Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
BENT 3711 Telecommunication Electronics Lab 1: RF Tuned Amplifier
Încărcat de
Gilew LensaTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
BENT 3711 Telecommunication Electronics Lab 1: RF Tuned Amplifier
Încărcat de
Gilew LensaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
y
UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA
FACULTY OF ELECTRONIC AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING
BENT 3711 TELECOMMUNICATION ELECTRONICS LAB 1
RF TUNED AMPLIFIER
Department of Telecommunication Engineering Sem 1, 2012/2013
Lab 4 RF Tuned Amplifier
OBJECTIVES 1) To demonstrate the operation of tuned RF Amplifier 2) To demonstrate the frequency response characteristic of tuned RF amplifier 3) To design and calculate the resonant frequency, bandwidth and quality factor MATERIAL No. 1 Equipment Function generator Qty 1 No. 1 Components Resistors - 1k - 10k - 12k - 20k Capacitors 10nF - 10F - 100F Potentiometer - 100k Inductor - 100H Qty 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1
Digital Multimeter
3 4
Oscilloscope Dual DC power supply
1 1
3 4
THEORY A tuned amplifier is one, which is required to handle a relatively narrow band of frequencies centered on a particular radio frequency. Such an amplifier has two main functions: it must provide a specified gain over a given frequency band and it must provide the selectivity necessary to ensure that frequencies outside the wanted band are not amplified to the same extent. A parallel-resonant circuit acting as the collector or drain load for the transistor or FET general to obtains the required selectivity. The required LC product for resonance to occur at the desired center frequency, is fairly small and is easy to obtain, the stray and transistor capacitances that adversely, affect the high frequency performance of an unturned amplifier now contribute to the necessary tuned circuit capacitance. High power radio frequency tuned amplifiers must employ thermionic valves as the active device since the power dissipated within any present-day transistor is capable of handling. Transistors are subject to internal feedback of energy at radio frequencies and transistor-tuned amplifier must be designed to avoid instability. Generally, the common emitter configuration is chosen in preference to the common base because it provides the greatest gain, and its input and output impedances have more convenient values.
Lab 4 RF Tuned Amplifier
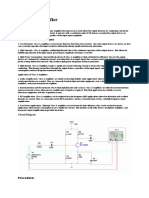
PRE LABORATORY WORK 1. 2. 3. 4. Construct and simulate the circuit in Figure 1. Obtained the relevant voltage and current across each component. Obtained the frequency response for the circuit. What should you do to tune the amplifier so that it operates at fo 155 KHz.
SAFETY GUIDE 1. Before making any connections to your circuit, always make sure that the power supply is turned off. 2. Ensure that the circuit Ground and Power connections are correct first before making any other connections. 3. Keep your working area clean and organized. Store away all unused components or equipment in their proper places. LAB PROCEDURE: 1) Construct the circuit as shown in Figure 1. 2) Using the rated values of L1 and C1, calculate the center frequency (resonant frequency) of the circuit, fo. 3) Observe and obtain the output voltage of the amplifier. 4) Adjust the amplitude of the amplifier input signal so that the maximum undistorted output can be achieved from the circuit.(Less than 1 V p-p) 5) Measure and record the actual of peak-to-peak output voltage, Vout and the resonant frequency, fo for the circuit. 6) Draw the frequency response of the circuit and determine the bandwidth. 7) Using the actual values, calculate the actual value of resonant frequency, fo, Bandwidth,BW, and quality factor, Q. 8) What should you do to obtain resonant frequency at 250 KHz. 9) Plot the frequency response for this circuit. 10) What component should you varies to tune the amplifier at 155KHz center Frequency. Plot the frequency response for this circuit.
Lab 4 RF Tuned Amplifier
2N3904
RL
Figure 1
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- C3 Signal Processing PDFDocument10 paginiC3 Signal Processing PDFShweta SridharÎncă nu există evaluări
- That You Read All The Background Information of This Laboratory BEFORE Proceding With The ExperimentDocument14 paginiThat You Read All The Background Information of This Laboratory BEFORE Proceding With The ExperimentRajith MohananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment No. 7: Ecx-212 Analog Communication Systems LaboratoryDocument5 paginiExperiment No. 7: Ecx-212 Analog Communication Systems LaboratoryJaspreet Singh SidhuÎncă nu există evaluări
- AclDocument53 paginiAclDeeksha KulshresthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBCC Amp 2Document5 paginiCBCC Amp 2sru_1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Wein Bridge Oscillator: f =1/2π√R1C1R2C2Document11 paginiWein Bridge Oscillator: f =1/2π√R1C1R2C2krishna goggiÎncă nu există evaluări
- AKNM - 3049 - AKNMGptcDocument53 paginiAKNM - 3049 - AKNMGptchod eceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laboratory Report on Integrator and Differentiator CircuitDocument22 paginiLaboratory Report on Integrator and Differentiator CircuitHrivu Dasmunshi (RA1911004010566)Încă nu există evaluări
- TSEK02 - Radio Electronics: L 1: R R MDocument14 paginiTSEK02 - Radio Electronics: L 1: R R MTessa AlgarraÎncă nu există evaluări
- ADC Expt4Document12 paginiADC Expt4harshit kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linear Integrated Circuits Question BankDocument17 paginiLinear Integrated Circuits Question BankDeepak SantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eca Lab-Min PDFDocument87 paginiEca Lab-Min PDFAkashita SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- R-22 Eca Lab ManualDocument59 paginiR-22 Eca Lab ManualGovardhan NunetiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECA HARDWARE ManualDocument44 paginiECA HARDWARE ManualKiranmai KonduruÎncă nu există evaluări
- World University of Bangladesh: Experiment # 7: To Study The Characteristics of Phase Shift Oscillators ODocument3 paginiWorld University of Bangladesh: Experiment # 7: To Study The Characteristics of Phase Shift Oscillators OshajibÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4-Channel Programmable FM Remote ControlDocument16 pagini4-Channel Programmable FM Remote ControljpatrÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 TWO STAGE RC COUPLED AMPLIFIERDocument7 pagini2 TWO STAGE RC COUPLED AMPLIFIERdamasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laboratory Manual: Unified Electronics Laboratory-IiDocument28 paginiLaboratory Manual: Unified Electronics Laboratory-IiAtul SainiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summing Amplifier.Document3 paginiSumming Amplifier.Majid AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 10 Sampling and Reconstruction: 10.1 Antialiasing FilterDocument16 paginiExperiment 10 Sampling and Reconstruction: 10.1 Antialiasing FilterHardikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab - 1 Amplitude Modulation and Demodulation: 1.1 ObjectiveDocument13 paginiLab - 1 Amplitude Modulation and Demodulation: 1.1 Objectivetendua_13Încă nu există evaluări
- Ece326 Lab 3 Exp 19Document8 paginiEce326 Lab 3 Exp 19max1039Încă nu există evaluări
- RC OscillatorDocument8 paginiRC OscillatorRavi TejaÎncă nu există evaluări
- OSCILLATORS AND GENERATORSDocument20 paginiOSCILLATORS AND GENERATORSswetha bagadi it's good but how it will workÎncă nu există evaluări
- Frequency Response of Switching Power SuppliesDocument2 paginiFrequency Response of Switching Power SuppliesRicardo SouzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Current Shunt Feedback AmplifierDocument4 paginiCurrent Shunt Feedback AmplifieresesesÎncă nu există evaluări
- LIC Manual MDocument76 paginiLIC Manual MjananirajuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eca Lab Manual PDFDocument56 paginiEca Lab Manual PDFrppvch100% (5)
- Experiment 2 Basic Operational Amplifier CircuitsDocument7 paginiExperiment 2 Basic Operational Amplifier CircuitsVasursharpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise On Analog Circuits: PHYS 331: Junior Physics Laboratory IDocument6 paginiExercise On Analog Circuits: PHYS 331: Junior Physics Laboratory Iviso167Încă nu există evaluări
- Audio Amplifier PDFDocument17 paginiAudio Amplifier PDFLuiz Clemente PimentaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Pa SystemDocument38 paginiFinal Pa SystemMohammad ShoebÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 1, AmpDocument5 paginiLab 1, AmpDavid KoskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ClasssA AmpDocument7 paginiClasssA AmpRamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elvis and Bode PlotsDocument7 paginiElvis and Bode PlotsKashif AmjadÎncă nu există evaluări
- EMI-Signal GeneratorsDocument7 paginiEMI-Signal GeneratorsVineela ThonduriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Two Stage Amplifier Lab ReportDocument4 paginiTwo Stage Amplifier Lab Reportdc22846Încă nu există evaluări
- New Lab Manual (ECA)Document50 paginiNew Lab Manual (ECA)Shrinivas SaptalakarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment No 1 AM TransmitterDocument6 paginiExperiment No 1 AM TransmitterashfaqiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Two Stage RC Amplifier CircuitDocument3 paginiTwo Stage RC Amplifier Circuitfarzana kousar100% (1)
- ReportDocument24 paginiReportanandaaa100% (4)
- Research Paper On AmplifierDocument5 paginiResearch Paper On Amplifiereh1dvt0m100% (1)
- Transistor Amplifier Design GuideDocument12 paginiTransistor Amplifier Design GuideRyan Kim PatronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analog Communication Lab ManualDocument30 paginiAnalog Communication Lab ManualANIRUDDHA PAULÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronic Circuit Lab ManualDocument158 paginiElectronic Circuit Lab ManualRamarao Gude50% (2)
- lab_manualDocument38 paginilab_manualsivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linear Wave Shaping: Name of The Component/Equipment Specifications QuantityDocument61 paginiLinear Wave Shaping: Name of The Component/Equipment Specifications QuantitySainadh YerrapragadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eca Lab-Manual PDFDocument87 paginiEca Lab-Manual PDFdedoga9086Încă nu există evaluări
- Test Instruments - Exams-1 MedicalDocument12 paginiTest Instruments - Exams-1 MedicalJon Alvin M SelisanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment # Aim: The Objective of This Experiment Is To Study A 950nm-Fiber Analog Link of An Analog Signal and Audio Signal. Apparatus RequiredDocument2 paginiExperiment # Aim: The Objective of This Experiment Is To Study A 950nm-Fiber Analog Link of An Analog Signal and Audio Signal. Apparatus RequiredKakaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ac Lab Manual NewDocument52 paginiAc Lab Manual NewKranthi KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to IDGPDDocument35 paginiIntroduction to IDGPDPratik VasagadekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laporan Lengkap - Am TX-RX Firdha KalsumDocument68 paginiLaporan Lengkap - Am TX-RX Firdha KalsumFirdha Kalsum Rizki ApriliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT LAB MANUAL by PRABHU PDFDocument76 paginiLINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT LAB MANUAL by PRABHU PDFprabhu4scribd100% (5)
- EC1 Lab Exp3 PDFDocument2 paginiEC1 Lab Exp3 PDFRitu RoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learn Amateur Radio Electronics on Your SmartphoneDe la EverandLearn Amateur Radio Electronics on Your SmartphoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amateur Radio Electronics on Your MobileDe la EverandAmateur Radio Electronics on Your MobileEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2De la EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Încă nu există evaluări
- Comparing signals with comparatorsDocument4 paginiComparing signals with comparatorswojakÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2014 Winter Model Answer PaperDocument25 pagini2014 Winter Model Answer Papernavneet100% (1)
- Basic Radio HandlingDocument26 paginiBasic Radio HandlingVlademir Geb Dubouzet100% (1)
- Graphics LCD Interfacing With Armv7 LPC 2148: Embedded System Design Mini ProjectDocument17 paginiGraphics LCD Interfacing With Armv7 LPC 2148: Embedded System Design Mini ProjectKiran BogamÎncă nu există evaluări
- VSC Course Lecture2Document27 paginiVSC Course Lecture2eng7senÎncă nu există evaluări
- Philips+Chassis+TPM18 6LDocument90 paginiPhilips+Chassis+TPM18 6LJackson FerreiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ficha Tecnica BateriasDocument2 paginiFicha Tecnica Bateriasbryan arancibiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SUL 181 h Analog Time Switch Under 40 CharactersDocument2 paginiSUL 181 h Analog Time Switch Under 40 CharactersMamas SanjayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hcia Lte GeralDocument48 paginiHcia Lte Geralvictor kudidissaÎncă nu există evaluări
- VLT Micro DriveDocument11 paginiVLT Micro DriveMiguel E RosasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Composite Reliability Analysis of 500 KV Jawa-Bali System Related To The Northern Jawa Generation and Transmission Expansion PlanDocument5 paginiComposite Reliability Analysis of 500 KV Jawa-Bali System Related To The Northern Jawa Generation and Transmission Expansion PlanMega SetiawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Reference Manual: Protect Line Distance Protection Terminal REL 521 2.5Document426 paginiTechnical Reference Manual: Protect Line Distance Protection Terminal REL 521 2.5george_cpp2Încă nu există evaluări
- Tom Lish: What Is A Dynamometer and How Does It Work?Document2 paginiTom Lish: What Is A Dynamometer and How Does It Work?Tiago AvilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is A Tandem IsolatorDocument3 paginiWhat Is A Tandem Isolatordebasis_cpp123100% (2)
- Gate 2014 Syllabus For Instrumentation Engineering inDocument6 paginiGate 2014 Syllabus For Instrumentation Engineering inrahulchangderÎncă nu există evaluări
- It Information Technology Department - B.E., ANNA UNIVERSITY Important Question and Answers - Regulation 2013,2017 - STUDY MATERIAL, NotesDocument5 paginiIt Information Technology Department - B.E., ANNA UNIVERSITY Important Question and Answers - Regulation 2013,2017 - STUDY MATERIAL, NotesKali ThaashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Layer ProceduresDocument145 paginiPhysical Layer ProceduresTanzyy.2018Încă nu există evaluări
- Disassembly Inkjet 2007109185837Document2 paginiDisassembly Inkjet 2007109185837Oliver TabagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tonepad - Rangemaster Brian May Treble BoosterDocument1 paginăTonepad - Rangemaster Brian May Treble BoosterBastiaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer 8 Fourth QuarterDocument8 paginiComputer 8 Fourth QuarterReygina Mae Sibayan PalaganasÎncă nu există evaluări
- FooDocument21 paginiFooEnrique Solano VásquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hanwha Q Cells Data Sheet Qplus L g4.1 330-340 2016-09 Rev02 enDocument2 paginiHanwha Q Cells Data Sheet Qplus L g4.1 330-340 2016-09 Rev02 enManoj ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impedance Measurement Instruments: 26.1. Introduction To Impedance MeasurementsDocument26 paginiImpedance Measurement Instruments: 26.1. Introduction To Impedance MeasurementsHeiner Farid Castillo AvellaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CEPT Novice 1Document26 paginiCEPT Novice 1Ster RncÎncă nu există evaluări
- User Manual Readwell Touch Elisa Plate Analyser Ve - 5ac1cece1723dd45806d81faDocument84 paginiUser Manual Readwell Touch Elisa Plate Analyser Ve - 5ac1cece1723dd45806d81faCarlos ReisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beko TV LCD 14-20 Chassis LCDocument33 paginiBeko TV LCD 14-20 Chassis LCwajkÎncă nu există evaluări
- ELX 121 - Digital Television MultiplexingDocument22 paginiELX 121 - Digital Television MultiplexingClark Linogao FelisildaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SA100 V 14 BulletinDocument8 paginiSA100 V 14 BulletinTeepoonsab somsaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM Based Home Automation System ApplicationDocument8 paginiGSM Based Home Automation System Applicationddarunk1989373Încă nu există evaluări
- Switch Gear and Protective Devices: Module-I (10 Hours) University Portion (80%) : (8 Hours)Document2 paginiSwitch Gear and Protective Devices: Module-I (10 Hours) University Portion (80%) : (8 Hours)biswajit04Încă nu există evaluări