Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
LAB 15 Thermometer
Încărcat de
roseDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
LAB 15 Thermometer
Încărcat de
roseDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
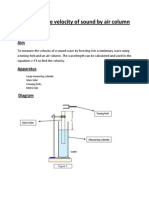
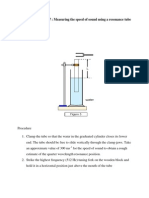
Lab # Resonant Thermometer Objective: Measure the temperature of a room with only a tuning fork and a tube of water.
Materials: Tuning fork, small tube open on both ends, larger tube closed on one end, ruler or meter stick. Procedure: 1. The lab equipment that you will need is two tubes and a tuning fork. Of the two tubes, fill the larger one with water. 2. Place the smaller diameter tube inside the larger one. The water in the large tube will work as an adjustable closed end to the smaller tube. 3. Set the tuning fork into vibrating by striking it against a rubber stopper, the rubber bottom of a soft shoe, or against your skin. Do NOT strike the tuning fork on any hard surface, as the tuning fork may shatter or chip. 4. Place the tuning fork over the mouth of the smaller open pipe, and raise or lower the pipe until a standing wave or resonance is made in the pipe. Measure the length of the pipe. This should be the smallest possible distance, so that the wavelength corresponds with the fundamental for the pipe. Hint: If the outer tube is opaque, you may wish to refill the large tube with water to its top. This will ease measuring the length of the smaller tube. 5. Calculate the wavelength of the wave. The equation that relates length and wavelength with a diameter correction is = 4(L + 0.4d), where L is the length and d is the diameter of the pipe. 6. Use the frequency stamped on the tuning fork and the wavelength found in step #5 to calculate the speed of sound in the pipe. v = f 7. Calculate the kelvin temperature of the room from the speed of sound.
) v = ( 331 m s
TK 273
8. Convert the accepted room temperature into kelvins, and find the absolute and relative error. O A Converting to kelvins gives a realistic error estimate for the procedure. Er = A 9. Repeat the above procedure with the tuning forks of different frequencies found on other lab stations. There will be at least four different tuning forks distributed throughout the lab stations. 10. Organize your data into a data table. Data: d = __________
f L
accepted T = _________oC = __________ K
v T, Kelvins % Error
Analysis:
1. Calculate the average of your temperature values.
M =
O
N
each
2. Calculate the absolute deviation of your measurements.
Da each = Oeach M
3. Calculate the average of your absolute deviations.
Da =
Da
N
each
4. Calculate the relative deviation of your measurements.
Dr = Da
5. Through what fraction of a vibration has the prong of the lowest frequency tuning fork moved while the sound wave traveled down to the surface of the water and was reflected back up to the tuning fork?
6. If a longer small tube were available, would it be possible to find another position where resonance is produced? Explain. 7. How would you modify the experiment to determine whether water vapor inside the tube affects the results?
8. How does the amplitude of vibration affect the data? Verify your answer by experimentation.
9. How would you modify the experiment to find the resonant length of an open pipe?
10. An observer sees a flash of light from a distant thunderstorm and 12 s later hears the sound of thunder. If the temperature of the air is 20 degrees, how far from the storm is the observer?
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Expt2 Sound PDFDocument3 paginiExpt2 Sound PDFaugustus willemÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Treatise on Meteorological Instruments: Explanatory of Their Scientific Principles, Method of Construction, and Practical UtilityDe la EverandA Treatise on Meteorological Instruments: Explanatory of Their Scientific Principles, Method of Construction, and Practical UtilityÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resonance LabDocument2 paginiResonance LabSantiago GaliciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Speed of Sound LabDocument2 paginiSpeed of Sound LabNWSPhysicsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Lab Report 02Document4 paginiSample Lab Report 02Linges LingeswaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Equipment NeededDocument2 paginiEquipment Neededahdil33Încă nu există evaluări
- Speed of SoundDocument2 paginiSpeed of SoundEti GoldbergÎncă nu există evaluări
- Longitudinal Standing Waves in An Air ColumnDocument3 paginiLongitudinal Standing Waves in An Air ColumnRamana Rao V GuthikondaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Speed of Sound LabDocument2 paginiSpeed of Sound LabDrake WellsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standing WavesDocument4 paginiStanding WavesSamar HannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 6 The Speed of Sound Using The Resonance of Longitudinal WavesDocument5 paginiExperiment 6 The Speed of Sound Using The Resonance of Longitudinal Wavesliezel_798041921Încă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 23 Physics 3Document10 paginiExperiment 23 Physics 3Mario Randy Spiroski100% (1)
- Speed of Sound LabDocument2 paginiSpeed of Sound LabMiguel simoÎncă nu există evaluări
- PWV 33 COMP Speed of SoundDocument5 paginiPWV 33 COMP Speed of SoundMark AL ShamsiÎncă nu există evaluări
- PH PR SoundexperimentsDocument10 paginiPH PR SoundexperimentsCharles AsagraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resonance of A Closed Air ColumnDocument11 paginiResonance of A Closed Air ColumnHo Ping100% (6)
- Physics Lab Report #24Document5 paginiPhysics Lab Report #24Claudia HuoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab - Speed of SoundDocument4 paginiLab - Speed of Sound한재인Încă nu există evaluări
- Physics Lab Report Speed of SoundDocument4 paginiPhysics Lab Report Speed of Soundapi-32527434057% (7)
- Physics Lab Report Speed of SoundDocument4 paginiPhysics Lab Report Speed of SoundTyrese SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2018 THDocument21 pagini2018 THDavid SiriusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resonance and Speed of SoundDocument2 paginiResonance and Speed of SoundLove1726Încă nu există evaluări
- Physics Sound LabDocument6 paginiPhysics Sound LabRyan Holinshead100% (1)
- Experiment - To Find The Speed of Sound in Air at Room Temperature Using A Resonance Tube by Two Resonance PositionsDocument1 paginăExperiment - To Find The Speed of Sound in Air at Room Temperature Using A Resonance Tube by Two Resonance PositionsTendai GwaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wa-11-Ex-9-Resonance TubeDocument3 paginiWa-11-Ex-9-Resonance Tubekalalund2562006Încă nu există evaluări
- Design - Speed of Sound ExperimentDocument10 paginiDesign - Speed of Sound ExperimentKazi Ayman RAHMANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Falling HeadDocument6 paginiLab Falling HeadNor SabilahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 5 - ResonanceDocument6 paginiExperiment 5 - ResonanceLeigh Dominique Zaragoza (Ji)Încă nu există evaluări
- Resonance in Open Air ColumnsDocument4 paginiResonance in Open Air ColumnsJobin IdicullaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Faculty of Engineering and Green Technology Bachelor of Engineering (HONS) Petrochemical EngineeringDocument9 paginiFaculty of Engineering and Green Technology Bachelor of Engineering (HONS) Petrochemical EngineeringDevakan BalaganeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Speed of Sound LabDocument3 paginiSpeed of Sound LabSantiago GaliciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 11 RealLab - 1 Speed of Sound With Tubes2021Document2 paginiUnit 11 RealLab - 1 Speed of Sound With Tubes2021Lauren OwenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flow Velocity: Measurement (Full Pipe) 1. DYE TESTING Is Done Into Two Phases, Main Line Dye Testing Examines Storm Sewers and Catch Basins Step 1Document9 paginiFlow Velocity: Measurement (Full Pipe) 1. DYE TESTING Is Done Into Two Phases, Main Line Dye Testing Examines Storm Sewers and Catch Basins Step 1Harold LandichoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phys 23 T6 The Speed of Sound Using The Resonance of Longitudinal WavesDocument5 paginiPhys 23 T6 The Speed of Sound Using The Resonance of Longitudinal WavesIslahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Falling HeadDocument4 paginiFalling HeadSyed Zulfaizzuan AljufriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Speed Sound LabDocument2 paginiSpeed Sound Labmechanical_lecturerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Measuring The Velocity of Sound Report.Document4 paginiMeasuring The Velocity of Sound Report.tashfeen2klÎncă nu există evaluări
- Falling Head Permeability TestDocument9 paginiFalling Head Permeability TestFaeez Zain83% (6)
- :- When you check air pressure in a tyre, a little air always escapes; the process of making the measurement changes the quantity being measured. Think of other examples of measurements that change or disturb the quantity being measured.Document18 pagini:- When you check air pressure in a tyre, a little air always escapes; the process of making the measurement changes the quantity being measured. Think of other examples of measurements that change or disturb the quantity being measured.BittuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 11 - Velocity of Sound in AirDocument6 paginiLab 11 - Velocity of Sound in AirLinges Lingeswaran100% (1)
- 15-Experiment 12Document3 pagini15-Experiment 12balaram jiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat Transfer in Finned Tubes Lab ReportDocument6 paginiHeat Transfer in Finned Tubes Lab ReportHarikrishnan Cb0% (1)
- Experiment 6 The Speed of Sound Using The Resonance of Longitudinal WavesDocument5 paginiExperiment 6 The Speed of Sound Using The Resonance of Longitudinal WavesDavid PayneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module p3 BiologyDocument16 paginiModule p3 BiologynazilahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 7Document18 paginiLab 7coopere23100% (1)
- Experiment 11 1213Document8 paginiExperiment 11 1213MAYANKÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diffusion CompileDocument11 paginiDiffusion CompileSharing CaringÎncă nu există evaluări
- Student Code of Ethic (SCE) : Dept. of Civil Engineering Technology Faculty of Engineering TechnologyDocument16 paginiStudent Code of Ethic (SCE) : Dept. of Civil Engineering Technology Faculty of Engineering TechnologyonlyuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Mechanics Lab Manual - R2Document7 paginiFluid Mechanics Lab Manual - R2Deact DiyanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phys Practical Booklet - Exp No 7Document4 paginiPhys Practical Booklet - Exp No 7aby251188Încă nu există evaluări
- 26-Sep-10 PHYS102 - 3: Resonance in Air ColumnDocument4 pagini26-Sep-10 PHYS102 - 3: Resonance in Air ColumnAhmad SalehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Diffusion ExperimentDocument18 paginiGas Diffusion ExperimentMuhammad NasrulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Last Minute Revision: Paper 4 - Alternative To CourseworkDocument28 paginiLast Minute Revision: Paper 4 - Alternative To CourseworkAliha AbbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 2 - Velocity of SoundDocument6 paginiExperiment 2 - Velocity of SoundAngelica UyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Laboratory FormatDocument15 paginiChemistry Laboratory FormatAbesamis RanmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Resonance Caitlin StrongDocument5 paginiPrinciples of Resonance Caitlin StrongCaitlin StrongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Osborne Reynold'S Demonstration: Experiment No. 7Document10 paginiOsborne Reynold'S Demonstration: Experiment No. 7Jemuel FloresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Velocity of SoundDocument9 paginiVelocity of SoundYcarta SleumasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Constant Head TestDocument5 paginiConstant Head TestTutor_KLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Weekly Calendar LayoutDocument3 paginiWeekly Calendar LayoutroseÎncă nu există evaluări
- ZondervanDocument2 paginiZondervanroseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bible ReadingDocument1 paginăBible Readingrose100% (1)
- MathDocument1 paginăMathroseÎncă nu există evaluări
- MathDocument7 paginiMathroseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Weekly Calendar LayoutDocument3 paginiWeekly Calendar LayoutroseÎncă nu există evaluări
- PhysicsDocument3 paginiPhysicsroseÎncă nu există evaluări
- PhysicsDocument2 paginiPhysicsroseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Who What Impact/Effect Old TestamentDocument2 paginiWho What Impact/Effect Old TestamentroseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tissues, Glands, and Membranes: Ontent Earning CtivityDocument14 paginiTissues, Glands, and Membranes: Ontent Earning CtivityroseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effective CommunicationDocument36 paginiEffective CommunicationroseÎncă nu există evaluări
- eREAD 1Document19 paginieREAD 1Christine Overdosed MatagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Functional Group Priority GroupingDocument2 paginiFunctional Group Priority GroupingroseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worship Musician! Magazine - MayJune 2011Document56 paginiWorship Musician! Magazine - MayJune 2011CMS ProductionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ultrasonic InterferometerDocument5 paginiUltrasonic InterferometersilentÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wizoo Cubase SX Mixing and Mastering Sample Chapter PDFDocument51 paginiWizoo Cubase SX Mixing and Mastering Sample Chapter PDFJairo Dallos100% (1)
- Deger Mi Hic - PartiturDocument2 paginiDeger Mi Hic - PartiturJulian ElsesserÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 1 What Are The Importance Elements of Impressionism Music?Document1 paginăWeek 1 What Are The Importance Elements of Impressionism Music?Harlyn May GerianeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mixing Modern Orchestral MusicDocument61 paginiMixing Modern Orchestral Musicpiciw mitigadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infinity Alpha1200s Subwoofer SMDocument27 paginiInfinity Alpha1200s Subwoofer SMAdrian DivorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Guide IEMDocument19 paginiBasic Guide IEMBob VanceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Why Does Your Recording Sound Like AssDocument408 paginiWhy Does Your Recording Sound Like AssTrevor Nierendorf100% (1)
- CLMD4A Science8Document40 paginiCLMD4A Science8Marie France Suarin100% (1)
- Wei Jun Zhu Mek FM Ep 2004 01Document105 paginiWei Jun Zhu Mek FM Ep 2004 01com_truiseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dm1 User GuideDocument26 paginiDm1 User GuideRobert BocognanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Cello Answer and Questions PDFDocument8 paginiThe Cello Answer and Questions PDFBahar Bilgen Şen100% (1)
- Auditory Illusions in Modern Film Industry and Music: S. HurskiyDocument3 paginiAuditory Illusions in Modern Film Industry and Music: S. HurskiyjuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ultra Sound Absorption Baffles & Wall Panels: BarricadeDocument2 paginiUltra Sound Absorption Baffles & Wall Panels: Barricadehitanshu sutharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Architectural AcousticDocument33 paginiArchitectural AcousticSampada Mgr100% (1)
- Qudelix-5K Application NoteDocument11 paginiQudelix-5K Application NoteLeonardo DinizÎncă nu există evaluări
- A New Diagnostic Tool For Detecting Dental Caries and Tooth Wear: Ultrasonic SystemDocument4 paginiA New Diagnostic Tool For Detecting Dental Caries and Tooth Wear: Ultrasonic SystempoojaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Service Manual: NSX-SZ51Document4 paginiService Manual: NSX-SZ51Alberto MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pick Up The Pieces: Average White Band Arr. Sir Ronald Hamlet IVDocument19 paginiPick Up The Pieces: Average White Band Arr. Sir Ronald Hamlet IVanastasioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Questions Nde Level 1-2-UTDocument57 paginiQuestions Nde Level 1-2-UTMOhammed PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Grade 11 Physics Ch12 Force Momentum and ImpulseDocument112 paginiPhysics Grade 11 Physics Ch12 Force Momentum and Impulseapi-19999615Încă nu există evaluări
- Science of Sound-Unit1Document45 paginiScience of Sound-Unit1Nivedita Teja GadamsettyÎncă nu există evaluări
- SUMMARY - Oscillations and WavesDocument19 paginiSUMMARY - Oscillations and Wavessethupanic macanic gamedzeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Avenged Sevenfold - Waking The Fallen (Album Tab)Document51 paginiAvenged Sevenfold - Waking The Fallen (Album Tab)api-3851724Încă nu există evaluări
- Tinnitus Causes and TreatmentDocument3 paginiTinnitus Causes and TreatmentEar-AchesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Autumn Leaves ArrDocument19 paginiAutumn Leaves ArrHoàng ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 2020-Cu Coperta PDFDocument177 pagini2 2020-Cu Coperta PDFMonica RonceaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Review of Damage Risk Contours For Occupational Noise ExposureDocument43 paginiA Review of Damage Risk Contours For Occupational Noise ExposureWilliam Lopez Jaramillo100% (1)
- Ic Engine Performance CharacteristicDocument30 paginiIc Engine Performance CharacteristicAjitKumarPandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceDe la EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (51)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessDe la EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (6)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldDe la EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (64)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseDe la EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (69)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesDe la EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (2193)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingDe la EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (5)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyDe la EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidDe la EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1395)
- The Beauty of Falling: A Life in Pursuit of GravityDe la EverandThe Beauty of Falling: A Life in Pursuit of GravityÎncă nu există evaluări
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterDe la EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (410)
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectDe la EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (20)
- Chernobyl 01:23:40: The Incredible True Story of the World's Worst Nuclear DisasterDe la EverandChernobyl 01:23:40: The Incredible True Story of the World's Worst Nuclear DisasterEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (264)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismDe la EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (500)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseDe la EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (13)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldDe la EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (60)
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsDe la EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (94)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowDe la EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (49)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldDe la EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (8)
- Let There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessDe la EverandLet There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (57)
- Vibration and Frequency: How to Get What You Want in LifeDe la EverandVibration and Frequency: How to Get What You Want in LifeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (13)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeDe la EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (3)
- Chasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombDe la EverandChasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (8)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldDe la EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (54)