middle and north Andamans. The Andamanese, who are extremely limited in number, live along the coastal areas. inhabit the little Andaman and Rutland island are found in the Sentinel island. confined along the eastern and south-eastern coast of Great Nicobar island. They are also reported from the banks of Dagmar, Alexandra and Galathoa rivers respectively. inhabiting these small islands are highly unevenly distributed and only in the two islands, the Car Nicobar and Chowra.
The Topic is not yet over. Ill publish part II soon. Previous Posts
[Misc.GK] Persons in News (2012-13), Sports, Books, Awards for SSC-CGL, SBI-PO, UPSC-CSAT [Download] Indian Culture and Heritage Study Material (Hindi/English) from NOS/NIOS for Free [Culture] Indian Art, Architecture and Painting Schools (Mindmap cum note) [PIN] Persons in News 2012 for 2 Markers, GK and MCQ [Culture] UNESCO Memory World Register: Seerat-e-Firozshahi and Shantinath Charitra [Culture] Fairs of India for 2 markers in UPSC GS Mains [Culture] Festivals of India: Characteristics (2 markers and Essay fodder) [Notes]Important Places in ancient India
Print || PDF 15 comments to [Culture] Tribals of India: Classification, Geographical Spread For GS Mains Paper I (Need Chrome)! (Culture + Human Geography)
Subscribe (free!)
Alok
Reply to this comment It seems data has been updated e.g. Most of Tribal from UP now in Uttarakhand. Similarly it stated that Bastar is in MP ( not in CG) and no mention of Jharkhand and CG- two tribal dominated states. These states were created in 2000 so data must be obsolete by at least 12 years. Please update these accordingly.
Mrunal
Reply to this comment yes this is taken from an old IGNOU course.
anitha
Reply to this comment Respected Sir Please clarify and explain about the following. 1. What is intrusive regulation against fake deposits scheme or ponzi scheme? 2. Why soli sorabjee declares that nuclear liability rules and act is ULTRA VIRES AND INVALID? 3. Centre announced nutrient based subsidy for fertilizers instead of MRP method.Tamilnadu C.M is against this? On what ground she rejects this?Please explain the background,reasons and pros and cons of both mode. 4.Please explain all the important government schemes,latest commitees. Thank you
Anurag
mrunal.org/2012/07/culture-tribalsp1.html
Reply to this comment
5/7
3/7/13
[Culture] Tribals of India: Classification, Geographical Spread For GS Mains Paper I (Culture + Human Geography) Mrunal
Reply to this comment Hello Mrunal..plzzz tell me the possible way of finding April 2012 kurukshetra magzine..I m in urgent need of it ? Thanks in advance Regards
shashi
Reply to this comment pls describe about GAAR and NCTC and its pros and cons
PARTHO
Reply to this comment http://mrunal.org/2012/05/economy-general-anti-avodiance-rules.html GAAR already explained.
PARTHO
Reply to this comment http://www.ipcs.org/pdf_file/issue/IB181-Chari-NCTC.pdf Above link will be helpful for understanding the NCTC debate.
tripti
Reply to this comment prelims result out gudluck buddies
UJJWAL KUMAR DAS
Reply to this comment Dear Mrunal .the civil services preliminary results 2012 .. has been declared ..
alok
Reply to this comment I was getting abt 215 but still out of race.Any guess abt cutoff ?
Ashutosh
Reply to this comment Last time it was 198.but this time it should be 180-190.
K Swapna
Reply to this comment There is a rumour that cut off went upto 208-210 this time for general category.
Aruna
Reply to this comment Mrunal , as per my knowledge narmada and godavari rivers divide satpura range and deccan plateau which comprises western part of India whereas chotanagpur plateau is eastern part , In the Chhotanagpur Plateau, along the dividing line between peninsular India and Indo-Gangetic basin, live many tribal communities like the Bhumij, Gond, Ho, Oraon, Munda, Santhal, Bhil, etc. They belong to Proto-Australoid group. This group occupy the mountain belt between Narbada and the Godavari the central barrier that divides the north from the Peninsular India has provided a shelter for these tribes from very ancient mrunal.org/2012/07/culture-tribalsp1.html
6/7
3/7/13
[Culture] Tribals of India: Classification, Geographical Spread For GS Mains Paper I (Culture + Human Geography) Mrunal
shelter for these tribes from very ancient times. hows this possible??????
samuel
Reply to this comment Dear Mrenal i would like to disagree with your descriptions of tribals of Assam. You are right in saying that Bodo Kachari are the higest in terms of numerical strength, but Mizo are not found in Assam , rather they are found in Mizoram. and in Manipur Imphal East and West doesnot have any native tribal populations. Tribals in Manipur are found in the hill district of curachandpur, chandel,ukhrul, Tamenglon, Senapati. ANd according to 2001 Census or any previous census the Thadou tribes are the highest in numbers followed by Tangkhul tribes, Tribes which you mentioned are never a major tribes in Manipur in fact they are only a few thousands in numbers. ( refer census 2001)
Matt
Reply to this comment Hi Mrunal, You might want to review the tribe list CHIRU & ANAL you provided under Gujarat and Maharashtra, as far as I know, these two tribes are from Manipur. Thanks,
mrunal.org/2012/07/culture-tribalsp1.html
7/7
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Disturbing Trends in Disturbing Trends in Judicial ActivismDocument5 paginiDisturbing Trends in Disturbing Trends in Judicial ActivismBhaiya KamalenduÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Economy) SEBI-Sahara OFCD Case - Optionally Fully-Convertible Debentures - Meaning Explained MrunalDocument6 pagini(Economy) SEBI-Sahara OFCD Case - Optionally Fully-Convertible Debentures - Meaning Explained MrunalBhaiya KamalenduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 17Document21 paginiUnit 17Bhaiya KamalenduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 13Document12 paginiUnit 13Bhaiya KamalenduÎncă nu există evaluări
- DancesDocument13 paginiDancesgorleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 12Document15 paginiUnit 12Bhaiya KamalenduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ethics of TerrorismDocument16 paginiEthics of TerrorismBhaiya KamalenduÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Economy Q) Headline Vs Core Inflation Difference MrunalDocument2 pagini(Economy Q) Headline Vs Core Inflation Difference MrunalBhaiya KamalenduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 18Document21 paginiUnit 18Bhaiya KamalenduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 16Document19 paginiUnit 16Bhaiya KamalenduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 11Document13 paginiUnit 11Bhaiya KamalenduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 14Document18 paginiUnit 14Bhaiya KamalenduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 9Document20 paginiUnit 9Bhaiya KamalenduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 10Document15 paginiUnit 10Bhaiya KamalenduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 6Document18 paginiUnit 6Bhaiya KamalenduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 7Document13 paginiUnit 7Bhaiya KamalenduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 5Document17 paginiUnit 5Bhaiya KamalenduÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 Ethics in Modern Indian PhilosophyDocument13 pagini8 Ethics in Modern Indian PhilosophyBhaiya KamalenduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To EthicsDocument15 paginiIntroduction To EthicsLakshmi NarayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mains SylabusDocument4 paginiMains SylabusBhaiya KamalenduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Badmephisto Speedcubing Method PDFDocument3 paginiBadmephisto Speedcubing Method PDFJoey Yeo0% (1)
- Sociology Papers 1964 2010Document50 paginiSociology Papers 1964 2010Bhaiya KamalenduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abc AbtDocument37 paginiAbc AbtVarada TambeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motivation & Its Effect On Performance On Nurses in AramcoDocument72 paginiMotivation & Its Effect On Performance On Nurses in AramcoBhaiya Kamalendu75% (4)
- Business Quiz FinalDocument19 paginiBusiness Quiz Finalaski1987Încă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Growing Mother's Language Literation in A Family EnvironmentDocument14 paginiGrowing Mother's Language Literation in A Family EnvironmentAnisa Nur IndahsariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Europe and North Africa Map Year 311 AcDocument1 paginăEurope and North Africa Map Year 311 AcSorin StanescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- LearnEnglish Magazine Indigenous Peoples Support Pack 1Document3 paginiLearnEnglish Magazine Indigenous Peoples Support Pack 1SujithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mindanao LiteratureDocument16 paginiMindanao LiteratureJasmine PimentelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Demographics of India:: Human Sex Ratio Medical Advances Green RevolutionDocument3 paginiDemographics of India:: Human Sex Ratio Medical Advances Green RevolutionYash VoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indigenous PeopleDocument3 paginiIndigenous PeopleKjmen 2345Încă nu există evaluări
- Native Peoples North AmericaDocument4 paginiNative Peoples North AmericaEsteban ZapataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Albern at AkoDocument4 paginiAlbern at AkoClarkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Poster Scythians MariJarveDocument1 paginăPoster Scythians MariJarveJan KowalskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 Cultural GeographyDocument3 paginiChapter 2 Cultural GeographyRainima EbrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indigenous Ethnic Groups in MalaysiaDocument2 paginiIndigenous Ethnic Groups in Malaysiastellalim05Încă nu există evaluări
- Philippine Indigenous ReligionDocument6 paginiPhilippine Indigenous Religionmarie cristina marianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ethnic Conflict in Southeast Asia PDFDocument2 paginiEthnic Conflict in Southeast Asia PDFKristinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Saudi German Hospital - Dubai Batch 12 IncompleteDocument10 paginiSaudi German Hospital - Dubai Batch 12 IncompleteMenaLabs Reception DXBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Celts in The British IslesDocument2 paginiCelts in The British IslesBilingual CapriconÎncă nu există evaluări
- RPD 2022 THRU 3 31 Use of Force Demographics MarchDocument3 paginiRPD 2022 THRU 3 31 Use of Force Demographics MarchOpenOversightVA.orgÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2344 5833 1 PBDocument13 pagini2344 5833 1 PBchuyasazaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- SOC/315 Multicultural Matrix AnalysisDocument9 paginiSOC/315 Multicultural Matrix AnalysisGregory DrewÎncă nu există evaluări
- JewsDocument14 paginiJewsMergim ShalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Globalization and CultureDocument30 paginiGlobalization and CulturechelsealivesforeverÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jackson Co., MN 1870Document61 paginiJackson Co., MN 1870NancyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essays On The Kuki-Naga Conflict - A Review-LibreDocument10 paginiEssays On The Kuki-Naga Conflict - A Review-Libredennis misaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 4 Assignment - Pamulaan SchoolDocument2 paginiModule 4 Assignment - Pamulaan SchoolBr. Henry FSC100% (1)
- Meoce saukunis qarTuli mwerlobis winare etapiDocument497 paginiMeoce saukunis qarTuli mwerlobis winare etapiNana LipartelianiÎncă nu există evaluări
- AFRS 10 - Intro To Africana Studies Course ScheduleDocument4 paginiAFRS 10 - Intro To Africana Studies Course ScheduleTHasanjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fon Benin PDFDocument2 paginiFon Benin PDFFabiano Pires dos Santos FernandesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bangsamoro TribesDocument10 paginiBangsamoro TribesAvliah Tabao DatimbangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics research impacts religious identityDocument32 paginiGenetics research impacts religious identityRandley GonçalvesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quechua in Chile The Key To The Salvation of An Endangered CultureDocument6 paginiQuechua in Chile The Key To The Salvation of An Endangered CultureChileMetodologiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hispanic American DiversityDocument6 paginiHispanic American Diversitymitsubishi224724Încă nu există evaluări