Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
U3cea06 Engineering Mechanics Key
Încărcat de
kiranphdTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
U3cea06 Engineering Mechanics Key
Încărcat de
kiranphdDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
B.E / B.Tech.
DEGREE EXAMINATIONS, NOV/DEC 2011
SEMESTER-III
CIVIL ENGINEERING
U3CEA06 / ENGINEERING MECHANICS KEY
1. Principle of transmissibility is stated as follows:
A force need not be considered to be considered to act at a point but may be
considered to be applied at any point on its line of action without affecting the net
effects external to the rigid body on which it acts.
2. Two systems of forces are said to be equivalent when they can be replaced by the
same force couple system at a given point.
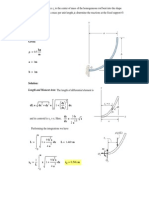
3. 10N 10N 40N
a. 3m 5m
A B
b. Equivalent single force = 10 10 + 40 = 40 N acting vertically upwards
40 x = 40 8 10 3
(Or) x = 7.25m from A
4. A rigid body is one on which when force is applied there is no deformation in shape
and size of the body. Thus there is no change in its dimensions.
5. A diagram which is separated from its surroundings (wall mountings, hinges, etc)
focused by the force system with the introduction of reaction forces is called as free
body diagram.
6. F
x
= 0; F
y
o; M = 0
7. It states that, If the moment of inertia of a plane area about an axis through its
centroid be denoted by I
G
, the moment of inertia of the area about an axis AB; parallel
to the first and at a distance h from the centre of gravity is given by,
a. I
AB
= I
G
+ Ah
2
8. It states that, If I
xx
and I
yy
be the moment of inertia of a plane section about two
perpendicular axes meeting at O, the moment of inertia I
zz
about the axis z-z,
perpendicular to the plane and passing through the intersection of x x and y y is
given by the relation,I
zz
= I
xx
+ I
yy
9. The second moment of area about a pole O is called the polar moment of inertia
(I
p
).i.e., I
p
= I
xx
+ I
yy
10. The motion of a particle is said to be curvilinear, if it moves along a curved path.
11. It state that When a particle moves from position s
1
to s
2
. under the action of a force
F
1
the change in kinetic energy of the particle is equal to the work of the force F.
12. Ft = m(v-u),Where F=Impulsive force,T=time taken, M=mass of the body, U=Initial
velocity,V=final velocity
13. Rolling wheel,Sliding rod.
14. =
o
+ t, =
o
t + t
2,
2
=
o
2
+ 2,where
o
= Initial angular velocity, =
Final angular velocity, = angular acceleration, = angular displacement.
15. A rigid body is said to be in translation if the linear displacement of every point in the
rigid body is the same. i.e., the orientation of any line drawn on the body remains
unchanged, but its position is changed.
PART-B
16. A).i.Given data with unit conversion-2 marks
Ii.formulae-2 marks
iii. -10 marks
2 2 2
x Y z
2 2 o 2 o
Y
2 2 o 2 o
Y
2
Y
Y
o
Y
Y
0
Y
Y
cos cos cos 1
cos cos 69.3 cos 57.9
cos cos 69.3 cos 57.9
cos 0.592
cos 0.769
140.3 or 39.73
Since is negative
140.3
cos is negative
+ +
t
1
1
1
]
Y
Y
F
F
cos
174
F
0.769
F 226.26N
X X Z z
o o
X z
x z
F Fcos : F Fcos
F 226.26 cos69.3 ; F 226.26cos57.9
F 79.97N : F 120.23N
16.B).i.Given data with unit conversion-2 marks
Ii.formulae-2 marks
iii.Free body diagram-2 marks
iv.Solution -6 marks
X y
F 0 or F 0; F 0
( )
( ) ( )
PA PB
PB
PB
or 0.71F 0.42F 2kN 2
1 2 gives 0.49 F 1kN
1kN
or F 2.04kN
0.49
+
Substituting F
PB
= 2.04kN in eqn
PA
PA
PA
0.71F 0.91 2.04kN 3kN
or 0.71F 3kN 1.86kN 1.14kN
1.14kN
or F 1.61kN
0.71
+
v.Result -2 marks
(i) Tension in cable PA = 1.61 kN
(ii) Tension in cable PB = 2.04 kN
17. A.i.Given data with unit conversion -2 marks
ii.formulae -2 marks
iii. Solution -8 marks
2 2
x y
R R R +
Where R
x
= F
A
; R
y
=F
y
Let
1
and
2
be the angles of 374 N and 550 N with horizontal axis respectively.
1
1
o
1
1
2
o
2
375
tan
200
61.92
375
tan
500
36.86
,
_
Fig. Free body diagram
F
x
=374 cos (61.92
o
)-550cos36.86
o
-836
F
x
=-1100N
F
y
=660+374 sin 61.92+550sin36.86
F
y
=1320N
( ) ( )
2 2
y 1
x
1
o
R 1100 1320
R 1718.25N
F
tan
F
1320
tan
1100
50.194
+
_
,
_
,
iv.Result -2 marks
(a) Resultant of the forces, R= 1718.25N.
(b) Resultant meet the base edge AD at 450mm from D and the edge AB at 300 mm from A.
17. B. i.Given data with unit conversion -2 marks
ii.formulae -2 marks
iii. Solution -8 marks
Applying conditions of equilibrium.
F
x
=0 H
A
+50 cos 70 -18 cos 50 =0
H
A
=-5.530 N
y
F 0
A B
A B
V 50sin70 30 18sin50 6 V 0
V V 96.77N
+
+
Taking moment about A,
A
M 0
[ ]
B
B
A A B
-30 200-18sin50 350-6 950+V 1100 0
V 15.024N
V 81.746N V V 96.77N
+ Q
Now, H
A
= -5.53 N
V
A
= 81.746 N
We know that,
2 2
A A A
R H V +
( ) ( )
2 2
A
A
R 81.746 5.530
R 81.93N
+
iv.Result -2 marks
(a) Pin reaction at A, R
A
=81.93 N
(b) Knife edge reaction at B, V
B
=15.024 N.
18.A) i.Given data with unit conversion -2 marks
ii.formulae -2 marks
iii. Solution -8 marks
3 3
xx yy
bd db
I ; I
12 12
El
ement
Ar
ea m
2
X
i
m
Y
i
m
I
xx
m
4
I
yy
m
4
A
i
h
1i
m
4
A
i
h
2i
m
4
1 8 0 4 4 0 8 16
+
H
A
= 5.53 N
+
+
2
3
4
16
8
8
.5
5
5
9
.5
7
3
4
2.67
5
.333
0
.666
4
2.67
.6667
8
5.33
4
2.67
0
.6667
64
32
8
2
0
0
16
2
40 9
1.339
1
29.333
11
2
32
4
i i
x
A x
x
A
i i
x
8 0.5+16 5+8 5+8 9.5
x=
8+16+8+8
x=5m
A y
y
A
_
C C
8 4+16 7+8 3+8 4
y=
8+16+8+8
y=5m
x 5m, y 5m
_
we have
i
2
xcxc xx i 1
I I Ah +
; where
( )
i
1 i
h y y
C C
C C
x x
4
x x
I 91.339 112
I 203.34m
+
similarly,
( )
i i
2
ycyc yy i 2 2 i
I I Ah ; Where h x x +
C C
C C
y y
4
y y
I 129.333 324
I 453.33m
+
iv.Result -2 marks
(i) moment of inertia,
C C
4
x x
I 203.34m
(ii) moment of inertia,
C C
4
y y
I 453.33m
18. B) i.Given data with unit conversion -2 marks
ii.formulae -2 marks
iii. Solution -8 marks
E
lement
Area
m
2
X
i
m
Y
i
m I
xx
m
4
I
yy
m
4
A
i
h
1
2
i
m
4
A
i
h
2
2
I
m
4
1 18 4 1 10 4
2
3
90= 1620
18
144=2592
18
90=1620
90
45
2
72+
18
2
=81
90
45
2
18
9
2
18+
144
2
=90
162+
18
2
=171
3740
4
478976
4
3740
093500
6
9984
1
093500
628820
0
10
628820
14720
1
036800
4
14720
5.832
10
3
4
566456
2
256984
21
257640
1
866240
3 3
xx yy
bd db
I ; I
12 12
( )
( )
2
xx xx i i
2
yy yy i i
i i
i
I I A y y
I I A x x
A x
x
A
+
+
x 61mm
,
y 90mm ( Q
The area is symmetrical about x axis)
i i
i
A y
y
A
( )
( )
( )
3
1 1
xx
1
3
4
xx
1
3
2 2
xx
2
b d
I
12
90
18
12
I 43740mm
b d
I
12
( )
( )
4
xx
2
3
3 2
xx
3
3
I =4478976 mm
b d
I =
12
90
= 18
12
( )
( ) ( )
( )
( )
4
xx
3
2
2
i 1 1 1
1
2
2
I =43740mm
Ah =A y y
= 1620 9-90
= 1620 -81
( )
2
xx xx i 1
i
4
xx
7 4
xx
Now I I Ah
I =25824096 mm
I 2.582 10 mm
+
( )
3
1 1
yy
1
b d
I
12
( )
( )
3
4
yy
2
3
3 3
yy
3
144
18
12
I =69984 mm
d b
I =
12
( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
3
4
yy
3
2
2
i 2 1 1
1
2
2
i 2
1
18
90
12
I 1093500 mm
Ah A x x
Ah 1620 45 61
( )
( ) ( )
( )
2 4
i 2
1
2
2
i 2 2 2
2
2
Ah 414720mm
Ah A x x
= 2592 81-61
( )
( ) ( )
( )
2 4
i 2
2
2
2
i 2 3 3
3
2
Ah 1036800 mm
Ah A x x
= 1620 45-61
( )
( )
2 4
i 2
3
2
yy yy i 2
i
Ah =414720 mm
I I Ah
+
yy
4
yy
6 4
yy
I 2256984 + 1866240
I =412344 mm
I 4.1232 10 mm
iv.Result -2 marks
i.I
xx
= 25.82 10
6
mm
4
ii.I
yy
= 4.123 10
6
mm
4
19.A) i.Given data with unit conversion -2 marks
ii.formulae -2 marks
iii. Solution & result -10 marks
Draw FBD and assume the tension in the rope and the direction of motion.
The weight can be resolved in to components
Consider 20kg Block
N
i
= 20g cos 30,f
1
= 20g cos 30 = 50.9742 N
Net force in the direction of motion = mass acceleration
T 98.1 n50.9742 = 20 a ------- (1)
Consider 40kg block
N
2
= 40 g cos 60 = 20 g
f
2
= 0.3 20 g = 58.86 N
Force into direction of motion = mass acceleration
40g sin 60 T 58.86 = 40a ------- (2)
Adding (1) and (2),131.894 = 60a
a = 2.1982 m/s
2
T = 193.039 N
Using Kinematics equation,u = 0, t = 4 sec
a = 2.1982 m/s
2,
v = u + at
= 8.7923 m/s.
19.B) i.Given data with unit conversion -2 marks
ii.formulae -2 marks
iii. Solution & result -10 marks
In this pulley system, it is observed that if 150 kg block moves downward by distance
x, 50kg block moves up by 2x.
Let a be the acceleration of 150 kg block, then the acceleration of 50 kg block is 2a.
Consideration 150 kg Block,Applying conditions of dynamic equilibrium,
2T+150a = 150x 9.81 1
=>T = --- {150(9.81-a}
Considering 50kg Block
Applying conditions of dynamic equilibrium.
T-50(2a) = 50x9.81
=> T = 100a +490.5
To determine the tension in the rope
From (1) & (2)
a = 1.401m/sec
2 ,
Substituting the value of a in equation (2), we get.
T = 100 x1.401+490.5.N
=> T=630.642N
Answers:
i) Acceleration of 50 kg Block = 2.802 m/sec
2
ii) Acceleration of 150 kg Block = 1.401 m/sec
2
iii) Tension in the rope, T = 630.642 N
20.A) i.Given data with unit conversion -2 marks
ii.formulae -2 marks
iii. Solution & result -10 marks
0
0
30 rpm
2 30
= rad/ s
60
6rev = 12 rad
mass moment of inertia
2
1555.2kgm
And kinematic equation,
( )
2 2
0
2
2
0 0
2
0.13089rad/s
2 12
M I
=1555.2 0.13089=203.575 Nm
+
Alternately
1. Using work energy principle
2 2
0
2
1
M I
2
1555.2
M 203.575 Nm
2 12
1
]
1
]
2. Using impulse momentum principle
0
t
0 0.13089 t
t 24 sec
+
+
[ ]
0
M t I
M 24 1555.2
M 203.575 Nm.
20.B) i.Given data with unit conversion -2 marks
ii.formulae -2 marks
iii. Solution & result -10 marks
2
0
1
2 2
I 20kgm
s r
s/ r 2/ 0.4 5 radians
/ r 3/ 0.4 7.5rad/ s
/ r
Because of no external force, we can use work energy principle,
Work done system = change in KE of the system
Work done by system = 2000 x 2 80 x .(1)
4000 80 5 3600 Nm
( )
2 2
1 1 1
2 2
2
2 2
2 2 2
2
2
1 1
KE m I
2 2
1 2000 1
3 20 7.5 1479.931 Nm
2 9.81 2
1 2000 20
KE
2 9.81 2
0.4
164.43679
+
+
+
Work energy principle,
3600 = 164.43679
2
2
1479.931
2
5.558 m/s.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Free Body DiagramsDocument4 paginiFree Body DiagramskiranphdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problems On AgesDocument1 paginăProblems On AgeskiranphdÎncă nu există evaluări
- CentroidDocument46 paginiCentroidkiranphd100% (2)
- Force Lecture NotesDocument53 paginiForce Lecture NoteskiranphdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Free-Body Diagram NotesDocument5 paginiFree-Body Diagram NoteskiranphdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics of Electricity & Magnetism: What's An Electron?Document6 paginiBasics of Electricity & Magnetism: What's An Electron?kiranphdÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Jurnal Kacang Hijau Dan MaduDocument7 paginiJurnal Kacang Hijau Dan Madusri margiatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kamal Din - Trainer Profile-2019 PDFDocument2 paginiKamal Din - Trainer Profile-2019 PDFChoy Hau Yan100% (1)
- Tom Wolf Mit ThesisDocument5 paginiTom Wolf Mit Thesisjpcbobkef100% (1)
- Activity 1-Introduce Biological ToolsDocument3 paginiActivity 1-Introduce Biological ToolsHaroldÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Genetics: Ms MB KekanaDocument31 paginiHuman Genetics: Ms MB Kekanavulkaan van huisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Professionalism in The Dental Office, Part One: I Chairside Conscience IDocument3 paginiProfessionalism in The Dental Office, Part One: I Chairside Conscience IKingjokerÎncă nu există evaluări
- MEV 015 Environmental Pollution 1Document281 paginiMEV 015 Environmental Pollution 1satabdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seed Health Testing in Field Crops Seeds........... AaaaaaaDocument37 paginiSeed Health Testing in Field Crops Seeds........... AaaaaaaJagadish GowdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Coaching - FundaDocument3 paginiFinal Coaching - FundaenzoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tryout Un Bahasa Inggris SMKDocument9 paginiTryout Un Bahasa Inggris SMKSMK Miftahul HikmahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Becoming An "Intimate Publics"Document5 paginiBecoming An "Intimate Publics"Gabriela PetrucciÎncă nu există evaluări
- ResumeDocument38 paginiResumeRiyaz SiddiqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business Plan PDFDocument86 paginiBusiness Plan PDFNicholas SalisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sentence HangmanDocument1 paginăSentence Hangmanwalbee2023Încă nu există evaluări
- Cultural Appropriation in The Fashion IndustryDocument2 paginiCultural Appropriation in The Fashion IndustrykristiancobaesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Father William - Poem by Lewis CarrollDocument1 paginăFather William - Poem by Lewis CarrollRachid AfrznaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week Logical FallaciesDocument79 paginiWeek Logical FallaciesSaqib AbbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Imovie 2020 PDF Guide PDFDocument2 paginiImovie 2020 PDF Guide PDFTanushka MalhotraÎncă nu există evaluări
- May (2012) Nonequivalent Comparison Group DesignsDocument21 paginiMay (2012) Nonequivalent Comparison Group Designsmathworld_0204Încă nu există evaluări
- Gear CouplingDocument10 paginiGear CouplingKlmdaya BashisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prevalencia Geofagia - 2014Document108 paginiPrevalencia Geofagia - 2014Farmaceutico RaulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Behavior Intervention PlanDocument22 paginiBehavior Intervention Planapi-343163369100% (1)
- Odisha PWD Registration in CDMSDocument2 paginiOdisha PWD Registration in CDMSSabyasachi Naik (Zico)Încă nu există evaluări
- Day 3 Reflection Paper - CmeDocument4 paginiDay 3 Reflection Paper - Cmeapi-322527937Încă nu există evaluări
- Stoeger Airguns Product Catalog 2022Document10 paginiStoeger Airguns Product Catalog 2022Jack JackÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proposed USG Boral Ceiling System For Tropicana MiyuDocument5 paginiProposed USG Boral Ceiling System For Tropicana MiyuLorraineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discrete Mathematics MATH 006 (TIP Reviewer)Document12 paginiDiscrete Mathematics MATH 006 (TIP Reviewer)James LindoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The 5-Phase New Pentagon Driver Chip Set: 1. Excitation Sequence GeneratorDocument11 paginiThe 5-Phase New Pentagon Driver Chip Set: 1. Excitation Sequence GeneratorFreddy MartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- TRIAS - Master ProposalDocument12 paginiTRIAS - Master ProposalHafidGaneshaSecretrdreamholicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Escalation Estimating Principles and Methods Using IndicesDocument4 paginiEscalation Estimating Principles and Methods Using IndicesAlejandro RuizÎncă nu există evaluări