Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Bearings
Încărcat de
Joann NgDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Bearings
Încărcat de
Joann NgDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
1
55 m
A 45 m
125 m 20 68 m 93 D
C
In the diagram, AC and BC are straight paths on level ground, leading to a vertical building ABYX. B is due east of A. Given AB = 125m, AC = 45m, ACB = 93 and BAD 20 . A new path AD is a shortcut to meet path BC at point D. Calculate (i) (ii) (iii)
CAD ,
[3] [2] [2]
the length of BC, the bearing of C from A.
(iv)
A 3m high lamp-post, whose top is T, is erected vertically at point D. A person at the
[2]
top of the building at point X looks at the top of the lamp-post. Calculate the angle of depression from X to T.
(v)
Another person walks from point D directly towards the building line AB. Calculate the [2]
shortest distance from D to AB.
2.
In the diagram, A, B, C and D are four markers on a horizontal field. AC = 350 m, BAC 32 and BCA 90
(a) Calculate AB. (b) The bearing of B from A is 042. CAD 45 and CDA 72 . Calculate (i) the bearing of D from A, (ii) the bearing of D from C, (iii) the shortest distance from C to the path AB. (c) An aircraft was hovering vertically above the point A. The angle of elevation of the bottom of the aircraft from B is 29. (i) Calculate the height at which the aircraft is hovering. (ii) Find the angle of depression of the marker C from the aircraft.
[2]
[1] [2] [2]
[1] [2]
3.
A, B, C are points on level ground. The bearing of C from A is 045 and the bearing of B from A is 075 . Given that AB = BC = 25 m, calculate (a) (b) (c) (d)
ABC
[2] [3] [2]
distance AC, the shortest distance from B to AC, A bird is hovering at a height of 20 m above point B. Calculate the greatest angle of elevation of the bird when viewed from any point on the path AC.
[2]
25 m
45o 25 m A
4.
A vertical pole QT stands at one corner of a horizontal rectangular field PQRS as shown. If SR = 10 m, PS = 6 m and the angle of elevation of T from P is 24 .
T
P 6m S
24
10 m
Calculate (a) (b) QT ,
RTS .
[2] [4]
5.
In the diagram below, ABD lies on a horizontal ground. BCD is a straight line, BC = 5.6 m, AC = 7.9 m, AD = 6.4 m,ADC = 80 and CE is a vertical flagpole at C such that CE = 8 m
E D
8.0 m 6.4 m 7.9 m
C
5.6 m
A
Calculate (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v)
B
ACD the area of triangle ABC the length of AB, the shortest distance from C to the path AB the angle of elevation of point E when viewed from A. [2] [2] [3] [2] [2]
6.
(a)
A, B, C and D are four towns. B, C and D lie on a straight line. B is 3.7km due south of A. The bearing of C from B is 0420, AC = 2.8km and CD = 3.3km.
Calculate (i) (ii) (iii) (b) the bearing of B from C,
ACD ,
[2] [3] [2]
the distance AD.
A vertical tower, AT has its base at A. Given that the angle of elevation of T from a boat, which is 3.5 km away from A, is 2.40 and , calculate (i) (ii) the height, in metres, of the tower AT, Given that there is another boat C which is 6.7 km away from AT, find the angle of depression of C from T. [2] [3]
7.
(a)
A , B and C are three points on level ground. The bearing of C from A is 052 and ACB 112 . AC 42 m and BC 26 m. Calculate (i) the bearing of C from B , (ii) the length of AB , (iii) the area of triangle ABC .
A man walks from A to B . Calculate (i) the distance from C when he is nearest it. (ii) his largest angle of elevation of a 5 m flagpole erected at C .
[2] [2] [1]
(b)
[2] [2]
8.
In the diagram below, P, Q, R and S are four markers in a horizontal field. Given that PS 40m , PR 36m , RPS 50 , PQR 38 , PRQ 90 and S is due west of P. (a) Calculate (i) the bearing of P from R, [1] (ii) the bearing of P from Q. [1] (b) Calculate (i) PQ, (ii) RS, (iii) the area of PSR , (iv) the shortest distance from S to PR.
[2] [2] [2] [2]
(c)
A vertical pole of height 7.5 m is planted at S. A man walks along the path PR. Find the greatest angle of elevation of the top of the pole when viewed from any point along the path. [2]
N
S 40
50
36
R 38
o
9.
In the diagram, TC is a vertical tower 40m high. A, B and C are three points on level ground whereby A is due west of B. Given BC = 24m, AB = 36.8m and the angle of elevation of T from A is 52.2 ,
40m
C 52.2 A 36.8m
24m
(a)
Calculate (i) AC, [2] [2] [2] [3] [2]
(ii) ACB (iii)area of triangle ABC, (iv) bearing of C from A (v) shortest distance from B to AC, (b) Another vertical tower is located on point B. The angle of elevation of this tower from C is 32. Find (i) (ii) the height of the tower. the greatest angle of depression viewed by a man at the top of the tower on a car moving in a straight line along AC.
[2]
[2]
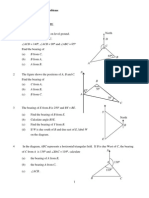
10. N Q 45o R 6 4 53o P 3 2 8 0 S
In the diagram above, PQRS are points on the level ground. Q is due north of P, R is 64 m from P and the bearing of R from P is 053o. Angle PQR = 45o, RS is 32 m and RP is 80 m. (a) Calculate (i) (ii) the length of PQ, angle RPS, [2] [2] [1]
(iii) the bearing of P from S.
(b)
A vertical pole RT was raised with the foot at R and RT = 14 m. Calculate the angle of elevation of T from Q. [3]
(c)
A man walks from P along the line PS until he reaches the point X which is the nearest point from R. (i) (ii) Calculate the distance of X from R. [1]
Calculate the greatest angle of elevation of the top of the pole, T from the man. [1]
11.
8.4 m
7.2 m 9.5 m
6.4 m
P Q
In the diagram, P, Q, R and S are four markers on a horizontal ground and QRS is a straight line.
PSR 78, PS = 7.2 m, PR = 9.5 m and QR = 6.4 m.
(a) Calculate (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (b)
PRS,
the area of triangle PQR, the length of PQ, the shortest distance from R to the path PQ.
[2] [2] [3] [2]
RT is a vertical flagpole at R such that RT = 8.4 m. Calculate the greatest angle of elevation of T as seen from the path PQ. [2]
12. The figure below is a 3-dimensional solid. V is the vertex directly above D. VDA = GAE = AEF = 90 and BC = FG are parallel. Given that ABCD is a square of 6cm, AE = 1.5 cm, EF = 5.4 cm and VD = 11cm, calculate (i) the length of VA , (ii) (iii) [1] [1]
BFE,
the volume of the solid. [3]
13.
The bearing of B and C from A is 045o and 119o respectively. ABC = 32o and AC = 23 m.
a) Find, i) ii) iii) iv) the length BC area of triangle ABC bearing of A from B bearing of B from C [1] [2] [2] [2]
b) Calculate the shortest distance from point A to line BC.
[2]
c) Given that there is a lamppost 15 m high at A, find the greatest angle of elevation from a point on the line BC to the top of the lamppost. [2]
14.
89
100
North
A D 120 B C 93
Three points A, B and C on level ground are such that A is due north of B. An observer at C sees a hot air balloon hovering at E, which is 100 m vertically above A. A vertical tower BD stands at B and the angle of elevation of D, from C is 30o. DC =120 m, ED = 89 m and AC = 93 m.
(a)
Calculate (i) (ii) the height of the tower BD, the distance BC. [1] [1]
(b)
Show that AB = 79.5 m.
[1]
(c)
Calculate (i) (ii) (iii) the largest angle of ABC , the shortest distance from C to AB, the bearing of A from C. [3] [2] [2]
15.
Z 65o B Y
40o
X A glider flies from X to Y then to Z. The journey from X to Y is 16.5 km on a bearing of 040o and the journey from Y to Z is 9.8 km on a bearing of 065o. Given that A is north of Y and west of Z, B is west of Y. Find the (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) distance of BX, bearing of A from B, distance of XZ, area of triangle XYZ [2] [2] [2] [2]
16.
North
A 38 D 10 km C 56 6 km
In the diagram, A, B, C and D are points on level ground, with A due North of B, BAD 38o ,
ADB 56o , BD 6 km and CD = 10 km. Given that ADC is a straight line, calculate
(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) BC,
DBC ,
[2] [2] [1] [2] [2] [1]
the bearing of D from C, the bearing of B from C, the bearing of D from B, the shortest distance from D to BC.
17.
N 112 D 11 m C
15 m B 14 m
In the diagram above A, B, C and D are points on level ground. D is due west of C, CD = 11m, BC = 14 m, AC = 15m and angle ACD = 112. It is given that the bearing of C from A is 202 and the bearing of A from B is 318. Calculate (a) (b) (c) (d) AD, the bearing of A from C, angle ABC, shortest distance from A to BC, [3] [1] [3] [2]
A vertical pole of height 15 m is standing at point A. (e) Calculate the greatest angle of elevation of the top of the pole when [2]
viewed from any point along the line BC.
18.
The diagram shows a horizontal field ABCD where C is due south of A.
D 32 , AD B 18 . C 82 and AC BC = 16.8 m, AD = 11.9 m, AC
N A
16.8 18o 32o
11.9
82o D
C
(a) Show that AC 22.24 m, correct to 4 significant figures. [1]
(b) Calculate (i) (ii) (iii) the area of triangle ACD, AB, the bearing of C from D, [2] [3] [1] [2]
(iv) how far D is south of A.
(c) A tower of height 10 m is erected at a point X, along the path BC such that the angle of elevation of the top of the tower from C is 35. Calculate the distance CX. [2]
19. P, Q, R and S are points on the level ground such that R is due south P and Q is due east of P. S is a point on QR. It is given that RS = 27 m, PR = 100m and PQ = 80m. A tower TP of height 20 m stands on P, (a) Calculate (i) the bearing of R from Q , (ii) the distance PS , (iii) the area of PQS, (b) A man walks along RQ. Calculate his largest angle of elevation of the top of the tower T. T
[2] [3] [2] [4]
P 100m
80m
S 27m
20. B
150 m
D A In the diagram, A, B, C and D are four markers in a horizontal field.
C 38 and AB C 90 . AB = 150 m, BA
(a) (b)
Calculate the length of AC in metres. The bearing of B from C is 310 . Calculate (i) (ii) the bearing of B from A, the bearing of A from C.
[2]
[2] [1]
(c)
From the top of a building at C, the angle of depression of A is 34 . Calculate the height of the building. [2]
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- IB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1Document5 paginiIB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1Ayush MunotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linear LawDocument4 paginiLinear LawJoann NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quiz - Congruency and SimilarityDocument5 paginiQuiz - Congruency and SimilarityTimothy HandokoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2019 JC1 H2 Math Term 2 Revision Test (Marking Scheme) Q2 UpdatedDocument5 pagini2019 JC1 H2 Math Term 2 Revision Test (Marking Scheme) Q2 UpdatedTimothy HandokoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 (A) Solve The Inequality (B) Hence, State The (I) (Ii)Document13 pagini1 (A) Solve The Inequality (B) Hence, State The (I) (Ii)Joann NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACFrOgAKyT2lWc0c338OjLiBxz RO x8p YICpFWTezvDX 7ugC2AUM8xvSSl D TzW5Sd 80U4uIi 66 V8iWabtu KI3DqaxgzefGuxzqeRoyHXrqlXfve Y8fSz QN3IgQa7wL968V6jZ4PCDocument3 paginiACFrOgAKyT2lWc0c338OjLiBxz RO x8p YICpFWTezvDX 7ugC2AUM8xvSSl D TzW5Sd 80U4uIi 66 V8iWabtu KI3DqaxgzefGuxzqeRoyHXrqlXfve Y8fSz QN3IgQa7wL968V6jZ4PCTimothy HandokoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quad FN Worksheet 2Document7 paginiQuad FN Worksheet 2jan12th2004Încă nu există evaluări
- 2020 JC 2 H2 Math Consolidation Test (Solutions)Document14 pagini2020 JC 2 H2 Math Consolidation Test (Solutions)Timothy HandokoÎncă nu există evaluări
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 15 MSDocument29 paginit2 Chem Revision Ex 15 MSNicholas Ow100% (1)
- AnglesDocument23 paginiAnglesJoann NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Questions On Geometrical Proofs 10: 8 - 0 Sin BacDocument16 paginiQuestions On Geometrical Proofs 10: 8 - 0 Sin BacJohn GohÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2019 JC1 H2 Math Term 2 Revision Test (Questions)Document1 pagină2019 JC1 H2 Math Term 2 Revision Test (Questions)Timothy HandokoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Algebraic Word Problem Revision Sec 3Document3 paginiAlgebraic Word Problem Revision Sec 3Kajana Sivarasa ShenthanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Algebra Practice: Name: - CL Ass: 2H2Document11 paginiAlgebra Practice: Name: - CL Ass: 2H2Timothy HandokoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unity Secondary School Physics Chapter 3: Forces Answers: Apushorapull Magnitude Direction NewtonDocument14 paginiUnity Secondary School Physics Chapter 3: Forces Answers: Apushorapull Magnitude Direction NewtonFrancis Ho HoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Differentiation 3Document11 paginiDifferentiation 3Sc KhooÎncă nu există evaluări
- TJC Chemistry H2 Y1 2009Document21 paginiTJC Chemistry H2 Y1 2009OccamsRazor100% (1)
- 2020 JC2 H2 Math Lecture Test 1 (Solution)Document5 pagini2020 JC2 H2 Math Lecture Test 1 (Solution)Timothy HandokoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assign Sheet TrigDocument3 paginiAssign Sheet TrigChirag Hablani100% (1)
- Unity Secondary School Physics Chapter 22: Electromagnetic Induction AnswersDocument20 paginiUnity Secondary School Physics Chapter 22: Electromagnetic Induction AnswersFrancis Ho HoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 13-Differentiation 2 MDISDocument10 paginiChapter 13-Differentiation 2 MDISterrygoh6972Încă nu există evaluări
- Additional Athematics Form 5: Linear LawDocument30 paginiAdditional Athematics Form 5: Linear LawMohd Isyhar Fikri Bin IbrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2020 JC 2 H2 Math Consolidation Test II (Solutions)Document13 pagini2020 JC 2 H2 Math Consolidation Test II (Solutions)Timothy HandokoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answers - H2 Topical Chemistry 2014Document99 paginiAnswers - H2 Topical Chemistry 2014Ruel Arila Jr.Încă nu există evaluări
- 1 Thermo and Equil - Remedial - AnswerDocument6 pagini1 Thermo and Equil - Remedial - AnswerNur Afiqah Mohd ZakiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2023 Tut 2b Probability (Solution)Document9 pagini2023 Tut 2b Probability (Solution)HANNAH GOH (TJC)Încă nu există evaluări
- Sec 1E - Chapter 4 - Introduction To AlgebraDocument12 paginiSec 1E - Chapter 4 - Introduction To Algebrayusdi afandiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jurong Secondary School Secondary 3NT Science 2015 Sem II Class Test 2 - Straight Line GraphsDocument2 paginiJurong Secondary School Secondary 3NT Science 2015 Sem II Class Test 2 - Straight Line GraphsPing HuiÎncă nu există evaluări
- SL - MathDocument2 paginiSL - MathastargroupÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2015 PJC Prelim Paper 1 SolutionsDocument15 pagini2015 PJC Prelim Paper 1 SolutionsnasyrahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Functions Note and Exercise and WorksheetDocument8 paginiFunctions Note and Exercise and WorksheetEmily ZhengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 Measurement 3E SP WS3 Vernier 2011Document2 paginiChapter 1 Measurement 3E SP WS3 Vernier 2011Chandini JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics: Applications and Interpretation: Practice Paper 2 HL Total 110Document7 paginiMathematics: Applications and Interpretation: Practice Paper 2 HL Total 110Ruth HiltonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2019 JC1 H2 Math Term 2 Revision Test (Questions)Document1 pagină2019 JC1 H2 Math Term 2 Revision Test (Questions)Timothy HandokoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sec 2 Term 1 - 1 NotesDocument35 paginiSec 2 Term 1 - 1 NotesWolfie Saraswathi Santhosham100% (1)
- Chapter 5 and 6 Questions: (58 Marks)Document21 paginiChapter 5 and 6 Questions: (58 Marks)aurennosÎncă nu există evaluări
- The City School: University Road Campus Math Worksheet, Topic: Coordinate GeometryDocument3 paginiThe City School: University Road Campus Math Worksheet, Topic: Coordinate GeometryZeeshan Ahmed0% (1)
- 0402-6 WS Chemical EquationsDocument6 pagini0402-6 WS Chemical EquationsJulie MaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2020 JC 2 H2 Maths Lecture Test 2 (Solutions)Document7 pagini2020 JC 2 H2 Maths Lecture Test 2 (Solutions)Timothy HandokoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Constructions (FH) - Edexcel GCSE MathsDocument3 paginiConstructions (FH) - Edexcel GCSE MathsRenad Mahmoud FawzyÎncă nu există evaluări
- MathHL QB3 T2Document25 paginiMathHL QB3 T2Nikola PetrovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- IB DP Prescribed PracticalsDocument24 paginiIB DP Prescribed PracticalsMitul HariyaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3D Angles QuestionsDocument4 pagini3D Angles QuestionsyddapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ah Sem 2Document10 paginiAh Sem 2JASON_INGHAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4047 SP 01Document6 pagini4047 SP 01MaverickÎncă nu există evaluări
- Markscheme: Trigonometry Worksheet 3 With Mark Scheme (Graphs of Trig. Functions) 1a. (2 Marks)Document11 paginiMarkscheme: Trigonometry Worksheet 3 With Mark Scheme (Graphs of Trig. Functions) 1a. (2 Marks)Ella JonasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4016 Mathematics Topic 1: Numbers and AlgebraDocument7 pagini4016 Mathematics Topic 1: Numbers and AlgebraMohammad AshfaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACSIAM1Document3 paginiACSIAM1JASON_INGHAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- WS Household Electricity 2014 (Sol)Document4 paginiWS Household Electricity 2014 (Sol)Lowry GuettaÎncă nu există evaluări
- O LVL Chemistry Hwa Chong Prelim 2010 PDFDocument39 paginiO LVL Chemistry Hwa Chong Prelim 2010 PDFSOÎncă nu există evaluări
- HL Paper 2: Full Electron Configuration of The Ruthenium (II) IonDocument20 paginiHL Paper 2: Full Electron Configuration of The Ruthenium (II) IonfuduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sec3classtest - Preparation of Salts - Marking SchemeDocument4 paginiSec3classtest - Preparation of Salts - Marking Schemescientia est potentiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CC Grade 11 Chemistry Energetics CWDocument3 paginiCC Grade 11 Chemistry Energetics CWMaliq MorrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quadratic Graphs & EquationsDocument2 paginiQuadratic Graphs & EquationsJamaliah DaudÎncă nu există evaluări
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 16 Answer Scheme Ver 2Document19 paginit2 Chem Revision Ex 16 Answer Scheme Ver 2Nicholas OwÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2013 HCI Prelim Paper 2 Mark SchemeDocument13 pagini2013 HCI Prelim Paper 2 Mark SchemeYan Shen TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vectors Review IB Paper 2 QuestionsDocument4 paginiVectors Review IB Paper 2 QuestionsJasmine YimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigo (E) Worksheet 2Document8 paginiTrigo (E) Worksheet 2Sohail Merchant100% (1)
- 28-Trigonometry Paper 2Document6 pagini28-Trigonometry Paper 2iyaad MubarakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pythagoras Theorem and Trigonometry Ratios RevisionDocument5 paginiPythagoras Theorem and Trigonometry Ratios RevisionAng Mae ChenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compound Interest R P: Mathematical FormulaeDocument21 paginiCompound Interest R P: Mathematical FormulaeJoann NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prac 1 P1Document20 paginiPrac 1 P1Joann NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Estimation and ApproximationDocument13 paginiEstimation and ApproximationJoann NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- AnglesDocument23 paginiAnglesJoann NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Estimation and ApproximationDocument13 paginiEstimation and ApproximationJoann NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Secondary 1 AlgebraDocument55 paginiSecondary 1 AlgebraJoann NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Direct and Indirect ProportionDocument15 paginiDirect and Indirect ProportionJoann NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0580 s11 Ms 11 PDFDocument3 pagini0580 s11 Ms 11 PDFJoann NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answer: $Document18 paginiAnswer: $Joann NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- F170 User ManualDocument6 paginiF170 User ManualJoann NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Angles and Parallel LinesDocument15 paginiAngles and Parallel LinesJoann NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Area and VolumeDocument33 paginiArea and VolumeJoann NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resume 202309040934Document5 paginiResume 202309040934dubai eyeÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDS Air CompressorDocument1 paginăPDS Air Compressordhavalesh1Încă nu există evaluări
- Wind Turbines Fundamentals Technologies Application Economics 2nd EditionDocument3 paginiWind Turbines Fundamentals Technologies Application Economics 2nd Editionhafidztampan0% (1)
- Raport de Incercare TL 82 Engleza 2015 MasticDocument3 paginiRaport de Incercare TL 82 Engleza 2015 MasticRoxana IoanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irazu EULA AgreementDocument7 paginiIrazu EULA AgreementLiqiang HeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric Baseboard StelproDocument4 paginiElectric Baseboard StelprojrodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Khrone 5 Beam Flow Meter DatasheetDocument16 paginiKhrone 5 Beam Flow Meter DatasheetAnoop ChulliyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Car Info PDFDocument1 paginăNew Car Info PDFSelwyn GullinÎncă nu există evaluări
- STAAD Seismic AnalysisDocument5 paginiSTAAD Seismic AnalysismabuhamdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study 05 PDFDocument5 paginiCase Study 05 PDFSaltNPepa SaltNPepaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ferrovial / BAA - A Transforming Acquisition: 3rd July 2006Document38 paginiFerrovial / BAA - A Transforming Acquisition: 3rd July 2006Andrew YangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sworn Statement of Assets, Liabilities and Net WorthDocument2 paginiSworn Statement of Assets, Liabilities and Net WorthFaidah Palawan AlawiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab - Report: Experiment NoDocument6 paginiLab - Report: Experiment NoRedwan AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- PX4211 2Document3 paginiPX4211 2kalpanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Caso 1 - Tunel Sismico BoluDocument4 paginiCaso 1 - Tunel Sismico BoluCarlos Catalán CórdovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 1 Process Heat TransferDocument4 paginiTutorial 1 Process Heat TransferSuraya JohariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Autonics KRN1000 DatasheetDocument14 paginiAutonics KRN1000 DatasheetAditia Dwi SaputraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Katalog Bonnier BooksDocument45 paginiKatalog Bonnier BooksghitahirataÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Study On Mental Health and Quality of Work Life Among Teachers Working in Corporate SchoolsDocument6 paginiA Study On Mental Health and Quality of Work Life Among Teachers Working in Corporate SchoolsKannamma ValliÎncă nu există evaluări
- S No. Store Type Parent ID Partner IDDocument8 paginiS No. Store Type Parent ID Partner IDabhishek palÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tingalpa Green New Townhouse Development BrochureDocument12 paginiTingalpa Green New Townhouse Development BrochureMick MillanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uploading, Sharing, and Image Hosting PlatformsDocument12 paginiUploading, Sharing, and Image Hosting Platformsmarry janeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hey Can I Try ThatDocument20 paginiHey Can I Try Thatapi-273078602Încă nu există evaluări
- High-Rise Climb V0.6a Smokeydots PDFDocument10 paginiHigh-Rise Climb V0.6a Smokeydots PDFHer Lan OÎncă nu există evaluări
- Siemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 223Document1 paginăSiemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 223mydearteacherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impact of Carding Segments On Quality of Card Sliver: Practical HintsDocument1 paginăImpact of Carding Segments On Quality of Card Sliver: Practical HintsAqeel AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- MockboardexamDocument13 paginiMockboardexamJayke TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- IllustratorDocument27 paginiIllustratorVinti MalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- About FW TaylorDocument9 paginiAbout FW TaylorGayaz SkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dorma 2012 Price ListDocument284 paginiDorma 2012 Price ListSecurity Lock DistributorsÎncă nu există evaluări