Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Electro Pneumatic
Încărcat de
Nurhidayah AzmiTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Electro Pneumatic
Încărcat de
Nurhidayah AzmiDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
Contents :1. What is Electro-Pneumatics : a definition 2. Electro-Pneumatic Signal Control system 3. Electro-Pneumatics Basic control components 4. Application Example
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
1.1 Definition of Electro-Pneumatics
WikiAnswers.com wrote,
Pneumatics is a method to transfer energy from one point to another using actuators which are driven by fluids under pressure. Pneumatics restricts itself to gaseous fluids while hydraulics uses liquids to transfer the energy. The transferring of energy in pneumatics such as pumping air into a pneumatic cylinder must be controlled. You can control the pressure by manually opening a valve, automatically by detecting its pressure, or by sending an electrical signal. The control of pneumatic components by electrical impulses is known as electro-pneumatics.
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
1.2 Other Definition of Electro-Pneumatics
Both pneumatic & electro-pneumatic controllers have a pneumatic power section. In an electro-pneumatics control, the signal control section is made up of a electrical components, such as electrical input buttons, proximity switches, relays, or a programmable logic controller (PLC).
Source : Electropneumatics A basic, G Prede, D Scholz
Question 1 : What is your definition for Electro-Pneumatics? _____________________________________ _____________________________________
[3 marks]
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
1.3 Our Definition of Electro-Pneumatics
Definition : Electro-pneumatic term is defined from the words of electro which means electrical and pneumatic which means air pressure. The electro-pneumatics equipments and system is an integration of electrical and mechanical components with compressed air source. Electro pneumatic is a pneumatic control system where air pressure and direction of valve are controlled by an electrical current.
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
1.4 Electro-Pneumatics circuit
Electro pneumatic is integration of two control circuit 1. Pneumatic Circuit 2. Electrical Circuit
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
(a) Pneumatic circuit
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
(b) Electrical circuit
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
1.5 Combination of Pneumatic circuit and Electrical circuit
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
2.1 A Background Basic Control system
Command Execution
Power component
Signal Output
Final Control element
Signal Processing
Processing element
Signal Input
Input element
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
2.2 Signal flow and component of an ElectroPneumatic control system
Source : Electropneumatics Basic Level by G Prede, D Scholz
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
2.3 Pneumatic power section
Directional control valves form the interface between the signal control section (electrical) and the pneumatic power section in an Electropneumatic system.
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
2.4 Electrical signal control section
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
2.5 Advantages of using Electro-Pneumatics
1. Lesser wear-off parts. Lesser installation jobs. i.e., Electrical control valve, Electrical switches 2. Replace tube in pneumatic system to electrical wire in electro-pneumatic 3. Less parts are used Reduce working space. 4. Sensor and Controller (such as PLC) can be included in the system
E-260 Electrical signal input (switch panel) Push Button
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
2.3 Assignment 1
Question : List-up (at least) 2 advantages and 2 disadvantages of Pneumatic system.
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
3.0 Introduction to Electro-pneumatic control component
Question : By using suitable pneumatic circuit, show pneumatic component classification.
Source: 2009 Sem2 DNT241 Final exam question
This year final exam Question(?) List-up 4 component classifications in Electropneumatic control system and give 2 example for each component.
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
3.1 Input Element component
Switches : There are 3 types of electrical switches used in design Electro-pneumatic circuit. 1. Normally Open switch 2. Normally Close switch 3. Multiple contact switches Sensors : 1. Mechanical Position sensor (Limit switch) 2. Proximity sensor 3. Reed switch
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
3.2 Switching Contact and type of actuation
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
3.3.1 Normally Open (N.O) and Normally Close (N.C)
In pneumatic circuit : For example : 3/2-way Push button (valve)
Normally Open In electrical circuit :
Normally Close
For example : Push button switch Normally Open Normally Close
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
3.3.2 Normally Open (N.O) and Normally Close (N.C)
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
3.4 Mechanical Position sensor
(Pneumatic) 3/2-way N.C valve with roller (Limit switch)
(Electro-Pneumatic) Mechanical Position sensor (Limit switch)
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
3.5 Proximity sensor
Proximity sensor contain a transistor which conducts and switches (trigger ON) when something comes near to the sensors. Some of the proximity sensor only work with steel material components Inductive proximity sensor
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
3.5.1 Proximity sensor Symbol and Sample Circuit
Proximity Sensor
Question :
1. 2.
Name the switch type used for START and STOP button. What is the different between A1 and A2 in Electrical circuit?
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
3.6 Reed switch
Reed switch is one of the sensor which is operated by the magnetic field. Usually fit directly onto cylinder with clips. The piston of the cylinder has a magnet built into it and when the piston comes close to the reed switch, the contact is close (ON).
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
3.7 Processing element - Relay
Relay is an electrically actuated switch, contains a coil and a contactor switch or multiples contactors. When power is applied to relay coil, the core magnetizes, drawing the contact assembly in. This will change the state of all the contacts in the relay (i.e., N.O contact becomes closed or N.C contact becomes open). Relay uses small amount of power to control switching (advantage). The voltage applied to the coil doesnt have to be the same as that in control circuit. Relay is used to allow low voltage control systems to switch large current/ high voltage (function / advantage)
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
3.7.1 Sample circuit
E-140 Contactor
Coil
When Toggle switch 1S3 is pressed, power is applied to Relay (K1) coil which result to the all contactors in relay change their state (open close or close open). Solenoid valve 1Y1 activate to ON
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
3.7.2 N.O and N.C wire connection
Normally Close (N.C) Example : Pin 21 22 Normally Open (N.O) Example : Pin 41 44
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
3.7.3 Animation (Relay OFF)
Source : UniKL Electro-Pneumatic Lecture Note, 2008
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
3.7.4 Animation (Relay ON)
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
3.7.5 More about Relays
Relay has a few functions as a safety device:
1. The high voltage output (i.e. 240V) can be switched ON through a contactor using relay with low voltage (i.e. 24V) supplied to a coil. 2. The high current output can be switched ON through a contactor using relay with low current supplied to a coil. 3. Functioned as Safety control circuit for emergency power cut-off (EMERGENCY START and STOP button) to the whole circuit. Use in automation process Switching more than one outputs simultaneously using relay with a coil and multiple contactors. To control ON and OFF of various outputs sequences using several Relay.
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
Solenoid valve is an electro-mechanical device that built-in with a coil (solenoid) and a pneumatic Directional control valve. Solenoid actuated Directional control valve (DCV) convert electrical signals to pneumatic signals. They are used to start, to stop and/or to change the direction of air flow. There 3 main types of solenoid valve. 1. 3/2-way Solenoid valve with spring return 2. 5/2-way Solenoid valve with spring return 3. 5/2-way Double solenoid valve
3.8 Final control element Solenoid DCV
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
3.8.1 Solenoid DCV
5/2-way Double solenoid valve
5/2-way Solenoid valve with spring return 3/2-way Solenoid valve with spring return
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
3.8.2 Symbol and sample circuit
(Pneumatic) Pilot actuated 5/2-way Directional control valve (Electro-Pneumatic) Solenoid actuated 5/2-way Directional control valve
Pneumatic Power Component --- cylinder
Final Control element --- Solenoid valve
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
3.8.3 Symbol in Electrical circuit
Solenoid
When Pushbutton switch (SW1) is pressed, power is applied to Solenoid S1 which then change the electrical signal to pneumatic signal and allow air flow to cylinder A (single acting with spring return) for rod to extend.
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
3.8.4 Sample Circuit connection
Red cable is connection from 24V line. Blue cable is connection to GND (0 V).
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
3.8.5 Solenoid - Structure
Source : UTeM Chapter 4 --- ElectroPneumatic
4.0 Supply / Power component
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
In Electro-Pneumatic system, the supply or power source component is divided into two, based on the system component. 1. Pneumatic Compressor 2. Electrical AC / DC power supply Symbol for 24V DC IEC Standard JIC Standard
4.1 Self-Latching concept
START STOP
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
Self-latching circuit
Self-latching will enable the automation system to run in automatic mode after the START button is pressed and the system repeats until STOP button is pressed. The advantage of having self-latching in the system is that it can be used as power switching and emergency button.
4.2 Electro-Pneumatic Application
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
In this section, we will learn some of the actual application for Electro-pneumatic system. 1. Single-acting cylinder (with spring return) 2. Double-acting cylinder (1 unit) 3. Double-acting cylinder (2 units) Based on the system / operation given, the students should capable to : a) Understand the systems operation and draw / sketch Displacement-step diagram b) Design Pneumatic circuit and Electrical circuit for the system.
4.3 Application 1
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
Using a sorting device, parts are to be transferred from conveyor belt. By pressing the pushbutton switch, the piston rod of a singleacting cylinder pushes the part off the conveyor belt. When the pushbutton is released, the piston rod returns to the retracted end position.
4.3.1 Pneumatic circuit and Electrical circuit
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
Pneumatic circuit
Electrical circuit
Question : Complete the missing part in Electrical circuit.
4.4 Application 2
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
Wooden planks are to be pushed along from a gravity feed magazine to a clamping device. By pressing a pushbutton switch one plank is pushed by the slide out of the gravity feed magazine. After the slide has reached the forward end position it is returned to its start position.
4.4.1 Pneumatic circuit
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
Question : Please design complete Electrical circuit to control above pneumatic circuit.
4.5 Application 3
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
Using a transfer station blocks are to be transferred from a magazine to a processing station. The blocks are pushed out of the magazine by cylinder A and transferred to the processing station by cylinder B. The piston rod of cylinder A may only return when the piston rod of cylinder B has reached the retracted end position. The magazine is monitored by means of limit switches. If there are no more blocks in the magazine, it is not possible to start the cycle. This is indicated by means of push button to act as a sensor. The control is to be operated in single cycle.
Cylinder A
Cylinder B
4.5.1 Displacement-step Diagram
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
1. The blocks are pushed out of the magazine by cylinder A and
transferred to the processing station by cylinder B. 2. The piston rod of cylinder A may only return when the piston rod of cylinder B has reached the retracted end position. 3. The magazine is monitored by means of limit switches. If there are no more blocks in the magazine, it is not possible to start the cycle. This is indicated by means of push button to act as a sensor, named as Part_detect sensor. 4. The control is to be operated in single cycle.
Abbreviation notation : A+ B+ B- ADisplacement-step Diagram :
4.6 Other components in Electro-Pneumatic
1. AND / OR Logic 2. Timer ON / Timer OFF. 3. Pressure Switch. 4. Counter 5. LED
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
Etc
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
We should be :
5.0 What has been learned in this session?
1. Understand what has been called as ElectroPneumatics and can simply describe it. 2. Understand the 5 main components in Electropneumatic control system 3. Understand the name and symbol of each component and how its working in the electrical circuit (function). 4. Understand on how to design Pneumatic and Electrical circuit based on the given applications. 5. Can demonstrate the theories learning in class to practical.
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
6.0 Answer
Application 1 Application 2
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
6.1 Application 3
Pneumatic circuit
Electrical circuit
Introduction to Electro Pneumatics
6.2 Include Self-latching circuit
Pneumatic circuit
Electrical circuit
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Electro PneumaticDocument40 paginiElectro PneumaticMasrur Afifin100% (2)
- Pneumatic SymbolsDocument2 paginiPneumatic Symbolssike_99100% (1)
- PerkinsDocument2 paginiPerkinsJacques Van NiekerkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumatic Circuit DesignDocument17 paginiPneumatic Circuit DesignSriram SastryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electro Pneumatics m2 StudentDocument21 paginiElectro Pneumatics m2 StudentArt NidayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Manual of Pneumatics ControlDocument110 paginiLab Manual of Pneumatics ControlKhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- This Document Is Printed From SPI . Not For RESALE: 1600 Series Industrial Engine Electrical SystemDocument2 paginiThis Document Is Printed From SPI . Not For RESALE: 1600 Series Industrial Engine Electrical SystemJacques Van Niekerk100% (1)
- ESQUEMA ELECTRICO c9 PDFDocument2 paginiESQUEMA ELECTRICO c9 PDFOswaldo AndradeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cat Gen 2Document2 paginiCat Gen 2Alfonso Barrantes100% (1)
- Full Report HydraulicsDocument18 paginiFull Report HydraulicsNurulSyafiqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plano Electrico CF 950-962HDocument16 paginiPlano Electrico CF 950-962Hrmatico1234100% (1)
- RENR1439Document2 paginiRENR1439omarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renr9959 00Document2 paginiRenr9959 00Ahmer CamdzicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exp. 2 Pneumatic Control of A Double-Acting CylinderDocument10 paginiExp. 2 Pneumatic Control of A Double-Acting CylinderLuke-man Akim0% (1)
- c3 - Pneumatics Circuit DesignDocument126 paginic3 - Pneumatics Circuit DesignBazil Suhaimi100% (2)
- EEC 129 PracticalDocument48 paginiEEC 129 PracticalVietHungCao100% (6)
- Worksheets Pneumatics Basic LevelDocument144 paginiWorksheets Pneumatics Basic Levelvrjr0% (1)
- Pneumatics ProblemsDocument22 paginiPneumatics ProblemsMatthew Laureano ResurreccionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumatic NotesDocument26 paginiPneumatic Notessaliana binti sanusi85% (13)
- Esquema Electrico C7.1UENR0630UENR0630-00 - SISDocument7 paginiEsquema Electrico C7.1UENR0630UENR0630-00 - SISNANCY DEL ROSARIO JACINTO SIADENÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problems of Pneumatic Circuit DesignDocument13 paginiProblems of Pneumatic Circuit Designvijay75% (4)
- TUTORIAL 2-NewDocument17 paginiTUTORIAL 2-NewGeetha Sai KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity 3 - Motor Control CircuitDocument11 paginiActivity 3 - Motor Control CircuitAJ LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interactive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768Document8 paginiInteractive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768Hamid EssarboutiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 3 Intro To ElectroPneumaticsDocument8 paginiModule 3 Intro To ElectroPneumaticsIvy Totanes TaborÎncă nu există evaluări
- JKM Pneumatic CIRCUIT SystemDocument50 paginiJKM Pneumatic CIRCUIT SystembeselamuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Camion Minero 979. Parte 2Document35 paginiCamion Minero 979. Parte 2Hules FrankÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3512B PDFDocument2 pagini3512B PDFSolomonÎncă nu există evaluări
- DOL StarterDocument7 paginiDOL StarterHuzAirie SuhAimi89% (9)
- MODULE 5 Pneumatic Control Circuits PDFDocument108 paginiMODULE 5 Pneumatic Control Circuits PDFchandrashekar m100% (1)
- Electropneumatics Basic Level: Workbook TP 201Document54 paginiElectropneumatics Basic Level: Workbook TP 201Saúl Ríos0% (2)
- Lab 1 Pneumatic FullDocument22 paginiLab 1 Pneumatic Fullbella100% (12)
- ESQUEMA ELECTRICO c9 PDFDocument2 paginiESQUEMA ELECTRICO c9 PDFOswaldo AndradeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report For PneumaticDocument6 paginiReport For PneumaticMirza Farouq Beg100% (1)
- Chapter 5 NozzleDocument20 paginiChapter 5 NozzleNurhidayah AzmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Battery Compartment Right Rear of Machine: Electrical System 320D ExcavatorDocument2 paginiBattery Compartment Right Rear of Machine: Electrical System 320D ExcavatorJoycee ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study PneumaticDocument16 paginiCase Study PneumaticHazwan Jamhuri100% (6)
- Pneumatic Lab ReportDocument9 paginiPneumatic Lab ReportAsyraf Yusoff71% (7)
- Pneumatics Exercises Solution SheetDocument26 paginiPneumatics Exercises Solution SheetJames Paligumba56% (9)
- Mecha Lab Report (Pneumatics Results and Discussion)Document3 paginiMecha Lab Report (Pneumatics Results and Discussion)Shamni KarthegesuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 5 Introduction To Electro PneumaticDocument46 paginiLecture 5 Introduction To Electro PneumaticMary Hazel Sarto, V.Încă nu există evaluări
- Electro Pneumatics StudentDocument24 paginiElectro Pneumatics StudentbooÎncă nu există evaluări
- I E - P S: Ntroduction To Lectro Neumatic YstemDocument25 paginiI E - P S: Ntroduction To Lectro Neumatic YstemJohn Paul Daliopac100% (1)
- Faculty of Engineering Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering TechnologyDocument15 paginiFaculty of Engineering Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering TechnologyNur Syuhada YaacobÎncă nu există evaluări
- LAB Pneumatic FinalDocument25 paginiLAB Pneumatic FinalshamizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multi Cylinder CircuitDocument4 paginiMulti Cylinder Circuitnurhatiqahzainal100% (1)
- Hydraulic Lab 1Document12 paginiHydraulic Lab 1Afiq HamidiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electropneumatics ExamDocument4 paginiElectropneumatics ExamEarl FloresÎncă nu există evaluări
- MODULE 2 Intro - Lab HydraulicDocument3 paginiMODULE 2 Intro - Lab HydraulicHafiz Melliani100% (1)
- Clamping Camera HousingDocument4 paginiClamping Camera HousingNitin BuZz67% (3)
- Hydraulic Lab FinalDocument12 paginiHydraulic Lab FinalHafiz MellianiÎncă nu există evaluări
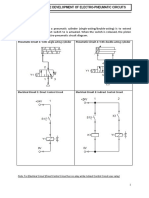
- Exercises On The Development of Electro-Pneumatic Circuits: Problem1Document7 paginiExercises On The Development of Electro-Pneumatic Circuits: Problem1Julius Chavez100% (1)
- Basic Pneumatics Laboratory ManualDocument50 paginiBasic Pneumatics Laboratory Manualashier dave calulot100% (1)
- Basic Pure Pneumatic Circuit Design: Experiment: 1 Title: Duration: 2 Hours: 1 0F 3Document3 paginiBasic Pure Pneumatic Circuit Design: Experiment: 1 Title: Duration: 2 Hours: 1 0F 3shirleyna saraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Labsheet 1 SWITCHDocument16 paginiLabsheet 1 SWITCHஅருண்ராஜ் கிருஷ்ணன்சாமிÎncă nu există evaluări
- V2 EXP2 Logic Valve and Sequence Control For Multiple Cylinder OperationDocument12 paginiV2 EXP2 Logic Valve and Sequence Control For Multiple Cylinder OperationJane Ruby GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case StudyDocument2 paginiCase StudySyed Mohd FirdausÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 7 - Hydraulic Operation Circuit and ApplicationDocument19 paginiChapter 7 - Hydraulic Operation Circuit and ApplicationMuhammad AbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electropneumatic and Hydraulic DNT241: Experiment No. 4Document7 paginiElectropneumatic and Hydraulic DNT241: Experiment No. 4Izz Hanzalah AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design & Simulation of Electro-Pneumatic SystemDocument54 paginiDesign & Simulation of Electro-Pneumatic SystemSaravanan Mathi0% (2)
- JJ512 Hydraulic Lab 4Document7 paginiJJ512 Hydraulic Lab 42cekalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circuit ApplicationsDocument65 paginiCircuit ApplicationsAman Baviskar100% (1)
- Hydraulic Lab ReportDocument2 paginiHydraulic Lab ReportAllaFonteÎncă nu există evaluări
- SKEM 3742 Electro Hydraulic LabsheetDocument6 paginiSKEM 3742 Electro Hydraulic Labsheetcikgu_relaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Manual PneumaticsDocument19 paginiLab Manual PneumaticsGautam Anikirala0% (1)
- 1.automotive Electrical LabDocument16 pagini1.automotive Electrical LabSathya NarayananÎncă nu există evaluări
- DiscussionDocument3 paginiDiscussionXeno Genesis100% (3)
- Electro-Pneumatics: Prepared by Approved byDocument30 paginiElectro-Pneumatics: Prepared by Approved byPrakash KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Electro-HydraulicsDocument20 paginiIntroduction To Electro-HydraulicsDhiyauZola100% (2)
- Lab 2 Part 1Document31 paginiLab 2 Part 1Zainuddin BusuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electro PneumaticsDocument51 paginiElectro Pneumaticshansanadesilva098Încă nu există evaluări
- MCU Central Control Circuit: 3. Electrical Network Design PartDocument15 paginiMCU Central Control Circuit: 3. Electrical Network Design PartPhong NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learning Objectives Upon Completion of This Chapter, Student Should Be Able ToDocument54 paginiLearning Objectives Upon Completion of This Chapter, Student Should Be Able ToSalvador JovenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electro Hydraulic and Pneumatic TheoryDocument8 paginiElectro Hydraulic and Pneumatic TheoryMuhammad Anaz'sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Restoran Borhan OwnerDocument1 paginăRestoran Borhan OwnerNurhidayah AzmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teamwork Rubric (Example)Document3 paginiTeamwork Rubric (Example)Nurhidayah AzmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumatic & Hydraulic SystemsDocument7 paginiPneumatic & Hydraulic SystemsNurhidayah AzmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Dynamics IIDocument27 paginiFluid Dynamics IINurhidayah AzmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid DynamicDocument15 paginiFluid DynamicNurhidayah AzmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid StaticDocument24 paginiFluid StaticNurhidayah AzmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jj309 - Exercise 1Document1 paginăJj309 - Exercise 1Nurhidayah AzmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quiz 1 Fluid MechanicsDocument1 paginăQuiz 1 Fluid MechanicsNurhidayah AzmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 320GC DKJDocument6 pagini320GC DKJBORIS FIRMIN MOMENE DONGMOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cat Dcs Sis Controller-120m PDFDocument8 paginiCat Dcs Sis Controller-120m PDFChristian Vinueza VillavicencioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interactive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768Document13 paginiInteractive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768Trung HuyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagrama C18 Industrial TaladroDocument11 paginiDiagrama C18 Industrial Taladrodinny blanco rojas100% (1)
- Buchholzrelay MBR For Liquid Immersed Transformers and Reactors With Conservator in Accordance With EN 50216-2Document13 paginiBuchholzrelay MBR For Liquid Immersed Transformers and Reactors With Conservator in Accordance With EN 50216-2snooty.eli.gamedogsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uenr2534uenr2534-01 SisDocument15 paginiUenr2534uenr2534-01 SisPizarro Andres100% (1)
- Sentrol ManualDocument146 paginiSentrol Manual1DonhudlowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interactive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768Document28 paginiInteractive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768RobertoÎncă nu există evaluări
- View All Callouts: Function Isolation ToolsDocument14 paginiView All Callouts: Function Isolation ToolsJari GoethuysÎncă nu există evaluări
- KS0349 Keyestudio 48 in 1 Sensor Kit PDFDocument183 paginiKS0349 Keyestudio 48 in 1 Sensor Kit PDFhexapodo2100% (1)
- Interactive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768Document8 paginiInteractive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768Hamid EssarboutiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manufacturing Automation Using PLCsDocument19 paginiManufacturing Automation Using PLCssbpathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interactive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768Document9 paginiInteractive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768Elie Abisaad100% (1)