Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
SPM Fizik Tingkatan 4,5 - Paper2 - 20120724090124
Încărcat de
Noratiqah Binti Mohd AminDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
SPM Fizik Tingkatan 4,5 - Paper2 - 20120724090124
Încărcat de
Noratiqah Binti Mohd AminDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
SMK KEPONG
PHYSICS Paper 2
<Test Name> Class : <Date> Time : Marks :
This question paper consists of three sections: Section A, Section B and Section C. Kertas soalan ini mengandungi tiga bahagian: Bahagian A, Bahagian B dan Bahagian C. Section A Bahagian A [60 marks] [60 markah] Answer all questions in this section. Jawab semua soalan dalam bahagian ini. 1. Diagram below shows a boat moving towards a beach. The movement of the waves is shown in Diagram below. Rajah di bawah menunjukkan bot bergerak ke arah pantai. Pergerakan ombak ditunjukkan dalam Rajah di bawah.
Diagram /Rajah (a) (i) What will happen to boat M when the water waves pass through boat M? Apakah yang akan berlaku kepada bot M apabila ombak air bergerak melalui bot M? __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ [1 mark/1 markah] (ii) Give your reason for your answer in (a)(i). Berikan sebab untuk jawapan anda di (a)(i). __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ [1 mark/1 markah] (b) (i) State two differences between the water waves at points A and B. Nyatakan dua perbezaan antara ombak air di titik A dan B. __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________
1
[2 marks/2 markah] (ii) State one similarity between the water waves at points A and B. Nyatakan satu persamaan antara ombak air di titik A dan B. __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ [1 mark/1 markah] (c) State the phenomenon involved at the point D. Nyatakan fenomena yang terlibat di titik D. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ [1 mark/1 markah] (d) If the frequency of the waves is 20 Hz, calculate the velocity of the waves at point B. Jika frekuensi ombak ialah 20 Hz, hitung halaju ombak di titik B.
[2 marks/2 markah] 2. The circuit below is used to investigate how the resistance of a lamp changes. Litar di bawah digunakan untuk menyiasat bagaimana rintangan satu lampu berubah.
Diagram / Rajah (a)Explain how component X allows a set of results to be obtained. Terangkan bagaimana komponen X membenarkan satu set keputusan diperoleh. _____________________________________________________________________________________ [2 marks/2 markah] (b The results obtained are used to plot a graph. ) Keputusan yang diperoleh digunakan untuk memplotkan satu graf.
Diagram / Rajah (i) Calculate the resistance of the lamp when the voltage is 4 V. Hitungkan rintangan lampu itu apabila voltan ialah 4 V.
[3 marks/3 markah] (ii)Explain how the graph shows that the resistance of the lamp increases as the voltage increases. Terangkan bagaimana graf itu menunjukkan rintangan lampu itu bertambah apabila voltan bertambah. ____________________________________________________________________________________ _ [1 mark/1 markah] 3. Table A shows three electrical appliances, their ratings and the number of hours they are used in a month. Jadual A menunjukkan tiga alat elektrik, kadar dan bilangan jam pengunaan dalam masa satu bulan. Electrical appliance Alat elektrik Television Televisyon Refrigerator Peti Sejuk Fan Kipas Rating Kadar 240 V, 2 000 W 240 V, 1 000 W 240 V, 500 W Number of hours used Bilangan jam pengunaan 200 100 300
Table A / Jadual A (a) i. What is meant by the rating 240 V, 2 000 W for a television? Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan kadar 240V, 2000 W pada televisyen? __________________________________________________________________________________ [1 mark/1 markah] ii. When the television functions normally, what is the current flowing through it? Apabila sebuah televisyon berfungsi secara normal, berapakah nilai arus yang mengalir melaluinya?
[2 marks/2 markah] iii. What is the most suitable value of fuse used for the television? Explain your answer. Berapakah nilai fius yang sesuai digunakan oleh televisyon? Terangkan jawapan anda. __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ [2 marks/2 markah] (b) Table B shows the tariff for the use of electrical energy in public housing in one month. Jadual B menunjukkan kadar tarif pengunaan tenaga elektrik untuk rumah kediaman awam dalam masa satu bulan. Electrical energy Tenaga elektrik First 100 unit 100 unit pertama Second 200 unit 200 unit kedua Every additional unit Setiap pertambahan unit Rate per unit Kadar per unit RM 0.20 RM 0.23 RM 0.25
Table B / Jadual B Based on Table B, calculate the total cost of using electrical energy for the electrical appliances listed in Table A. Berdasarkan Jadual B, kirakan jumlah kos penggunaan tenaga elektrik untuk peralatan elektrik dalam Jadual A.
[2 marks/2 markah] 4. Diagram A shows the structure of a simple d.c. generator. An e.m.f. is induced when the coil is set into rotation. The output of the generator is displayed on a CRO as shown in Diagram B. The time base of the CRO is set at 10 ms cm1 and the Y-gain at 50 mV cm1. Rajah A menunjukkan struktur satu penjana a.t. ringkas.Satu d.g.e. diaruhkan apabila gegelung itu disetkan ke putaran. Output penjana itu dipaparkan di atas OSK seperti ditunjukkan dalam Rajah B. Dasar masa bagi OSK disetkan pada 10 m s cm1 dan gandaan pada 50 mV cm1.
Diagram A/Rajah A
Diagram B/Rajah B (a) State the polarity at end R of the solenoid RS. Nyatakan kutub bagi hujung R solenoid RS. _____________________________________________________________________________________ [1 mark/1 markah] (b) Name the components labelled E and F. Namakan komponen yang dilabellkan E dan F. _____________________________________________________________________________________ [2 marks/2 markah] (c) Which points, (I, II, III and IV), in Diagram B correspond to the instants at which the plane of the coil is perpendicular to the magnetic field? Titik yang manakah (I, II, III dan IV) dalam Rajah B bersesuaian dengan saat di mana satah gegelung adalah berserenjang dengan medan magnet? _____________________________________________________________________________________ [1 mark/1 markah] (d) Find the peak voltage and frequency of the output of the generator. Cari voltan puncak dan frekunesi bagi voltan output penjana itu. _____________________________________________________________________________________ [1 mark/1 markah] (e) Describe what happens to the peak voltage and frequency of the output of the generator if Terangkan apa yang berlaku kepada voltan puncak dan frekuensi bagi output penjana itu jika (i) the speed of rotation of the coil is increased. laju putaran gegelung ditambahkan. __________________________________________________________________________________ [1 mark/1 markah] (ii) the resistance of the rheostat is increased. rintangan reostat ditambahlan. __________________________________________________________________________________ [1 mark/1 markah] (f) Name one alternation to the structure to change the d.c. generator to a.c. generator. Namakan satu gantian struktur yang mengubahkan penjana a.t. kepada penjana a.u. _____________________________________________________________________________________ [1 mark/1 markah]
5.
DIAGRAM / RAJAH Diagram above shows the arrangement of four diodes in a bridge rectifier for a step-down transformer used for full-wave rectification. Rajah di atas menunjukkan susunan empat diod dalam bentuk tetimbang bagi suatu transformer injak turun yang digunakan untuk rektifi kasi gelombang penuh. (a) Why is the circuit not connected directly to the 240 V a.c. power supply? Mengapakah litar itu tidak boleh disambung terus ke bekalan elektrik 240 V a.u.? _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ [1 mark/1 markah] (b) Which of the four diodes shown in the circuit is connected in the reverse direction? Antara empat diod yang ditunjukkan dalam litar, manakah yang disambung terbalik? _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ [1 mark/1 markah] (c) If the mistake in the connection in (b) is corrected, sketch the shape of the trace observed on the CRO screen when the time-base is on. Jika kesilapan penyambungan dalam (b) dibetulkan, lakarkan bentuk surih yang diperhatikan pada skrin OSK apabila dasar masa dihidupkan. [1 mark/1 markah]
(d) (i) If a student connects a capacitor in parallel across a resistor R, sketch the shape of the trace obtained. Jika seorang pelajar menyambungkan satu kapasitor secara selari dengan perintang R, lakarkan bentuk surih yang diperoleh. [1 mark/1 markah]
(ii) What is the function of the capacitor? Apakah fungsi kapasitor itu? __________________________________________________________________________________ [1 mark/1 markah] (e) Sketch the shape of the trace observed on the CRO screen if diode D3 malfunctions. Jika diod D3 telah rosak, lakarkan bentuk surih yang diperhatikan pada skrin OSK. [1 mark/1 markah]
6.
The signals in Diagram A are applied to inputs A and B of the logic gate in Diagram B. (Note: 5 V denotes a high state of voltage and 0 V denotes a low state of voltage.) Isyarat-isyarat dalam Rajah A diaplikasikan kepada input A dan B bagi gek logik dalam Rajah B. (Perhatian: 5 V menandakan satu keadaan voltan tinggi dan 0 V menandakan satu keadaan voltan rendah.)
Diagram A/Rajah A Diagram B/Rajah B
Diagram B/Rajah B (a) (i) Name the gate shown in Diagram B. Namakan get yang ditunjukkan dalam Rajah B. [1 mark/markah] (ii) Draw the waveform of the output C of the logic gate. Lukiskan bentuk gelombang bagi output C bagi get logik itu. [2 marks/markah] (b) Box X in Diagram C represents an unknown logic gate. The variations of input voltages and the corresponding output voltage are shown in Diagram D. Kotak X dalam Rajah C mewakili satu get logik yang tidak diketahui. Perubahan voltan input dan voltan output yang sepadan ditunjukkan dalam Rajah D.
Diagram C/Rajah C
Diagram D/Rajah D (i) What is X? Apakah X? [1 mark/markah] (ii) Construct a truth table for X. Binakan jadual kebenaran bagi X. [2 marks/markah] 7. A radioactive substance X of mass number 234 and atomic number 91 undergoes decay to emit a radioactive particle and is transformed into another nuclide. When the particle passes through a magnetic field pointing into a piece of paper, it is deflected as shown in Diagram below. Satu bahan radioaktif X dengan nombor jisim 234 dan nombor atom 91 mengalami reputan untuk memancar satu zarah radioaktif dan ditukarkan kepada nuklid yang lain. Apabila zarah-zarah itu melalui satu medan magnet yang menuju ke dalam kertas, zarah-zarah itu terpesong seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam Rajah di bawah.
Diagram / Rajah (a) What type of radioactive particle is emitted by X? Apakah jenis zarah radioaktif yang dipancarkan oleh X? [1 mark/markah] (b) Write one equation to show the decay of X. Use the symbol Y to represent the daughter nuclide. What is the neutron number of the daughter nuclide Y? Tuliskan satu persamaan untuk menunjukkan reputan X. Gunakan simbol Y untuk mewakili anak nuklid. Apakah nombor neutron bagi anak nuklid Y? [2 marks/markah] (c) When the activity of radiation of X is recorded, a curve is obtained as shown in Diagram below. Apabila aktiviti bagi sinaran X dicatatkan, satu lengkungan diperoleh seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam Rajah di bawah.
Diagram / Rajah (i) Suggest one device which is suitable for detecting the activity of the radiation. Cadangkan satu alat yang sesuai untuk mengesan aktiviti bagi sinaran itu. [1 mark/markah] (ii) Why are the points not exactly on the smooth curve? Mengapakah titik-titik itu tidak berada tepat di atas lengkungan itu? [1 mark/markah] (iii Find the half-life of X as shown by the above diagram. ) Cari setengah hayat bagi X seperti yang ditunjukkan oleh rajah di atas. [1 mark/markah] (d) (i) The radioactive sample X is used as a tracer to investigate the digestive system of a patient by a doctor. Explain whether it is suitable by considering its half-life and the type of radiation. Sampel radioaktif X digunakan sebagai penyurih untuk menyiasat sistem penghadaman seorang pesakit oleh doktor. Terangkan sama ada ia sesuai dengan mengambil kira setengah hayatnya dan jenis sinaran. [1 mark/markah] (ii) Explain your answer. Terangkan jawapan anda. [2 marks/markah] 8. (a) Diagram A shows the arrangement of radioactive fuel rods in a nuclear reactor. Rajah A menunjukkan susunan rod bahan bakar radioaktif dalam satu reaktor nuklear.
Diagram A/Rajah A
Diagram B/Rajah B (i) The nuclear reactor is surrounded by steel inside a thick concrete shield. Explain why. Reaktor nuklear itu dikelilingi oleh keluli dalam satu perisai konkrit yang tebal. Terangkan mengapa. __________________________________________________________________________________ [2 marks/2 markah] (ii) State two harmful effects of radiation on humans. Nyatakan dua kesan sinaran yang berbahaya kepada manusia. __________________________________________________________________________________ [2 marks/2 markah] (iii Explain why precautions are taken for storing the radioactive fuel rods when they are removed from a ) reactor. Terangkan mengapa langkah-langkah berjaga diambil untuk menyimpan rod bahan bakar radioaktif itu apabila dialihkan dari reaktor itu. __________________________________________________________________________________ [1 mark/1 markah] (b) Diagram B shows the nuclear reaction taking place in a reactor. Rajah B menunjukkan tindak balas nuklear yang berlaku dalam satu reaktor. (i) What type of nuclear reaction is shown in the diagram? Apakah jenis tindak balas nuklear yang ditunjukkan dalam rajah itu? __________________________________________________________________________________ [1 mark/1 markah] (ii) What type of energy is transferred to barium and krypton in this reaction? Apakah jenis tenaga yang dipindahkan ke barium dan kripton dalam tindak balas ini? __________________________________________________________________________________ [1 mark/1 markah] (iii Explain how the energy produced in this reaction can be used to generate electricity in a nuclear power ) plant. Terangkan bagaimana tenaga dihasilkan dalam tindak balas ini boleh digunakan untuk menjana elektrik dalam satu loji kuasa nuklear. __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________
10
__________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ [3 marks/3 markah] Section B Bahagian B [20 marks] [20 markah] Answer any one question from this section. Jawab mana-mana satu soalan daripada bahagian ini. 9. Diagram A shows a cork floating on the water surface in a ripple tank. It is found that the cork oscillates up and down when a vibrating plastic sphere is dipped into the water surface. Diagram B shows a candle flame that is displaced from side to side when it is placed in front of a blasting loudspeaker. Rajah A menunjukkan satu gabus terapung di permukaan air suatu tangki riak. Didapati gabus bergetar turun-naik apabila permukaan air dikacau oleh suatu pencelup sfera yang bergetar. Rajah B menunjukkan api lilin yang disesarkan ke kiri dan ke kanan apabila diletakkan di hadapan suatu pembesar suara yang berbunyi.
Diagram A/Rajah A
Diagram B/Rajah B (a) (i) Explain the meaning of oscillation. Terangkan maksud getaran. [1 mark/1 markah] (ii) Based on the observations made on Diagram A and B, state the characteristics that are common and that are contrasting between the two situations. Hence, relate the characteristics of the oscillations of the cork and the candle flame to deduce a relevant physics concept.
11
Berdasarkan pemerhatian pada Rajah A dan B, nyatakan ciri-ciri sepunya dan berbeza bagi keduadua situasi itu. Seterusnya, hubungkaitkan ciri-ciri itu untuk membuat satu kesimpulan tentang konsep fizik yang berkaitan. [5 marks/5 markah] (b) A source of sound is placed at X, the centre of a wall in a room PQRS measuring 40 m 40 m. Suatu sumber bunyi diletakkan pada titik tengah X sebuah dinding pada sebuah bilik PQRS yang berukuran 40 m 40 m.
Diagram C / Rajah C (i) On Diagram C, draw the path of the sound wave from X, where it is transmitted , until it returns to X after reflections by each of the three walls. Lukiskan lintasan gelombang bunyi yang dipancarkan dari X dan kembali kepada X selepas dipantulkan oleh setiap tiga dinding yang lain itu. [1 mark/1 markah] (ii) State two reasons why the sound returned to X is less loud than the sound sent out from X. Nyatakan dua sebab mengapa kenyaringan bunyi yang kembali kepada X kurang daripada kenyaringan bunyi yang dipancarkan. [3 marks/3 markah] (c) Diagram D shows one of the uses of ultrasound . It is used to check the condition of the foetus in the mothers womb.The ultrasound used is usually of high frequency, about 100 times higher than the maximum frequency that is audible to humans. Rajah D menunjukkan kegunaan gelombang ultrasonik untuk mengesan keadaan fetus dalam kandungan ibu. Gelombang ultrasonik yang biasa digunakan mempunyai frekuensi lebih kurang 100 kali lebih tinggi daripada frekuensi maksimum yang boleh didengar oleh manusia.
Diagram D / Rajah D (i) Determine the approximate frequency of the ultrasound used. Tentukan nilai frekuensi anggaran ultrasonik yang digunakan. [1 mark/1 markah] (ii) Explain briefly the functions of the transmitter P and then receiver R in the process of foetus inspection. Terangkan secara ringkas fungsi pemancar P dan penerima R dalam proses pemeriksaan fetus. [2 marks/2 markah] (iii How does the ultrasound distinguish between the tissues and bony parts of the foetus? ) Bagaimanakah gelombang ultrasonik dapat membezakan antara bahagian tisu dengan tulang dalam badan fetus itu?
12
[2 marks/2 markah] (iv)Give one reason why X-rays are not suitable for foetus inspection. Berikan satu sebab mengapa sinar-X tidak digunakan untuk pemeriksaan fetus. [2 marks/2 markah] (v) State three differences between X-rays and ultrasound. Nyatakan tiga perbezaan antara sinar-X dengan gelombang ultrasonik. [3 marks/3 markah] 10. The national grid is an important system which ensures that the electric power supply is always continuous. After electrical energy is generated at the power generator, the electrical energy will be transferred through a few substations that contain transformers before reaching the consumers. Table A shows the current and potential difference of the electrical energy before and after passing through substation A during the transfer of electrical energy. Sistem rangkaian grid nasional merupakan satu sistem yang penting untuk memastikan bekalan kuasa elektrik adalah berterusan. Selepas tenaga elektrik dijanakan di stesen jana kuasa, tenaga elektrik itu akan dipindah melalui beberapa substesen yang mengandungi transformer sebelum sampai kepada penggunanya. Jadual A menunjukkan arus dan beza keupayaan tenaga elektrik sebelum dan selepas melalui suatu substesen A semasa penghantaran tenaga elektrik.
Table A/Jadual A Table B shows the current and the potential difference of the electrical energy before and after passing through substation B during the reception of electrical energy by the consumers. Jadual B menunjukkan arus dan beza keupayaan tenaga elektrik sebelum dan selepas melalui suatu substesen B semasa penerimaan tenaga elektrik oleh pengguna.
Table B/Jadual B (a) (i) What is the meaning of potential difference? Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan beza keupayaan? [1 mark/markah] (ii) By using only the information in Tables A and B, compare the characteristics of the power of the electric power that is transmitted and received by the consumers. Then state the relationship between current and potential difference when transmitting and receiving electrical energy. Menggunakan hanya maklumat dalam Jadual A dan B, bandingkan ciri-ciri kuasa elektrik yang dihantar dan diterima oleh pengguna. Seterusnya nyatakan hubungan antara arus dengan beza keupayaan semasa penghantaran dan penerimaan tenaga elektrik [5 marks/markah] (b) Generating electrical power involves the use of renewable sources and nonrenewable sources of energy. By using suitable examples, compare the 2 types of sources.
13
Penjanaan kuasa elektrik melibatkan penggunaan sumber tenaga yang boleh diperbaharui dan sumber tenaga yang tidak boleh diperbaharui. Dengan menggunakan contoh-contoh yang sesuai, bandingkan kedua-dua jenis sumber itu. [4 marks/markah] (c) When transferring and receiving electrical energy, poles such as those shown in Diagram below play an important role. Semasa penghantaran dan penerimaan tenaga elektrik, tiang-tiang seperti pada Rajah di bawah memainkan peranan yang sangat penting.
Diagram / Rajah By using your knowledge on the transfer of electrical energy and Diagram above, explain; Menggunakan pengetahuan anda tentang penghantaran tenaga elektrik dan Rajah di atas, terangkan; (i) the safety features that are needed to build the poles, ciri-ciri keselamatan yang diperlukan untuk membina tiang, (ii) the properties of the cables that are used. ciri-ciri kabel yang digunakan. [10 marks/markah] Section C Bahagian C [20 marks] [20 markah] Answer any one question from this section. Jawab mana-mana satu soalan daripada bahagian ini. 11. Diagram A shows a heating element in an electric kettle. Table A shows the characteristics of some materials that can be used for making a heating element. Rajah A menunjukkan satu unsur pemanas dalam sebuah cerek elektrik. Jadual A menunjukkan ciri-ciri bahan yang boleh digunakan untuk membuat unsur pemanas.
Diagram A/Rajah A
14
Table A/Jadual A (a) i. What is meant by resistance? Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan rintangan? [1 mark/1 markah] ii. You are assigned to investigate the characteristics of the materials in Table A for use in the making of a heating element as shown in Diagram A. Anda ditugaskan untuk mengkaji ciri-ciri bahan dalam Jadual A untuk digunakan bagi membuat unsur pemanas seperti pada Rajah A. Explain the suitability of each characteristic in Table A and then determine the most suitable material for making into a heating element. State the reasons for your choice. Terangkan kesesuaian setiap ciri dalam Jadual A dan seterusnya tentukan bahan yang paling sesuai untuk membuat unsur pemanas itu. Berikan sebab-sebab untuk pilihan anda. [10 marks/10 markah] (b) Diagram B shows a circuit for determining the electromotive force and the internal resistance of a dry cell. Rajah B menunjukkan satu litar untuk menentukan daya gerak elektrik dan rintangan dalam sel bagi satu sel kering.
Diagram B/Rajah B i. Sketch a graph of potential difference against current for the circuit. Use your graph to explain how the electromotive force and the internal resistance of a dry cell can be determined. Lakarkan graf beza keupayaan melawan arus bagi litar itu. Gunakan graf anda untuk menerangkan bagaimana daya gerak elektrik dan rintangan dalam sel kering dapat ditentukan. [4 marks/4 markah] ii. The total resistance for both the resistors and rheostat in the circuit is 5 ohm. Calculate the current in the circuit if the potential difference before the switch is on and after the switch is on are 6 V and 5 V respectively. Then, calculate the internal resistance of the dry cell. Jumlah rintangan bagi kedua-dua perintang dan reostat dalam litar itu ialah 5 ohm. Hitungkan arus dalam litar jika beza keupayaan sebelum suis ditutup dan selepas suis ditutup masing-masing ialah 6 V dan 5 V. Seterusnya, kirakan rintangan dalam sel kering itu. [5 marks/5 markah]
15
12. Diagram below shows a sign indicating Danger! Ionising Radiations commonly seen outside a nuclear and radioactivity laboratory. Rajah di bawah menunjukkan suatu tanda yang menyatakan Bahaya! Sinaran Pengionan yang biasa dilihat di luar suatu makmal Nuklear dan Radioaktif.
Diagram / Rajah (a) (i) What is meant by radioactivity? Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan radioaktiviti? [1 mark/1 markah] (ii) Name the three types of ionizing radiation produced by a radioactive source. Berikan nama tiga jenis sinaran pengionan yang dihasilkan oleh suatu sumber radioaktif. [2 marks/2 markah] (iii State the nature of each type of ionizing radiation given in your answer in (a)ii. ) Nyatakan ciri asli setiap jenis sinaran pengionan dalam jawapan anda di (a)(ii). [2 marks/2 markah] (b) In a hospital, a doctor intends to use a radioisotope as a tracer to detect blood clots in a patients leg. Table below shows the characteristics of five radioisotopes. Di sebuah hospital, seorang doktor ingin menggunakan suatu radioisotop sebagai penyurih untuk mengesan pembekuan darah pada kaki seorang pesakit. Jadual di bawah menunjukkan ciri-ciri bagi lima radioisotop itu.
TABLE / JADUAL (i) Explain the suitability of the characteristics of the radioisotopes to be used as medical tracers to detect blood clots. Terangkan kesesuaian ciri-ciri radioisotop itu untuk digunakan sebagai penyurih perubatan untuk mengesan kedudukan pembekuan darah. (ii) Hence determine the most suitable choice of the radioisotope and give reasons for your choice. Dengan demikian, tentukan radioisotop yang paling sesuai dan berikan sebab bagi pemilihan anda.
16
[10 marks/10 markah] (c) Diagram below shows the activity of a certain radioisotope, X. Rajah di bawah menunjukkan aktiviti bagi suatu radioisotop X.
Diagram / Rajah (i) Estimate the half-life of radioisotoped X. Anggarkan setengah-hayat bagi radioisotop X. [1 mark/1 markah] (ii) A freshly prepared sample of radioisotope X has an initial activity of 3 200 counts per minute. How long does it take for its activity to be reduced to 400 counts per minute? Suatu radioisotop X yang baru disediakan mempunyai aktiviti 3 200 bilangan per minit. Berapa lamakah yang diambil untuk aktivitinya berkurang kepada 400 bilangan per minit? [2 marks/2 markah] (iii Radioisotope decays to a nuclide, Y, by alpha particle emission. ) Write an equation to represent this radioactive decay. Radioisotop mereput menjadi nuklid Y dengan memancarkan zarah alfa. Tuliskan satu persamaan untuk mewakili pereputan radioaktif ini. [2 marks/2 markah]
SMK KEPONG Jawapan
SPM Fizik Tingkatan 4,5 - SOALAN FORM 5 PAPER 2 Kertas 2
1. (a) (i) Boat M will be moving up and down. Bot M bergerak ke atas dan ke bawah. (ii) The molecules of water move perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the water. Molekul air bergerak berserenjang dengan arah perambatan air. (b) (i) The wavelength of water waves is shorterat A. Panjang gelombang air lebih pendek di A. The velocity of water waves is slower at A. Halaju air lebih perlahan di A. (ii) Has the same frequency Mempunyai frekuensi yang sama (c) Diffraction Pembelauan (d)
17
2.
(a) Component X can vary its resistance. This affects the current in the circuit. When the resistance is low, the current fl owing in the circuit is high. (b) (i) When V = 4 V, I = 1.6 A Using formula, V = IR 4 = (1.6)(R) R = 2.5 ohm
(ii) T he resistance is increases, the gradient decreases, the resistance increases. inversely proportional to gradient the gradient. When the voltage
3.
(a) i. Television needs 240 V source to function normally and the power of the television is 2 000 W. Televisyen memerlukan sumber 240 V untuk berfungsi dengan normal dan kuasa televisyen ialah 2000 W.
iii. A current of 9 A exceeds the normal situation. The fuse will melt and break the electric circuit/electricity immediately. Arus sebanyak 9 A melebihi situasi yang normal. Fius akan mencair dan memutuskan litar elektrik/ arus elektrik dengan segera. (b) The use of electrical energy Penggunaan tenaga elektrik = 2 kW 200 h + 1 kW 100 h + 0.5 kW 300 h = 400 kWh + 100 kWh + 150 kWh = 650 kWh The cost of electricity Kos penggunaan elektrik = 100 RM 0.20 + 200 RM 0.23 + 350 RM 0.25 = RM 153.50 4. (a) North (b) E: half-ring F: carbon brush (c) I and III (d) Peak voltage = 50 mV
18
(e) (i) Peak voltage increases. Frequency of the output increases. (ii) Peak voltage decreases. Frequency of the output remains unchanged. (f) Use a slip-ring instead of the half-ring. 5. (a) High voltage will cause malfunction of the diode Voltan yang terlalu tinggi akan merosakkan diod. (b) D4 (c)
(d) i.
ii. Acts as a current regulator/smoother Bertindak sebagai perata arus. (e)
6.
(a) i. OR gate ii.
(b) i. NOR gate ii.
7.
(a) X emits particles.
(b)
Neutron number of Y = 234 92 = 142 (c) i. GM tube
19
ii. Radiation has a random nature. iii. Half-life = 3 hours (d) i. The half-life is suitable to be used since it is short enough to reduce the harmful effect and long enough for the doctor to make diagnosis. ii. The type of radiation, b, is not suitable since the penetrating power of b is not large enough to pass to the outside of the human body for detection. 8. (a) (i) To prevent the escape of radioactive rays and keep radiation in the radiator. Alpha and beta radiation cannot penetrate through thick concrete and gamma radiation can be reduced by thick concrete (ii) Can cause cell mutation which results in cancer Severe skin burns Damage to the reproductive cells (iii) Radioactive fuel rods contain dangerous radioactive wastes which emit harmful radioation rays (b) (i) Nuclear fission (ii) Heat energy (iii) Nuclear fission of uranium produces a high amount of heat energy The heat liberated heats up the surrounding water in the nuclear power plant Heat changes water to steam The steam generated drives the turbines which turn the electrical generator Electricity is generated 9. (a) (i) An oscillation is a to-and-fro motion along a fixed path. (ii) 1. The sphere and the candle flame are in vibration. [1 m] 2. Vibrating sphere produces water waves. [1 m] 3. Water waves transfer energy from the sphere to the ball. [1 m] 4. The vibrating cone of the speaker produces sound waves. [1 m] 5. Sound waves transfer energy from the cone to the candle flame. [1 m] 6. Vibrations of water waves are vertical, perpendicular to the direction of wave motion. [1 m] 7. Vibrations of sound waves are horizontal, parallel to the direction of wave motion. [1 m] 8. Physics concept: wave A wave transfers energy from the source to points around it by vibrations in the medium. (b) (i)
[1 m] (ii) 1. On each reflection, part of the sound energy is absorbed by the wall. [1 m] 2. The energy of sound decreases with distance travelled. [1 m]
20
3. The loudness of sound depends on the energy of the sound wave. [1 m] (c) (i) Maximum audible frequency, 0 = 20 000 Hz [1 m] Frequency of ultrasound used, = 1000 = 100 20 000 = 2.0 106 Hz [1 m] (ii) 1. Transmitter P emits ultrasound downwards to the foetus. [1 m] 2. Detector R receives the ultrasound reflected by the various parts of the foetus. [1 m] (iii) The soft tissues of the foetus absorb most of the incident ultrasound, reflect very little. The bony parts will absorb very little, but reflect most of the ultrasound. The reflected ultrasound will produce an image of contrasting brightness. [2 m] (iv) X-rays have high ionization power, can damage and kill the cells of the foetus. [1 m] (v) Differences
[3 m] 10. (a) i. The potential difference between 2 points is the work done to move a coulomb of charge from one point to another. [1 m] ii. At the power generator system, the electrical power produced is in the form of low potential difference. [1 m] After passing through substation A, the potential difference of electrical power increases while the current decreases so that the amount of power lost can be reduced. [1 m] Before reaching the consumers, the potential difference is lowered so that it is suitable for the consumers. [1 m] Potential difference can be increased by using a step-up transformer can be reduced by using a stepdown transformer. [1 m] When the potential difference is increased, the value of the current will decrease. This is also the same when potential difference is decreased, value of current will increase. [1 m] (b) Examples of non-renewable sources are coal, natural gas and nuclear energy. [1 m] These sources will be depleted if they are used frequently and will normally pollute the environment. [1 m] Examples of renewable sources are hydroelectric power, solar energy, biomass and wind energy. [1 m] These sources will not be depleted and their usage usually will not pollute the
21
environment. [1 m] (c) i. The poles need to be earthed. [1 m] This is to carry the extra charges straight to the earth. Glass or porcelain is fixed at the connecting areas of the cable at the poles. [1 m] so that the metal poles did not touch the electric cable directly. This will cause the poles to be at potential earth condition and is safe to touch. [1 m] Red light is fixed at high poles. [1 m] This is to give warning or signal for helicopters or aeroplanes so that collision does not happen. [1 m] ii. Aluminium cable that is cheap and has low resistance is chosen. [1 m] So that the amount of power lost when transferring can be reduced. [1 m] The cable must be insulated. [1 m] So that it is not dangerous when kites or other things got stuck at the cable. [1 m] 11. (a) i. Resistance is the ratio of potential difference to current. Rintangan adalah nisbah beza keupayaan kepada arus. ii. A high melting point Takat lebur yang tinggi So that the heating element does not melt easily at high temperatures Supaya elemen pemanasan tidak melebur dengan mudah pada suhu yang tinggi A low resistance Rintangan yang rendah So that a larger current can flow through it. This will produce a better heating effect. Supaya arus yang lebih besar boleh mengalir melaluinya. Ini akan menghasilkan suatu kesan pemanasan yang lebih baik Does not break easily at high temperatures Tidak berpecah dengan mudah pada suhu yang tinggi So that the heating element can last longer and is not spoilt at high temperatures. Supaya elemen pemanasan boleh tahan lebih lama dan tidak rosak pada suhu yang tinggi Not easily oxidised. Tidak mudah dioksidakan So that water that is boiled is free from chemicals. Supaya air yang dididihkan adalah bebas daripada bahan kimia Material P is chosen. Bahan P dipilih. This is because material P has a high boiling point, low resistance, not easy to break at high temperatures and is not very easily oxidised. Ini disebabkan bahan P mempunyai takat didih yang tinggi, rintangan rendah, tidak mudah pecah pada suhu yang tinggi dan tidak mudah sangat dioksidakan (b) i.
Electromotive force is determined by extending the graph to cut the y-axis (When x = 0) Daya gerak elektromagnet ditentukan dengan memanjangkan graf untuk memotong
22
pada paksi-y (apabila x = 0) Internal resistance of the dry cell is determined by the gradient of the graph. Rintangan dalam sel kering ditentukan oleh kecerunan graf ii. Potential difference that flows across the resistor when the switch is switched on is V = 5 V, Beza keupayaan yang merentasi perintang apabila suis dipasang pada V= 5V, with this the current that flows in the circuit is dengan arus ini yang mengalir dalam litar ialah I = _V _ = _ 5 R 10 = 0.5 A The potential difference that is lost in the dry cell is Beza keupayaan yang hilang dalam sel kering itu ialah V = 6 V -5 V = 1V The internal resistance of the dry cell is/ Rintangan dalam sel kering itu ialah r
12. (a) (i) Radioactivity is a process where an unstable nucleus decays spontaneously to become a more stable nucleus by emitting radioactive radiation. Keradioaktifan adalah proses di mana nukleus tak stabil mereput secara spontan menjadi nukleus yang lebih stabil dengan memancar sinaran radioaktif. (ii) Alpha particles, beta particles, gamma radiation. Zarah alfa, zarah beta, sinaran gama. (iii) An alpha particle is a helium nucleus. Zarah alfa adalah nukleus helium. A beta particle is a fast moving electron. Zarah beta adalah elektron yang bergerak cepat. Sinaran gamma radiation is an electromagnetic radiation. Sinaran gama adalah sinaran elektromagnet. (b) (i) The radioisotope must be in the liquid state, so that it is convenient to be injected into the bloodstream. Beta or low energy gamma rays are suitable, as they can penetrate body tissues. Energy of the radiation emitted must be low so that it does not damage/kill the living cells in the body. Half-life must be short, but long enough for doctors to measure the activity of the injected radioisotope. Radioisotop harus dalam keadaan cecair, supaya ia adalah sesuai untuk disuntik ke dalam aliran darah. Beta atau sinar gama yang bertenaga rendah adalah sesuai, sebab boleh menembusi tisu badan. Tenaga daripada sinaran yang dipancarkan harus rendah supaya ia tidak merosakkan/membunuh selsel hidup badan. Setengah hayat harus pendek, tetapi cukup masa untuk doktor mengukur aktiviti bagi radioisotop yang disuntik. (ii) Best choice = iodine-123, as it is in liquid state, emits low energy gamma rays and has a half-life
23
of 13.2 hours which is long enough for medical investigation, but will be harmless to the patient after a few days. Pilihan yang paling baik = Iodin-123, sebab ia adalah dalam keadaan cecair, memancarkan gama yang bertenaga rendah dan mempunyai setengah hayat 13.2 jam yang cukup panjang untuk penyiasatan perubatan. tetapi akan berbahaya kepada pesakit selepas beberapa hari. (c) (i) Half-life is the time taken for activity to decrease to half its original value. Setengah hayat adalah masa yang diambil untuk aktiviti berkurang kepada setengah nilai asalnya. At t = 0, activity/aktiviti = 2000 Cpm. Pada t = 10 min, activity/aktiviti = 1000 Cpm. Hence, half life = 10 minutes Maka, setengah hayat = 10 minit (ii)
(iii)
24
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Topic Test Oxfordaqa International Gcse Physics 9203 Generating and Distributing Electricity and Household UseDocument12 paginiTopic Test Oxfordaqa International Gcse Physics 9203 Generating and Distributing Electricity and Household Useandhi soesilo100% (2)
- Chapter 2 Force and MotionDocument26 paginiChapter 2 Force and MotionAdsham75% (4)
- Applied Combinatorics, Second Edition by Fred S Roberts, Barry TesmanDocument889 paginiApplied Combinatorics, Second Edition by Fred S Roberts, Barry TesmanAnil kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Turbo Expander TrainingDocument58 paginiTurbo Expander TrainingM Joko Susilo100% (6)
- Electromagnetism ExplainedDocument11 paginiElectromagnetism ExplainedruukiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Land Based SensorsDocument40 paginiLand Based SensorsJ.MichaelLooneyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fourth Monthly Exam T.L.E 7 S.Y. 2019 - 2020Document2 paginiFourth Monthly Exam T.L.E 7 S.Y. 2019 - 2020riela dhee lagramaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Text Linguistics and Classical Studies - Facebook Com LinguaLIBDocument129 paginiText Linguistics and Classical Studies - Facebook Com LinguaLIBEnglish Buzz100% (1)
- Bio PharmaceuticsDocument48 paginiBio PharmaceuticsRajan Kashyap100% (2)
- Stator Generator EolianDocument40 paginiStator Generator EolianCatalin BordeiÎncă nu există evaluări
- UI5 TrainingDocument110 paginiUI5 TrainingShailesh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Citect V7.0 Error Codes PDFDocument13 paginiCitect V7.0 Error Codes PDFWahyu PrakosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CO2 Production PlantsDocument4 paginiCO2 Production PlantsBoojie Recto100% (1)
- KUKA Sim 30 Installation enDocument49 paginiKUKA Sim 30 Installation enRégis Naydo0% (1)
- Welcome to the Official Opening Ceremony of ASEAN Awareness Exhibition 2013Document5 paginiWelcome to the Official Opening Ceremony of ASEAN Awareness Exhibition 2013Noratiqah Binti Mohd Amin100% (3)
- Principios Básicos para El Diseño de Instalaciones de Bombas CentrífugasDocument392 paginiPrincipios Básicos para El Diseño de Instalaciones de Bombas CentrífugasChristian Vargas94% (16)
- Topical Test WaveDocument24 paginiTopical Test WaveMazuva JaparÎncă nu există evaluări
- MODUL BERFOKUS FIZIK JPNPP 2015 BAB ELEKTRONIKDocument21 paginiMODUL BERFOKUS FIZIK JPNPP 2015 BAB ELEKTRONIKsyahrilizaham78Încă nu există evaluări
- The 555 Timer Astable OscillatorDocument3 paginiThe 555 Timer Astable Oscillatorregata4Încă nu există evaluări
- How the Number of Coil Turns Affects Transformer OutputDocument9 paginiHow the Number of Coil Turns Affects Transformer OutputkeiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Induced Potential Transformers Nat GridDocument81 paginiInduced Potential Transformers Nat Gridjennynwigwe187Încă nu există evaluări
- OxfordAQA International A Level Physics Magnetic Fields Test ExplainedDocument12 paginiOxfordAQA International A Level Physics Magnetic Fields Test Explainedandhi soesiloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity On DC Power Supply Circuits PDFDocument8 paginiActivity On DC Power Supply Circuits PDFRaymund TanapÎncă nu există evaluări
- N Y VMVFXNJ epjvbmd7IHTl20v9eiaxtY3GMxOPFp0rbYwwZAxVGFZuGfgt8K65IxqZK5eZq6YzP1tPnr0Q7cg - aTFQA G1kuw9WsqJyiqRI1Xxo7UMt - U3f 02TS6Q1 i5g3wSHSgstLDocument25 paginiN Y VMVFXNJ epjvbmd7IHTl20v9eiaxtY3GMxOPFp0rbYwwZAxVGFZuGfgt8K65IxqZK5eZq6YzP1tPnr0Q7cg - aTFQA G1kuw9WsqJyiqRI1Xxo7UMt - U3f 02TS6Q1 i5g3wSHSgstLIlyas Amiri Year 10Încă nu există evaluări
- P7.6 Loudspeakers and Micorphones Exam QDocument8 paginiP7.6 Loudspeakers and Micorphones Exam QParveen JonesÎncă nu există evaluări
- St. Joseph's Anglo-Chinese School: NSS Physics SBA Manual The Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO)Document5 paginiSt. Joseph's Anglo-Chinese School: NSS Physics SBA Manual The Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO)Alyssa ColeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3B Properties of WavesDocument16 pagini3B Properties of Wavesjryjh8s2s5Încă nu există evaluări
- Practical Skills RP7-12Document11 paginiPractical Skills RP7-12Deepesh SureshÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Rate and Extent of Chemical ChangeDocument11 paginiThe Rate and Extent of Chemical ChangeKirsten AntonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exp 4Document8 paginiExp 4Elisbeth MurugasÎncă nu există evaluări
- SULIT 1 4531/1 Key Physics ConceptsDocument19 paginiSULIT 1 4531/1 Key Physics ConceptsAdibah AliasÎncă nu există evaluări
- DOUBLE DIGIT PPR 2 QZ 2024 FINAL COPY (2)Document11 paginiDOUBLE DIGIT PPR 2 QZ 2024 FINAL COPY (2)vngerechaÎncă nu există evaluări
- p5 Pressure in Fluids and Atmospheric Pressure Phys OnlyDocument21 paginip5 Pressure in Fluids and Atmospheric Pressure Phys OnlyAlain EkwogeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Productivity Improvement and Centre of ExcellenceDocument2 paginiProductivity Improvement and Centre of Excellencekirubel DestaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PElabmanual (Fall 2022)Document32 paginiPElabmanual (Fall 2022)Qurat Ul AinÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2022 - Electric Motors and Drivers - Module 2Document6 pagini2022 - Electric Motors and Drivers - Module 2Ammarul NafikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Triac ExperimentsDocument6 paginiTriac ExperimentsLJ Asencion CacotÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSEC Physics January 2011 P2 PDFDocument17 paginiCSEC Physics January 2011 P2 PDFcxcchemistryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Med Rev MockDocument26 paginiMed Rev MockEmanAdhem100% (1)
- Kami Export - Aljawharah Alqahtani - Circuit LabDocument6 paginiKami Export - Aljawharah Alqahtani - Circuit LabAljawharah AlqahtaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCT-335 InM LabManual 01Document5 paginiMCT-335 InM LabManual 01MoazamÎncă nu există evaluări
- OxfordAQA International AS level Physics Topic Test: Oscillations and WavesDocument15 paginiOxfordAQA International AS level Physics Topic Test: Oscillations and Wavesandhi soesilo100% (1)
- Waves StationaryDocument8 paginiWaves Stationarysingh cos tanÎncă nu există evaluări
- G9 Measuring Current and Voltage 2018 AnnotatedDocument5 paginiG9 Measuring Current and Voltage 2018 Annotatedvan080080Încă nu există evaluări
- Fizik PPT 2014 t4Document11 paginiFizik PPT 2014 t4Nor Hasniyyah Ab HalimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stationary WavesDocument16 paginiStationary WavesKavya NemaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Magnetism Exam Questions StudentDocument11 paginiMagnetism Exam Questions StudentPAM NOBÎncă nu există evaluări
- As Practice 2Document30 paginiAs Practice 2gytiheceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sda PP3 MockDocument17 paginiSda PP3 MockRICH HOPEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Program Lonjakan Cemerlang Sains Upsr: 1. Diagram 1 Shows An Experiment That Has Been Carried Out by LimDocument7 paginiProgram Lonjakan Cemerlang Sains Upsr: 1. Diagram 1 Shows An Experiment That Has Been Carried Out by Limbohari77Încă nu există evaluări
- MagnetsDocument26 paginiMagnetsapi-422428700Încă nu există evaluări
- Stationary Waves Exam Q and ADocument20 paginiStationary Waves Exam Q and AVanessa AdetuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Measuring Earthquake WavesDocument8 paginiMeasuring Earthquake WavesAlexander Joe CamilleriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity 3Document12 paginiActivity 3Kurt Vendane VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 153D3F2BFF7CFF0729EB5088345643CEDocument10 pagini153D3F2BFF7CFF0729EB5088345643CENoor Ulain NabeelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transistor MultivibratorDocument5 paginiTransistor MultivibratorMatt ImriÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Electricity (F)Document23 pagini2 Electricity (F)arshpaunikar304Încă nu există evaluări
- Wheat Stone Bridge ReportDocument6 paginiWheat Stone Bridge Reportash1890Încă nu există evaluări
- Module Decision MakingDocument9 paginiModule Decision MakingSarimah AbuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phy Pp2 Quick Revision Series Exams 2Document208 paginiPhy Pp2 Quick Revision Series Exams 2griticenanjalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energy Questions Part 2: NameDocument79 paginiEnergy Questions Part 2: NameMark ParrÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5054 s16 QP 22 PDFDocument16 pagini5054 s16 QP 22 PDFAhmediqraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7 Magnetism and ElectromagnetismDocument20 pagini7 Magnetism and ElectromagnetismJust WadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Magnet Wire Movement Magnetic Field ExperimentDocument5 paginiMagnet Wire Movement Magnetic Field ExperimentashokÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics F3 OpenerDocument7 paginiPhysics F3 OpenerLawrence NyakangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- P1 - Test 6 Energy Advanced: Grade MarkDocument16 paginiP1 - Test 6 Energy Advanced: Grade MarkdamindaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.2.2 Quantum Exam Q and ADocument106 pagini3.2.2 Quantum Exam Q and ASameer UddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Activity No. Ohm's Law and Electric Power: PHINMA-University of PangasinanDocument10 paginiLab Activity No. Ohm's Law and Electric Power: PHINMA-University of Pangasinanstorage websiteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Waves-In-Air-Fluids-And-Solids - CGSE PDFDocument76 paginiWaves-In-Air-Fluids-And-Solids - CGSE PDFFelix WibowoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic Test: Oxfordaqa International A Level PhysicsDocument16 paginiTopic Test: Oxfordaqa International A Level Physicsandhi soesiloÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.2 Specific Heat CapacityDocument25 pagini4.2 Specific Heat CapacityNoratiqah Binti Mohd AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reinforcement Exercise Chapter 3Document3 paginiReinforcement Exercise Chapter 3Noratiqah Binti Mohd AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 - Fluid Mechanics - Fis - 2020Document69 paginiChapter 4 - Fluid Mechanics - Fis - 2020Noratiqah Binti Mohd AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 8 4.1 Thermal EquilbriumDocument16 paginiGroup 8 4.1 Thermal EquilbriumNoratiqah Binti Mohd AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reinforcement 11.05Document2 paginiReinforcement 11.05Noratiqah Binti Mohd AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ytp Hon Phy F5Document4 paginiYtp Hon Phy F5Noratiqah Binti Mohd AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics LessonDocument2 paginiPhysics LessonNoratiqah Binti Mohd AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Music Lineup for Majlis Bingkisan Pawana EventDocument1 paginăMusic Lineup for Majlis Bingkisan Pawana EventNoratiqah Binti Mohd AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teks Pengacara Majlis Sekalung Budi Sejambak Kasih - LaguDocument1 paginăTeks Pengacara Majlis Sekalung Budi Sejambak Kasih - LaguNoratiqah Binti Mohd AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Totally Reflecting Prisms: Total Internal Reflection MirrorDocument3 paginiTotally Reflecting Prisms: Total Internal Reflection MirrorNoratiqah Binti Mohd AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Assessment Framework of Physics Project 960/4 STPM 2019/2020 Sekolah Menengah JK Chung Hwa, Kelantan Assessment Project ReportDocument1 paginăThe Assessment Framework of Physics Project 960/4 STPM 2019/2020 Sekolah Menengah JK Chung Hwa, Kelantan Assessment Project ReportNoratiqah Binti Mohd AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Music Lineup for Majlis Bingkisan Pawana EventDocument1 paginăMusic Lineup for Majlis Bingkisan Pawana EventNoratiqah Binti Mohd AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Assessment Framework of Physics Project 960/4 STPM 2019/2020 Sekolah Menengah JK Chung Hwa, Kelantan Assessment Project ReportDocument1 paginăThe Assessment Framework of Physics Project 960/4 STPM 2019/2020 Sekolah Menengah JK Chung Hwa, Kelantan Assessment Project ReportNoratiqah Binti Mohd AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Silibus f6Document132 paginiSilibus f6Noratiqah Binti Mohd AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revising Physics ConceptsDocument3 paginiRevising Physics ConceptsNoratiqah Binti Mohd AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analisis Fizik STPM Updated 2018 ADocument11 paginiAnalisis Fizik STPM Updated 2018 ANoratiqah Binti Mohd AminÎncă nu există evaluări
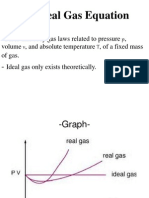
- Ideal Gas Equation PV=nRT ExplainedDocument6 paginiIdeal Gas Equation PV=nRT ExplainedNoratiqah Binti Mohd AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- CheckingDocument1 paginăCheckingNoratiqah Binti Mohd AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- It Is A RealityDocument1 paginăIt Is A RealityNoratiqah Binti Mohd AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Degrees of Freedom and Equipartition Law ExplainedDocument6 paginiDegrees of Freedom and Equipartition Law ExplainedNoratiqah Binti Mohd AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Degrees of Freedom and Equipartition Law ExplainedDocument6 paginiDegrees of Freedom and Equipartition Law ExplainedNoratiqah Binti Mohd AminÎncă nu există evaluări
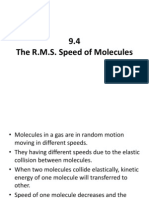
- 9.4 The R.M.S Speed of MoleculesDocument8 pagini9.4 The R.M.S Speed of MoleculesNoratiqah Binti Mohd AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Is It Simple To Explain Simple Experiments The Heavy Newspaper' Stick BreakDocument6 paginiIs It Simple To Explain Simple Experiments The Heavy Newspaper' Stick Break이온유Încă nu există evaluări
- in 01 en KATALOGDocument50 paginiin 01 en KATALOGSigma Ragam ManunggalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shop Exercise 5Document16 paginiShop Exercise 5Athena GrotesqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rudolf Steiner - Warmth Course GA 321Document119 paginiRudolf Steiner - Warmth Course GA 321Raul PopescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 10 - Dry Etching PDFDocument7 paginiLecture 10 - Dry Etching PDFSiddhant ModiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0620 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The March 2015 SeriesDocument6 pagini0620 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The March 2015 SeriesDark GreenÎncă nu există evaluări
- AS TRONIC, The ZF-AS TRONIC Software Can Be: 4.7.6 EOL Programming Documentation of The EOL ProgrammingDocument3 paginiAS TRONIC, The ZF-AS TRONIC Software Can Be: 4.7.6 EOL Programming Documentation of The EOL ProgrammingThylaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- 60 4690e PDFDocument3 pagini60 4690e PDFMarudhasalamMarudhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Procedure in Ribbon MakingDocument24 paginiProcedure in Ribbon MakingRucel Ann CarreonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Micro Shelter Product Description V5aDocument11 paginiMicro Shelter Product Description V5aIan JaredÎncă nu există evaluări
- Astm-e855 Изгиб МеталлаDocument8 paginiAstm-e855 Изгиб МеталлаАлесь БуяковÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refining of MaterialsDocument38 paginiRefining of MaterialsJAWAD AHMAD BURTÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Nuts and Bolts: 2.1 Deterministic vs. Randomized AlgorithmsDocument13 pagini2 Nuts and Bolts: 2.1 Deterministic vs. Randomized AlgorithmsEdmund ZinÎncă nu există evaluări
- ContentServer PDFDocument16 paginiContentServer PDFdaniel leon marinÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11xx12xx SMDocument44 pagini11xx12xx SMfanticelliÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSC4212 Lecture 3 - 3D Viewing - Projection TransformationDocument31 paginiCSC4212 Lecture 3 - 3D Viewing - Projection TransformationAhmad AbbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essay #1 - Second DraftDocument6 paginiEssay #1 - Second DraftHayden NganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review For Mastery: VocabularyDocument3 paginiReview For Mastery: VocabularyHala EidÎncă nu există evaluări