Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Pathophysiology of Cva-Hpnii-Hemorrhagic Stroke
Încărcat de
Larisse de LeonTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Pathophysiology of Cva-Hpnii-Hemorrhagic Stroke
Încărcat de
Larisse de LeonDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
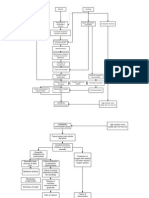
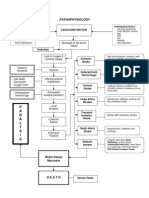
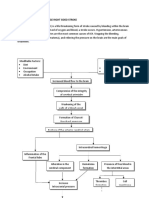
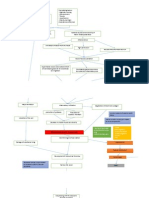
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
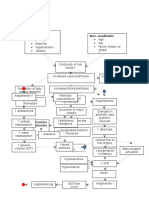
Modifiable Factors: Diet Environment Occupation Alcohol Intake Increased blood flow to the brain Non - Modifiable Factors: Gender Age Hereditary
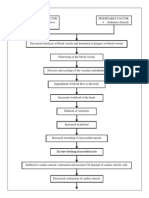
Compromise of the integrity of cerebral arterioles Weakening of the walls of a blood vessel Formation of CharcotBouchard aneurysm Rupture of the anterior cerebral artery
Intracerebral hemorrhage Inflammation of the Frontal lobe Alteration in the cerebral component Hematoma formation Presence of free blood in the interstitial areas
Increase Intracranial pressure
Thrombus formation CT SCAN and MRI
Cell membrane destruction
Compression of the brain components Stimulates further swelling and inflammatio n
Decrease oxygen supply
Compensatory mechanism
Cellular edema
Vasospasm
Electrolyte imbalance
Acidosis
-projectile vomiting, numbness of extremiities , visual disturbances
Ischemia
Stimulation of vasomotor centers
Scar Formation Alteration in the frontal lobe function Increase systemic pressure
Serum Electrolyte Test Decreased Mg and K ABG(Respiratory alkalosis) changes in the v/s
X RAY, CT scan, MRI
Brocas aphasia Hemiparesis Hemianopsia dysarthria incapable of abstract thinking
Increase BP Without Medical intervention Brain stem herniation With Medical Intervention
Comatose Stupor Worsening of the condition
Management: SURGICAL: craniectomy, craniotomy MEDICAL: Pharmacologic Therapy (citicholine, mannitol, dilatin, captopril, Nitroglycerin, furosemide, remopain, Kalium Durule, MgSO4)
Death
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Patel, Anita - Super Indian Snack and Street Food Recipes PDFDocument117 paginiPatel, Anita - Super Indian Snack and Street Food Recipes PDFBella ImèneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stroke PathophysiologyDocument3 paginiStroke PathophysiologyMaureen EricaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology HypertensionDocument1 paginăPathophysiology HypertensionAlinor Abubacar100% (3)
- Newton Interviews - Tookie AngusDocument12 paginiNewton Interviews - Tookie AngusPeter BellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stroke PathophysiologyDocument3 paginiStroke PathophysiologyMaureen Balagtas89% (9)
- Pathophysiology of Ischemic Stroke FinalDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of Ischemic Stroke FinalAcohCChao67% (3)
- 3 PathophysiologyDocument4 pagini3 PathophysiologySherlyn KirisakiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument2 paginiPathophysiology of StrokeACe JAy100% (2)
- Pathophysiology CVA (Final2)Document10 paginiPathophysiology CVA (Final2)Jayselle Costes FelipeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument2 paginiPathophysiology of StrokeJoy Rachelle Fermin100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular Disease: Predisposing Factors Etiology Precipitating FactorsDocument4 paginiPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular Disease: Predisposing Factors Etiology Precipitating FactorsLilot Antonio Rodriguez Vinarao100% (5)
- Marshall Abby - Chess Cafe - The Openings Explained - 1-63, 2015-OCR, 682pDocument682 paginiMarshall Abby - Chess Cafe - The Openings Explained - 1-63, 2015-OCR, 682pArtur MałkowskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stroke PathophysiologyDocument2 paginiStroke PathophysiologyJaessa Feliciano100% (2)
- Coronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyDocument3 paginiCoronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyElmer Balgos Alinsog50% (4)
- Concept Map of Subarachnoid Hemmorhage by Rhealyn NograDocument3 paginiConcept Map of Subarachnoid Hemmorhage by Rhealyn NograRhealyn NograÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of StrokeAqeel Al-Mahdaly0% (1)
- Path o Client BasedDocument3 paginiPath o Client BasedJane TuazonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology Diagram - StrokeDocument3 paginiPathophysiology Diagram - Strokemisstheatricality130100% (1)
- Pathophysiology CVADocument2 paginiPathophysiology CVATerence Valdehueza67% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Brain TumorsDocument2 paginiPathophysiology of Brain TumorsNavjot Brar92% (13)
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentPaulo de Jesus86% (7)
- Pathophysiology of CVADocument1 paginăPathophysiology of CVAYoussry JaranillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sandvik DD210Document4 paginiSandvik DD210Lener Elvin Lopez LavadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Congestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument3 paginiCongestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramJacinthaVanathayahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of CVD InfarctDocument2 paginiPathophysiology of CVD InfarctIris Caberte86% (7)
- Pathophysiology of HCVD, DM2, CVD (Left Basal Ganglia)Document1 paginăPathophysiology of HCVD, DM2, CVD (Left Basal Ganglia)rexale ria100% (1)
- Cervical CancerDocument7 paginiCervical CancerLarisse de LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case On Intracranial HemorrhageDocument17 paginiCase On Intracranial HemorrhageLorebell100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryDocument4 paginiPathophysiology of Acute Kidney Injurymariaclaramutya100% (1)
- Cerebrovascular Accident PathophysiologyDocument1 paginăCerebrovascular Accident PathophysiologyBerde KangleonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of CVADocument1 paginăPathophysiology of CVAChristine Joy Ilao PasnoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Predisposing Factors Precipitating/Aggravating FactorsDocument1 paginăPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Predisposing Factors Precipitating/Aggravating Factorsguillermojerry100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of CVADocument7 paginiPathophysiology of CVAsarzlasco0967% (3)
- Cap PathophysiologyDocument2 paginiCap PathophysiologyNoriel Henricks Acuna100% (3)
- Pathophysiology CVADocument2 paginiPathophysiology CVASewyel Garburi100% (6)
- Patho MIDocument2 paginiPatho MIbanyenye25100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument2 paginiPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentJohn Michael FernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coronary Artery Disease Pathophysiology PDFDocument3 paginiCoronary Artery Disease Pathophysiology PDFMohd Amir Bin Bashir0% (1)
- Case Presentation of Hemorrhagic Stroke (Subarachnoid Hemorrhage)Document69 paginiCase Presentation of Hemorrhagic Stroke (Subarachnoid Hemorrhage)verna88% (24)
- PathophysiologyDocument4 paginiPathophysiologyCee SanchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 paginiPathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsJames John Galac88% (8)
- Concept Map TBIDocument2 paginiConcept Map TBIraquel maniego67% (3)
- Pathophysiology CHFDocument3 paginiPathophysiology CHFKim Franzel M. Rabe100% (1)
- Pathophysiology Hemor CVADocument4 paginiPathophysiology Hemor CVAMatthew Emmanuel M. Martinez100% (2)
- Pathophysiology Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument1 paginăPathophysiology Hemorrhagic StrokeJeffrey Dela CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schematic Pathophysiology CVADocument10 paginiSchematic Pathophysiology CVAheiyu100% (5)
- Pathophysiology CVADocument1 paginăPathophysiology CVANenette Aquino100% (2)
- Stroke PathophysiologyDocument5 paginiStroke Pathophysiologycinnabon_heart9100% (3)
- HCVD Cad Cva InfarctionDocument2 paginiHCVD Cad Cva InfarctionMiguel Carlos Tacderan100% (1)
- Schematic Diagram of StrokeDocument1 paginăSchematic Diagram of StrokeCyrus De Asis100% (3)
- Pathophysiology CVDDocument1 paginăPathophysiology CVDPamela Shiermaine FilomenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument4 paginiPathophysiology of StrokeACe JAyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentByron Paz Te100% (1)
- CVD Infarct-HpniiDocument3 paginiCVD Infarct-HpniilarissedeleonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schematic Diagram: Signs and Symptoms: Headache, Unconsciousness, Nausea and Vomiting, Visual DisturbancesDocument3 paginiSchematic Diagram: Signs and Symptoms: Headache, Unconsciousness, Nausea and Vomiting, Visual DisturbancesJosett RomanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strokes in - ChildrenDocument52 paginiStrokes in - ChildrenAbdulai WakoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schematic Diagram of StrokeDocument1 paginăSchematic Diagram of StrokeMaricar K. BrionesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schematic Diagram of StrokeDocument1 paginăSchematic Diagram of StrokeChester NicoleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shock PresentationDocument21 paginiShock Presentationapi-283170120Încă nu există evaluări
- General Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 paginiGeneral Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsIrish Nicole DCÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology Non-Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsDocument3 paginiPathophysiology Non-Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsErrol B. TiozonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluation of Shock in AdultsDocument99 paginiEvaluation of Shock in AdultsekramsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intracerebral Hemorrhage Right Sided StrokeDocument2 paginiIntracerebral Hemorrhage Right Sided StrokeDinarkram Rabreca EculÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brain Tumors and EpilepsyDocument7 paginiBrain Tumors and EpilepsyNavjot BrarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concept Map AAADocument6 paginiConcept Map AAASandrine BarredoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Questions For Face To Face Culture Video Assignment - F2021Document1 paginăSample Questions For Face To Face Culture Video Assignment - F2021Larisse de LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology of CHOLELITHIASISDocument4 paginiAnatomy and Physiology of CHOLELITHIASISLarisse de LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument5 paginiDrug StudyLarisse de LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology of CHOLELITHIASISDocument4 paginiAnatomy and Physiology of CHOLELITHIASISLarisse de LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Breastfed Babies Cry MoreDocument3 paginiBreastfed Babies Cry MoreLarisse de LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Requirement - MDH 9fDocument1 paginăRequirement - MDH 9fLarisse de LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dysrhythmias: Normal Electrical ActivityDocument32 paginiDysrhythmias: Normal Electrical ActivityLarisse de LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fields of NursingDocument3 paginiFields of NursingLarisse de LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Lessons I LearnedDocument1 pagină10 Lessons I LearnedLarisse de LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing EthicsDocument1 paginăNursing EthicsLarisse de LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Legal Roles of A NurseDocument3 paginiLegal Roles of A NurseLarisse de LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Paradigm (Nursing)Document3 paginiNursing Paradigm (Nursing)Larisse de LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Paradigm (Spirituality and Family)Document5 paginiNursing Paradigm (Spirituality and Family)Larisse de LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of NursingDocument3 paginiHistory of NursingLarisse de LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Paradigm (Culture)Document3 paginiNursing Paradigm (Culture)Larisse de LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Modelling of Internal Permanent Magnet Motor (#764846) - 1189475Document25 paginiDesign and Modelling of Internal Permanent Magnet Motor (#764846) - 1189475Tejas PanchalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nature Generator (Emtech Concept Paper)Document3 paginiNature Generator (Emtech Concept Paper)Min SugaÎncă nu există evaluări
- V + V Plus - EN1Document6 paginiV + V Plus - EN1james.anitÎncă nu există evaluări
- FPS Module 1Document28 paginiFPS Module 1RickÎncă nu există evaluări
- Figure Eight Island Homeowners' Association, Inc. Case StudyDocument16 paginiFigure Eight Island Homeowners' Association, Inc. Case StudyYoong YingÎncă nu există evaluări
- i1000SR System Quick Troubleshooting GuideDocument2 paginii1000SR System Quick Troubleshooting GuideEarliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2 - CT2Document45 paginiUnit 2 - CT2Jagrit DusejaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Perbedaan Fermentasi Dan Respirasi Anaerob (Campbell Biology 12th Ed.)Document4 paginiPerbedaan Fermentasi Dan Respirasi Anaerob (Campbell Biology 12th Ed.)Oppof7 OppoÎncă nu există evaluări
- INTERVIEW QUESTIONS - Verilog - PART-1Document9 paginiINTERVIEW QUESTIONS - Verilog - PART-1charan tejaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pakistan RailwayDocument38 paginiPakistan RailwayمحمودعليÎncă nu există evaluări
- Turnitin Originality ReportDocument20 paginiTurnitin Originality ReportNaomi Deirdre ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Description Features: PT6964 LED Driver ICDocument15 paginiDescription Features: PT6964 LED Driver ICDhivya NÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rama Varma Anagha Research PaperDocument12 paginiRama Varma Anagha Research Paperapi-308560676Încă nu există evaluări
- Fuhs - Towards An Integral EpistemologyDocument39 paginiFuhs - Towards An Integral EpistemologyjmcmichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Safety Data Sheet: 1. IdentificationDocument7 paginiSafety Data Sheet: 1. IdentificationKhobeb MuslimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Penerapan Metode Sonikasi Terhadap Adsorpsi FeIIIDocument6 paginiPenerapan Metode Sonikasi Terhadap Adsorpsi FeIIIappsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment Oumh2103 English For Science Technical PurposesDocument12 paginiAssignment Oumh2103 English For Science Technical PurposesKhairul AnuarÎncă nu există evaluări
- External Otitis (OE)Document24 paginiExternal Otitis (OE)Hannah BLissÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zbus and Symmetrical Fault AnalysisDocument20 paginiZbus and Symmetrical Fault Analysishj203800Încă nu există evaluări
- 24 Port - 48 Port CAT6A Patch PanelDocument2 pagini24 Port - 48 Port CAT6A Patch PanelSajid KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- BR Safetymatrix enDocument12 paginiBR Safetymatrix enHamidreza MoaddeliÎncă nu există evaluări
- 13 - Oxygen Removal From Boiler WaterDocument12 pagini13 - Oxygen Removal From Boiler Waterarunkumar23101100% (1)
- Mixing L 6-7Document60 paginiMixing L 6-7hyde2520015754Încă nu există evaluări
- Poem Summary - Keeping QuietDocument3 paginiPoem Summary - Keeping QuietVignesh Mohan100% (2)
- Industrial TYROLITc 21Document611 paginiIndustrial TYROLITc 21kamilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ancient CivilizationsDocument9 paginiAncient CivilizationsMarienne LaoÎncă nu există evaluări