Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Prokaryoticandeukaryotic Cells Close Reading
Încărcat de
api-165869000Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Prokaryoticandeukaryotic Cells Close Reading
Încărcat de
api-165869000Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Name:_____________________Per:_____ Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Directions: 1. Read this short article on Prokaryotic cells vs. Eukaryotic cells.
2. While you read underline these terms: Prokaryotic, Eukaryotic, Nuclei, Plasma Membrane, Cytoplasm, Ribosome, DNA, Cell Wall, Antibiotic. 3. Circle any differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells, put a Box around any similarities. 4. Answer the questions that are provided after the reading. 5. Complete the Concept Map Provided
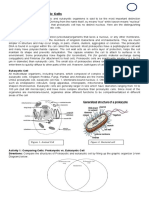
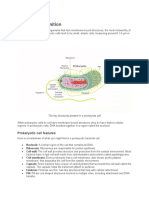
All organisms (living things) have at least one or more cells. Cells in our world come in two basic types, prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Pro means before. "Eu" means true, or good. Karyo" means nucleus of a cell. So Prokaryotic means "before a nucleus," and Eukaryotic means possessing a true nucleus. A nucleus is a protective compartment for DNA and is usually in the center of eukaryotes. This is a big hint about one of the differences between these two cell types. Prokaryotic cells have no nuclei, while Eukaryotic cells have true nuclei. (Nuclei is the plural of Nucleus) Both have organelles (little cell parts) but Eukaryote organelles are protected by membranes and so we call them membrane-bound organelles. Here's a simple visual comparison between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell:
This particular eukaryotic cell happens to be an animal cell, but the cells of plants, fungi and protists are also eukaryotic. All bacteria are prokaryotic cells. Despite their apparent differences, these two cell types have a lot in common. They perform most of the same kinds of functions, and in the same ways. Both are enclosed by plasma membranes (protective barrier that controls the movement of things in and out of the cell), filled with cytoplasm, the liquid inside the cell and loaded with small structures called ribosomes, for protein building. Both have DNA which carries the instructions for operating the cell and the genetic code. The DNA of a prokaryotic cell is exactly the same genetic code used in eukaryotic cells. Some things which seem to be differences aren't. For example: all prokaryotic cells have a cell wall. This animal cell does not, However, some eukaryotic cells do have cell walls like plant and fungi cells. Eukaryotic cells are much larger and much more complex than prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus, bound by a double membrane. Prokaryotic cells have no nucleus. Eukaryotic DNA is linear; prokaryotic DNA is circular (it has no ends). It is believed by scientists that prokaryotes were the first organisms on earth, appearing about 3.6 billion years ago according to prokaryote fossils. Then eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes and the rest is history! VIRUSES: act alive when they are in host cells, but donot have any characteristic of living things while outside the cell. They are the smallest when compared to Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells. Bacteria can be killed by: rubbing alcohol, antimicrobial wipees, and antibiotics. Antibiotics are medicines like penicillin, that destroy the cell walls of bacteria and eventually destroy the whole cell. (ANTI=against, BIOTIC= living thing)
QUESTION Does it have a nucleus? Does it have membrane-bound organelles? Does it have a cell membrane? Does it have DNA? Does it have liquid cytoplasm? Does it have ribosomes? Does it have cell walls? When did it evolve? Is it simple or complex? Is it small, smallest or biggest in size of the three? Is it Multicellular, unicellular or both? Which of the 5 kingdoms have this type? What is your way to remember these words?
PROKARYOTES
EUKARYOTES
VIRUSES
Organizing Life Concept Map Place the following 14 words or phrases into the concept map correctly: o Fungi, bacteria, animals, plants, protists, eukaryote, All organisms, prokaryote, unicellular, nucleus, cells, viruses, 9 characteristics of life, membrane-bound organelles
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Mapping The Ed Body in Trauma, Narrative, and InterventionDocument19 paginiMapping The Ed Body in Trauma, Narrative, and Interventionworldsaway100% (4)
- The Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksDe la EverandThe Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANSWERS Worksheets Cell Structure FunctionsDocument24 paginiANSWERS Worksheets Cell Structure FunctionsAnghel LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spinal Cord and Spinal NervesDocument9 paginiSpinal Cord and Spinal NervesJharaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument2 paginiProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsSerena Adeline RiveraÎncă nu există evaluări
- IVMS Introduction To Cell Biology - AP High School Health Sciences Track Study GuideDocument138 paginiIVMS Introduction To Cell Biology - AP High School Health Sciences Track Study GuideMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.Încă nu există evaluări
- Cell Composition, Structures and Cell As ReactorsDocument10 paginiCell Composition, Structures and Cell As ReactorsFirdaus Asha'riÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Cell/ All About CellsDocument35 paginiThe Cell/ All About CellsJandrew Gomez DimapasocÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compost Tea Brewing ManualDocument91 paginiCompost Tea Brewing ManualJanetS14338100% (1)
- Group 3 Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells HandoutsDocument4 paginiGroup 3 Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells HandoutsClaire Angelie Ruaya100% (1)
- Biology of CitrusDocument240 paginiBiology of CitrusEvaldoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell StructureandFunctionOfeliaDocument10 paginiCell StructureandFunctionOfeliapiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PCR Troubleshooting and OptimizationDocument608 paginiPCR Troubleshooting and Optimizationlaytailieu20220% (1)
- Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes WorksheetDocument1 paginăProkaryotes and Eukaryotes WorksheetonroxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prokaryote Vs Eukaryote WorksheeetDocument3 paginiProkaryote Vs Eukaryote Worksheeetsomeone swagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Endoplasmic ReticulumDocument10 paginiProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Endoplasmic ReticulumChristopher PhilipÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology ReportDocument3 paginiBiology ReportKathlene Anne MENDOZAÎncă nu există evaluări
- LESSON 3 - Prokaryotid Vs Eukaryotic CellsDocument41 paginiLESSON 3 - Prokaryotid Vs Eukaryotic CellsHyacinth RaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prokaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsDocument5 paginiProkaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsAngelica FloraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic CellsDocument20 paginiProkaryotic & Eukaryotic CellsZay SalazarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellDocument10 paginiChapter 2 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellKylie VillafloresÎncă nu există evaluări
- All About CellsDocument49 paginiAll About CellsJeanine CristobalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prokaryote Vs Eukaryote Worksheet: Read The Passage Below. Then Answer The Questions That FollowDocument2 paginiProkaryote Vs Eukaryote Worksheet: Read The Passage Below. Then Answer The Questions That Followapi-242868690100% (1)
- Cell Types: Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument4 paginiCell Types: Prokaryotes and Eukaryotesمصطفى رسول هاديÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prokaryote Vs Eukaryote WorksheetDocument2 paginiProkaryote Vs Eukaryote WorksheetAra Hella JordasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 3-P. E. CellsDocument4 paginiModule 3-P. E. CellsRylle SimonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prokaryotic Eukaryotic CellsDocument11 paginiProkaryotic Eukaryotic CellsKriezhel Kim TadleÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Theme of Prokaryotic Cell Structure and Function in CellsDocument8 paginiThe Theme of Prokaryotic Cell Structure and Function in CellschrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecturer 3Document22 paginiLecturer 3Rao ChandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell and Cell OrganellesDocument53 paginiCell and Cell OrganellesShiffa SaheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prokaryote Definition: Prokaryotic Cell FeaturesDocument5 paginiProkaryote Definition: Prokaryotic Cell FeaturesAli ShanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument9 paginiProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsKwo Chai Wing100% (1)
- Prokaryotic vs. EukaryoticDocument2 paginiProkaryotic vs. EukaryoticJaniya KellyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prokaryotes Topic BuilderDocument3 paginiProkaryotes Topic Builderapi-281171147Încă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 2 The Cell: Prepared By: Asley Raven MacatiagDocument29 paginiLesson 2 The Cell: Prepared By: Asley Raven MacatiagescribdeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell (Biology) : Navigation SearchDocument5 paginiCell (Biology) : Navigation SearchChan WaiyinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument21 paginiProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellskenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biochemistry Lecture 1Document16 paginiBiochemistry Lecture 1azraawsÎncă nu există evaluări
- JOHN-AHL MATIAS - W3-Reading Material On Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells and Plant vs. Animal TissuesDocument9 paginiJOHN-AHL MATIAS - W3-Reading Material On Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells and Plant vs. Animal TissuesJOHN-AHL MATIASÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Cells bsn1Document15 paginiProkaryotic Eukaryotic Cells bsn1porchypepita37Încă nu există evaluări
- 2.3: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Two Types of CellsDocument3 pagini2.3: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Two Types of CellsJubaer UtshobÎncă nu există evaluări
- BiologyDocument6 paginiBiologyBlue TechÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 - 3Document32 paginiUnit 1 - 3Sunita SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CeluarDocument7 paginiCeluarJef PerezÎncă nu există evaluări
- GB1 Module 1.2Document4 paginiGB1 Module 1.2beatriz OndilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eukaryotic CellsDocument2 paginiEukaryotic CellsLolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sadava MSCDocument118 paginiSadava MSCNikkizGogasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prokaryotic Cells: Main Article: ProkaryoteDocument6 paginiProkaryotic Cells: Main Article: ProkaryoteGian Carlo MagdalenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prokaryotic Cells. BacteriaDocument6 paginiProkaryotic Cells. BacteriaAndreea VrabieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology-Chapter 2 CellsDocument2 paginiBiology-Chapter 2 CellsWen Jun LohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio 101 General BiologyDocument7 paginiBio 101 General BiologyMohammed kashimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genbio NotesDocument9 paginiGenbio NotesErika DalmaciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human CellDocument12 paginiHuman CellCrystal GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-I Basic Cell BiologyDocument116 paginiUnit-I Basic Cell Biologyvishav sharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell - The Building Blocks of LifeDocument4 paginiCell - The Building Blocks of LifeUzair SoomroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prokaryotes VS EukaryotesDocument15 paginiProkaryotes VS EukaryotesChool Cydrick B. BascosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prokaryotes VS EukaryotesDocument15 paginiProkaryotes VS EukaryotesGamu GamuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rozy KhanDocument18 paginiRozy KhanBANTU RANAÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Biology 1: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsDocument58 paginiGeneral Biology 1: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsKurt DimacaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviewer For Science 11Document7 paginiReviewer For Science 11Bea Hannah FarrenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell (Biology) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument15 paginiCell (Biology) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaShabbir Hussain MaloobhaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prokaryote Vs EukaryoteDocument19 paginiProkaryote Vs EukaryotehamnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The CellDocument5 paginiThe CellAfida Razuna AveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro2 - Different Types of CellsDocument22 paginiIntro2 - Different Types of CellsCheryl MountainclearÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Two Types of CellsDocument2 paginiProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Two Types of CellsJanelle ArañaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eco Tube ProjectDocument1 paginăEco Tube Projectapi-165869000Încă nu există evaluări
- s2 Week 8 TasksheetDocument2 paginis2 Week 8 Tasksheetapi-165869000Încă nu există evaluări
- s2 w11 Tasksheet 1Document2 paginis2 w11 Tasksheet 1api-165869000Încă nu există evaluări
- Biology Honors 2 Test ConceptsDocument1 paginăBiology Honors 2 Test Conceptsapi-165869000Încă nu există evaluări
- Genetic Study GuideDocument2 paginiGenetic Study Guideapi-165869000Încă nu există evaluări
- Cell Energy Mitosis and Meiosis Test Study GuideDocument1 paginăCell Energy Mitosis and Meiosis Test Study Guideapi-165869000Încă nu există evaluări
- Respiration and Cell Cycle WorksheetDocument2 paginiRespiration and Cell Cycle Worksheetapi-165869000Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 10 TasksheetDocument2 paginiWeek 10 Tasksheetapi-165869000Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 1b Tasksheet 1Document2 paginiWeek 1b Tasksheet 1api-165869000Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 14 TasksheetDocument2 paginiWeek 14 Tasksheetapi-165869000Încă nu există evaluări
- Osmosis Diffusion Lab-1Document7 paginiOsmosis Diffusion Lab-1api-1658690000% (1)
- Week 13 TasksheetDocument2 paginiWeek 13 Tasksheetapi-165869000Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 12 TasksheetDocument2 paginiWeek 12 Tasksheetapi-165869000Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 11 TasksheetDocument2 paginiWeek 11 Tasksheetapi-165869000Încă nu există evaluări
- Cell Theory Scientists Types Reinforcement WorksheetDocument2 paginiCell Theory Scientists Types Reinforcement Worksheetapi-165869000Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 8 TasksheetDocument2 paginiWeek 8 Tasksheetapi-165869000Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2 Vocabulary ListDocument2 paginiUnit 2 Vocabulary Listapi-165869000Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 7 TasksheetDocument2 paginiWeek 7 Tasksheetapi-165869000Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 4 TasksheetDocument2 paginiWeek 4 Tasksheetapi-165869000Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 6 TasksheetDocument2 paginiWeek 6 Tasksheetapi-165869000Încă nu există evaluări
- Weekly Task Sheet wk3Document3 paginiWeekly Task Sheet wk3api-165869000Încă nu există evaluări
- Vocab Unit 1Document1 paginăVocab Unit 1api-165869000Încă nu există evaluări
- Vegetative Propagation Cape BiologyDocument11 paginiVegetative Propagation Cape BiologyOrlanda EllisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Weaning Off Babies From A DiseaseDocument272 paginiWeaning Off Babies From A DiseaseJun MagdaraogÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diffusion EssayDocument2 paginiDiffusion Essayapi-242424506Încă nu există evaluări
- Ess - Final SUBJECT OUTLINEDocument15 paginiEss - Final SUBJECT OUTLINEYosi AdriyantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Estrous Cycle in Female Mudhol Hound Dogs-An Indigenous BreedDocument4 paginiEstrous Cycle in Female Mudhol Hound Dogs-An Indigenous BreedDrRameem Bloch0% (1)
- Sweeteners Lab ReportDocument6 paginiSweeteners Lab ReportclingleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio ElectrodesDocument26 paginiBio ElectrodesSharok Nancy JoshuvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spots For Hematology PracticalDocument17 paginiSpots For Hematology PracticalPhysiology by Dr RaghuveerÎncă nu există evaluări
- June 2018 (IAL) QP - Unit 1 Edexcel Biology A-Level PDFDocument24 paginiJune 2018 (IAL) QP - Unit 1 Edexcel Biology A-Level PDFMoataz NassefÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emilia García E. & Stephan G. BeckDocument26 paginiEmilia García E. & Stephan G. BeckAlexander DamiánÎncă nu există evaluări
- Twincubator Use and Maintenance: Document Type: SOPDocument4 paginiTwincubator Use and Maintenance: Document Type: SOPfelix bazanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Morph Overfiew - Docx Versi 1Document27 paginiMorph Overfiew - Docx Versi 1Bimo PamungkasÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBSE Class 10 Life Processes MCQ Practice SolutionsDocument14 paginiCBSE Class 10 Life Processes MCQ Practice SolutionsRAJESH BÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arbovirus-Mosquito Vector-Host Interactions and The Impact On Transmission and Disease Pathogenesis of ArbovirusesDocument14 paginiArbovirus-Mosquito Vector-Host Interactions and The Impact On Transmission and Disease Pathogenesis of ArbovirusesLúcia ReisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cystatin-C AU400 480 640 680 2700Document2 paginiCystatin-C AU400 480 640 680 2700Nghi NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simulating Environment With Winogradsky Report 2Document3 paginiSimulating Environment With Winogradsky Report 2Kai ChenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dna DissertationDocument6 paginiDna DissertationCustomCollegePaperUK100% (1)
- Solving Material Balance Problems For Single Units Without ReactionsDocument24 paginiSolving Material Balance Problems For Single Units Without ReactionsVanessa Arrieta HernándezÎncă nu există evaluări
- GORRES - Activity #4Document1 paginăGORRES - Activity #4Carol GorresÎncă nu există evaluări
- AssignmentDocument5 paginiAssignmentMELAKU ADIMASÎncă nu există evaluări
- Restriction Enzymes: Restriction Enzymes Is An Enzyme That Cuts Double Stranded or SingleDocument3 paginiRestriction Enzymes: Restriction Enzymes Is An Enzyme That Cuts Double Stranded or SingleArafat MiahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 BM 2008-09Document26 pagini2 BM 2008-09Nagham Bazzi100% (2)
- 13 DPP Thnote+19c-19e Dpps+Ans+SolDocument56 pagini13 DPP Thnote+19c-19e Dpps+Ans+SolVaibhav SrivastavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- OTBDocument21 paginiOTBMwandoza MnyiphapheiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ex. 5 DNA Extraction PDFDocument3 paginiEx. 5 DNA Extraction PDFAlyssa Pauline PalacioÎncă nu există evaluări