Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
AVAC AIDS Tipping Point
Încărcat de
murphmanDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
AVAC AIDS Tipping Point
Încărcat de
murphmanDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
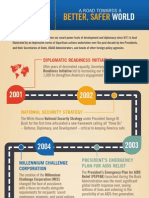
THE TIPPING POINT
Understanding a crucial milestone in the AIDS response
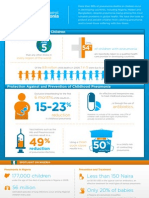
One way to measure progress in fighting AIDS is to compare the number of new HIV infections with the increase in HIV positive people on antiretroviral therapy (ART) over a given time period. An AIDS epidemic reaches its tipping point when the number of annual new HIV infections falls below the annual increase in patients starting ART. Coverage matters. A first milestone is treating approximately two thirds of the people in need in a given country. Once that level is reached, countries and advocates can track progress to the tipping point. However, a country can reach the tipping point and then cross backreturning to a situation where incidence outstrips rate
of ART initiation. Thats why it is essential to achieve optimal coverage rates of high-impact prevention including voluntary medical male circumcision, male and female condoms and harm reduction. Newer strategies such as PrEP and, eventually, a microbicide or vaccine should also be used for maximum impact. The pace at which treatment and prevention are scaled up is key. To reach the tipping point the rate at which people are started on treatment should accelerate immediately. To stay on course countries and donors need to increase financial and human resource commitments to strategic combination prevention.
Botswana
Increase in people on ART New HIV infections
New Infections in Botswana in 2012
12,000 95%
Estimated ART Coverage in 2012
1
Tipping Point Ratio
25,614
Increase in Patients on Treatment in Botswana in 2012 New Infections in Kenya in 2012
0.47
Rate of ART treatment scale-up outpaces HIV incidence.
4
TIPPING POINT
When rate of scale-up = incidence, tipping point ratio = 1. Countries that have reached tipping point have values < 1; Countries that have not have values > 1.
Kenya
Global and regional figures Countries that have not reached the tipping point
2
98,000 81%
Estimated ART Coverage in 2012
Rwanda
1
Tipping Point Ratio
1.5
1
Countries that have reached the tipping point
65,044
Increase in Patients on Treatment in Kenya in 2012
1.5
0.47
0
Mozambique
Cameroon
India
Cote d'Ivoire
Global
Zimbabwe
Ethiopia
South Africa
Swaziland
Tanzania
Burundi
Nigeria
Uganda
Lesotho
Zambia
sub-Saharan Africa
Namibia
Malawi
Ghana
DRC
Haiti
Botswana
Kenya
Global progress in reducing new HIV infections and scaling up antiretroviral treatment by 2012
1 Based on WHO 2010 Guidelines; WHO issued updated guidelines in June 2013, Consolidated Guidelines on the Use of Antiretroviral Drugs for Treating and Preventing HIV Infection: Recommendations for a public health approach. www.who.int/hiv/pub/guidelines/arv2013/download/en/index.html 2 UPEPFAR. PEPFAR Blueprint: Creating an AIDS-free generation. November 2012. www.pepfar.gov/documents/organization/201386.pdf 3 UNAIDS. UNAIDS report on the global AIDS epidemic 2013. www.unaids.org/en/media/unaids/contentassets/documents/epidemiology/2013/gr2013/UNAIDS_Global_Report_2013_en.pdf 4 UNAIDS. UNAIDS report on the global AIDS epidemic 2012. www.unaids.org/en/media/unaids/contentassets/documents/epidemiology/2012/ gr2012/20121120_UNAIDS_Global_Report_2012_with_annexes_en.pdf
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Guidelines On Seventh Day Automatic Stop OrderDocument3 paginiGuidelines On Seventh Day Automatic Stop OrderJohnny Dee100% (2)
- 3 Puntland Health Policy FrameworkDocument46 pagini3 Puntland Health Policy Frameworkkunciil100% (1)
- National EPI 2021 PDFDocument40 paginiNational EPI 2021 PDFyeabsira gashawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Protocol For Needle Stick Injur1Document1 paginăProtocol For Needle Stick Injur1Prem KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- USGLC RoadmapDocument1 paginăUSGLC RoadmapmurphmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- WFP 229327Document1 paginăWFP 229327murphmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumonia InfographicDocument1 paginăPneumonia InfographicmurphmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prev Spotlight Condoms FinalDocument8 paginiPrev Spotlight Condoms FinalmurphmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Map 3010Document1 paginăMap 3010murphmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 08.31.12 - USAID-DCHA Sahel Food Insecurity and Complex Emergency Program Map #15Document1 pagină08.31.12 - USAID-DCHA Sahel Food Insecurity and Complex Emergency Program Map #15murphmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worldwide HumanitarianAidWorkers 2012aug15 HIU U618Document1 paginăWorldwide HumanitarianAidWorkers 2012aug15 HIU U618markleongoldber3215Încă nu există evaluări
- Senate CR For State DepartmentDocument6 paginiSenate CR For State DepartmentmurphmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Developing Influence ADocument1 paginăDeveloping Influence AmurphmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Good Works W/ Malava ArticleDocument11 paginiGood Works W/ Malava ArticlemurphmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yellow Fever Vaccine Center in IndiaDocument6 paginiYellow Fever Vaccine Center in IndiaManalik KediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5RequiredReadingList 8 21 08Document1 pagină5RequiredReadingList 8 21 08Sara NordÎncă nu există evaluări
- Certificat de Vaccinare Împotriva Covid-19 Vaccination Certificate Against COVID-19Document1 paginăCertificat de Vaccinare Împotriva Covid-19 Vaccination Certificate Against COVID-19Артем ТерÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asuhan Pranikah PDFDocument57 paginiAsuhan Pranikah PDFDessy PratiwiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ABILIFY® (Aripiprazole) Savings Card ProgramDocument2 paginiABILIFY® (Aripiprazole) Savings Card ProgramGisele PhaloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hardam Furigay Colleges Foundation Inc. Board of Midwifery: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument15 paginiHardam Furigay Colleges Foundation Inc. Board of Midwifery: Republic of The Philippinesjohn_esturcoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interview QuestionsDocument7 paginiInterview QuestionsRitesh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Task 2 Candidate A Test 1 Alternative Therapies: Oral InteractionDocument6 paginiTask 2 Candidate A Test 1 Alternative Therapies: Oral InteractionMaria RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- 482 839 1 SMDocument10 pagini482 839 1 SMianatun Nisa'Încă nu există evaluări
- Caballero Savanna Resume 2022Document1 paginăCaballero Savanna Resume 2022api-621816262Încă nu există evaluări
- World Health Organization Headquarters : (As of 10 May 2021)Document13 paginiWorld Health Organization Headquarters : (As of 10 May 2021)nasikuning emailÎncă nu există evaluări
- Food Safety and Standards (Food or Health Supplements, Nutraceuticals, Foods For Special Dietary Uses, Foods For Special Medical Purpose, Functional Foods and Novel Food) Regulations, 2016Document131 paginiFood Safety and Standards (Food or Health Supplements, Nutraceuticals, Foods For Special Dietary Uses, Foods For Special Medical Purpose, Functional Foods and Novel Food) Regulations, 2016Latest Laws TeamÎncă nu există evaluări
- SSP032 M5 SDG3Document23 paginiSSP032 M5 SDG3Henry Darius NamocÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study CovidDocument6 paginiCase Study CovidAngel Faith TirolÎncă nu există evaluări
- DD Cheat Sheet 21-22Document2 paginiDD Cheat Sheet 21-22loki anshÎncă nu există evaluări
- BASILIO, Performance Task Module1&2Document2 paginiBASILIO, Performance Task Module1&2Tricia lyxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Penguatan Peran Bidan Dalam Pemberdayaan Perempuan Untuk Mendukung Program Sustainable Development Goal'SDocument6 paginiPenguatan Peran Bidan Dalam Pemberdayaan Perempuan Untuk Mendukung Program Sustainable Development Goal'SMita RiskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sbi FormsDocument70 paginiSbi Formsdiomedescolar.13Încă nu există evaluări
- Penerapan Aplikasi Sahabat Ibu Hamil (ASIH) Terhadap Peningkatan Kualitas Pelayanan Antenatal Di PedesaanDocument8 paginiPenerapan Aplikasi Sahabat Ibu Hamil (ASIH) Terhadap Peningkatan Kualitas Pelayanan Antenatal Di PedesaanHaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Covid BingDocument4 paginiCovid Bingaustinederick606Încă nu există evaluări
- Open Letter To Pravind Jugnauth Re: WE ARE AT WAR: EVERY LIFE MATTERSDocument2 paginiOpen Letter To Pravind Jugnauth Re: WE ARE AT WAR: EVERY LIFE MATTERSLe MauricienÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bookshelf NBK64923 PDFDocument332 paginiBookshelf NBK64923 PDFAsystolic MakerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hubungan Antara Pendamping Persalinan Dengan Kelancaran Proses Persalinan Kala Ii Di Puskesmas Tambusai Kecamatan Tambusai Kabupaten Rokan HuluDocument8 paginiHubungan Antara Pendamping Persalinan Dengan Kelancaran Proses Persalinan Kala Ii Di Puskesmas Tambusai Kecamatan Tambusai Kabupaten Rokan HuluArdianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Outbreak InvestigationDocument47 paginiOutbreak Investigationsarguss14100% (1)
- Ar 3Document1 paginăAr 3Joemar TagiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dapus SkripsiDocument3 paginiDapus SkripsiGaluh MahardikaÎncă nu există evaluări