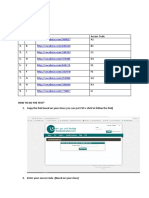
Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
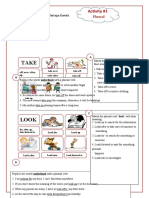
Part of Speech
Încărcat de
beatrizgraciaDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Part of Speech
Încărcat de
beatrizgraciaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
An adverb is a word that changes or qualifies the meaning of a verb, adjective, other adverb,clause, sentence or any other word
or phrase, except that it does not include the adjectivesand determiners that directly modify nouns.
ADVERBS OF MANNER :This adverb usually comes after the direct object or if there is no direct object, after the verb. ADVERBS OF PLACE - This adverb usually comes after the object, otherwise after the verb. ADVERBS OF TIME This adverb usually comes either at the very beginning of the sentence or at the end. ADVERBS OF FREQUENCY This adverb comes after the verb 'to be': ADVERBS OF DEGREE This adverb can modify an adverb or an adjective and comes before the word it modifies:
Conjunctions are joining words or phrases that connect together phrases to form longer sentences.
Compound conjunctions
Compound conjunctions come as phrases, where several words together act as a join.
ubordinating conjunctions
A Subordinating conjunction joins a subordinate clause to the main clause.
Correlative conjunctions
Correlative conjunctions surround a word or phrase and show how the two phrases are correlated (often causally).
ARTICLE_: A somewhat arbitrarily defined small group of determiners that are placed before nouns.
Definite article: The word The is the definite article and it indicates that the noun that follows has already been defined in some way. Indefinite article: Indefinite articles are the words a and an. They refer to some object not particularly known to the person to whom you are talking. No article: No articles are also called as zero articles. No article is used in the following cases.
Noun:Nouns name people, places, things, or ideas. Common: These name general, nonspecific people, places, things, or ideas. They start with a lowercase letter unless they begin a sentence. For example: writer, city, park, religion Proper: These name specific people, places, things, or ideas. They always start with a capital letter. For example: Victor Hugo, Paris, Disneyland, Christianity Abstract: These are the opposite of concrete. They name something that you cannot perceive with your five senses - something that does not physically exist. For example: happiness, freedom, Christianity Concrete: These name something that you can perceive with your five senses something that physically exists. For example: cat, chocolate, Martha Countable: Yep. You guessed it. These can be counted, and they use both the singular and the plural forms. Anything that you can make plural is a countable noun. For example: clock/clocks, David/Davids, poem/poems Uncountable: These guys cannot be counted. Since they cannot be counted, they only use the singular form. For example: milk, rice, water *Note that you would never ask for milks, rices, or waters! That just sounds crazy! Compound: These are made up of two or more smaller words. For example: tablecloth, haircut, applesauce Collective Nouns: These are singular nouns that refer to a group of things as one whole. For example: class, audience, swarm Singular: These refer to one person, place, thing, or idea. For example: box, face, road, ball Plural: These refer to more than one person, place, thing, or idea. They generally end in with an s.
Verb: A verb is a word that expresses action or a state of being.
Transitive Verbs: These verbs involve a direct object. Intransitive Verbs: These verbs do not involve a direct object.
Regular Verbs.Those verbs that form their past participle with d or ed are regular verbs Irregular Verbs.Those verbs that undergo substantial changes when changing forms between tenses are irregular verbs.
Lexical Verbs.A lexical verb is the main verb of the sentence.
Auxiliary verbs: always precede main verbs within a verb phrase.
transitive verbs: Transitive verbs are action verbs that have an object to receive that
action.
intransitive verbs: Intransitive verbs are action verbs but unlike transitive verbs, the do not have an object receiving the action.
Adjective:An adjective describes a noun or a pronoun. DESCRIPTIVE ADJECTIVE: These types of adjectives add detail or description to the noun. LIMITING ADJECTIVE: These types of adjectives specify or limit the noun. PREDICATE ADJECTIVE: This is a special type of adjective that follows a linking verb and modifies (directly refers to) the subject of the sentence. Preposition: Sometimes it helps to start with examples and pictures.
Preposition for Place. Prepositions in, on or at are usually used for different places.
Prepositions for Time. (in, on, at)
Prepositions used for time of different natures are in, on at etc.
Preposition for Direction. (to, toward, through, into)
Prepositions like to, towards, through, into are used to describe the direction.
Preposition for Agent. (by)
Preposition for agent is used for a thing which is cause of another thing in the sentence.
Preposition for device, instrument or machine.
Different preposition are used by different devices, instruments or machines.
Preposition for Agent. (by)
Preposition for agent is used for a thing which is cause of another thing in the sentence
Interjection: An interjection is a word that shows emotion.
Punctuating Interjections
Interjections are punctuated with an exclamation mark or a comma. Diagramming sentences is a visual way to show how the words in a sentence are related to each other.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- LorenaFernández - It PaperDocument7 paginiLorenaFernández - It PaperbeatrizgraciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Education 2.0Document1 paginăEducation 2.0beatrizgraciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- By: Lorena Fernández, Sindi Granados and Marisol CruzDocument4 paginiBy: Lorena Fernández, Sindi Granados and Marisol CruzbeatrizgraciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- By: Lorena Fernández, Sindi Granados and Marisol CruzDocument4 paginiBy: Lorena Fernández, Sindi Granados and Marisol CruzbeatrizgraciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- How To Integrate Blogs in The English ClassroomDocument1 paginăHow To Integrate Blogs in The English ClassroombeatrizgraciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Part of SpeechDocument4 paginiPart of SpeechbeatrizgraciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- How To Integrate Blogs in The English ClassroomDocument1 paginăHow To Integrate Blogs in The English ClassroombeatrizgraciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Digital Natives, Digital ImmigrantsDocument2 paginiDigital Natives, Digital ImmigrantsbeatrizgraciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Digital Natives, Digital ImmigrantsDocument2 paginiDigital Natives, Digital ImmigrantsbeatrizgraciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- Digital Natives, Digital ImmigrantsDocument2 paginiDigital Natives, Digital ImmigrantsbeatrizgraciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adverb: Is A Word That Tells Us More About A Verb.: Adjective: An Adjective Describes A Noun or A PronounDocument1 paginăAdverb: Is A Word That Tells Us More About A Verb.: Adjective: An Adjective Describes A Noun or A PronounbeatrizgraciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Advertising Is An Activity of Attracting Public Attention To A Product or BusinessDocument8 paginiAdvertising Is An Activity of Attracting Public Attention To A Product or Businessgbhavani_hbs12Încă nu există evaluări
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- All Ready 1 Lesson PlansDocument89 paginiAll Ready 1 Lesson PlansYamileth Carreño Salazar50% (4)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Grade 11 Ela Curriculum MapDocument16 paginiGrade 11 Ela Curriculum Mapapi-320980022Încă nu există evaluări
- Maxim Gorky The WriterDocument4 paginiMaxim Gorky The WriterMaksim PlebejacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Vocabulary Size TestDocument5 paginiVocabulary Size TestDemelia WulandariÎncă nu există evaluări
- BAKER - Thematic Roles and Syntactic StructureDocument66 paginiBAKER - Thematic Roles and Syntactic StructureRerisson CavalcanteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spontaneous Spoken LanguageDocument16 paginiSpontaneous Spoken Languagenadin_lazarovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Assessing ListeningDocument26 paginiAssessing Listeningkarensun21100% (1)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Interdisciplinary Center For Narratology-EditedDocument16 paginiInterdisciplinary Center For Narratology-Editedde061185Încă nu există evaluări
- времената в таблицаDocument2 paginiвремената в таблицаGeorgi TodorovÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Basic Counseling SkillsDocument16 paginiBasic Counseling SkillsRachel MiguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- SWR Rule Pages & Grammar - by SectionDocument2 paginiSWR Rule Pages & Grammar - by Sectionpaxbonum24Încă nu există evaluări
- Performance Tasks For English Language ArtsDocument20 paginiPerformance Tasks For English Language ArtsMelisa StoccoÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Short List of PrefixesDocument8 paginiA Short List of PrefixesedykeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity #1: María Ángel Madariaga BandaDocument1 paginăActivity #1: María Ángel Madariaga BandaJuan MadariagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Isilimela Hospital Speech Therapy DepartmentDocument2 paginiIsilimela Hospital Speech Therapy DepartmentSuné GreeffÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER 9 PronounsDocument32 paginiCHAPTER 9 PronounszubayersumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Adverbs of MannerDocument2 paginiAdverbs of MannerAngélica Vidal PozúÎncă nu există evaluări
- XII - Expert-Cae-Advanced XII FDocument4 paginiXII - Expert-Cae-Advanced XII FBogdan ZancuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Decoding Power High Frequency Word Cards 1Document466 paginiDecoding Power High Frequency Word Cards 1api-234790734Încă nu există evaluări
- French Language Education in Nigeria, Challenges and ProspectsDocument12 paginiFrench Language Education in Nigeria, Challenges and ProspectsDerick AshuabuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grades 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Plan School Corcuera National High Grade Level 12Document5 paginiGrades 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Plan School Corcuera National High Grade Level 12Bernadette FalcesoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Have Have GotDocument3 paginiHave Have GotManuel Garcia GrandyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 41-Article Text-211-1-10-20181216 PDFDocument5 pagini41-Article Text-211-1-10-20181216 PDFJovana Joja MilosevicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oxford TCC ExamDocument36 paginiOxford TCC ExamLolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plan de Lectie Clasa A 9aDocument2 paginiPlan de Lectie Clasa A 9aAura AvonÎncă nu există evaluări
- AlliterationDocument2 paginiAlliteration3000wattsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reading Meeting Me and Uncle Romie Day 2Document3 paginiReading Meeting Me and Uncle Romie Day 2api-252145631100% (1)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- 06 - Overcoming Communication BarriersDocument23 pagini06 - Overcoming Communication Barriersnafis20Încă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 23 - ㅎ Irregular - Korean Colors, 이렇다, 그렇다 and 저렇다Document16 paginiLesson 23 - ㅎ Irregular - Korean Colors, 이렇다, 그렇다 and 저렇다Andreea DanielaÎncă nu există evaluări