Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
7.4 Stength of Acid Bases (Students Copy)
Încărcat de
Peter EdwardDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
7.4 Stength of Acid Bases (Students Copy)
Încărcat de
Peter EdwardDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
7.4 Relative strength of Bronsted- Lowry Acids and Bases 1.
The relative strength of Bronsted- Lowry cid and bases can be determined by measuring two quantites :A) ______________________________________________
B) __________________________________________ 2.What relative strength means ? To compare two or more Bronsted- Lowry cid and bases respectively in terms of
ability to ____ or _____ protons. 3.The relative strength of Bronsted-Lowrys acids means by comparing two or more Bronsted-Lowry acids on the ability to _____ a proton to a base 4.The relative strength of Bronsted-Lowrys means by comparing two or more Bronsted-Lowry on the ability to _______ a proton from an acid. A. Measuring Strength of Bronsted- Lowrys acids and bases using degree of dissociation, a
5.
The degree of dissociation , = [Amount dissociated]
[Original amount]
The degree of dissociation , (fraction) = [Amount dissociated] =
[Original amount]
The degree of dissociation , (percentage) =
6. The_______the degree of dissociation of a acid(or a base) the ________ is the acid/base. 7.The lower the degree of dissociation of an acid(or a base) the ______is the acids (or base) . 8. A stronger acid(or a base) will have ______degree of dissociation to almost ______
compared to a weaker acid (or base).
9. H2S04 /mol dm-3 or NaOH Degree of dissociation/% 0.01 100 0.10 100 1.00 100
Therefore the degree of dissociation of a stronger acid(or base) _____________ to its concentration . 10.
CH3COOH/mol dm-3 0.01 0.10 1.00 Degree of 4.24 1.34 0.42 dissociation/% Therefore the dissociation of a weaker acid(or a base ) is __________ on its concentration . 11. When comparing the strength of weak acids(or weak bases) we must ensure the _____________ of the solutions under investigation are the ________. Types of acids/mol dm-3 Degree of dissociation/% H2SO4 100 HNO2 6.6 CH3COOH 1.34 HSO429.0
We can arrange the four above acids in order decreasing strength : _______________________________________________________ B. Measuring strength of Measuring Strength of Bronsted- Lowrys acids and bases using Acid and Base Dissociation constants, Ka , Kb
12. We can derive the Acid and Base Dissociation constants, Ka , Kb respectively by applying the ____________ _____ .Please refer page 224(text book) B. Derivation of Acid Dissociation constant, Ka for weak monobasic acid. 13. Consider a weak monobasic acid, HA of concentration C mol dm-3 with a degree of dissociation of
Write the reversible ionisation equation for the above dissociation
_____________________________________________________________ Or HA (aq) HO3+ (aq) + A-(aq)
14. Reactants or products /mol dm-3 Initial / mol dm-3 Change in degree of dissociation/mol dm-3 Final / mol dm-3 HA c -c c-c H+ 0 +c 0+c= c A0 +c 0+c= c
=c(1-)
15. By applying The equilibrium law:- Please refer page 224(text book) We get :[H+] [A- ] =dissociation Constant for the acid , Ka [HA] 16. Why the [H2O] is not included in the above equation ? __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ 17. The acid dissociation, Ka is another form of ___________ __________by applying the equilibrium law. Characteristics of the acid dissociation, Ka 18. Note that ____________weak acid has ____________ magnitude of Ka . 19.The strength of a weak acid is measure by the dissociation constant (Ka ) of the acid. The _________the magnitude of Ka ,the ____________the acid
the greater the extent of dissociation. 20.The magnitude of Ka for CH3COOH and other weak acids are usually very _______ . (pls refer page 260 no.5) and page (345-346) 21. Since the values are very small a more convenient way to use the values, is by using pKa to compare the strength of acids where:pKa = ____________ where p=-log10 22. Notice the larger the value of pKa ,the _________the value of Ka ,and the ____________ the acid. Please refer page 260.no.5 23. The acid dissociation constant, like the equilibrium constant is dependent on ____________ . The value use are usually quoted at 25oC(298K) .
Derivation of Base Dissociation constant, Kb for weak base. 24. For a weak base ,B that dissociates in water to equation : B(aq) + H2O(l) HB+(aq) + OH-
By using the same method to derive Ka ,by applying the equilibrium law We get [HB+][OH-] = Kb [B] and p Kb = 25. The characteristic of the value Ka also can be applied to____ the base ,
.
26. The ________the value of Kb, the ______ the value of pKb ,the stronger
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Acid Base HomeworkDocument5 paginiAcid Base HomeworkAriel ChuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acids and Bases (Summary)Document20 paginiAcids and Bases (Summary)api-3784087100% (3)
- PH MeterDocument37 paginiPH MeterMelroy Castalino100% (1)
- Acid Base ReviewDocument4 paginiAcid Base ReviewJeffrey HuangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Project: Comparitive Study of Commercial AntacidsDocument22 paginiChemistry Project: Comparitive Study of Commercial Antacidsarsh100% (14)
- Solution Chemistry: Essential Chemistry Self-Teaching GuideDe la EverandSolution Chemistry: Essential Chemistry Self-Teaching GuideÎncă nu există evaluări
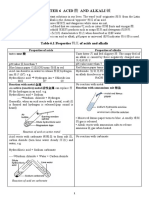
- F2 Chapter 6 Acid and AlkaliDocument6 paginiF2 Chapter 6 Acid and AlkaliMei Shuen CheamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Making - Salts - Worksheet Ishita Roy Chemistry Year 9Document2 paginiMaking - Salts - Worksheet Ishita Roy Chemistry Year 9Ishita Roy0% (1)
- Oxoacids of Chlorine by H To O ChemistryDocument44 paginiOxoacids of Chlorine by H To O ChemistryRitu JoharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acid Base Solutions Student DirectionsDocument2 paginiAcid Base Solutions Student Directionsloly62006100% (1)
- Acid-Base Equilibria and ApplicationDocument32 paginiAcid-Base Equilibria and Applicationfechem92100% (1)
- Section 2 Strengths of Acids and BasesDocument3 paginiSection 2 Strengths of Acids and BasesDevine RawlsÎncă nu există evaluări
- This Study Resource Was: Activity: Strong vs. Weak AcidsDocument2 paginiThis Study Resource Was: Activity: Strong vs. Weak AcidsJelaena Dean NavalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acids and BasesDocument15 paginiAcids and BasesC-SHINEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acids and Bases: Section 4 NeutralizationDocument4 paginiAcids and Bases: Section 4 NeutralizationDevine RawlsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Short Note - 22-12-2022Document9 paginiShort Note - 22-12-2022turkiÎncă nu există evaluări
- D Review of Solubility Principles and Calculations 2013Document7 paginiD Review of Solubility Principles and Calculations 2013Anonymous KePCfOMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Revision Sheet T2 - Questions 2Document3 paginiFinal Revision Sheet T2 - Questions 2malakbasahalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.12 Acids and BasesDocument7 pagini1.12 Acids and BasesDonald McDonaldÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit Guide AcidsBasesDocument1 paginăUnit Guide AcidsBasesAli McDillonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 - Water The SolventDocument27 pagini2 - Water The SolventMel VilÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 - Amino Acids and PeptidesDocument30 pagini3 - Amino Acids and PeptidesMel VilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exam 1 Review Chem. 204: Intro To Organic Oct. 12, 2010: Part 1: Acids and BasesDocument6 paginiExam 1 Review Chem. 204: Intro To Organic Oct. 12, 2010: Part 1: Acids and BasesHannahDoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review of Acid and BasesDocument6 paginiReview of Acid and BasesCharlotte NgaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch14 Salt HydrolysisDocument1 paginăCh14 Salt HydrolysisКанат ТютеновÎncă nu există evaluări
- STPM May Evaluation Chemistry 2Document7 paginiSTPM May Evaluation Chemistry 2Ventus TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asid, Bes Dan GaramDocument6 paginiAsid, Bes Dan GaramTENGKU AHMAD NAQIUDDIN BIN TENGKU NADZUAN MoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP Chem Review Part 6Document14 paginiAP Chem Review Part 6Annabeth ChaseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acids and Bases QuestionsDocument14 paginiAcids and Bases Questionsmariam saikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name - Chemistry I-2 HONORS Study Guide For Acids and Bases (Chapter 17)Document2 paginiName - Chemistry I-2 HONORS Study Guide For Acids and Bases (Chapter 17)api-3706290Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 7 Released FrqsDocument2 paginiUnit 7 Released Frqsjames mwashimbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6-Chemistry Ii Final Exam ReviewDocument10 pagini6-Chemistry Ii Final Exam ReviewNesrine LaradjiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 15.FdfDocument33 paginiChapter 15.FdfPhương Lan100% (1)
- Worksheet NamingDocument2 paginiWorksheet NamingKristoff Avila0% (1)
- More QuestionsDocument86 paginiMore QuestionssuccesshustlerclubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Post Lecture Activity 2 - Acids and BasesDocument3 paginiPost Lecture Activity 2 - Acids and BasesSophia Aliyah Miel MacabeoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Type Your Answers in Blue PleaseDocument5 paginiType Your Answers in Blue PleaseChristinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TitrationSE PDFDocument7 paginiTitrationSE PDFAmaan Allana33% (3)
- Acid Base TitrationDocument4 paginiAcid Base TitrationAngelikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acid Base Webquest Friday 10 27 17Document4 paginiAcid Base Webquest Friday 10 27 17api-262586446Încă nu există evaluări
- Acid Base Target Sheet HLDocument2 paginiAcid Base Target Sheet HLAa BÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch14 Quick Check 3Document1 paginăCh14 Quick Check 3Канат ТютеновÎncă nu există evaluări
- IGCSE Chemistry Section 3 and 4Document25 paginiIGCSE Chemistry Section 3 and 4Bineta NdiayeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15 Atomic Structure Practice WorksheetDocument2 pagini15 Atomic Structure Practice WorksheetJeffrey DavisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acids and BasesDocument28 paginiAcids and BasesAlaric IskandarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry 12 Worksheet 4-6 Anhydrides, Acid Rain and TitrationsDocument6 paginiChemistry 12 Worksheet 4-6 Anhydrides, Acid Rain and TitrationsBekki VanderlendeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Test Review - Mar 2023Document4 paginiChemistry Test Review - Mar 2023rblxproÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theory Worksheet: Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument4 paginiTheory Worksheet: Acids, Bases and Saltsخانزاده بلال احمدخان لودہیÎncă nu există evaluări
- G11 Chemistry Worksheet L14.2Document3 paginiG11 Chemistry Worksheet L14.2em.alnajjarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simultaneous Spectrophotometric Determination of The PK of A Weak AcidDocument10 paginiSimultaneous Spectrophotometric Determination of The PK of A Weak Acidjoanne_blanco100% (1)
- GHS Honors Chem Acid Base Titration LabDocument5 paginiGHS Honors Chem Acid Base Titration LabWilliam SandovalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrocarbons. Section 21.1 Introduction To HydrocarbonsDocument5 paginiHydrocarbons. Section 21.1 Introduction To HydrocarbonsAhmad asaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper 2 Exam Final f4Document13 paginiPaper 2 Exam Final f4Roni SopainÎncă nu există evaluări
- IGCSE Chemistry Section 3 and 4Document17 paginiIGCSE Chemistry Section 3 and 4Soraya DeenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acids and Bases QPDocument26 paginiAcids and Bases QPtomiogunnorinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neutralisation Is The Reaction Between To Produce - 2. During The Process, Combine With To ProduceDocument8 paginiNeutralisation Is The Reaction Between To Produce - 2. During The Process, Combine With To ProduceWong Hui XinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise: HCL + H O (Aq) + CL (Aq)Document3 paginiExercise: HCL + H O (Aq) + CL (Aq)baskieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alkenes and Alkynes Notes - Student VersionDocument21 paginiAlkenes and Alkynes Notes - Student VersionHannah LiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matter & Change Course: Molarity and MolalityDocument5 paginiMatter & Change Course: Molarity and MolalityAlex DelgadilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 (Inorganic & Physical) : University Predictor Examination 2018Document13 paginiCHEMISTRY PAPER 1 (Inorganic & Physical) : University Predictor Examination 2018Lisa PintoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Test FRQDocument3 paginiPractice Test FRQКанат ТютеновÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Questions Unit 2Document13 paginiPractice Questions Unit 2Kaitlyn CarrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acid D Bases Work SheetDocument2 paginiAcid D Bases Work Sheetrayyan asadÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 10Document4 paginiCH 10Zeeshan MahdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 7 The Halogens QPDocument18 paginiGroup 7 The Halogens QPWilliam TsuiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stoichiometry: Essential Chemistry Self-Teaching GuideDe la EverandStoichiometry: Essential Chemistry Self-Teaching GuideÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arrhenius Bronsted Lewis Acids: Acids: AcidsDocument3 paginiArrhenius Bronsted Lewis Acids: Acids: AcidsBianca Del RosarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problemas de Quimica Acidos BaseDocument11 paginiProblemas de Quimica Acidos BaseSebastian VasquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- A2 Chemistry - Ionic EquilbriumDocument2 paginiA2 Chemistry - Ionic EquilbriumPaul MurrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 AlkalinityDocument1 pagină1 AlkalinityprakashÎncă nu există evaluări
- hssc1502t SecquizDocument3 paginihssc1502t SecquizMarwan MahmoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acids Bases and Salts Review W KeyDocument19 paginiAcids Bases and Salts Review W KeyJosephine Charles HoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10th Acid Base and Salt Notes 2011Document5 pagini10th Acid Base and Salt Notes 2011Ashraf Husain100% (4)
- Universal Indicator - WikipediaDocument1 paginăUniversal Indicator - WikipediaNoha ShaabanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 07 Acids Bases and SaltsDocument7 pagini07 Acids Bases and Saltsrudi_zÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acids and Alkalis NotesDocument14 paginiAcids and Alkalis Notesrana alweshahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 16Document42 paginiChapter 16Sigmund PohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acid Base and SaltDocument7 paginiAcid Base and SaltHimanshu GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organic Chemistry Synthesis Problems On AminesDocument30 paginiOrganic Chemistry Synthesis Problems On AminesKiseo TabsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acid-Base FRQ 1970-2009 WTH AnsDocument37 paginiAcid-Base FRQ 1970-2009 WTH AnsbigÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument61 paginiAcids, Bases and SaltsJohnRenzoMolinarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dissociation Constant: (Item No.: P3031101)Document6 paginiDissociation Constant: (Item No.: P3031101)Zaid YahyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Titrametric Analysis Lab ReportDocument11 paginiTitrametric Analysis Lab Reportapi-546161612Încă nu există evaluări
- CHEM 1412. Chapter 16. Acids and Bases - Homework - SDocument13 paginiCHEM 1412. Chapter 16. Acids and Bases - Homework - STrisha Anne SyÎncă nu există evaluări
- IdkDocument6 paginiIdkDanice LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2, Unit 2, Pharmaceutical Analysis, B Pharmacy 1st Sem, Carewell PharmaDocument7 paginiChapter 2, Unit 2, Pharmaceutical Analysis, B Pharmacy 1st Sem, Carewell Pharmayash08jan01Încă nu există evaluări
- Pre-Lab Questions: The Nature of Acids and Bases: Exploring The PH ScaleDocument4 paginiPre-Lab Questions: The Nature of Acids and Bases: Exploring The PH ScalenameÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1b Worksheet Naming AcidsDocument2 pagini1b Worksheet Naming Acidsapi-369690183Încă nu există evaluări
- Acid - Base TitrationDocument21 paginiAcid - Base TitrationketantchaudhariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Honors: Lesson 6 Acids and BasesDocument3 paginiChemistry Honors: Lesson 6 Acids and BasesCarl Zenon GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări