Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
NCP Stroke
Încărcat de
Michael John F. NatividadTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
NCP Stroke
Încărcat de
Michael John F. NatividadDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
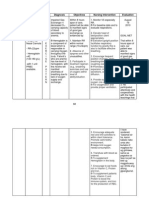
Assessment S= Not Applicable O=The patient manifested the ff:
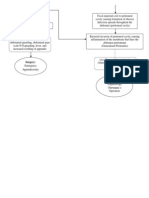
Diagnosis of stroke and right sided paralysis Lethargy decreased level of consciousness (GCS 3 E1V1M1) depressed cough reflex difficulty swallowing without choking
Nursing Diagnosis Risk for aspiration r/t decreased level of consciousness
Planning SHORT TERM: After 1 hour of Nursing Interventions, the patients significant other will verbalize understanding of importance of elevating head of bed to prevent aspiration. LONG TERM: After 7 days of Nursing Interventions, the patient will remain free from aspiration as evidenced by absence of dyspnea, normal vital signs, and absence of crackles.
Interventions
Monitor level of consciousness.
Rationale
A decreased level of consciousness is a prime risk factor for aspiration. A depressed cough or gag reflex increases the risk of aspiration Decreased gastrointestinal motility increases the risk of aspiration because food or fluids accumulate in the stomach. Aspiration of small amounts can occur without coughing or sudden onset of respiratory distress, especially in patients with decreased levels of consciousness.
Evaluation SHORT TERM: After 1 hour of Nursing Interventions, the patients significant other verbalized understanding of importance of elevating head of bed to prevent aspiration. LONG TERM: After 7 days of Nursing Interventions, the patient remained free from aspiration as evidenced by absence of dyspnea, normal vital signs, and absence of crackles.
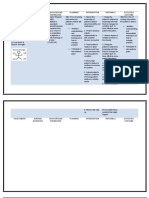
Assess cough and gag reflexes.
Auscultate bowel sounds to evaluate bowel motility.
Assess pulmonary status for clinical evidence of aspiration. Auscultate breath sounds for development of crackles and/or rhonchi. Keep suction setup available and use as needed. Notify the physician or other health care provider immediately of noted decrease in cough and/or gag
This is necessary to maintain a patent airway.
Early intervention protects the patients airway and prevents aspiration.
reflexes or difficulty in swallowing. Position patients who have a decreased level of consciousness on their sides.
This protects the airway. Proper positioning can decrease the risk of aspiration. Comatose patients need frequent turning to facilitate drainage of secretions. A displaced tube may erroneously deliver tube feeding into the airway. High amounts of residual (>50% of previous hours intake) indicate delayed gastric emptying and can cause distention of the stomach leading to reflux emesis. Promotes cooperation
Check placement of NGT before feeding. Check residuals before feeding. Hold feedings if residuals are high and notify the physician.
Explain importance of elevating HOB to SO. Maintain upright position for 30 to 45 minutes after feeding. Assist with postural drainage.
The upright position facilitates the gravitational flow of food or fluid through the alimentary tract. Mobilizes thickened secretions.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Stroke NCPDocument5 paginiStroke NCPChantal Caragan100% (1)
- NCP For StrokeDocument4 paginiNCP For StrokeJASON OGALESCOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument185 paginiIneffective Breathing PatternSusi LambiyantiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument4 paginiNursing Diagnosis: Impaired Gas ExchangeShen Paril0% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 paginiNursing Care PlanJayalakshmi David50% (2)
- CAD NCP Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument3 paginiCAD NCP Decreased Cardiac OutputLeizel Apolonio100% (3)
- Impaired Physical Mobility Related To Neuromuscular ImpairmentDocument17 paginiImpaired Physical Mobility Related To Neuromuscular ImpairmentAileen Lopez83% (6)
- NCPDocument17 paginiNCPbalongetzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Causes and Nursing Care of Pleural EffusionDocument4 paginiCauses and Nursing Care of Pleural EffusionHania Polangi100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Disuse SyndromeDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan: Risk For Disuse SyndromeRozsy FakhrurÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDocument2 paginiNCP Activity Intolerancea22hous0% (1)
- NCP PROPER Pain and Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument3 paginiNCP PROPER Pain and Decreased Cardiac OutputErienne Lae Manangan - CadalsoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP - Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 paginiNCP - Impaired Gas Exchangejanelee2824Încă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument22 paginiNursing Care PlanjamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glaucoma NCPDocument4 paginiGlaucoma NCPChantal CaraganÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP For PediaDocument10 paginiNCP For PediavonkinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan For Acute Head InjuryDocument4 paginiNursing Care Plan For Acute Head InjuryAngie Mandeoya67% (3)
- NCP Tissue PerfusionDocument4 paginiNCP Tissue PerfusionLisa Tandog100% (1)
- NCP 1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 paginiNCP 1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceDivine Jane PurciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals & Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: NDX: Goal: Independent: Goal EvaluationDocument5 paginiCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals & Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: NDX: Goal: Independent: Goal EvaluationNash DimarucotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity IntoleranceDocument2 paginiActivity Intoleranceayra_alegreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern As Evidenced by Use of Accessory Muscles and Episodes of DyspneaDocument3 paginiIneffective Breathing Pattern As Evidenced by Use of Accessory Muscles and Episodes of DyspneaNiel MinatozakiÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP AneurysmDocument4 paginiNCP AneurysmJanielle Christine Monsalud100% (1)
- Possible NCP For CVDDocument6 paginiPossible NCP For CVDVincent Bulla50% (2)
- Pleural Effusion FdarDocument1 paginăPleural Effusion FdarvanessabdeveraÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP PTBDocument2 paginiNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP For CTTDocument1 paginăNCP For CTTJen Rhae LimÎncă nu există evaluări
- NURSINGCAREPLANDocument7 paginiNURSINGCAREPLANMonica Gagarin Cortez100% (1)
- Risk For InjuryDocument2 paginiRisk For InjuryRo-anne AkuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument10 paginiAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationLean Ashly Tuddao Macarubbo0% (1)
- Activity IntoleranceDocument3 paginiActivity IntoleranceGen RodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsDocument3 paginiNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP For OxygenationDocument6 paginiNCP For OxygenationChriz LechÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cva NCPDocument1 paginăCva NCPxiang jinÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPDocument3 paginiNCPJezza RequilmeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Care Plan Prep May 13 Rheumatic FeverDocument16 paginiCare Plan Prep May 13 Rheumatic Feverapi-256360167Încă nu există evaluări
- Diarrhea Care PlanDocument2 paginiDiarrhea Care Planzepoli_zepoly6232100% (1)
- Transient Ischemic Attack: A Case StudyDocument44 paginiTransient Ischemic Attack: A Case Studytinay100% (8)
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 paginiImpaired Gas ExchangeAura Salve Ildefonso Allas100% (3)
- Ncp-Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument3 paginiNcp-Ineffective Airway Clearancelouanne0550% (2)
- NCP (BODY WEAKNESS)Document3 paginiNCP (BODY WEAKNESS)Jum ChumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument20 paginiDrug StudydjanindÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 paginiNCP - Ineffective Airway Clearancelarapatricia1215Încă nu există evaluări
- Activity Intolerance Related To Decrease Blood FlowDocument3 paginiActivity Intolerance Related To Decrease Blood FlowDarkCeades100% (3)
- Assessing and Managing Sleep DeprivationDocument2 paginiAssessing and Managing Sleep DeprivationDavid Brillo100% (1)
- NCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYDocument4 paginiNCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYMa. Elaine Carla Tating100% (2)
- NCP For Acvute PainDocument6 paginiNCP For Acvute PainGlenn ValerioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Delayed Surgical RecoveryDocument10 paginiDelayed Surgical Recoveryapi-283151124Încă nu există evaluări
- Risk For Aspiration: Risk For Aspiration: at Risk For Entry of Gastrointestinal Secretions, Oropharyngeal SecretionDocument6 paginiRisk For Aspiration: Risk For Aspiration: at Risk For Entry of Gastrointestinal Secretions, Oropharyngeal SecretionAngie MandeoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 paginiAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationNicole Marin-ChingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Desired OutcomesDocument4 paginiDesired Outcomesapi-302415380Încă nu există evaluări
- NCP For ChildrenDocument17 paginiNCP For ChildrenRachel Niu IIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seminar: Albert J Bredenoord, John E Pandolfi No, André J P M SmoutDocument10 paginiSeminar: Albert J Bredenoord, John E Pandolfi No, André J P M SmoutIsmael SaenzÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPDocument8 paginiNCPzharienabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing responsibilities for magnesium sulfate, ferrous sulfate, antibiotics, and postoperative careDocument13 paginiNursing responsibilities for magnesium sulfate, ferrous sulfate, antibiotics, and postoperative careabrokenheartedgirlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pyloric Stenosis WDocument11 paginiPyloric Stenosis WKlaue Neiv CallaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patient Information: Acid Reflux (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) in Adults (Beyond The Basics)Document10 paginiPatient Information: Acid Reflux (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) in Adults (Beyond The Basics)wandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Untitled 2Document2 paginiUntitled 2Mark MarivelesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nasogastric Tube Care and Post-Op Patient AssessmentDocument7 paginiNasogastric Tube Care and Post-Op Patient AssessmentabezareljvenÎncă nu există evaluări
- PregnancyDocument18 paginiPregnancyEdwYenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resume and Application Letter NotesDocument2 paginiResume and Application Letter NotesMichael John F. NatividadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resume and Application Letter NotesDocument2 paginiResume and Application Letter NotesMichael John F. NatividadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mastertally FormDocument21 paginiMastertally FormMichael John F. NatividadÎncă nu există evaluări
- L5J Linda Smith Resume Chronological Targeted Branded V4Document2 paginiL5J Linda Smith Resume Chronological Targeted Branded V4Michael John F. NatividadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plan of Activities MJFNDocument2 paginiPlan of Activities MJFNMichael John F. NatividadÎncă nu există evaluări
- ResumesDocument2 paginiResumesMichael John F. NatividadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monitoring Sheet NewDocument1 paginăMonitoring Sheet NewMichael John F. NatividadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Application LettersDocument3 paginiSample Application LettersMitchie GumeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSWD Field Office AddressDocument2 paginiDSWD Field Office AddressMichael John F. NatividadÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP HemothoraxDocument3 paginiNCP HemothoraxMichael John F. NatividadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hemodialysis at Home ARTICLEDocument3 paginiHemodialysis at Home ARTICLEMichael John F. NatividadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology SantolDocument2 paginiPathophysiology SantolMichael John F. NatividadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accounting SampleDocument2 paginiAccounting SampleMichael John F. NatividadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resume WorksheetDocument4 paginiResume WorksheetMichael John F. NatividadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample ResumesDocument5 paginiSample ResumesMichael John F. NatividadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guide 1Document2 paginiGuide 1Saithila ThilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample CV (Nursing)Document3 paginiSample CV (Nursing)gina puspitasariÎncă nu există evaluări
- CspdsampleresumeDocument2 paginiCspdsampleresumeapi-235269449Încă nu există evaluări
- AUB Finance Grad Seeks Financial Analyst RoleDocument1 paginăAUB Finance Grad Seeks Financial Analyst RoleAnu SathwikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tan Kumar Ali: Sample & Format of A Resume (A)Document5 paginiTan Kumar Ali: Sample & Format of A Resume (A)Nadeem SahilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Examination For PneumoniaDocument5 paginiPhysical Examination For PneumoniaMichael John F. NatividadÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPDocument3 paginiNCPMichael John F. NatividadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Date Doctor'S Order Nursing Responsibilities AnalysisDocument6 paginiDate Doctor'S Order Nursing Responsibilities AnalysisMichael John F. NatividadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Community Acquired Pneumonia, A Case StudyDocument26 paginiCommunity Acquired Pneumonia, A Case StudyMenggay SanDiego57% (7)
- Discharge Planning PTBDocument2 paginiDischarge Planning PTBMichael John F. NatividadÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Solicitation LetterDocument1 paginăNew Solicitation LetterMichael John F. NatividadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument2 paginiAnatomy and PhysiologyMichael John F. NatividadÎncă nu există evaluări
- GORDONs For PNEUMONIA Final and EditedDocument2 paginiGORDONs For PNEUMONIA Final and EditedMichael John F. Natividad67% (3)
- Certfor NSGWEEKDocument2 paginiCertfor NSGWEEKMichael John F. NatividadÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP GunshotDocument13 paginiNCP GunshotMichael John F. Natividad0% (1)
- NewTrendsInLeadershipandManagement ArikkokDocument32 paginiNewTrendsInLeadershipandManagement Arikkoksocofem288Încă nu există evaluări
- Defining Public RelationsDocument4 paginiDefining Public RelationsKARTAVYA SINGHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Turabian Sample PaperDocument9 paginiTurabian Sample Paperemme_lopez908133% (3)
- MBA 2020: Research on Online Shopping in IndiaDocument4 paginiMBA 2020: Research on Online Shopping in Indiaprayas sarkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Powers of Central Govt under Environment Protection ActDocument13 paginiPowers of Central Govt under Environment Protection Actsirajudeen IÎncă nu există evaluări
- S 212 Pre Course WorkDocument5 paginiS 212 Pre Course Workafiwierot100% (2)
- ManuscriptDocument2 paginiManuscriptVanya QuistoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Primary 2 (Grade 2) - GEP Practice: Contest Problems With Full SolutionsDocument24 paginiPrimary 2 (Grade 2) - GEP Practice: Contest Problems With Full Solutionswenxinyu1002100% (1)
- IonosondeDocument3 paginiIonosondeFaizan GoharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Frequently Asked Questions: Wiring RulesDocument21 paginiFrequently Asked Questions: Wiring RulesRashdan HarunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acid content in fruitsDocument2 paginiAcid content in fruitsbone fire100% (1)
- EMarketer Time Spent With Media SnapshotDocument13 paginiEMarketer Time Spent With Media SnapshotWei ShingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Historical Source Author Date of The Event Objective of The Event Persons Involved Main ArgumentDocument5 paginiHistorical Source Author Date of The Event Objective of The Event Persons Involved Main ArgumentMark Saldie RoncesvallesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Graphic Organizers for Organizing IdeasDocument11 paginiGraphic Organizers for Organizing IdeasMargie Tirado JavierÎncă nu există evaluări
- MMADDocument2 paginiMMADHariharan SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clustering Social Network GraphsDocument12 paginiClustering Social Network GraphsRáhùl SréédhãrÎncă nu există evaluări
- HUMAN RIGHTS, RATIONALITY, AND SENTIMENTALITYDocument13 paginiHUMAN RIGHTS, RATIONALITY, AND SENTIMENTALITYJohn HunterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matrices Class 12 Maths Important Questions Chapter 3 - Learn CBSEDocument41 paginiMatrices Class 12 Maths Important Questions Chapter 3 - Learn CBSEkhateeb ul islam qadriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Primavera Inspire For Sap: Increased Profitability Through Superior TransparencyDocument4 paginiPrimavera Inspire For Sap: Increased Profitability Through Superior TransparencyAnbu ManoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strata KT Office OpportunityDocument41 paginiStrata KT Office OpportunitySanskar SurekaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Direction: Read The Questions Carefully. Write The Letters of The Correct AnswerDocument3 paginiDirection: Read The Questions Carefully. Write The Letters of The Correct AnswerRomyross JavierÎncă nu există evaluări
- Temptations in MinistryDocument115 paginiTemptations in MinistryJoseph Koech100% (1)
- Project Report VajDocument15 paginiProject Report VajTamil SelvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPSS-TEST Survey QuestionnaireDocument2 paginiSPSS-TEST Survey QuestionnaireAkshay PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ir Pc-1: Pre-Check (PC) Design Criteria For Freestanding Signs and Scoreboards: 2019 CBCDocument15 paginiIr Pc-1: Pre-Check (PC) Design Criteria For Freestanding Signs and Scoreboards: 2019 CBCAbrar AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- T Cells & Autoimmunity, s3Document21 paginiT Cells & Autoimmunity, s3LiaAriestaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gujarat Technological University: Emester ViDocument4 paginiGujarat Technological University: Emester ViPradeep SutharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neural Network For PLC PDFDocument7 paginiNeural Network For PLC PDFMarcelo Moya CajasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gregory University Library Assignment on Qualities of a Reader Service LibrarianDocument7 paginiGregory University Library Assignment on Qualities of a Reader Service LibrarianEnyiogu AbrahamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual EDocument12 paginiManual EKrum KashavarovÎncă nu există evaluări