Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
SPM Biology
Încărcat de
Brintha GanapathyTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
SPM Biology
Încărcat de
Brintha GanapathyDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
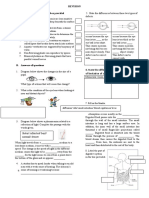
SPM BIOLOGY TRIALS REVISION 1. Compare ruminants and rodents cellulose digestion Ruminant Differences Type of nutrition No.
of stomach chamber Caecum Presence of cellose digestion bacteria and protozoa Cellulose digestion Regurgitation of food Ingestion of faeces No. of times food pass through alimentary canal 2. Ruminant digestion of cellulose When a cow feeds on grass, it partially chews the grass. This partially chewed food is swallowed into the _____________, the largest compartment of the stomach. Here, cellulose is broken down by the _____________ produced by symbiotic microorganisms such as bacteria and protozoa. As the food enters the _____________, the cellulose undergoes further hydrolysis. The content of the reticulum, called the _____________, is then regurgitated bit by bit into the mouth to be thoroughly chewed again. This process helps soften and break down cellulose, making it more accessible to further microbial action in other parts of the stomach. The cud is then re-swallowed and moves into the _____________. Here, large particles of food are broken down into smaller pieces by _____________. Water is removed from the cud. The food particles finally move into the _____________, the true stomach of the cow. Here, _____________ juices containing digestive enzymes complete the digestion of proteins and other Rodent
food substances. The food then passes through the _____________ intestine to be digested and _____________ in the normal way. 3. Rodents digestion of cellulose Rodents have big and well developed ______________ to make digestive process of cellulose efficient. It is large as it contains bacteria and protozoa that secrete ______________ for digestion of cellulose. However it present after the small intestine. Absorption of nutrients only occurs in the small intestine. So, the digestion and absorption of nutrient for the 1 st time is incomplete. Thus rodents will ______________their faeces to ______________ more nutrients from the faeces. Faeces for the 1st time is ______________, contain lots of nutrients and undigested food. They are produced at ______________. Faeces for the second time are ______________ and ______________. They are released during the ______________. 4. Effect of rate on the rate of photosynthesis __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________ 5. Dark and light reaction
6. Mechanism of inhalation and exhalation
a. Respiratory centre is stimulated by 3 factors; _____________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ _______________________ b. Sequence of respiratory regulatory mechanism
c. Inhalation mechanism
d. Characteristics of alveoli; ____________________________________________________________ e. Explain oxygen deficit and oxygen debt
7. Definition Colonisation is the process whereby living organisms move into a _____________ formed area which is devoid of life. Succession is the gradual process by which one community _________________ its environment so that it is __________________ by another community. Colonization and Succession in Mangrove Swamp The pioneer species of a mangrove swamp are the
______________________ and ______________________. The presence of these species gradually changes the physical environment of the habitat. The ______________________ root systems of these plants trap and ______________________ sediments, including organic matters from decaying plant parts. As time passes, the soil becomes more ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ and ______________________. the pioneer of the This condition The sp favours the growth of the ______________________. Gradually, the replaces root species. Rhizophora system
______________________ silt and mud, creating firmer soil structure overtime. The ground becomes ______________________. As a result, the soil is ______________________ because it is less submerged by sea water. The condition now becomes more suitable for another mangrove species, the ______________________, which replaces the Rhizophora sp. The ______________________ root system of the Bruguiera sp forms loops which extend from the soil to ______________________ more silt and mud. As more sediment is deposited, the shore extends further to the sea. The old shore is now further away from the sea and is like terrestrial ground. Over time, terrestrial plants like the nipah
palm and Pandanus sp begin to replace the Bruguiera sp. The gradual transition and succession from a mangrove swamp to a terrestrial forest and eventually to a tropical rainforest, which is a ______________________ community, takes a long time.
8. a. Acid rain Acidic gases such as nitrogen oxide, nitrogen dioxide and sulphur dioxide released from the factories and motor vehicles dissolves in rain water to form __________________________________________________________________ respectively. These fall on the ground as acid rain. Effects of acid rain are In ____________________________ plant it causes __________________________________________________________________ _______________________. ___. b. Greenhouse effect __________________________________________________________________
c. What is greenhouse in actual? In actual, a greenhouse is used to grow vegetable and plants in temperate climate especially during _________________. A greenhouse is designed to trap __________________ energy.
Sunlight penetrates the glass roof of a greenhouse to warm the ______________. However the heat given off by soil cannot pass through the _________________. Thus the heat remains inside the greenhouse. This is suitable for _________________ and _____________________ activity of plants.
9. Synapses
The transmission of information is by no means electrical but chemical in nature. When the nerve impulse reaches the end of the presynaptic end of the neurone, it will stimulate the release of chemicals named neurotransmitters in the synaptic vesicles. The synaptic vesicles then fuse with the cell membrane, releasing the neurotransmitters through exocytosis. The neurotransmitters then cross the synapse where they may be accepted by the next neurone at a specialised site called a receptor. The neurotransmitters then fuse with the receptor thus transmitting the nerve impulse to the next neurone. Vesicles containing the neurotransmitters are only in the presynaptic end and the receptors are only on the postsynaptic end, therefore the synapse ensures that the flow of impulses in one direction only.
Spinal cord
a. Indicate using arrow the nerve impulse pathway. b. State the type of action involved. __________________________________________________________________ _______________________ c. Name the impulse transmission pathway. __________________________________________________________________ _______________________ d. State the function of this action. __________________________________________________________________ _______________________ e. State the reason why this action only involves spinal cord and not brain. __________________________________________________________________ _______________________ f. State three examples of this type of action. __________________________________________________________________ _______________________
Test for Biochemical Oxygen Demand 1. Add methylene blue solution to the water sample. 2. Record the time taken for the sample to be decolourised. 3. The shorter the time taken to decolourise the water sample, the more polluted the water sample is.
Determination of vitamin C content in fruit juices
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Wild Animals Reading Writing WorksheetDocument2 paginiWild Animals Reading Writing WorksheetRRKATAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abnormal VermisDocument1 paginăAbnormal VermiscalmlandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evolution HandoutDocument38 paginiEvolution HandoutMagaly XuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final 1 - Digestive SystemDocument3 paginiFinal 1 - Digestive SystemPriscille Yvana SipaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Act 10Document3 paginiAct 10Rose CostaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Level Biology Summer Workbook Name - Topics To Be Covered: Gas Exchange in Plants Digestive System Mass Transport in PlantsDocument23 paginiA Level Biology Summer Workbook Name - Topics To Be Covered: Gas Exchange in Plants Digestive System Mass Transport in PlantsZJ UÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.2.6 Diffusion & Osmosis Worksheet 1Document6 pagini2.2.6 Diffusion & Osmosis Worksheet 1Vittada BadgeriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digestive System in Ruminents and RodentsDocument2 paginiDigestive System in Ruminents and RodentsNanaho0% (1)
- Bio270 Chapter 1 TutorialDocument5 paginiBio270 Chapter 1 TutorialNamÎncă nu există evaluări
- q4wk1 Grade 8 ScienceDocument8 paginiq4wk1 Grade 8 ScienceRoxanne QuebadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Absorption and AdaptationDocument1 paginăAbsorption and AdaptationYee Wai MunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio270 Chapter 1 TutorialDocument4 paginiBio270 Chapter 1 TutorialNur AthirahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Osmosis&diffusion 3NDocument8 paginiOsmosis&diffusion 3Nms_m_tan100% (7)
- Latihan Chap 7 f4Document3 paginiLatihan Chap 7 f4Faizal PejerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Els Finals ReviewerDocument6 paginiEls Finals ReviewerErika JimenezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Frog LBLDocument5 paginiFrog LBLchandumenswear3Încă nu există evaluări
- SPM Biology Chapter 6Document32 paginiSPM Biology Chapter 6birinthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition in Non-ChordatesDocument262 paginiNutrition in Non-ChordatesTapan Kumar PalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.1 From Algae To Terrestrial Plants-Student SheetDocument2 pagini3.1 From Algae To Terrestrial Plants-Student Sheeteshaaljamal27Încă nu există evaluări
- REVISION. 2016 Mid YearDocument4 paginiREVISION. 2016 Mid YearmektiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4: Ecosystems Section 4-1: Energy, Producers, and ConsumersDocument3 paginiChapter 4: Ecosystems Section 4-1: Energy, Producers, and ConsumersMia SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transport Across A MembraneDocument8 paginiTransport Across A MembraneAdah JoshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet: © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1Document4 paginiWorksheet: © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1Kaung Myat SanÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIT 5 Feeding RelationshipsDocument22 paginiUNIT 5 Feeding RelationshipsKelly ChamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week C Stage 4 ScienceDocument30 paginiWeek C Stage 4 ScienceVanjaSekulicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell NotesDocument12 paginiCell NotesP1Încă nu există evaluări
- Year 9 Biology Booklet Topic 1 - Cells NameDocument7 paginiYear 9 Biology Booklet Topic 1 - Cells Namedaisuke ʕ•ᴥ•ʔÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment No - 11 Digestive System (Alimentary System) Laboratory ProcedureDocument8 paginiAssignment No - 11 Digestive System (Alimentary System) Laboratory ProcedureRegina GambayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Nervous System - WorksheetDocument10 paginiThe Nervous System - WorksheetajoshuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digestive System Guided NotesDocument2 paginiDigestive System Guided NotesKathleen BonillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 22 Amoeba-Euglena Questions 1Document2 paginiCH 22 Amoeba-Euglena Questions 1api-444439435Încă nu există evaluări
- LAS1 FermilanDessaDocument8 paginiLAS1 FermilanDessaKiffa AngobÎncă nu există evaluări
- Y 5 - T 2 - W 11 - Review PackWR39wDocument10 paginiY 5 - T 2 - W 11 - Review PackWR39wbmxssbx8r4Încă nu există evaluări
- CSEC Biology June 2021 P2Document21 paginiCSEC Biology June 2021 P2Rianna SamsinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- 21697a1ef05dab2cf2d7cd0d12ce8710Document15 pagini21697a1ef05dab2cf2d7cd0d12ce8710Adrian DelatadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- QuestionnaireDocument4 paginiQuestionnaireJessieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio Essays f4 f5Document23 paginiBio Essays f4 f5Catherine Dharshini LabrooyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Resp Only ReadingDocument2 paginiCell Resp Only Readingapi-264004571100% (1)
- Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument9 paginiCell Structure and Cell OrganisationVictoria PetrusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulation in Living BeingsDocument3 paginiCirculation in Living BeingsGombroxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 3 MC100Document5 paginiLab 3 MC100Aj MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geologic Time WorksheetDocument2 paginiGeologic Time WorksheetA - UNO, France Jhondale B.100% (1)
- Biology EOCT - Answer KeyDocument21 paginiBiology EOCT - Answer KeyjamesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 8 Q4 Module 1 The Digestive System 2nd EdDocument12 paginiGrade 8 Q4 Module 1 The Digestive System 2nd EdJay's JawlineÎncă nu există evaluări
- SOL Review Answer SheetDocument15 paginiSOL Review Answer Sheetbrandonaniah7Încă nu există evaluări
- Cellular Respiration ReadingDocument5 paginiCellular Respiration ReadingJ15Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 04A - Diversity in Animals - Porifera To AnnelidaDocument156 paginiChapter 04A - Diversity in Animals - Porifera To AnnelidaRoop KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Setting Up Sealed Mesocosms To Try To Establish SustainabilityDocument4 paginiSetting Up Sealed Mesocosms To Try To Establish SustainabilityKhang LqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evoluition Final ExamsDocument1 paginăEvoluition Final ExamsJorgelindo Ramos LucasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 13Document49 pagini13luengsaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taking Care of The Digestive SystemDocument8 paginiTaking Care of The Digestive SystemamaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 - Ecosystem NewDocument38 paginiChapter 2 - Ecosystem NewZubair HUssainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Assignment - The Digestive SystemDocument2 paginiScience Assignment - The Digestive SystemF3DEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Epithelial Tissue WorksheetDocument5 paginiEpithelial Tissue WorksheetDaxx Kenu TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8th ScienceDocument15 pagini8th Sciencerhiana encinasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Invertebrate Digestive System2019 ModuleDocument11 paginiInvertebrate Digestive System2019 ModuleJeff Bryan Arellano HimorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 8 q1Document4 paginiScience 8 q1juswa coralÎncă nu există evaluări
- SC Form 1Document4 paginiSC Form 1Nurul NadiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 8 Fourth 4 DaysDocument4 paginiScience 8 Fourth 4 DaysAshley Lopez100% (5)
- Aquaponics systems, fish. Volume 2: Sistemas de acuaponíaDe la EverandAquaponics systems, fish. Volume 2: Sistemas de acuaponíaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Coral Reef Aquarium: An Owner's Guide to a Happy Healthy FishDe la EverandThe Coral Reef Aquarium: An Owner's Guide to a Happy Healthy FishEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (1)
- For The Strength of The Pack Is The Wolf, and The Strength of The Wolf Is The Pack.Document10 paginiFor The Strength of The Pack Is The Wolf, and The Strength of The Wolf Is The Pack.Phone Myat Pyaye SoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evolution Epidemiology and Etiology of Temporomandibular Joint DisordersDocument6 paginiEvolution Epidemiology and Etiology of Temporomandibular Joint DisordersCM Panda CedeesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surgery CssDocument13 paginiSurgery CssNaren ShanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abp 10 Years PDFDocument44 paginiAbp 10 Years PDFUtsabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Allergy Diagnostic TestingDocument149 paginiAllergy Diagnostic TestingArrow Ou100% (1)
- Rhino Basic FactsDocument20 paginiRhino Basic FactsNAMELESWARAN SANGARA NANDA MoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pertanyaan Yang Harus DijawabDocument6 paginiPertanyaan Yang Harus DijawabMuhammad RhezaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Improve Your Breathing With The Alexander Technique PDFDocument3 paginiImprove Your Breathing With The Alexander Technique PDFdoctorspenglerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Haematology, Biochemistry, Serology and Immunology, Microbiology, Cytology, Histopathology, Endocrinology, Ultrasonography & X-RayDocument2 paginiHaematology, Biochemistry, Serology and Immunology, Microbiology, Cytology, Histopathology, Endocrinology, Ultrasonography & X-RayPankaj BeniwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Studi Kasus: Pemalsuan Daging Sapi Dengan Daging Babi Hutan Di Kota Bogor Lailatun Nida, Herwin Pisestyani, Chaerul BasriDocument10 paginiStudi Kasus: Pemalsuan Daging Sapi Dengan Daging Babi Hutan Di Kota Bogor Lailatun Nida, Herwin Pisestyani, Chaerul Basriclarentina aristawatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 Brain and BehaviorDocument9 paginiChapter 2 Brain and BehaviorXin YiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Difference Between Mandibular First Molar and Second Molar: Manish PandeyDocument51 paginiDifference Between Mandibular First Molar and Second Molar: Manish Pandeymanishpankaj123100% (3)
- Perioperative Patient CareDocument6 paginiPerioperative Patient CareClark LlameraÎncă nu există evaluări
- French BulldogDocument6 paginiFrench BulldogOitseyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 2-Aviation Human Factor (Flight Physiology)Document47 paginiLecture 2-Aviation Human Factor (Flight Physiology)Richard Thodé Jr100% (1)
- Sakool ProfileDocument3 paginiSakool ProfileksakoolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Airway Management (Kuliah Panum)Document43 paginiAirway Management (Kuliah Panum)yudhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Istilah Kedokteran in JapaneseDocument8 paginiIstilah Kedokteran in JapaneseYusrina AdaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nodal Stations of The AbdomenDocument8 paginiNodal Stations of The Abdomenborst0% (1)
- Narrative TextDocument7 paginiNarrative TextNorma AyunitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6. The Circulatory System: Short QuestionsDocument31 paginiChapter 6. The Circulatory System: Short QuestionsParardha DharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Report - PromDocument16 paginiCase Report - PromFauziyyahrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polyvagal TheoryDocument24 paginiPolyvagal Theorymkrnhr100% (7)
- What Is The Effect of Swallowing Without Chewing Properly? What Happen With The Chewing Gum?Document15 paginiWhat Is The Effect of Swallowing Without Chewing Properly? What Happen With The Chewing Gum?Jorge Enrique Olaya LiévanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy of The Brain and FunctionsDocument4 paginiAnatomy of The Brain and FunctionsGopinadh GanjiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Meat Milk and Fish HygieneDocument74 paginiMeat Milk and Fish Hygieneransingh100% (1)
- Clostridium and MycobacteriumDocument40 paginiClostridium and MycobacteriumSAYMABANUÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous SystemDocument2 paginiNervous SystemShanel Aubrey AglibutÎncă nu există evaluări