Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Waja Thermochemistry Edited
Încărcat de
dalilacDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Waja Thermochemistry Edited
Încărcat de
dalilacDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
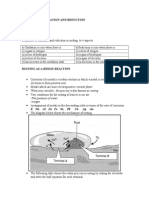
13 THERMOCHEMISTRY CONCEPT MAP
ENERGY LEVEL DIAGRAM
Energy product H : positive Reactant
Energy Reactant H : negative product
Endothermic reaction Heat energy absorbs
Exothermic reaction Heat energy releases
Energy change
THERMOCHEMISTRY types of heat of reaction
Heat of precipitation Meaning, Example of chemical reaction and equation
Heat of neutralization Meaning, Example of chemical reaction and equation
Heat of displacement Meaning, Example of chemical reaction and equation
Heat of precipitation Meaning, Example of chemical reaction and equation
13.1
ENERGY CHANGES IN CHEMICAL REACTION
( Refer to the form five text book page : 143 - 144 ) 1 What is exothermic reaction ? An exothermic reaction is a chemical reaction that gives out heat to the surroundings. Heat energy given out from the reaction is to the surroundings The temperature of the surroundings . 2 What is endothermic reaction ? An endothermic reaction is a chemical reaction that absorbs heat from the surroundings . The reactants . heat energy from the surroundings. The temperature of the surroundings . 3 Identify the following reactions as exothermic or endothermic reaction (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) Reaction Combustion of ethanol Burning of magnesium Neutralisation between acid and alkali Adding water to concentrated sulphuric acid Photosynthesis Reaction between acid and magnesium Reaction between acid and calcium carbonate Dissolving ammonium salt in water Thermal decomposition of copper(ll) carbonate Thermal decomposition of zinc nitrate Exothermic Endothermic
4 The amount of heat energy released or absorbed during a cemical reaction is called the heat of reaction. It is given a symbol . and the unit is .. 5 The heat of reaction , H = H products - H reactants Exothermic reaction : The reactants lose heat energy to form the products . Thus the products formed have less energy than the reactants, Therefore, H is . Endothermic reaction : The reactants absorbs heat energy to form the products . Thus the products formed have energy than the reactant,Therefore, H is positive sign. 6 Energy level diagram ( Refer to the text book page 145 - 146 ) (i) Energy level diagram for exothermic reaction : The products have less energy than the reactants,
Energy reactants H = negative products
Construct energy level diagram based on the chemical equation, Mg + H2SO4 ZnSO4 + H2 (reactants) ( products ) H = -467 kJ
(ii)
Energy level diagram for endothermic reaction : The products have more energy than the reactants, Energy products
reactants
H = negative
Construct energy level diagram based on the chemical equation CaCO3 CuO + CO2 H = + 178 kJ
(iii) Information that can be obtained from the energy level diagram Energy
Zn + CuSO4 H = - 190 kJ Cu + ZnSO4
Figure shows the energy level diagram for the reaction between zinc and copper(ll) sulphate, a) The reaction between and . is an .. reaction. b) During the reaction, the temperature of the mixture . c) The total energy of one mole of. and one mole of .. is . than the total energy of one mole of copper and one mole of zinc sulphate by . kJ d) When one mole of .. reacts with one mole of .. to form .. .. mole of copper and .. mole of zinc sulphate, .. kJ of heat is
Energy 2HI
H2 + I2
H = +53 kJ
Figure shows the energy level diagram for the reaction between hydrogen gas and iodine a) The reaction between and . is an .. reaction. b) During the reaction, the temperature of the mixture . c) The total energy of one mole of. and one mole of .. is . than the total energy of two moles of hydrogen iodide by kJ d) When one mole of .. reacts with one mole of .. to form .mole of hydrogen iodide..kJ of heat is 7 Explain the application of exothermic and endothermic reaction in our every day life, ( Refer to the text book page 147 - 148 ) (i) Instant cold packs : Instant cold packs are used to treat , have separate compartments of and in a plastic bag. When the barrier between the two is broken by squeezing the outer bag, the .. dissolve in .endothermically to provide instant coldness. (ii) First-aid chemical hot pack :
13.2
HEAT OF REACTION ( refer to the text book page : 149 - 169 )
HEAT OF REACTION The change in the amount of heat in a chemical reaction Symbol : . The
HEAT OF PRECIPITATION Meaning : .. .. HEAT OF NEUTRALIZATION Meaning : .. .. .. Complete the table Chemical equation Pb(NO3)2 + 2KI PbI2 + 2KNO3 Type of reaction
HEAT OF DISPLACEMENT Meaning : .. .. HEAT OF COMBUSTION Meaning : .. .. ..
Heat of reaction Heat of precipitation Heat of neutralization
Precipitation reaction Displacement reaction
C2H5OH + 3O2 2CO2 + 3H2O Precipitation reaction
The heat change in a reaction can be calculated using the formula , H = mc m = mass of solution, g c = specific heat capacity of the solution, J g-1 oC-1 = temperature change Assumption : i) The solution is dilute, it has the same density as water , 1 g cm-3 ( 1 cm3 = 1g ) ii) The solution has the same specific heat capacity as water, 4.2 J g-1 oC-1
Example : heat of reaction Guidelines for the calculation of the Steps to follow: Calculate the amount of heat change when H the temperature of 200 cm3 of water Step 1 - Calculate the heat change using the formula, = mc 0 is raised fromequation 280C to 40 C, equation for the reaction that occurs Step 2 - Write chemical or ionic H = mc = 200 g the following Step 3 - Calculate the number of moles of-1reactant that reacts m using either o 0 = 200 g x 4.2 J g C x 12 C c = 4.2 J g-1 oC-1 formulae : 0 = 10080 J Number of moles = mass or = 40 - 28 = 12 C = 10.08 kJ molar mass Number of moles = MV 1000 M : Molarity of the solution V : volume of the solution in cm3
Step 4 - Link the number of moles of reactants ( step 3 ) with the heat change ( step 1 ) Calculate the heat of reaction, H, by using the following formula :
Heat of reaction , H =
heat change ( answer from step 1 ) Number of moles ( answer from step 3 )
NUMERICAL PROBLEMS RELATED TO HEAT OF REACTION 1. HEAT OF PRECIPITATION Aim : To determine the heat of precipitation of silver chloride
25 cm3 0.5 mol dm-3 sodium chloride solution
25 cm3 0.5 mol dm-3 silver nitrate solution Procedure : 1. Measure 25 cm3 0.5 mol dm-3 silver nitrate solution and pour it into the polystrene cup, 2. Put the thermometer into the silver nitrate solution. Record the initial temperature, 3. Measure 25 cm3 0.5 mol dm-3 sodium chloride solution and record the initial temperature, 4. Pour the sodium chloride solution quickly into the silver nitrate solution in the polystyrene cup. 5. Stir the solution mixture with the thermometer and record the highest temperature achieved. Result : Initial temperature of silver nitrate solution Initial temperature of silver nitrate solution Highest temperature of the mixture = 290C = 290C = 320C Average initial temperature = 290C
Calculation Step 1 : Calculate the heat change using the formula H = mc
Changes of temperature, = 320C - 290C = 30C Heat change , H = mc H = .. J m = ( 25 + 25 ) g = 50 g c = 4.2 J g-1 oC-1 = 30 C
Step 2: Write chemical equation or ionic equation for the reaction that occurs
Chemical equation : AgNO3 (aq) + NaCl(aq) AgCl (s) + NaNO3 (aq)
precipitate
Ionic equation : . Deduce the mole ratio from the ionic equation mol silver ion, Ag+ react with mol of chloride ion, Clto produce . mol of silver chloride , AgCl
Step 3 : Calculate the number of moles of reactant that reacts
Number of moles of silver ion = the number of moles of silver nitrate = .. mol Number of moles of chloride ion = the number of moles of sodium chloride = .. mol Number of moles of silver chloride formed = .. mol
Step 4 Calculate the heat of precipitation of silver chloride, H
Heat of reaction , H =
heat change ( answer from step 1 ) Number of moles of silver chloride
= J H = - kJ mol - 1
Draw an energy level diagram for the reaction that occurs in this experiment
2. HEAT OF DISPLACEMENT Aim : To determine the heat of displacement of copper metal from a copper (ll) sulphate solution by zinc metal
zinc powder
25 cm3 0.2 mol dm-3 copper(ll) sulphate solution Procedure : 1. Measure 25 cm3 0.2 mol dm-3 copper(ll) sulphate solution and pour into a polystirene cup. 2. Put the thermometer into the silver nitrate solution. Record the initial temperature, 3. Add half a spatula of zinc powder( in excess) quickly into copper(ll) sulphate solution. 5. Stir the mixture with the thermometer and record the highest temperature achieved. Result : Initial temperature of silver nitrate solution Highest temperature of the mixture Calculation Step 1 : Calculate the heat change using the formula H = mc Step 2: Write chemical equation or ionic equation for the reaction that occurs Step 3 : Calculate the number of moles of reactant that reacts Step 4 Calculate the heat of displacement of copper, H = 300C = 400C
Changes of temperature, = 400C - 300C = 100C Heat change , H = mc H = .. J Chemical equation : Zn (s) + CuSO4(aq) Cu (s) + ZnSO4 (aq)
copper displaced
m = 25 g c = 4.2 J g-1 oC-1 = 100C
Deduce the mole ratio from the equation mol copper metal, Cu is displaced from .. mol of copper(ll) sulphate solution, CuSO4 by zinc Number of moles copper(ll) sulphate = .. mol Number of moles of copper = .. mol
Heat of reaction , H =
heat change ( answer from step 1 ) Number of moles copper
= J H = - kJ mol - 1 Draw an energy level diagram for the reaction that occurs in this experiment
10
3. HEAT OF NEUTRALISATION Aim : To determine the heat of neutralisation between a strong acid ( hydrochloric acid solution ) and a strong alkali ( sodium hydroxide )
50 cm3 2.0 mol dm-3 sodium hydroxide solution
50 cm3 2.0 mol dm-3 hydrochloric acid solution Procedure : 1. Measure 50 cm3 2.0 mol dm-3 sodium hydroxide solution and pour it into the polystrene cup, 2. Put the thermometer into the sodium hydroxide solution. Record the initial temperature, 3. Measure 50 cm3 2.0 mol dm-3 hydrochloric acid solution and record the initial temperature, 4. Pour the hydrochloric acid solution quickly into the sodium hydroxide solution in the polystyrene cup. 5. Stir the mixture with the thermometer and record the highest temperature achieved. Result : Initial temperature of silver nitrate solution Initial temperature of silver nitrate solution Highest temperature of the mixture Calculation Step 1 : Calculate the heat change using the formula H = mc Step 2: Write chemical equation or ionic equation for the reaction that occurs = 290C = 290C = 420C Average initial temperature = 290C
Changes of temperature, = 420C - 290C = .0C Heat change , H = mc H = .. J Chemical equation : . Ionic equation : . Deduce the mole ratio from the ionic equation : m = ( 50 + 50 ) g = 100 g c = 4.2 J g-1 oC-1 = .0C
11
mol hydrogen ion, H+ react with mol of hydroxide ion, OHto produce . mol of water , H2O Step 3 : Calculate the number of moles of reactant that reacts Number of moles of H+ = the number of moles of hydrochloric acid = .. mol Number of moles of OH- = the number of moles of sodium hydroxide = .. mol Number of moles of water formed = .. mol Step 4 Calculate the heat of neutralisation of hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide, H Heat of reaction , H = heat change ( answer from step 1 ) Number of moles water
= J H = - kJ mol - 1
Draw an energy level diagram for the reaction that occurs in this experiment
4. HEAT OF COMBUSTION Aim : To determine the heat of combustion of ethanol
12
Experiment to show heat of combustion. Procedure : 1. Measure 200 cm3 of water and pour it into a copper can. Record the initial temperature of the water and place the copper can on a tripod stand. 2. Fill a lamp with ethanol and weight it. Record the mass of the lamp together with its content. 3. Light up the wick of the lamp immediately. Stir the water continuously until the temperature of the water increases by about 30 0C. 5. Put off the flame and record the highest temperature reached by the water. Result : Mass of lamp before burning Mass of lamp after burning Initial temperature of water Highest temperature of water Calculation Step 1 : Calculate the heat change using the formula H = mc = 46.50 g = 46.15 g = 29.00C = 59.00C
Changes of temperature, = 59.00C - 29.00C = 300C Mass of water, m = 200 g Heat change , H = mc c = 4.2 J g-1 oC-1 = 300C H = .. J
Step 2: Write a balance chemical equation for the combustion of ethanol Step 3 : Calculate the number of moles of ethanol that is used in the experiment,
C2H5OH
O2
Mass of ethanol burnt/used = 46.50 - 46.15 = 0.35 g Number of moles of ethanol burnt = 0.35 = 0.35 molar mass ..
13
[ Relative atomic mass : H, 1 : C,12; O,16 ] Step 4 Calculate the heat of combustion of ethanol, H Heat of reaction , H =
.. mol
heat change ( answer from step 1 ) Number of moles of ethanol
= J H = - kJ mol - 1
Draw an energy level diagram for the combustion of ethanol in this experiment
EXTRA ACTIVITY ( Refer to the Chemistry Form Five text book page 149 - 168 ) 1 The thermochemical equation for the precipitation of calcium carbonate is given below, Ca2+ (aq) + CO32- (aq) CaCO3 (s) H = +12.6 kJ mol - 1 In an experiment, calcium carbonate, CaCO3 is precipitated when 100 cm3 of 0.5 mol dm-3
14
calcium nitrate, Ca(NO3)2 solution is added to 100 cm3 of 0.5 mol dm-3 sodium carbonate, Na2CO3 solution. What is the temperature change in the reacting mixture ? [ Specific heat capacity of solution : 4.2 J g-1 oC-1 . Density of solution : 1 g cm-3 ] Solution Step 1 : Calculate the number of moles of precipitate formed : Number of moles of calcium ion, Ca2+ = Number of moles of calcium nitrate, Ca(NO3)2 solution = . mol Number of moles of carbonate ion, CO32- = Number of moles of sodium carbonate, Na2CO3 solution = .mol Based on the ionic equation : Ca2+ (aq) + CO32- (aq) CaCO3 (s) 1 mol 1 mol 1 mol 1 mol of calcium ion, Ca2+ reacts with 1 mol of carbonate ion, CO32- to form . mol of calcium carbonate, CaCO3 From the calculation : . mol of calcium ion, Ca2+ reacts with . mol of carbonate ion, CO32- to form . mol of calcium carbonate, CaCO3 Step 2 : Calculate the heat change by using the heat of precipitation, Given that H = +12.6 kJ mol - 1 , this means that when 1 mol of calcium carbonate, CaCO3 is precipitated, the heat absorbed is Therefore when ..mol (from step 1 ) of calcium carbonate, CaCO3 pricipitated, the heat absorbed = kJ = ..J --------- (i) Step 3: Calculate the temperature change by using the heat change Mass of solution , m ..g Heat change (absorbed ) ,H = J ( from (i) ) H = mc = . x . x = J = 0C 2 In an experiment, excess magnesium powder is added to 50 cm3 of 0.5 mol dm-3 iron(ll) sulphate solution at 29.0 0C. The thermochemical equation is shown below, Mg(s) + Fe2+ (aq) Mg2+ (aq) + Fe (s) H = -80.6 kJ mol - 1
15
What is the highest temperature reached in this experiment ? Solution Step 1 : Calculate the number of moles of iron, Fe displaced The number of moles of iron(ll) ions , Fe2+ = the number of moles of iron(ll) sulphate solution =. mol Based on the ionic equation : Mg(s) + Fe2+ (aq) Mg2+ (aq) + Fe (s) 1 mol 1 mol 1 mol of iron(ll) ion, Fe2+ produces 1 mol of iron, Fe mol of iron(ll) ion, Fe2+ produces .mol of iron, Fe Step 2 : Calculate the amount of heat given out from the heat of displacement Given that H = -80.6 kJ mol - 1 This means that when 1 mol of iron, Fe is displaced, the heat given out is . kJ Therefore when mol of iron, Fe is displaced in the experiment, The heat given out , H = .kJ = .J --------- (i) Step 3 : Calculate the highest temperature reached using the heat given : Mass of the solution, m = .g The heat given out , H = . J ( from (i) )
H = mc = . x . x = J = 0C ---------- (ii) Therefore, the highest temperature reached : = 29.00C + = 0C
The thermochemical equation for the reaction between ethanoic acid and sodium hydroxide is given below,
16
CH3COOH (aq) + NaOH (aq) NaCH3COO (aq) + H2O (l)
H = -55 kJ mol - 1
Calculate the heat given out when 200 cm3 of ethanoic acid 0.5 mol dm-3 is added to 200 cm3 of sodium hydroxide 0.5 mol dm-3 Solution Step 1: Calculate the number of moles of water produced Number of moles of hydrogen ion, H+ = Number of moles of ethanoic acid solution = . mol Number of moles of hydrogen ion, OH- = Number of moles of sodium hydroxide solution = . mol The ionic equation : H+(aq) + OH- (aq) H2O (l) 1 mol 1 mol 1 mol Based on ionic equation, 1 mol of hydrogen ion, H+ reacts with 1 mol of hydroxide ion, OHto produce 1 mol of water, H2O, Therefore, mol of hydrogen ion, H+ reacts with mol of hydroxide ion, OHto produce mol of water, H2O --------- (i) Step 2 : Calculate the heat given out using the heat of neutralisation, Given that H = -55 kJ mol - 1 This means that when 1 mol of water is produced , the heat given out is 55 kJ Therefore, when .. ( from (i) ) is produced, The heat given out = .kJ = J
EXTRA EXERCISE
17
The table below shows the heat of combustion for alcohols . Type of alcohol Methanol Ethanol Propanol Butanol Molecular formula CH3OH C2H5OH C3H7OH C4H9OH Relative molecular mass 32 46 60 74 Heat of combustion/ kJ mol-1 - 715 - 1376 - 2017 - 2679
Based on information given in the table answer the following questions, (a) Draw a graph of the magnitude of the heat of combustion against the number of carbon atoms in an alcohol (b) State the relationship between the number of carbon atoms in an alcohol and the heat of combustion, . . (c) Predict the heat of combustion of hexanol (d) The fuel value of a fuel is the amount of heat energy given out when one gram of the fuel is completely burnt in excess of oxygen. By using the formula below, calculate the fuel value of the following alcohols Fuel value ( kJ g-1 ) = heat of combustion of alcohol ( kJ mol-1 ) molar mass (i) Methanol
(ii) Butanol
(e) Which alcohol is more effective to be used as fuel ? Give one reason for your answer .. 2 .. Table shows three thermochemical equations for experiment l, ll and lll
18
Experiment l ll lll
Thermochemical equation HCl (aq) + NaOH ( aq) NaCl (aq) + H2O(l) H = -57 kJ mol -1
CH3COOH(aq) + NaOH(aq) NaCH3COO(aq) + H2O(l) H = -55 kJ mol -1 H2SO4(aq) + 2NaOH(aq) Na2SO4(aq) + 2H2O(l) H = -114 kJ mol -1
Based on the thermochemical equations, answer the following questions (a) Explain why there is a difference in the heat of reaction for (i) Experiment l and ll (ii) Experiment l and lll [ 12 marks ] (b) If experiment lll is repeated by replacing the sodium hydroxide solution with potassium hydroxide solution, (i) predict the heat of reaction for the experiment (ii) Explain your answer in (b) (i) [ 5 marks ] (c) Based on thermochemical equation in experiment ll, calculate the heat change when 100 cm3 2 mol dm-3 ethanoic acid solution react with 100 cm3 2 mol dm-3 sodium hydroxide solution [ 3 marks ]
19
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- SCK 03 Balance Equation AnswerDocument2 paginiSCK 03 Balance Equation AnswerdalilacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Chapter 10 Space ExplorationDocument4 paginiChapter 10 Space ExplorationSiti Najiha Mohd AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 9 Stars and GalaxiesDocument9 paginiChapter 9 Stars and GalaxiesThiran VinharÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Chapter 10 Space ExplorationDocument4 paginiChapter 10 Space ExplorationSiti Najiha Mohd AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Atomic Particles (Metals & Noble Gases) Atomic Particles (Metals & Noble Gases)Document2 paginiAtomic Particles (Metals & Noble Gases) Atomic Particles (Metals & Noble Gases)dalilacÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Exercise Cell As The Basic Unit of Living ThingsDocument16 paginiExercise Cell As The Basic Unit of Living ThingsHidayatul ZawawiÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Cell As A Basic Unit of LifeDocument8 paginiCell As A Basic Unit of LifedalilacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Atomic Particles (Metals & Noble Gases) Atomic Particles (Metals & Noble Gases)Document2 paginiAtomic Particles (Metals & Noble Gases) Atomic Particles (Metals & Noble Gases)dalilacÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Atomic Particles (Metals & Noble Gases) Atomic Particles (Metals & Noble Gases)Document2 paginiAtomic Particles (Metals & Noble Gases) Atomic Particles (Metals & Noble Gases)dalilacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Chapter 12Document3 paginiChapter 12dalilacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Module Carbon CompoundsDocument23 paginiModule Carbon Compoundsdalilac100% (1)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- SC Form 3Document7 paginiSC Form 3dalilacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic Particles (Metals & Noble Gases) Atomic Particles (Metals & Noble Gases)Document2 paginiAtomic Particles (Metals & Noble Gases) Atomic Particles (Metals & Noble Gases)dalilacÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- Waja Thermochemistry EditedDocument19 paginiWaja Thermochemistry EditeddalilacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Science Form3 Chap 1Document7 paginiScience Form3 Chap 1wansuu100% (1)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Mohd Afiq Bin Mohamad RosliDocument1 paginăMohd Afiq Bin Mohamad RoslidalilacÎncă nu există evaluări
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Waja Thermochemistry EditedDocument19 paginiWaja Thermochemistry EditeddalilacÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Which Is The Second Most Abundant Element in The Earth's Crust? A Lead B Silicon C Carbon D OxygenDocument1 pagină1 Which Is The Second Most Abundant Element in The Earth's Crust? A Lead B Silicon C Carbon D OxygendalilacÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 What Is Formed in The Reaction Shown in The Figure Above?Document1 pagină1 What Is Formed in The Reaction Shown in The Figure Above?dalilacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yearly Teaching Plan 2013 Chemistry Form 5: Chapter/TopicDocument10 paginiYearly Teaching Plan 2013 Chemistry Form 5: Chapter/TopicdalilacÎncă nu există evaluări
- SC Form 3Document7 paginiSC Form 3dalilacÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- SC Form 3Document7 paginiSC Form 3dalilacÎncă nu există evaluări
- SC Form 3Document7 paginiSC Form 3dalilacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Form 3 Chapter 4 ReproductionDocument18 paginiScience Form 3 Chapter 4 ReproductionAutumn JJ100% (3)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Continuous Variation MethodDocument1 paginăContinuous Variation Methoddalilac100% (1)
- Sodium Iodide and AcetoneDocument4 paginiSodium Iodide and AcetoneBa'ist KhaerulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rates of Reaction Chapter 8Document2 paginiRates of Reaction Chapter 8Mariam BabarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 1 Chemical ReactionDocument6 paginiExperiment 1 Chemical ReactionJessamyn DimalibotÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (120)
- NIE - and - Particulate - Drawings - Worksheet - Answers at End - 2017-1Document8 paginiNIE - and - Particulate - Drawings - Worksheet - Answers at End - 2017-1Jane Ivanova100% (1)
- Smak 8 Penabur International Tanjung Duren: Detention From Practical ChemistryDocument10 paginiSmak 8 Penabur International Tanjung Duren: Detention From Practical ChemistryJodhi GushastokoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture-7 (Gravimetric Analysis)Document6 paginiLecture-7 (Gravimetric Analysis)Mohamed AbdelaalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 38 PDFDocument3 pagini38 PDFsanjay ukalkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fao Specifications and Evaluations For Agricultural PesticidesDocument27 paginiFao Specifications and Evaluations For Agricultural PesticideszilacxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shawon Notes Chem A LevelsDocument38 paginiShawon Notes Chem A LevelsEfath UddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 8 Separation of Group Ii CationsDocument5 paginiExperiment 8 Separation of Group Ii CationsKim AlexisÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHEM 3L Group 4 Cation 1Document6 paginiCHEM 3L Group 4 Cation 1Beatrice AlejeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pyrite Oxidation in Alkaline Solutions: Nature of The Product LayerDocument14 paginiPyrite Oxidation in Alkaline Solutions: Nature of The Product LayerAlejandro Valenzuela100% (1)
- STK1121 LabManual 2017 PDFDocument32 paginiSTK1121 LabManual 2017 PDFmirayeollieÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6.2.4 Conductometric Titrations: Electroanalytical Methods-IIDocument4 pagini6.2.4 Conductometric Titrations: Electroanalytical Methods-IIUtsab ChatterjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Metal Precipitation + Solid-Aqueous EquilibriaDocument26 paginiMetal Precipitation + Solid-Aqueous EquilibriaDotan NutodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complexes of 2,4 Diamino 6-Hydroxy PyrimidineDocument40 paginiComplexes of 2,4 Diamino 6-Hydroxy Pyrimidinepulimamidi SarithareddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHM 123L Lab 1 Due September 9, 2013 Gravimetric Analysis of Phosphorus in Plant FoodDocument6 paginiCHM 123L Lab 1 Due September 9, 2013 Gravimetric Analysis of Phosphorus in Plant FoodAhmed IsmailÎncă nu există evaluări
- Continuous Variation MethodDocument2 paginiContinuous Variation MethodplyanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mark Scheme: November 2001Document4 paginiMark Scheme: November 2001shabanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reaction of Metals With OxygenDocument9 paginiReaction of Metals With Oxygenmanery23Încă nu există evaluări
- Argento Me TryDocument5 paginiArgento Me TryGino GalanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Article: Synthesis of New Benzofuran-2-Carboxylic Acid DerivativesDocument8 paginiResearch Article: Synthesis of New Benzofuran-2-Carboxylic Acid Derivativesfatriani smakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Life Is A Huge Lab: Answers and Grading Schemes JULY 25, 2015 Baku, AzerbaijanDocument42 paginiLife Is A Huge Lab: Answers and Grading Schemes JULY 25, 2015 Baku, AzerbaijanLê Hoàng MinhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Qualitative Testfor Elementsin Organic CompoundDocument8 paginiQualitative Testfor Elementsin Organic Compoundidon'tgiveachogiwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Separation Process Compilation of Problem SetDocument55 paginiSeparation Process Compilation of Problem Setjames100% (1)
- 10 Science Notes 01 Chemical Reactions and Equations 1Document8 pagini10 Science Notes 01 Chemical Reactions and Equations 1aarushiranjan0802Încă nu există evaluări
- Concentration-Purification of Uranium From An Acid Leaching SolutionDocument7 paginiConcentration-Purification of Uranium From An Acid Leaching SolutionKhairul ScÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hsslive-xii-chemistry-lab-Scheme For Salt Analysis Simplified For 2020-21Document2 paginiHsslive-xii-chemistry-lab-Scheme For Salt Analysis Simplified For 2020-21Athul SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instant Download Design of Wood Structures Asd LRFD 6th Edition Donald Breyer Solutions Manual PDF Full ChapterDocument32 paginiInstant Download Design of Wood Structures Asd LRFD 6th Edition Donald Breyer Solutions Manual PDF Full Chaptermikadischerpro90% (10)
- Removal of Heavy Metals Using Waste EggshellDocument6 paginiRemoval of Heavy Metals Using Waste EggshellangelbroderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Offshore Wind Energy Generation: Control, Protection, and Integration to Electrical SystemsDe la EverandOffshore Wind Energy Generation: Control, Protection, and Integration to Electrical SystemsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fire on the Horizon: The Untold Story of the Gulf Oil DisasterDe la EverandFire on the Horizon: The Untold Story of the Gulf Oil DisasterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionDe la EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Power of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesDe la EverandPower of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (21)
- RV Living Collection: RV living for beginners, RV travel for the whole family, RV repair and RV mobile solar power: Experience Freedom on the roads alone or with your family with this collection. Learn how to repair your motorhome while using renewable energy!De la EverandRV Living Collection: RV living for beginners, RV travel for the whole family, RV repair and RV mobile solar power: Experience Freedom on the roads alone or with your family with this collection. Learn how to repair your motorhome while using renewable energy!Încă nu există evaluări
- Renewable Energy: A Very Short IntroductionDe la EverandRenewable Energy: A Very Short IntroductionEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (12)