Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Chemistry Report (Size of Reactant)
Încărcat de
Ain NajwaDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chemistry Report (Size of Reactant)
Încărcat de
Ain NajwaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
CHEMISTRY REPORT (The effect of the size of reactant on the rate of reaction) AIM PROBLEM STATEMENT HYPOTHESIS To investigate
the effect of the size of reactant on the rate of reaction Is the rate of reaction between calcium carbonate, CaCO and dilute hydrochloric acid, HCl affected by the size of the calcium carbonate, CaCO chips? The rate of reaction increases when smaller calcium carbonate, CaCO chips are used MANIPULATED VARIABLE : Size of calcium carbonate, CaCO chips or marble chips RESPONDING VARIABLE : The rate of reaction FIXED VARIABLES : Mass of marble chips; volume and concentration of dilute hydrochloric acid, HCl; temperature of reaction mixture. 100 cm conical flask; basin; burette; delivery tube with rubber stopper; retort stand with clamp; stop watch; measuring cylinder; mortar and pestle; weighing balance. 0.2 mol dm hydrochloric acid, HCl; small and large marble chips
VARIABLES
APPARATUS
MATERIALS PROCEDURE
1. A burette full with water is inverted in basin of water. 2. It is then clamped vertically using retort stand. 3. Set up the apparatus shown in diagram, 5g of large calcium carbonate chips is weighed and put inside the conical flask. 4. 50 cm of hydrochloric acid, HCl, 0.2 mol dm is measured and pored into the conical flask. 5. The conical flask is closed immediately with a stopper fitted with delivery tube as shown in the diagram.
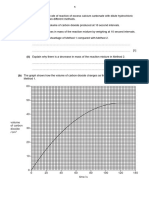
6. A stop-watch is started immediately. 7. The volume of gas released is recorded for every 1 minute. 8. Steps 1 to 7 are repeated using 5g small calcium carbonate chips to replace 5g large calcium carbonate chips. 9. The graphs of volume of carbon dioxide against time for the two experiments are plotted on the same axes. RESULTS A. Large calcium carbonate chips Time / m Burette reading / cm Volume of gas / cm B. Small calcium carbonate chips Time / s Burette reading / cm Volume of gas / cm 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5
ANALYSIS
1. Marble reacted with dilute hydrochloric acid, HCl to produce carbon dioxide, CO, gas. CaCO (s) + 2HCl (aq) CaCl (aq) + HO (l) + CO (g) 2. The average rate of reaction in 5 minutes for both reactions can be calculated as follows : Average rate of reaction of large marble chips = Average rate of reaction of small marble chips = 3. The rate of reaction at the 2nd minutes for both reactions can be calculated by drawing a tangent and then determining the gradient of the tangent at the particular time. Rate of reaction of large marble chips = = = Rate of reaction of small marble chips = = = 4. From the rate of reactions obtained from (2) and (3), it can be deduced that a) The rate of reaction between the small marble chips and dilute hydrochloric acid, HCl is higher compared to the rate of reaction between the large marble chips and dilute hydrochloric acid, HCl. b) The smaller the size of reactant, the higher the rate of reaction. A smaller reactant size has a larger total exposed surface area. 5. According to both graphs, the rate of reaction lessens with time (the gradient of the curve becomes less steep with time). This is because a) The concentration of hydrochloric acid, HCl becomes lower with time b) The mass (quantity) of marble reduces with time c) The total surface area of marble chips becomes smaller with time 6. The hypothesis is accepted.
CONCLUSION
The smaller the size of reactant, the higher the rate of reaction.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Chapter 10: Rate of ReactionDocument4 paginiChapter 10: Rate of ReactionAin FzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Swelling Concrete in Dams and Hydraulic Structures: DSC 2017De la EverandSwelling Concrete in Dams and Hydraulic Structures: DSC 2017Încă nu există evaluări
- 1.3 Rate of Reaction (1.2c)Document75 pagini1.3 Rate of Reaction (1.2c)Sha Tasha Natasha0% (1)
- EXP7-Rate (MG and HCLDocument5 paginiEXP7-Rate (MG and HCLNor Ashikin Ismail100% (10)
- Reactive Transport Modeling: Applications in Subsurface Energy and Environmental ProblemsDe la EverandReactive Transport Modeling: Applications in Subsurface Energy and Environmental ProblemsYitian XiaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surface Area: Experiment 1.1: To Investigate The Effect of The of A Reactant On The Rate of ReactionDocument75 paginiSurface Area: Experiment 1.1: To Investigate The Effect of The of A Reactant On The Rate of ReactionRakesh NairÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Text-book of Assaying: For the Use of Those Connected with Mines.De la EverandA Text-book of Assaying: For the Use of Those Connected with Mines.Încă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 1.1Document2 paginiExperiment 1.1marlina4Încă nu există evaluări
- Gas Hydrates 2: Geoscience Issues and Potential Industrial ApplicationsDe la EverandGas Hydrates 2: Geoscience Issues and Potential Industrial ApplicationsLivio RuffineÎncă nu există evaluări
- (M1.2) REVIEW & COMPLETE - Practical 4.1 The Kinetics of The Reaction Between CaCO3 and HCLDocument3 pagini(M1.2) REVIEW & COMPLETE - Practical 4.1 The Kinetics of The Reaction Between CaCO3 and HCLSalma ShakiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Saturday X-Tra X-Sheet: 16 Rates of Reaction: Key ConceptsDocument6 paginiSaturday X-Tra X-Sheet: 16 Rates of Reaction: Key ConceptsKingford MwesoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 Manual 2019Document18 paginiUnit 1 Manual 2019JozelleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geological Carbon Storage: Subsurface Seals and Caprock IntegrityDe la EverandGeological Carbon Storage: Subsurface Seals and Caprock IntegrityStéphanie VialleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rate NotesDocument16 paginiRate NotesMegan GohÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.3 Reaction Rates and Reversible ReactionsDocument18 pagini4.3 Reaction Rates and Reversible ReactionsVictor VC100% (5)
- Chapter 10 No 9Document8 paginiChapter 10 No 9Ain FzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Naskah Murid Modul 1-Rate of ReactionDocument14 paginiNaskah Murid Modul 1-Rate of ReactionIza MohdSabriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scientific MethodsDocument8 paginiScientific MethodsaloncitopopÎncă nu există evaluări
- MS Y12 - Chemical - Kinetics - Test - SL - May - 2023Document17 paginiMS Y12 - Chemical - Kinetics - Test - SL - May - 2023harampark0210Încă nu există evaluări
- GCE O Levels (Singapore) - Speed of ReactionDocument3 paginiGCE O Levels (Singapore) - Speed of ReactionChong56Încă nu există evaluări
- Experiment Rate of Reaction - SizeDocument2 paginiExperiment Rate of Reaction - SizeSyakir IzzatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gabrielle Robinson - 601 Labs 2021Document13 paginiGabrielle Robinson - 601 Labs 2021Gabrielle RobinsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effect of Surface Area On The Rate of ReactionDocument10 paginiEffect of Surface Area On The Rate of ReactionsuffyandaimÎncă nu există evaluări
- SMKCL Chemistry Monthly Test 1 F5 2009Document5 paginiSMKCL Chemistry Monthly Test 1 F5 2009MarziahAsmawiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.1 Rate of ReactionDocument71 pagini1.1 Rate of ReactionyiosahhÎncă nu există evaluări
- SLE Experiment (REPORT)Document8 paginiSLE Experiment (REPORT)Kuknesvary PuniamurthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Mock IADocument12 paginiChemistry Mock IAYAMAMOTO KeijiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rates of ReactionDocument64 paginiRates of Reactionhingleena100% (1)
- Experiment 2: Determination of The Valency of MagnesiumDocument4 paginiExperiment 2: Determination of The Valency of MagnesiumJc Goh100% (1)
- Rates of ReactionDocument77 paginiRates of ReactionFatema KhatunÎncă nu există evaluări
- IA - Metals and AcidsDocument3 paginiIA - Metals and Acids14nganhc1Încă nu există evaluări
- Form 5 Lesson 7 StructureDocument6 paginiForm 5 Lesson 7 StructureSammul IgnatiusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module Form 5 .Rate of ReactionDocument8 paginiModule Form 5 .Rate of ReactionChew Gee Lan100% (1)
- Example Planning Experiment Form 5Document14 paginiExample Planning Experiment Form 5Victoria PetrusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rate of ReactionDocument7 paginiRate of ReactionNubar MammadovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name of Student Tsui Yee Grade Y10 TrustDocument25 paginiName of Student Tsui Yee Grade Y10 Trustapi-361490645Încă nu există evaluări
- CeDocument59 paginiCeYee KatherineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 2K3Document10 paginiExperiment 2K3Inkiru N. BernardÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Extended Essay Final DraftDocument7 paginiChemistry Extended Essay Final DraftLynn SleimanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Noncatalytic Heterogeneous Kinetics in The Engel-Precht PotassiumDocument10 paginiNoncatalytic Heterogeneous Kinetics in The Engel-Precht PotassiumFilipe FreireÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sophomore Research 2017Document38 paginiSophomore Research 2017api-397358195Încă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Experiment 1Document8 paginiChemistry Experiment 1Shirah CoolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rate of Reaction Bwat SendiriDocument4 paginiRate of Reaction Bwat SendiriNor Ashikin IsmailÎncă nu există evaluări
- RATES - Past Paper QuestionsDocument7 paginiRATES - Past Paper QuestionsEsteban OrtegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Determination of The Valency of MagnesiumDocument7 paginiDetermination of The Valency of MagnesiumJiaxinOoiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 1 - Rate of ReactionDocument63 paginiChemistry Form 5 Chapter 1 - Rate of ReactionSiti Nursyafiqah100% (7)
- Magnesium Reacts With Dilute Hydrochloric Acid in A Conical Flask Which Is Connected To An Inverted Measuring Cylinder in A Trough of WaterDocument4 paginiMagnesium Reacts With Dilute Hydrochloric Acid in A Conical Flask Which Is Connected To An Inverted Measuring Cylinder in A Trough of Waterวสุ เกตุสิริÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Effects of Surface Area On The Rate of A ReactionDocument16 paginiThe Effects of Surface Area On The Rate of A ReactionNick SchlobohmÎncă nu există evaluări
- My TestDocument33 paginiMy TestqusaielnoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chem F.6 Full Report 1Document11 paginiChem F.6 Full Report 1stephenliyuting_1992100% (2)
- 10 TH DeceDocument4 pagini10 TH DeceOmaru NimagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rate of ReactionDocument6 paginiRate of ReactionNubar MammadovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Instuctions For Marble ChipsDocument3 paginiLab Instuctions For Marble Chipsstamsam100% (2)
- Unit 5 Chemical KineticsDocument37 paginiUnit 5 Chemical KineticsSanjay SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rate of Reaction 1Document12 paginiRate of Reaction 1MalaysiaBoleh100% (18)
- Dissolution of Calcium Carbonate in Aqueous Solutions of Acetic AcidDocument3 paginiDissolution of Calcium Carbonate in Aqueous Solutions of Acetic AcidMichelle M. SalvadorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liquid Crystal DisplayDocument2 paginiLiquid Crystal DisplayreshusaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Viva QuestionDocument4 paginiViva QuestionBarathkannan Lakshmi PalanichamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sensitometry: Describing Photographic PerformanceDocument55 paginiSensitometry: Describing Photographic PerformanceilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscles Revision QuestionsDocument20 paginiMuscles Revision QuestionsalexdarcyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Service Bulletin: Commissioning Procedure For HydracapDocument10 paginiTechnical Service Bulletin: Commissioning Procedure For HydracapValesh MonisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carvalho KL Magalhaes WF 2012 Food Addit Contam Part A v29 n4.p679-93Document15 paginiCarvalho KL Magalhaes WF 2012 Food Addit Contam Part A v29 n4.p679-93Xochilt BlandónÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brochure - Joint Sealants For Building Envelope WaterproofingDocument36 paginiBrochure - Joint Sealants For Building Envelope WaterproofingBudi Max100% (1)
- Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2010: IGCSE Chemistry (4335) Paper 1FDocument16 paginiMark Scheme (Results) Summer 2010: IGCSE Chemistry (4335) Paper 1FCoolman PoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- FINAL LCCP Handbook v2.1 With Appendix - JAN 2015Document67 paginiFINAL LCCP Handbook v2.1 With Appendix - JAN 2015Sean CrossÎncă nu există evaluări
- WHO Monograph CurcumaDocument8 paginiWHO Monograph CurcumaMuhammad Miftahul HudaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dykem Steel RedDocument4 paginiDykem Steel RedMark Evan SalutinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zangar C Water Percolation 5 Water OcrDocument86 paginiZangar C Water Percolation 5 Water Ocrreem.ranoom.moonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thapar University, Patiala Department of Chemical Engineering E To D (February 2018)Document2 paginiThapar University, Patiala Department of Chemical Engineering E To D (February 2018)Vinay DograÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handbook of Fat ReplacersDocument295 paginiHandbook of Fat Replacersgoldennanuk100% (1)
- Ijftr 34 (2) 137-143Document7 paginiIjftr 34 (2) 137-143Mohammad HussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Semiconductor - Experiment PDFDocument116 paginiSemiconductor - Experiment PDFMuthu KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fabr Pneumatic 033009Document28 paginiFabr Pneumatic 033009daniper89Încă nu există evaluări
- New Substance Is Made, Like When Water Turns To Ice.: Physical and Chemical ChangesDocument3 paginiNew Substance Is Made, Like When Water Turns To Ice.: Physical and Chemical ChangesAccounting SolmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCES3083 Topic 5 FluidDocument44 paginiSCES3083 Topic 5 Fluid胡佳玲Încă nu există evaluări
- P Radiator Valves en PDFDocument16 paginiP Radiator Valves en PDFpolitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Free EnergyDocument17 paginiFree EnergyDolih GozaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geo PolymerizationDocument19 paginiGeo PolymerizationAhmed EssamÎncă nu există evaluări
- C1130Document4 paginiC1130dinhtung2210Încă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of Tent StructuresDocument65 paginiAnalysis of Tent Structuressri_amartÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Gas Chromatography (Techniques in Analytical Chemistry) (2009 Ed.)Document250 paginiBasic Gas Chromatography (Techniques in Analytical Chemistry) (2009 Ed.)Jirut Wattoom75% (4)
- SDS of Hydrogen Iodide0Document8 paginiSDS of Hydrogen Iodide0Wici WiciÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Magazine April 07 2006 PDFDocument144 paginiScience Magazine April 07 2006 PDFAndrés FrankowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Methods-Water Leak DetectionDocument6 paginiMethods-Water Leak DetectionAbhijeeth NagarajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Past Mechanical Engineering Board Exam Question Set 2Document5 paginiPast Mechanical Engineering Board Exam Question Set 2Creation Your67% (3)