Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Beam & Column
Încărcat de
Anonymous nwByj9LDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Beam & Column
Încărcat de
Anonymous nwByj9LDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
BEAM & COLUMN 1.
In a building beams are normally provided over the columns,
under the walls and under heavy concentrated loads to avoid these loads directly coming on slabs. Columns are provided at spacing of 12, 15,18,20 and 24 intervals. 2. In general, maximum span of beams carrying live loads up to 4 KN / m2 may be limited to the following values: Supported Cantilevers condition Rectangular Flanged 3. 3.0 M 5.0 M supported 6.0 M 10.0 M continuous 8.0 M 12.0 M Simply Fixed /
Practical Depth Beam: Loading Span in metre 3m to 4m 5m to 10m 10m : Rectangular T beam for interior beams and L Span/Depth ratio L/d 15 to 20 12 to 15 10 to 12
Light Medium to Heavy Heavy 4. Beam section at support
Beam section at mid span : beam for exterior beams 5. If Mu < Mr -
Tee beam requires 9% lesser reinforcement as
required for rectangular beam. 6. If Mu = Mr. The beam requires 20% lesser than that required for rectangular beam. For span > 4 m where there is appreciable B.M., it is advisable to design beam at mid span as Tee or Ell beam.
Based on support condition beam depth can be assumed as follows: Support condition Depth of beam Simply supported and continuous 1/10 to 1/12 of clear span beams Tee beams Cantilever beams COLUMNS:1. The spacing of columns shall be such that the span of the beam is not less than 2.5M nor greater than 10.0M. Spans of 4 M to 6 M give normal sizes of beams. Single bay Portal frames may be adopted for spans ranging from 6.0m to 12.0m. The spacing of frame may vary from 3.50m to 4.0m. 2. 3. Columns are having width equal to width of wall or beam. Usually 9. Depth may be taken as 9, 12, 15,18, 21, 24 and so on in multiples of 3. Projections of columns outside the wall should be avoided as far as possible. 1/12 to 1/15 of clear span 1/5 to 1/6 of clear span
4.
The columns should be so oriented that the depth of column should be perpendicular to the major axis of bending. b D b
X Y
XX YY D b
Major axis of bending Minor axis of bending 1r to axis of bending 11 to axis of bending
5. When the effective length of column in one plane is greater than that in the orthogonal plane, the greater dimensions shall be in the plane, having larger effective length so as to reduce leff/D ratio to increase the load carrying capacity of the column. COLUMN TRIAL SECTION 1. The column section can be assumed by any one of the method: (a) Based on Load: Ag (Gross area) required = 80 to 100 mm2 per every 1KN ultimate load carried by the column depending on the grade of concrete used. Ac= C.s. are of column D= large dimension of column =Ac/b b=width of column. For 600KN ultimate load, area required= 80x 600 =48000 mm2 If b=230mm, D=48000/230=209mm say 230mm. Size of column is 230 x 230mm. (b) Based on tributary load carried by the column: Area required is mm2/m2 of area covered by the column Grade of concrete M15 M20 External column 2500 2000 Internal column 1800 1500
M25 1800 1200 For example for 3 storeyed building interior column with M20 concrete with 3m by 4m grid Area required = (3 storey) x tributary area (3x4)x 1500 mm2 =54000mm2 Assuming width of column b=230 mm Depth required D = 54000/230 =235mm say 300mm The size of column to be adopted is 230 x 300 mm. Rough guidance for load carrying capacity of column : Load carried by concrete = 4t for M15, 5t for M20 and 6t for M25 for 100 cm2 of concrete area. Load carried by steel (for each bar) = 12mm rod =2.03t; 16mm=3.62t; 20mm= 5.65t; 25mm=8.83t 28mm=11.08t; 32mm=14.47t Total load= load carried by concrete+ load carried by steel E.g 230 x 230 with 4 Nos. 12mm rod ={(23x23)/100}x 5t +(4 x 2.03) =34.57t. This is the minimum capacity that the column can safely carried. (c) Estimation of Load on column by thumb rule: Column Position Interior column Side or end column Corner column Residential building 1.2t/m2 1.7t/m2 2.2t/m2 Office/commercial building 1.4t/m2 1.9t/m2 2.4t/m2
Size of column assumed based on loads Load (tons) (mm) Up to 45 46 to 80 81 to 110 111 to 150 230 230 x 450 230 300 x 600 x 230 or 300x 300 x 600 or 230 x 750 Column size
151 to 195 Above 195
300 x 750 or 450 x 450 300 x 830
(d) Based on thumb rule : (i)Based on height or span of the beam Column depth is 3 to 5% of total height of building For example 8 storeyed building with 3m height The depth of column is (8x3=24m )x3/100= 0.72m say 750mm. If the beam span is 4.5m, along transverse direction, width (b) = 1/12 of span of beam b= 1/12x4.50 =0.375m say 380 mm. (ii)Based on storey/ span of beam If building height is 3 storeys or less: If beam span is < 6m, D=300mm; If beam span is between 6.0 to 9m, D=350mm If the beam span is more than 12.0m, D=400mm. If the building height is 4 to 9 storeys: If beam span is < 6m, D=400mm; If beam span is between 6.0 to 9m, D=500mm If the beam span is more than 12.0m,D=600mm (e) Based on Load and moment: Assume 2% of C.S area for fy=250N/mm2 (i) If the line of action of the eccentric load is outside c.s area =Pu/0.4 fck (ii) If the line of action of the eccentric load is inside (within the section) c.s. area =Pu/0.45fck Example: Pu=2460KN; Mu=91KNM; fck=20N/mm2 ;fy=415N/mm2 Calculate eccentricity of load =Mu/Pu =91/2460= 0.037m Assume that line of action of axial load is inside the section and check this later. c.s area required =2460x103 /0.45x20x106 =0.273m2 If one dimension is 460mm, the other needs to be =0.273/0.46=0.59m say 0.60m Section is 460mm x 600mm Area of steel reinforcement= 0.02x0.273x(250/415)x106 =3289.16 mm2
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Reinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignDe la EverandReinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Beams and Slabs Systems PDFDocument43 paginiBeams and Slabs Systems PDFNisha VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 3 BatteryDocument40 paginiTopic 3 BatterynisaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 250 Conversation StartersDocument22 pagini250 Conversation StartersMarithe Le Blanc100% (2)
- Column Design 1. Guideline For Fixing The Position and Orientation of Columns in The LayoutDocument14 paginiColumn Design 1. Guideline For Fixing The Position and Orientation of Columns in The LayoutV.m. RajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concrete Rules of ThumbDocument8 paginiConcrete Rules of Thumbdeekchik121Încă nu există evaluări
- Beam PlanDocument6 paginiBeam PlanrajanciviltnebÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis & Design of Multi Storeyed Buildings V.M.RAJAN, M.E. (Struct), FIE, Former CE/Civil/TANGEDCODocument25 paginiAnalysis & Design of Multi Storeyed Buildings V.M.RAJAN, M.E. (Struct), FIE, Former CE/Civil/TANGEDCOV.m. RajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pile CapDocument8 paginiPile Capcabaas hassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- RCC Member Design TipsDocument8 paginiRCC Member Design TipsAbhishek ChaudhariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pile Cap Design - Structural GuideDocument6 paginiPile Cap Design - Structural GuideA KÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculate The Effective Depth of The SlabDocument9 paginiCalculate The Effective Depth of The Slabtapan kumar bhanjoÎncă nu există evaluări
- RCC Thumb RuleDocument7 paginiRCC Thumb RuleRahat ullah100% (6)
- Structural TipsDocument7 paginiStructural Tipsbalacr3Încă nu există evaluări
- RCC Member Design TipsDocument9 paginiRCC Member Design TipsNaren ViratÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural Tips / Thumb RulesDocument7 paginiStructural Tips / Thumb Ruleswindspace3Încă nu există evaluări
- Structural Design-IiDocument75 paginiStructural Design-Iisanjithr619Încă nu există evaluări
- Preliminary Design Rules of ThumbDocument11 paginiPreliminary Design Rules of Thumbnimal1234Încă nu există evaluări
- RCC Design TipsDocument9 paginiRCC Design Tipssatoni12Încă nu există evaluări
- Axial Load Column CapacityDocument3 paginiAxial Load Column Capacityaditya2053100% (1)
- Slab DesignDocument45 paginiSlab DesignOkino CharlesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 8Document12 paginiChapter 8gilbert850507Încă nu există evaluări
- Lintel BeamDocument27 paginiLintel Beamjaffna100% (1)
- 8 - Design of Slab Part 1 One Way SlabDocument27 pagini8 - Design of Slab Part 1 One Way SlabyakaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Continuous Beam For RCDocument44 paginiContinuous Beam For RCHammad AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of SlabsDocument17 paginiDesign of SlabsAmay mishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rules of Thumb by RowingengineerDocument6 paginiRules of Thumb by RowingengineerOyens EstoyeÎncă nu există evaluări
- STRL Design Rules of Thumb PDFDocument11 paginiSTRL Design Rules of Thumb PDFsakti prasanna sahuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beam Design ThumbruleDocument5 paginiBeam Design ThumbrulehipreyashÎncă nu există evaluări
- SlabsDocument29 paginiSlabsPimpa Mwiinga100% (2)
- One Way Slab DesignDocument19 paginiOne Way Slab DesignMandar NadgaundiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concrete Rules of ThumbDocument15 paginiConcrete Rules of ThumbNoble Obeng-Ankamah100% (1)
- Structural Design of Timber To BS 5268Document14 paginiStructural Design of Timber To BS 5268Niceman Natiqi80% (10)
- CH 1Document49 paginiCH 1Gurinder PalsinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of SlabDocument7 paginiDesign of SlabAlam Mohammad Parvez SaifiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Floating Roof DesinDocument5 paginiFloating Roof Desindimdaliak_985662241Încă nu există evaluări
- Slabs FinalDocument30 paginiSlabs FinalMwa100% (1)
- Design Guide Pt2 RoofsDocument20 paginiDesign Guide Pt2 RoofsEdward Millward50% (2)
- Design of Rectangular Reinforced Concrete BeamDocument13 paginiDesign of Rectangular Reinforced Concrete BeamChie SierraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rules of ThumbDocument14 paginiRules of ThumbAntoniette Samantha Nacion100% (1)
- Combined Footing Vtu DocumentDocument22 paginiCombined Footing Vtu DocumentSyed IsmailÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multistoreyed Building 3 PDF FreeDocument26 paginiMultistoreyed Building 3 PDF FreeHbk xboyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lintel BeamDocument5 paginiLintel BeamAnonymous nwByj9LÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maximum Spacing of PilesDocument10 paginiMaximum Spacing of Pileskaleswara_tellakulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9 - Reinforced Concrete Column Part 1Document26 pagini9 - Reinforced Concrete Column Part 1yakaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shear WallsDocument25 paginiShear WallsGerald MagingaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment On Yield LineDocument1 paginăAssignment On Yield LineAbhishek AdhikariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural Masangkay Quiz 3Document6 paginiStructural Masangkay Quiz 3Sharmaine FalcisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flexural TestDocument13 paginiFlexural TestAliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lintel BeamDocument3 paginiLintel BeamVarinder SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slender ColumnsDocument110 paginiSlender ColumnsvishaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Piles DesignDocument15 paginiPiles Designvenkatesh19701Încă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Notes on Reinforced Concrete DesignDe la EverandLecture Notes on Reinforced Concrete DesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strength Of Beams, Floor And Roofs - Including Directions For Designing And Detailing Roof Trusses, With Criticism Of Various Forms Of Timber ConstructionDe la EverandStrength Of Beams, Floor And Roofs - Including Directions For Designing And Detailing Roof Trusses, With Criticism Of Various Forms Of Timber ConstructionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stair-Building and the Steel Square: A Manual of Practical Instruction in the Art of Stair-Building and Hand-Railing, and the Manifold Uses of the Steel SquareDe la EverandStair-Building and the Steel Square: A Manual of Practical Instruction in the Art of Stair-Building and Hand-Railing, and the Manifold Uses of the Steel SquareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Turf Wall Architecture and Turf Furniture Assembly GuideDe la EverandTurf Wall Architecture and Turf Furniture Assembly GuideÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reinforced Concrete Grade Beams, Piles & Caissons: A Practical Guide for Hillside ConstructionDe la EverandReinforced Concrete Grade Beams, Piles & Caissons: A Practical Guide for Hillside ConstructionÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Short Guide to the Types and Details of Constructing a Suspension Bridge - Including Various Arrangements of Suspension Spans, Methods of Vertical Stiffening and Wire Cables Versus Eyebar ChainsDe la EverandA Short Guide to the Types and Details of Constructing a Suspension Bridge - Including Various Arrangements of Suspension Spans, Methods of Vertical Stiffening and Wire Cables Versus Eyebar ChainsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsDe la EverandCylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsÎncă nu există evaluări
- ETABS Example-1Document64 paginiETABS Example-1Anonymous nwByj9L0% (1)
- Staad Auto Load CombinationDocument1 paginăStaad Auto Load CombinationAnonymous 48jYxR1CÎncă nu există evaluări
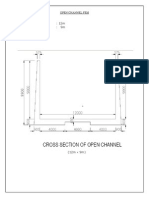
- Staad Pro-Open ChannelDocument5 paginiStaad Pro-Open ChannelAnonymous nwByj9LÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pushover CE&CRDocument9 paginiPushover CE&CRAnonymous nwByj9LÎncă nu există evaluări
- Continuous Beam 2Document6 paginiContinuous Beam 2Anonymous nwByj9LÎncă nu există evaluări
- Planwin / RCDC Is A Total End To End Solution For RCC Building Design and Drawing. It Offers FollowingDocument4 paginiPlanwin / RCDC Is A Total End To End Solution For RCC Building Design and Drawing. It Offers FollowingAnonymous nwByj9LÎncă nu există evaluări
- Etabs: Extended Three Dimensional Analysis For Building System Example 1Document41 paginiEtabs: Extended Three Dimensional Analysis For Building System Example 1Anonymous nwByj9L100% (2)
- Staad Pro-Open ChannelDocument5 paginiStaad Pro-Open ChannelAnonymous nwByj9LÎncă nu există evaluări
- Is 808-1989 Steel TableDocument24 paginiIs 808-1989 Steel TableAtul Kumar Engineer86% (28)
- Compound WallDocument3 paginiCompound WallAnonymous nwByj9L0% (1)
- WindDocument9 paginiWindAnonymous nwByj9LÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 7 Battery Room: S C A D A RTCCDocument1 pagină8 7 Battery Room: S C A D A RTCCAnonymous nwByj9LÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steps To E-Filing For ITDocument4 paginiSteps To E-Filing For ITAnonymous nwByj9LÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Aspects On Detailing of RCC Members in Building Construction BY V.M.Rajan Ce/Civil/MtppDocument21 paginiPractical Aspects On Detailing of RCC Members in Building Construction BY V.M.Rajan Ce/Civil/MtppAnonymous nwByj9L100% (1)
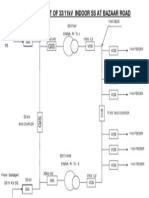
- Schematic Layout of Bazaar Road SSDocument1 paginăSchematic Layout of Bazaar Road SSAnonymous nwByj9LÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section VIIDocument29 paginiSection VIIAnonymous nwByj9LÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section Viii AnnexuesDocument11 paginiSection Viii AnnexuesAnonymous nwByj9LÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trench 2Document1 paginăTrench 2Anonymous nwByj9LÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section IDocument37 paginiSection IAnonymous nwByj9LÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section IIDocument105 paginiSection IIAnonymous nwByj9LÎncă nu există evaluări
- sch-2 - 06.01.2014Document1 paginăsch-2 - 06.01.2014Anonymous nwByj9LÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bazzar Road SS-GFDocument1 paginăBazzar Road SS-GFAnonymous nwByj9LÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schematic Layout of Bazaar Road SSDocument1 paginăSchematic Layout of Bazaar Road SSAnonymous nwByj9LÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section VDocument18 paginiSection VAnonymous nwByj9LÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trench 1Document1 paginăTrench 1Anonymous nwByj9LÎncă nu există evaluări
- Staad FoundationDocument25 paginiStaad FoundationAnonymous nwByj9L100% (2)
- Fire Barrier Wall: Cable TrenchDocument1 paginăFire Barrier Wall: Cable TrenchAnonymous nwByj9LÎncă nu există evaluări
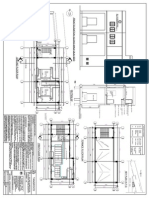
- Bazzar Road Control Room Building DesignDocument39 paginiBazzar Road Control Room Building DesignAnonymous nwByj9LÎncă nu există evaluări
- WindDocument139 paginiWindAnonymous nwByj9LÎncă nu există evaluări
- Staad Pro NotesDocument134 paginiStaad Pro NotesAnonymous nwByj9L100% (31)
- Startup-Shutdown Oracle LinuxDocument4 paginiStartup-Shutdown Oracle LinuxJosé Florencio de QueirozÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tugas Week 6 No 8.23Document5 paginiTugas Week 6 No 8.23Mikael MuhammadÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Journey To SomnathDocument8 paginiA Journey To SomnathUrmi RavalÎncă nu există evaluări
- TIFR Pamphlet On Homological MethodsDocument105 paginiTIFR Pamphlet On Homological MethodsRAMJANÎncă nu există evaluări
- School Work - The Marriage CrisisDocument2 paginiSchool Work - The Marriage CrisisTreesy NgoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 07 Indian WeddingDocument2 pagini07 Indian WeddingNailah Al-FarafishahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Villaroel Vs EstradaDocument1 paginăVillaroel Vs EstradaLylo BesaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Naija Docs Magazine Issue 6Document46 paginiNaija Docs Magazine Issue 6Olumide ElebuteÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Beginner's Guide To Reading Jung - Jungian Center For The Spiritual SciencesDocument6 paginiA Beginner's Guide To Reading Jung - Jungian Center For The Spiritual SciencesRosa ChacónÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scientific Writing VerbsDocument3 paginiScientific Writing VerbsNejdetEXn100% (1)
- Design ManagementDocument21 paginiDesign ManagementKarishma Mittal100% (1)
- Feminist Literary CriticismDocument11 paginiFeminist Literary Criticismbela2011Încă nu există evaluări
- Lim vs. Pacquing (G.R. No. 115044. January 27, 1995)Document1 paginăLim vs. Pacquing (G.R. No. 115044. January 27, 1995)Joyce Sumagang ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- IIT JEE Maths Mains 2000Document3 paginiIIT JEE Maths Mains 2000Ayush SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MultidisciplinaryDocument20 paginiMultidisciplinaryrabiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Meditation Club of RUET Asif EEE 17 PDFDocument2 paginiMeditation Club of RUET Asif EEE 17 PDFShovonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fornilda vs. Br. 164, RTC Ivth Judicial Region, PasigDocument11 paginiFornilda vs. Br. 164, RTC Ivth Judicial Region, PasigJenny ButacanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Question Bank of Financial Management - 2markDocument16 paginiQuestion Bank of Financial Management - 2marklakkuMSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2: Demand, Supply & Market EquilibriumDocument15 paginiChapter 2: Demand, Supply & Market EquilibriumRaja AfiqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catherine The Great: Catherine II, Empress of RussiaDocument7 paginiCatherine The Great: Catherine II, Empress of RussiaLawrence James ParbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arup Kumar Mandal (New Format)Document2 paginiArup Kumar Mandal (New Format)sharafat_321Încă nu există evaluări
- University of Mumbai: Bachelor of Management Studies (Finance) Semester VIDocument73 paginiUniversity of Mumbai: Bachelor of Management Studies (Finance) Semester VIPranay ShettyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reflection Chapter 13 and 14Document2 paginiReflection Chapter 13 and 14Vanessa Zevallos HernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Devi Strotam PDFDocument9 paginiDevi Strotam PDFDiary Of A Wise ManÎncă nu există evaluări
- 332-Article Text-1279-1-10-20170327Document24 pagini332-Article Text-1279-1-10-20170327Krisdayanti MendrofaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mythbusters - Archimedes Cannon QuestionsDocument2 paginiMythbusters - Archimedes Cannon QuestionsVictoria RojugbokanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mercado Vs Manzano Case DigestDocument3 paginiMercado Vs Manzano Case DigestalexparungoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan Form Day 2 / 3 (4) Webquest Data GatheringDocument1 paginăLesson Plan Form Day 2 / 3 (4) Webquest Data GatheringMarkJLanzaÎncă nu există evaluări