Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Automation in Clinical Chemistry
Încărcat de
Kate Alyssa CatonDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Automation in Clinical Chemistry
Încărcat de
Kate Alyssa CatonDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
AUTOMATION IN CLINICAL CHEMISTRY Machine systems that incorporate continuously monitoring of the product (information), with the results
s of the checking process used to control the entire process. Operates in the principle of "feedback" Automatic analyzers do the following: 1. Control the following operations Sampling Addition of reagents Photometric and oher mmts. Calibration Calculation of results
Continuous Flow Analyses Ex : Technician Autoanalyzer Typical Feature: Continuous pumping of samples and reagents using peristaltic pumps Protein removal by dialysis Segmentation of sample and reagent streams, separation of one sample for the next by air bubbles. Flow through cuvettes un interferences filter photometer Recorder read-out (basic systems) collated patient reports in latest symptoms (SMAC) Modular design
Self-checking and other diagnostic processes Error detection Curve fitting programs for true kinetic enzyme systems Quality control processes (calibration curves and quality control values)
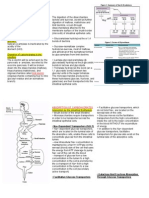
Upper surface of disk are concentric rings of shaped cavities Centrifugal force transfers and mixes the reagents and samples and transfers them into the cuvettes Each cuvette is read by the photometric system every 130 milliseconds
TYPES OF AUTOMATIC ANALYZERS Technician continuous flow system Discrete analyzers Centrifugal analyzers Thin-fil analyzers An analyzer may be Discretionary Non Discretionary 1. The test or tests to be run on each sample can be predetermined or every sample can be processed for a test or series of tests
Discrete Analysis Each specimen is handled as a separate process in its own reaction vessel A logical replacement of manual processes in the Clin. Chem Lab. Test or combiantion of tests can be presented using a keyboard. Computer determines the sequence in shich the various tests will be run. Small volumes required (60-500)
Discrete Analyzers with Discretionary Ability Examples: Beckman Astra4 4' Astra 8 analyzers American Monitor KDA DuPont ACA (Automatic Clinical Analyzers)
Test or combination of tests
can be preselected using a keyboard
Computer determines the
sequence in which the various tests will be run Small volumes (60-500)
Each cuvette is read by the photometric system every 130 milliseconds
Thin Film Analyses
Discrete Analyzers without specific Discretionary Ability Examples: Abbott ABA -100 Bichromatic Analyzer ABA -200 VP Analyzer Gilford Clinical Chemistry Analyzers
Reaction vessels and cuvettes
1. Example: - Kodak "Ektachem"
are combined into a single dsposable plastic compartment molding Uses ultra micro volumes (5l) Absorbance readings taken at two wavelenths Very sensitive (0.00015 absorbance)
Unique due to the following features: Only fluid used is the sample Exact measurement replaced by drop wise dispensing Transmission spectrophotometry replaced by reflectance spectrophotometry Utilizes a square chip with several layers Completely discretionary 10l sample needed Suitable for pediatric analysis 60500mciroliter)
Centrifugal Analysers Examples: ENI GeMSAEC Automatic Fast Analyzer Rotochem II Centrichem
Operate usinf the GeMSAEC principle (National Institute of General Medical Science and the U.S Atom Energy Commission) The heart of the system is a thick Telefon roto disc which can be spun at high speed Upper surface of disk are concentrc rings of shaped cavities Centrifugal force transfers and mixes the reagents and samples and transfers them into the cuvettes
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Parasitology Table: ProtozoaDocument10 paginiParasitology Table: ProtozoaKate Alyssa CatonÎncă nu există evaluări
- CLINICAL CHEMISTRY: Passbooks Study GuideDe la EverandCLINICAL CHEMISTRY: Passbooks Study GuideÎncă nu există evaluări
- NMAT Practice Set Part IIDocument32 paginiNMAT Practice Set Part IIAlfred Benjamin Cajita93% (107)
- Donor Screening and Component PreparationDocument91 paginiDonor Screening and Component PreparationDominic BernardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Pathology UnitDocument22 paginiChemical Pathology UnitLee Yann Na IbrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood Smear Examination 1معدل Document74 paginiBlood Smear Examination 1معدل Kenesa100% (1)
- Pocket Guide On Red Cells 2012Document8 paginiPocket Guide On Red Cells 2012Dave OrlandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood BankingDocument7 paginiBlood BankingRoiland Atienza BaybayonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio ChemistryDocument28 paginiBio ChemistryHilbert100% (1)
- Chemical Pathology HODocument17 paginiChemical Pathology HOMurali TiarasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preanalytical ErrorsDocument99 paginiPreanalytical ErrorsSulakshmi KurlekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- UrinalysisDocument120 paginiUrinalysisKate Alyssa Caton100% (1)
- UrinalysisDocument120 paginiUrinalysisKate Alyssa Caton100% (1)
- Basic Clinical Chemistry TestsDocument49 paginiBasic Clinical Chemistry TestsMegbaru100% (1)
- Principles of Clinical Chemistry AutomationDocument25 paginiPrinciples of Clinical Chemistry AutomationChristine Rodriguez-Guerrero50% (2)
- Hemodynamic Disorders, Thromboembolic DiseasesDocument100 paginiHemodynamic Disorders, Thromboembolic DiseasesKate Alyssa Caton100% (1)
- Urine AnalysisDocument69 paginiUrine AnalysisAffan ElahiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5-Westgard QC StrategiesDocument36 pagini5-Westgard QC StrategiesMarcos FernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Method ValidationDocument46 paginiLecture Method Validationsarah575Încă nu există evaluări
- Biosynthesis Fatty AcidsDocument59 paginiBiosynthesis Fatty AcidsKate Alyssa Caton100% (1)
- Blood Bank ProceduresDocument33 paginiBlood Bank Procedures99noname100% (1)
- Common Medical Laboratory Errors PDFDocument2 paginiCommon Medical Laboratory Errors PDFRosalyn100% (1)
- Automation in Clinical ChemistryDocument28 paginiAutomation in Clinical ChemistryJoyce VitalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Relevance of Serum Tumor MarkersDocument25 paginiRelevance of Serum Tumor MarkersDrPawan KirtaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- IFCC TF Ethics in Lab MedicineDocument16 paginiIFCC TF Ethics in Lab MedicineDr.Deepanshu SinghalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 04 Welding SOPDocument3 pagini04 Welding SOProhan khariwaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cargo Conditioning, Reliquefaction and Boil-Off Control Requirement For A Liquefied Gas CarrierDocument7 paginiCargo Conditioning, Reliquefaction and Boil-Off Control Requirement For A Liquefied Gas Carrierarlucky5459Încă nu există evaluări
- Criteria For Specimen AcceptabilityDocument3 paginiCriteria For Specimen AcceptabilityFatwa100% (1)
- Chemical Pathology Stage A Examination Sample QuestionsDocument10 paginiChemical Pathology Stage A Examination Sample QuestionsHabib UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 9 SolutionsDocument11 paginiChapter 9 Solutionssaddam hussain80% (5)
- Automation in Clinical ChemistryDocument20 paginiAutomation in Clinical Chemistryakongke20Încă nu există evaluări
- Usefulness of Enzyme Linked Immune Sorbent Assay: Various Methods For Disease Diagnosis and MonitoringDocument60 paginiUsefulness of Enzyme Linked Immune Sorbent Assay: Various Methods For Disease Diagnosis and MonitoringAdarshBijapurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagnostic Microbiology and Laboratory MethodsDocument70 paginiDiagnostic Microbiology and Laboratory MethodsArulmany SelliahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec1 Introduction To Immunohematology1Document20 paginiLec1 Introduction To Immunohematology1Dalia M. MohsenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 832R12011 (Emerging Technologies For Wastewater Treatment - 2nd Ed.)Document188 pagini832R12011 (Emerging Technologies For Wastewater Treatment - 2nd Ed.)Anonymous owMJ21JRzC100% (3)
- Histopathologic TechniquesDocument9 paginiHistopathologic TechniquesKate Alyssa Caton100% (11)
- Histopathologic TechniquesDocument9 paginiHistopathologic TechniquesKate Alyssa Caton100% (11)
- Elisa Reader & Microplate Washer: Farheen Saba PH.D Ist Year Deptt. of Zoology ManuuDocument30 paginiElisa Reader & Microplate Washer: Farheen Saba PH.D Ist Year Deptt. of Zoology ManuuPious SabaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 68th AACC Annual Scientific Meeting Abstract eBookDe la Everand68th AACC Annual Scientific Meeting Abstract eBookÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laboratory Quality ControlDocument50 paginiLaboratory Quality Controlstarryy.eyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- NDT Method SummaryDocument3 paginiNDT Method SummaryNguyen Anh TungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical ChemistryDocument10 paginiClinical ChemistryKristine Jamella Maris Narag100% (1)
- Innovation of LNGCDocument63 paginiInnovation of LNGCpadangiringÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Policies Sysmex XS 1000i Procedure Lab 1501 PDFDocument26 paginiLab Policies Sysmex XS 1000i Procedure Lab 1501 PDFakiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mixing TimeDocument7 paginiMixing TimeakoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood Banking Lab Manual 3rdDocument7 paginiBlood Banking Lab Manual 3rdDanna Angelick ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automation in Clinical ChemistryDocument2 paginiAutomation in Clinical ChemistrySEBASTIEN ZOE RODRIGUEZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quality Assurance IN Histopathology: QC Should Consider The Whole ProcessDocument38 paginiQuality Assurance IN Histopathology: QC Should Consider The Whole Processalrasheed2020Încă nu există evaluări
- 11013003Document1 pagină11013003Johnmar AquinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Diagnostic Uses of ElectrophoresisDocument20 paginiThe Diagnostic Uses of ElectrophoresisAkinduko Dammy SamsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.5 Antibody ScreeningDocument5 pagini2.5 Antibody ScreeningBALAJIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anti-Globulin Test AGT (Coomb's Test) Direct, IndirectDocument26 paginiAnti-Globulin Test AGT (Coomb's Test) Direct, Indirectlubna aloshibiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ImmunoassayDocument7 paginiImmunoassaySanthosh PÎncă nu există evaluări
- Orientation To Clinical Biochemistry-PreanalyticalDocument6 paginiOrientation To Clinical Biochemistry-PreanalyticalasjxhiBBniu01j2Încă nu există evaluări
- Urea Nitrogen AnalyzerDocument16 paginiUrea Nitrogen AnalyzerSkywalker_92Încă nu există evaluări
- Abs Elu HandoutDocument6 paginiAbs Elu HandoutSiti Fadhilla TsabithaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quality Assurance in HaematologyDocument27 paginiQuality Assurance in HaematologyDennis Valdez100% (5)
- Preparing A Blood SmearDocument10 paginiPreparing A Blood Smearalan_kadirÎncă nu există evaluări
- نماذج اسئلة الهيئة السعودية للتخصصات الصحية للاخصائيين والاطباء بالمختبراتDocument68 paginiنماذج اسئلة الهيئة السعودية للتخصصات الصحية للاخصائيين والاطباء بالمختبراتAhmed GaberÎncă nu există evaluări
- Packed Cell Volume (PCV)Document24 paginiPacked Cell Volume (PCV)Eyasu demsewÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quality Control2Document32 paginiQuality Control2Mustafa KhandgawiÎncă nu există evaluări
- EXPT3-IMSELAB-Screening Test For Phagocytic EngulfmentDocument21 paginiEXPT3-IMSELAB-Screening Test For Phagocytic EngulfmentJulie Ann GarceraÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Result of Any Laboratory Test Is Only As Good As The Sample Received in The LaboratoryDocument16 paginiThe Result of Any Laboratory Test Is Only As Good As The Sample Received in The LaboratoryZeeshan YousufÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Approach in Investigation of Haemostasis: Coagulation InstrumentsDocument24 paginiGeneral Approach in Investigation of Haemostasis: Coagulation InstrumentsArnab GhoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automated Hematology Cell Counters - ImpedanceDocument14 paginiAutomated Hematology Cell Counters - ImpedanceNoth MT Bnk100% (1)
- Specimen Collection and Processing For Hemostasis TestingDocument22 paginiSpecimen Collection and Processing For Hemostasis TestingTom Anthony Tonguia100% (1)
- Final Exam QuizDocument75 paginiFinal Exam QuizLauren Napoli0% (1)
- 3 Concentration Techniques SedimentationDocument18 pagini3 Concentration Techniques SedimentationFatihah JahsmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Renal FunctionDocument5 pagini1 Renal FunctionChristopher BucuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assay Summary: ADVIA Centaur CPDocument16 paginiAssay Summary: ADVIA Centaur CPGuneyden GuneydenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 14 - Routine and Point of Care Testing in HematologyDocument10 paginiChapter 14 - Routine and Point of Care Testing in HematologyNathaniel Sim100% (1)
- Point of Care TestingDocument16 paginiPoint of Care TestingCookie MonsterÎncă nu există evaluări
- RNA VirusesDocument11 paginiRNA VirusesKate Alyssa CatonÎncă nu există evaluări
- RNA VirusesDocument11 paginiRNA VirusesKate Alyssa CatonÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHO Digestion and AbsorptionDocument4 paginiCHO Digestion and AbsorptionKate Alyssa CatonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Lab - Index CardDocument5 paginiPower Lab - Index CardKate Alyssa CatonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glycolysis Index CardDocument2 paginiGlycolysis Index CardKate Alyssa CatonÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Impairment ClauseDocument1 paginăThe Impairment ClauseKate Alyssa CatonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glycogen Metabolism - Index CardDocument3 paginiGlycogen Metabolism - Index CardKate Alyssa CatonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biosynthesis of Cortisol Ics-2Document3 paginiBiosynthesis of Cortisol Ics-2Kate Alyssa CatonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Republic Act No. 8371Document7 paginiRepublic Act No. 8371Kate Alyssa CatonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bar Reforms in The Philippine Legal SystemDocument32 paginiBar Reforms in The Philippine Legal SystemKate Alyssa CatonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To AmbahanDocument3 paginiIntroduction To AmbahanKate Alyssa CatonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Estrada v. EscritorDocument7 paginiEstrada v. EscritorKatrina Anne Layson YeenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Extintor CO2 B10V-1 - BADGER PDFDocument2 paginiExtintor CO2 B10V-1 - BADGER PDFCoordinador TecnicoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stainless Steel Putty (ST) : Technical Data SheetDocument2 paginiStainless Steel Putty (ST) : Technical Data SheetSreenivasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formulating Biologicals For Agriculture: Croda, March 2023Document9 paginiFormulating Biologicals For Agriculture: Croda, March 2023Fernanda Amaral FariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MSDS Burnshield Sachets 4BDocument5 paginiMSDS Burnshield Sachets 4BJarrod Currin100% (1)
- Green DieselDocument11 paginiGreen DieselYuvia KusumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nanomaterials in Structural EngineeringDocument19 paginiNanomaterials in Structural EngineeringAniket DubeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 4: Classification, Properties and Applications of S.G. and C.G.Iron S.G.IRONDocument11 paginiTopic 4: Classification, Properties and Applications of S.G. and C.G.Iron S.G.IRONsandeep kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Papercrete4 PDFDocument9 paginiPapercrete4 PDFPrasad TekadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2002Document38 pagini2002B GirishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ecotoxicology and Environmental SafetyDocument10 paginiEcotoxicology and Environmental SafetyUlfa Mudia SariÎncă nu există evaluări
- ARO 2019 PX20X 2 Inch Metallic Diaphragm Pump Manual Fluid SectionDocument12 paginiARO 2019 PX20X 2 Inch Metallic Diaphragm Pump Manual Fluid Sectionduc tranÎncă nu există evaluări
- 202 Introduction To Materials ScienceDocument435 pagini202 Introduction To Materials ScienceRK SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Untitled PresentationDocument10 paginiUntitled Presentationanurag singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stefan Boltzmann Law PDFDocument3 paginiStefan Boltzmann Law PDFESAKKIMALA SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Camelina Derived Jet Fuel and Diesel - Sustainable Advanced BiofuelsDocument11 paginiCamelina Derived Jet Fuel and Diesel - Sustainable Advanced Biofuelsvitorio netoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation: Darwisa G. Hawari Dip-Ems 1ADocument35 paginiPresentation: Darwisa G. Hawari Dip-Ems 1AZeal Alexis MontellorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chem Academy: Enolate ChemistryDocument13 paginiChem Academy: Enolate ChemistryHamit RanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 30 Sewage Treatment PlanDocument63 pagini30 Sewage Treatment PlanYuri Duri100% (1)
- Chemistry Project: Organic PreparationDocument12 paginiChemistry Project: Organic PreparationAthul Oscar RonaldoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comp Mode of Jominy Test Paper ID1396Document5 paginiComp Mode of Jominy Test Paper ID1396fdcarazoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geochemical Analysis of Iron Ore - SGSDocument2 paginiGeochemical Analysis of Iron Ore - SGSAnton De la ruaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 Elements, Mixtures and Compounds: WorksheetDocument3 pagini4 Elements, Mixtures and Compounds: WorksheetMfanafuthiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2005-Bonalde-Kinetic Analysis of The Iron Oxide Reduction Using Hydrogen-Carbon Monoxide Mixtures As Reducing AgentDocument6 pagini2005-Bonalde-Kinetic Analysis of The Iron Oxide Reduction Using Hydrogen-Carbon Monoxide Mixtures As Reducing AgentRubin ZengÎncă nu există evaluări
- FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRO-RETENTIVE FLOATING TABLET OF QUETIAPINE FUMARATE Shanti Sagar, Srividya. L, B.K NanjawadeDocument14 paginiFORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRO-RETENTIVE FLOATING TABLET OF QUETIAPINE FUMARATE Shanti Sagar, Srividya. L, B.K NanjawadeiajpsÎncă nu există evaluări