Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Pathophysiology: Polydipsia
Încărcat de
Michael Erick Valera VirtucioTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Pathophysiology: Polydipsia
Încărcat de
Michael Erick Valera VirtucioDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Pathophysiology
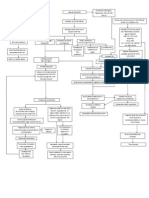
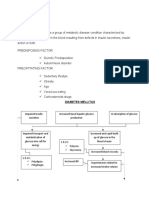
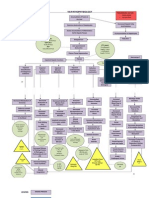
Precipitating/Modifiable Sedentary Lifestyle Smoker since 19 (3sticks/day) for 30 yrs Diet (high in fats & sweets) Pre-obese (BMI= 27.49) Predisposing/Nonmodifiable Age (58 y/old) Father (DM Type 2
Insulin Resistance Exhaustion of beta cells Decrease insulin production of beta cells
Decrease absorption of glucose by cell Glucogenolysis
Cell starvation
Stimulation of hunger mechanism via hypothalamus Polyphagia
Increase glucose production by the liver
Increase serum glucose level (HbA1C= 10.9) Osmotic diuresis Increase serum osmolarity
Polyuria & albuminuria (U/A + Albumin)
F&E imbalance Increase blood viscosity Loss of Na & K (Na: 129mmol/L; + K : 3.0mmol/L) Intracellular dehydration Sluggish blood circulation Decrease circulatory blood volume 12 (RBC 2.66x10 /L; HGB 79g/L; Hct .237; ESR 70mm/hr)
Tissue dehydration
Decrease blood flow to organs and extremities
Polydipsia
+Dry mouth; generalized weakness; dizziness; Increase RR (32breaths/min)
Impaired delivery of blood component (RBCs &WBCs) Inadequate nutritional support
Hypovolemia (A/G ratio: 0.40) Delayed wound healing Decrease perfusion of major organs
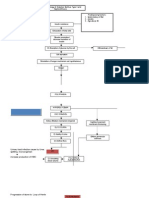
Disrupted skin integrity Bacteria enters and adheres to cell of liver (Liver Biopsy Result) Gram Positive cocci occurring singly: some Gram Positive bacilli: few Leukocytes: some
Decrease myocardial contractility Decrease cardiac output
Decrease Glomerular Filtration Rate Decrease urine output (5cc/hr)
Inflammatory response initiated by 9 Kupffer cells (WBC= 32.8x10 /L; ESR 70mm/hr)
Histamine
Kinin
Progstaglandin Contraction of smooth muscles
Increase capillary permeability
Blood vessels Dilation
+Edema (Albumin 15g/L)
+Redness, heat o (fever = 38.8 C)
Chemotaxis
Neutrophils initiate phagocytosis
Platelet adheres to damaged site Platelet plug/white thrombus forms
Macrophages aid in phagocytosis Anchored platelets release serotonin to go into vasospasm
Coagulation events B
B Gram (-) bacteria releases endotoxins & exotoxins (Klebsiella pneumoniae: light growth)
Endotoxins further activates inflammatory response and increase the activity of fibrinolysis inhibitor by releasing plasminogen activator inhibitor Formation intravascular clots Hepatic artery obstruction Decrease blood flow to liver Decrease blood flow to right thigh Decrease oxygen and nutrient supply to tissues Increase multiplication and growth anaerobic bacteria causing further inflammatory activation + calf pain (homans sign) Clots dislodged and travels into deep vein in right thighs
Abscess formation
Poor liver function: 1. Poor bacterial clearance *presence of gram + cocci and gram + bacilli 2. Low Albumin Albumin: 175 G/L CT Scan result minimal ascites and grade 2 edema on both lower extremities 3. Hepatomegaly 4. Decreased formation coagulation factors bleeding PT: 24.2 secs (prolonged) Decrease RBC (2.66 12 x 10 /L); Decrease Hgb (79g/L) Hypotension (70/40mmHg) 5. Decrease production thrombopoietin 9 (Plt 17 x 10 /L)
Elevated SGPT SGOT: 64U/L SGPT: 59 U/L
Tissue ischemia Tissue Necrosis CT Scan Result: Gangrene, right thigh
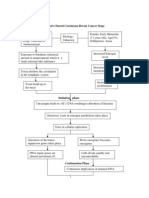
Endothelial damage
Inflammation
Attract inflammatory cells (monocytes, macrophages)
Macrophage ingest lipids
Release biochemical substance
Can further damage endothelium
Attracts plts and initiate clotting
Formation of fibrous cap by smooth muscle
Formation of plaque
Dec. coronary tissue perfusion
Coronary Ischemia
Dec. myocardial oxygenation
M.I Old Infarct
C Activation of complement cascade
Hyperdynamic state
Increase Cardiac Output HR= 120s
Decrease peripheral resistance BP= 70/40mmHg
Production of chemical mediators
Marked capillary permeability and third space loss
Hypovolemia
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Residential Lease AgreementDocument5 paginiResidential Lease AgreementElias Chembe100% (4)
- Group 8: Parik Rabasto Patel, D Patel, J Raghuwanshi Regis Moleta Moreno NaromalDocument35 paginiGroup 8: Parik Rabasto Patel, D Patel, J Raghuwanshi Regis Moleta Moreno NaromalDominique RabastoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of DMDocument4 paginiPathophysiology of DMNicole Louise N. VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cancer Pathophysiology To Be EditedDocument5 paginiCancer Pathophysiology To Be EditedEyySiEffVeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colorectal CancerDocument3 paginiColorectal CancerAriane May Rubio50% (2)
- Case Study #5Document2 paginiCase Study #5Jenny Jenders100% (1)
- Aan 202 CourseworkDocument17 paginiAan 202 CourseworkCris GalendezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Qtsoi Concept MapDocument5 paginiQtsoi Concept MapGenella BabantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Managing Nause and Vomiting-Crit-Care-Nurse-2003-Garrett-31-50 PDFDocument22 paginiManaging Nause and Vomiting-Crit-Care-Nurse-2003-Garrett-31-50 PDFpmuftiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renal Concept MapDocument8 paginiRenal Concept MapRob DavilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Community Health Nursing Practice Questions With RationalesDocument15 paginiCommunity Health Nursing Practice Questions With RationalesFelice Lamzon Labrador100% (2)
- Wilds Beyond Witchlight One Page Campaign GuideDocument1 paginăWilds Beyond Witchlight One Page Campaign GuideSend JunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Addison's Disease. FinalDocument10 paginiAddison's Disease. FinalAnn KelseaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology-Kni Ns PLZZZDocument8 paginiPathophysiology-Kni Ns PLZZZAnna Lira Manluyang MungcalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schematic Diag DMDocument1 paginăSchematic Diag DMReynaKatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cefadroxil: Antibiotic ClassDocument2 paginiCefadroxil: Antibiotic ClassTariÎncă nu există evaluări
- PATHODocument9 paginiPATHOj_averilla2012Încă nu există evaluări
- Hepatocellula R CarcinomaDocument45 paginiHepatocellula R Carcinomamhean azneitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name of Drug Mechanism: MemantineDocument4 paginiName of Drug Mechanism: MemantineCarlmeister Ambray JudillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colorectal CancerDocument29 paginiColorectal CancerLeeyanBhadzzVagayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluoracil Drug StudyDocument3 paginiFluoracil Drug StudyNicole Louize CaloraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology (Client Base) :: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument1 paginăPathophysiology (Client Base) :: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factorsleslie_macasaetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review MSDocument8 paginiReview MSPatrycyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Potassium Chloride Injection: Product MonographDocument18 paginiPotassium Chloride Injection: Product MonographMatthew ParsonsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Breast CancerDocument4 paginiPathophysiology of Breast CancerChiqui Lao DumanhugÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pa Tho Physiology of RaDocument7 paginiPa Tho Physiology of Ralisalmar2008Încă nu există evaluări
- Cva PathophysiologyDocument2 paginiCva PathophysiologyMaryjoy MertallaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiolgoy Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument3 paginiPathophysiolgoy Coronary Artery DiseaseNursesLabs.comÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type II and NephrolithiasisDocument6 paginiPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type II and Nephrolithiasisdiane_mananganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophy - Nephrotic SyndromeedDocument1 paginăPathophy - Nephrotic Syndromeedianecunar100% (1)
- DM Case StudyDocument21 paginiDM Case StudyBern TolentinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cancer Pathophysiology FinalDocument3 paginiCancer Pathophysiology FinalAngelique Ramos Pascua100% (1)
- Bladder CancerDocument1 paginăBladder CancerCarmina AguilarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pa Tho Physiology of Cad NstemiDocument2 paginiPa Tho Physiology of Cad Nstemianreilegarde100% (1)
- Pancretic Cancer Case Study - BurkeDocument52 paginiPancretic Cancer Case Study - Burkeapi-282999254Încă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology: Rectal CarcinomaDocument25 paginiPathophysiology: Rectal CarcinomaCristina CristinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Impaired Physical MobilityDocument9 paginiNCP Impaired Physical MobilityChristian Apelo SerquillosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Path o PhysiologyDocument9 paginiPath o PhysiologyKyle Ü D. CunanersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cancer PathophysiologyDocument10 paginiCancer PathophysiologyGia Bautista-AmbasingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute PancreatitisDocument20 paginiAcute PancreatitisMariquita BuenafeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver CancerDocument1 paginăLiver CancerTarantado67% (3)
- NPI Process RecordingDocument7 paginiNPI Process RecordingChristine ElbanbuenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver Case StudyDocument6 paginiLiver Case StudyGhulam MustafaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Breast MassDocument18 paginiBreast MassMishti Mokarrama100% (1)
- Renal Concept MapDocument8 paginiRenal Concept MapXtine CajiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liceo de Cagayan University: Acute AppendicitisDocument2 paginiLiceo de Cagayan University: Acute AppendicitisKylie AstrudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes Mellitus: Hyperglycemia (304 MG/DL, 13.2 MG/DL)Document3 paginiDiabetes Mellitus: Hyperglycemia (304 MG/DL, 13.2 MG/DL)John Henry ValenciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CholelithiasisDocument6 paginiCholelithiasismarkzamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ulcerative ColitisDocument14 paginiUlcerative ColitisdeepuÎncă nu există evaluări
- CholelitiasisDocument42 paginiCholelitiasisEdwin YosuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology FinalDocument2 paginiPathophysiology FinallarissedeleonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final PathophysiologyDocument3 paginiFinal Pathophysiologyemely p. tangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Esophagea L Cancer: By: Krizzia S. Bunagan-Legasi, RNDocument20 paginiEsophagea L Cancer: By: Krizzia S. Bunagan-Legasi, RNAnn SalvatierraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology CKDDocument2 paginiPathophysiology CKDSugar Capule - ManuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- V. Pathophysiology Modifiable: Non - ModifiableDocument2 paginiV. Pathophysiology Modifiable: Non - ModifiableMary Grace BanezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Malignant Neoplasm (Ovarian Cancer)Document4 paginiMalignant Neoplasm (Ovarian Cancer)nursing concept mapsÎncă nu există evaluări
- InTech-Diabetic Foot and GangreneDocument25 paginiInTech-Diabetic Foot and GangrenePutu Reza Sandhya PratamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument5 paginiPa Tho PhysiologynhiqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Protein BiosynthesisDocument33 paginiProtein BiosynthesisRangga DarmawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument3 paginiPa Tho PhysiologyswetlanieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Protein BiosynthesisDocument33 paginiProtein BiosynthesisLucy WijayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schemdi NcaDocument8 paginiSchemdi NcaEiram Esoj SalcedoÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Editing Certification Form: Type Your Manuscript Title Here (Use Title Case)Document1 paginăEnglish Editing Certification Form: Type Your Manuscript Title Here (Use Title Case)Michael Erick Valera VirtucioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Thesis FormatDocument35 paginiSample Thesis FormatMichael Erick Valera Virtucio100% (1)
- The Menstrual Cycle Dra GoDocument94 paginiThe Menstrual Cycle Dra GoMichael Erick Valera VirtucioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tetanus PathoDocument4 paginiTetanus PathoMichael Erick Valera VirtucioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gaylord Diocese Report FinalDocument130 paginiGaylord Diocese Report FinalJustinHinkleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agra Case DigestDocument10 paginiAgra Case Digestapplegee liboonÎncă nu există evaluări
- BDC Assessment FormDocument4 paginiBDC Assessment Formsadz100% (20)
- Manzano vs. PerezDocument5 paginiManzano vs. PerezaudreyracelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Christmas Carols Medley Guitar ChordsDocument3 paginiChristmas Carols Medley Guitar ChordsCarlo Emil100% (1)
- Saxons: Sahson Seaxan, Old Saxon: Sahson, Low German: Sassen, Dutch: Saksen) Were A Group of GermanicDocument15 paginiSaxons: Sahson Seaxan, Old Saxon: Sahson, Low German: Sassen, Dutch: Saksen) Were A Group of GermanicNirmal BhowmickÎncă nu există evaluări
- NOTES IN CIVIL PROCEDURE Oct2020Document5 paginiNOTES IN CIVIL PROCEDURE Oct2020Joselle ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic and SourcesDocument2 paginiTopic and Sourcescarter.henmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guballa vs. CaguioaDocument3 paginiGuballa vs. CaguioaMp Cas100% (1)
- Distribución de Asesores Por Avance Académico 2022Document13 paginiDistribución de Asesores Por Avance Académico 2022Lily TorrezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Davi v. HeinDocument31 paginiDavi v. HeinCato InstituteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organized CrimeDocument78 paginiOrganized CrimeRabora Jenzkie100% (2)
- T01C03 People V Prieto 80 Phil 138Document3 paginiT01C03 People V Prieto 80 Phil 138CJ MillenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 438 AuthortiesDocument8 pagini438 Authortiesamit HCSÎncă nu există evaluări
- DEMANDT, Alexander. (2013) Zeitenwende. Aufsätze Zur Spätantike, Cap.08Document15 paginiDEMANDT, Alexander. (2013) Zeitenwende. Aufsätze Zur Spätantike, Cap.08Juan Manuel PanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Update Jan 22Document2 paginiUpdate Jan 22Khfr Skhm Htp100% (1)
- Drug User's RehabilitationDocument4 paginiDrug User's Rehabilitationramadhani annisa sekar langitÎncă nu există evaluări
- American Trade Union HistoryDocument2 paginiAmerican Trade Union HistoryDadhich YemulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Associated Gun Clubs of Baltimore Candidate 2010 Election RecommendationsDocument1 paginăAssociated Gun Clubs of Baltimore Candidate 2010 Election RecommendationsAmmoLand Shooting Sports NewsÎncă nu există evaluări
- CRIMINAL-PROCEDURE - Q&aDocument28 paginiCRIMINAL-PROCEDURE - Q&aJeremias CusayÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Progressive Reform Era (1890-1920) : America: Pathways To The PresentDocument31 paginiThe Progressive Reform Era (1890-1920) : America: Pathways To The PresentKi NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schools of Thought in PsychologyDocument57 paginiSchools of Thought in PsychologySophia Marie MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7 People V TemporadaDocument152 pagini7 People V TemporadaFrench TemplonuevoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refineries in Middle EastDocument8 paginiRefineries in Middle EastAmitbhscribdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Famous People Quiz: Wh-Questions With Was/were Quiz ADocument1 paginăFamous People Quiz: Wh-Questions With Was/were Quiz Adeathnote lÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 - Comprehension PassageDocument5 pagini10 - Comprehension PassageMichael TateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Piercing Names and PlacementDocument2 paginiPiercing Names and PlacementYpsilanti0% (1)
- Delpher Trades Corporation and DELPHIN PACHECO, Petitioners, vs. Intermediate Appellate Court and Hydro Pipes Philippines, Inc., RespondentsDocument8 paginiDelpher Trades Corporation and DELPHIN PACHECO, Petitioners, vs. Intermediate Appellate Court and Hydro Pipes Philippines, Inc., RespondentsFD BalitaÎncă nu există evaluări