Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Form 5 Lesson 7 Structure
Încărcat de
Aidah AmirDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Form 5 Lesson 7 Structure
Încărcat de
Aidah AmirDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
OMEGA TUITION CENTRE
Students name : ____________________________________ ________________________ Teachers Name : Mr Chew Chin Kuen Subject : Chemistry Form 5 Class Attend : 5 Chemistry 6 Chapter 1 : Rate of reaction lesson 7 : 2nd Feb 2013 (2.30 4.30 PM)
Paper 2
As catalyst
Manganese (IV) oxide / Iron (III) oxide
Rate of reaction is inversely proportional with time, as the rate of reaction decreased with time
reaction is completed
mol of KClO3 = MV / 1000 ; mol of KClO3 = (1.0)(4.0)/1000 = 0.004 mol From equation 2 mol KClO3 = 1 mol of O2 mol of O2 = 0.002 mol V of O2 = mol x Vm ; V of O2 = 0.002 mol x 24 dm3 / mol = 0.048 dm3 @ 48 cm3
Rate
= (48 cm3 - 0) / (45 s - 0) = 1.067 cm3 / s
all hydrochloric acid in the mixture is used up
Mass of CO2 / g
Time / s at the first 60 rate = 3.5 - 0.0 / 60 - 0 = 0.583 g / s
By using marble in powder form / increase the temperature / add concentration of HCl
Fe (s) + H2SO4 (aq) FeSO4 (aq) + H2 (g)
; mol = 3.0 / 56 = 0.0536 mol mol of H2SO4 = MV / 1000 ; mol = (0.5)(30) / 1000 mol = 0.015 mol (limitant) since 1 mol of H2SO4 = 1 mol of H2 ; mol of H2 = 0.015 mol Vgas = mol x Vm @ Vgas = 0.015 x 24 Vgas = 0.36 dm3 @ 360 cm3
mol of Fe = mass / Ar
Even though the type of acid used are different, but the mol of H+ is the same for both H2SO4 and HCl, since H2SO4 is a diproctic acid, while HCl is a monoproctic acid
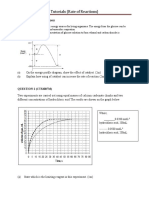
Rate of reaction in C is higher than A, since catalyst is add into the mixture, CuSO4 helps to lower the activation energy by providing alternative routes for reaction to occur
The temperature used in Exp B is higher than A. This will increase the kinetic energy of particles hence caused the collision between reactants become more rapids
Mg (s) + 2 H+ (aq) Mg2+ (aq) + H2 (g)
Since ethanoic acid is weak acid while HCl is strong acid. the concentration of H+ in HCl is higher, hence caused a higher frequency of effective collision
Since the amount of H+ given by H2SO4 is 2 times greater than amount of H+ given by HCl. Higher the concentration of H+, higher the frequency of effective collision
Rate of reaction in S is higher than Q, since catalyst is add into the mixture, CuSO4 helps to lower the activation energy by providing alternative routes for reaction to occur
Time taken for the reaction to occur will be lower than 35 second, as temperature increase, rate of reaction also increase. This is due to, particles has higher kinetic energy which caused a higher frequency of effective collision.
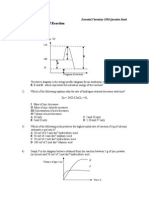
Carbon dioxide gas is liberated when limestone reacts with dilute acids. Figure below shows the volume of carbon dioxide gas collected at room conditions during the duration of the reaction.
(a)
Write an equation for the reaction of limestone with dilute hydrochloric acid.
CaCO3 (s) + 2 HCl (aq) CaCl2 (aq) + CO2 (g) + H2O (l) .
(b) (i) How long did the reaction last?
210 s
(ii) (iii)
70 cm What is the total volume of carbon dioxide gas evolved? .
Calculate the average speed of the reaction.
Rate = 70 / 210 = 0.33 cm3 / s
(c) Calculate the rate of reaction at t = 60 s and t = 90 s. At 60 s, rate = (80 - 40) / (120 - 30) = 0.444 cm3 / s At 90 s, rate = (80 - 50) / (165 - 30) = 0.222 cm3 / s
(d)
Calculate the mass of limestone reacted.
mol = 70 / 24000 cm3 / mol = 0.00292 mol From the chemical equation ; 1 mol of CO2 = 1 mol of CaCO3 Hence mol of CaCO3 = 0.00292 mol Mass of CaCO3 = mol x RMM ; mol = 0.00292 mol x [40 + 12 + 3(16)] mass = 0.292 g Using mol of CO2 = V / Vm ; (e) The concentration of the hydrochloric acid is 0.25 mol dm-3. Calculate the volume of hydrochloric acid reacted. From mol of CO2 reacted = 0.00292 mol ; Since 2 mol HCl = 1 mol CO2 ; mol of HCl = 0.00146 mol Volume of HCl = mol x 1000 / M ; VHCl = 0.00146 x 1000 / 0.25 VHCl = 5.84 cm3
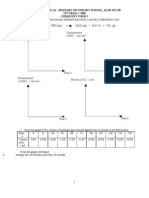
Figure below shows the set-up used to investigate the reaction between calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid.
The volume of carbon dioxide was recorded at 10-minute intervals under room conditions. Some of the calcium carbonate remained undissolved at the end of the experiment. The results of the experiment are given in the following table. Time (min) Volume of CO2 collected (cm3) (a)
2-
0 0
20 700
40 975
60 1140
80 1175
100 1200
120 1200
Write an ionic equation for the reaction between calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid.
3 2 2 . (b) (i) Complete the table below.
CO
(s) + 2 H+ (aq) + CO (g) + H O (l)
Time interval (min) 0 - 20 20 - 40 40 - 60 60 - 80
Volume of gas collected (cm3)
700 275 165 25
(ii) Explain the variation in the volumes of carbon dioxide collected during these intervals. Volume of the gas collected decrease with the interval time due to the amount of reactants used for the reaction become smaller with time. Hence the amount of product obtained will be lower with time (c) Why did the reaction stop after 100 minutes?
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Rate NotesDocument16 paginiRate NotesMegan GohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ap Unit7 WorksheetDocument4 paginiAp Unit7 Worksheetburcak gecÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.3 Reaction Rates and Reversible ReactionsDocument18 pagini4.3 Reaction Rates and Reversible ReactionsVictor VC100% (5)
- 64edf0f4e41caDocument6 pagini64edf0f4e41caDanzell JonathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revision StoichiometryDocument12 paginiRevision StoichiometryFangru CaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- RTS Chemistry SPM Question Bank Chapter 10Document8 paginiRTS Chemistry SPM Question Bank Chapter 10dobbybibiÎncă nu există evaluări
- GCE O Levels (Singapore) - Speed of ReactionDocument3 paginiGCE O Levels (Singapore) - Speed of ReactionChong56Încă nu există evaluări
- HKDSE CHEMISTRY - Book 4A AnsDocument48 paginiHKDSE CHEMISTRY - Book 4A AnsSteven Chu100% (1)
- Ans SL MC Test r2 The Amount of Chemical ChangeDocument9 paginiAns SL MC Test r2 The Amount of Chemical ChangeALIÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Solution Stoichiometry (S)Document11 pagini5 Solution Stoichiometry (S)Mr TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- RTS Chemistry SPM Question Bank Chapter 10Document8 paginiRTS Chemistry SPM Question Bank Chapter 10Scorched ZenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 1 Rate of ReactionDocument2 paginiTutorial 1 Rate of ReactionchenanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 4 (Mole) PAPER 4Document118 paginiUnit 4 (Mole) PAPER 4Muhammad Hasnain SikandarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry As Revision Questions F332Document23 paginiChemistry As Revision Questions F332LilliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Topic One QuestionsDocument30 paginiChemistry Topic One QuestionsAruba Dhaduk100% (1)
- Chemistry Past Paper Ch1.1Document20 paginiChemistry Past Paper Ch1.1Raymond ChanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantitative ChemistryDocument32 paginiQuantitative ChemistryElena EngiÎncă nu există evaluări
- C4.8 CalculationsChemsheets GCSE 1105 (Titrations 1)Document2 paginiC4.8 CalculationsChemsheets GCSE 1105 (Titrations 1)Bee AbeilleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 6/16 Kinetics (Rates of Reactions)Document14 paginiTopic 6/16 Kinetics (Rates of Reactions)Oyinkansola OsiboduÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Answer Key) Calculation Exercise - 元素の貓 - 免費dse化學練習Document6 pagini(Answer Key) Calculation Exercise - 元素の貓 - 免費dse化學練習Belladonna Lee100% (1)
- Chem F.6 Full Report 1Document11 paginiChem F.6 Full Report 1stephenliyuting_1992100% (2)
- Music 2Document18 paginiMusic 2JonathanNgÎncă nu există evaluări
- WORKSHEET - Chemical Formulae and EquationsDocument7 paginiWORKSHEET - Chemical Formulae and EquationsMaisha Islam100% (1)
- 2009 HCI Prelim P2Document15 pagini2009 HCI Prelim P2Felicia LimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chem G-9 Lesson 7 IGCSE Qs - Rates of ReactionDocument24 paginiChem G-9 Lesson 7 IGCSE Qs - Rates of ReactionKarim WaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1: Rate of Reaction: Larning Task 1.2 Problem SolvingDocument29 paginiChapter 1: Rate of Reaction: Larning Task 1.2 Problem Solvingamin_zamanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Engineering CorrelationDocument15 paginiBasic Engineering CorrelationJM CartañoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Y1 P2 Summative Topics 1.1 1.2 11.1Document7 paginiY1 P2 Summative Topics 1.1 1.2 11.124zaltayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revision of KS4 Calculations in Chemistry For KS5 WorksheetDocument6 paginiRevision of KS4 Calculations in Chemistry For KS5 WorksheetniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet Revision Calculations ks5Document6 paginiWorksheet Revision Calculations ks5James YangÎncă nu există evaluări
- IGCSE Prep - 3Document17 paginiIGCSE Prep - 3Yoel Friady HutabaratÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class Test 1 Rate of Reaction For Edexcel A2 ChemistryDocument7 paginiClass Test 1 Rate of Reaction For Edexcel A2 Chemistryjeffydaniel1972Încă nu există evaluări
- Tutorials (Rate of Reactions) : QUESTION 1 (2006 CT3 Jan)Document7 paginiTutorials (Rate of Reactions) : QUESTION 1 (2006 CT3 Jan)Subesh ShanmugamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic-1.1 Formulae, Equations and Amount of SubstancesDocument20 paginiTopic-1.1 Formulae, Equations and Amount of SubstancesAneeka KamalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of Rate ReactionDocument10 paginiApplication of Rate ReactionRahmawati PutrianasariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Determination of The Valency of MagnesiumDocument7 paginiDetermination of The Valency of MagnesiumJiaxinOoiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9 Thermochemistry (S)Document23 pagini9 Thermochemistry (S)Mr TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Experiment 1Document8 paginiChemistry Experiment 1Shirah CoolÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 2Document43 paginiCH 2Tamanna GaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ap Unit7 Worksheet AnswersDocument5 paginiAp Unit7 Worksheet Answersburcak gecÎncă nu există evaluări
- AS Level Topic 5 TestDocument10 paginiAS Level Topic 5 TestMorvan BarnesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mole Concept Moles Equations and MolarityDocument18 paginiMole Concept Moles Equations and MolarityNageya paulÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHEM101 2008 SetB-1Document6 paginiCHEM101 2008 SetB-1shishir kafleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial-Manual CH1002Document18 paginiTutorial-Manual CH1002Gift Chulu100% (2)
- Class 9 - 1st Term Calculation WorksheetDocument5 paginiClass 9 - 1st Term Calculation Worksheetabdulhadisaqib290Încă nu există evaluări
- Gas Liquid AbsorptionDocument9 paginiGas Liquid AbsorptionShashwat OmarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 1 - Rate of ReactionDocument63 paginiChemistry Form 5 Chapter 1 - Rate of ReactionSiti Nursyafiqah100% (7)
- Name of Student Tsui Yee Grade Y10 TrustDocument25 paginiName of Student Tsui Yee Grade Y10 Trustapi-361490645Încă nu există evaluări
- Expt01 HCL and NaOH AnsDocument3 paginiExpt01 HCL and NaOH AnsaragpdÎncă nu există evaluări
- As Expt 2.1 (4) - Enthalpy of Formation of CaCO3Document4 paginiAs Expt 2.1 (4) - Enthalpy of Formation of CaCO3Diddled_skittles100% (1)
- Succeed I Can WorksheetDocument8 paginiSucceed I Can WorksheetCorinne Amelia SimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Naskah Murid Modul 1-Rate of ReactionDocument14 paginiNaskah Murid Modul 1-Rate of ReactionIza MohdSabriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moles TestDocument5 paginiMoles TestMahedyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acid N Salt RevisionDocument6 paginiAcid N Salt RevisionTennarasu PannirselvamÎncă nu există evaluări
- As Unit 1 Chapter 1 Past PapersDocument20 paginiAs Unit 1 Chapter 1 Past PapersK K Chamath Aachinthya0% (1)
- DP10 Online Quiz RevisedDocument8 paginiDP10 Online Quiz RevisedjackyqinsjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 1 Quantitative SLHL Test ADocument9 paginiTopic 1 Quantitative SLHL Test APak Hei Marcus CHOWÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revision Exercise (Organic Chemistry) : Pahang 2010Document5 paginiRevision Exercise (Organic Chemistry) : Pahang 2010Sammul IgnatiusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effective PresentationsDocument2 paginiEffective PresentationsSammul IgnatiusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Students Matching F 5Document10 paginiStudents Matching F 5faezahsapixÎncă nu există evaluări
- Students Matching F 5Document10 paginiStudents Matching F 5faezahsapixÎncă nu există evaluări