Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Medical Gases Calculations
Încărcat de
sitehabDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Medical Gases Calculations
Încărcat de
sitehabDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Mechanical & Industrial Department CAIRO - EGYPT Subject Medical gases Building Adapazari Hospital
DESIGN CALCULATION SHEET
MEDICAL GASES
COMPRESSED GASES
VACUUM
NITROGEN
OXYGEN
NI
PRACTICAL PLUMBING DESIGN GIUDE
Project No. Sheet No. of Checked by T.Z.
Date 15/1/2002 Computed by Y.G. Approved by
CALCULATION
GASES
GEN
OXYGEN
NITROUS OXIDE
Project No. Mechanical & Industrial Department CAIRO - EGYPT Subject Building DESIGN CALCULATION SHEET Sheet No. of Checked by
Date 15/1/2002 Computed by Y.G. Approved by
LABORATORY SYSTEMS
GENERAL BUILDING SYSTEMS
COMPRESSED AIR AND VACUUM AIR SYSTEMS
CLINICAL SYSTEMS
DENTAL SYSTEMS
`
CLINICAL SYSTEMS
COMPRESSED AIR SYSTEM VOLUME/OU NUMBER OF USE TLET (CFM) OUTLETS FACTOR 2 2(3bar)+1(7bar) 100 2 1/bed 100 1 1/bed 50 2 1/room 100 1/room 2 1/bed 50 2 1/bed 50 1 1/4 bassinets 20 1 3/bassinet 100 1 1/bed 10 1 1/room 10 ENTER NO. OF TOTAL OUTLETS CFM 8 16 8 16 1 0.5 0 10 18 3 6 1 10 18 0.6 6 0 0.1
LOCATION Major operating rooms Trauma rooms Plaster room Delivery rooms Endoscopy Recovery ICU rooms Nurseries Special care Nurseries Pre-OP room CT Scan
then you get
67.2 VACUUM AIR SYSTEM
cfm of compressed air
LOCATION Operating room open heart, organ transplant, etc. (2/room) Major operating room (2/room) Minor operating room Cystoscopy and special procedures (2/room) Emergencya Emergencya (Isolation) Trauma room Plaster (fracture room) Delivery room Recovery first inlet/bed Recovery second inlet/bed Recovery additional inlet/bed ICU&CCU first inlet/bed ICU&CCU second inlet/bed ICU&CCU additional inlet/bed Patient rooms surgicalb Sometimes one inlet/bed Sometimes one inlet/2 beds) b Patient rooms medical Sometimes one inlet/bed Sometimes one inlet/2 beds) Labor rooms Nurseries Special care Nurseries Endoscopy rooms
CFM/INLET (@15-IN HG) 3.5 2 2 1 2 2 1 1 2 3 1 1 3 1 1 1 1
NUMBER OF USE OUTLETS FACTOR 100 100 100 40 100 100 100 100 100 100 50 10 100 50 10 50 50 1/bed 10 10 20 10 40 10
ENTER NO. OF ROOMS OR BEDS
TOTAL CFM 0 0 72 0 102 36 8 0 0 6 1 1.6 3 0.5 1.6 0 0 0 0 19.8 0 0 1.3 2.2 1.6 256.6
6/room 3/room
1/bed 3/bed 2/bed 1/room 6/room 2/bed 2/bed 2/bed 2/bed 2/bed 2/bed
51 6 8
0 0
2 2 16 1 1 16
1 1 1 1 1 1
188
1/4bassinet 2/bassinet 1/room
1 1 1
3 3 6
Number of outlets is 1/room except as noted
a
All outlets in the emergency department (area) should have 100% simultaneous use factor Where patient rooms are interchangeable (surgical or medical), use 50% simultaneous use factor for the first 4 rooms on the far end of the section of pipping and 20% thereafter
Then you get
256.6
cfm of vacuum air
Go to
O2&N2O
15/1/2002 Computed by Y.G. Approved by
Mechanical & Industrial Department CAIRO - EGYPT Subject CFM Estimation Building Adapazari Hospital
DESIGN CALCULATION SHEET
OXYGEN
SIMULTA NEOUS USE FACTOR 100 100 100 ENTER NO. OF ROOMS OR OUTLET S 1 1 2 1/bed 100 100 75 50 33 25 100 100 100 50 30 20 6/room 100 100 100 50 30 20 2/bed 100 60 50 45 100 100 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 10 10 10 10 10 1/room 100 100 75 50 33 25 100 100 75 50 33 25 100 100 75 50 33 25 100 100 75 50 33 25 100 100 75 50 33 25 100 100 75 50 33 25 20 10 10 10 10 10 1/4 bassinet 20 10 10 10 10 10 2/bassinet 20 10 10 10 10 10 1/bed 20 10 10 10 10 10 1/bed 20 10 10 10 10 10 1/bed 20 10 10 10 10 10 1/room 1 1 20 10 0 0 0 0 1 20 0 0 0 0 0 1 2 1 20 20 7.5 0 0 0 1 2 3 20 20 22.5 0 0 0 1 2 20 20 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 8 4 4 4 18 160 48 40 36 360 0 0 0 0 20 10 10 10 10 10 2/bed 1 1 2 50 30 40 1 2 8 8 20 17 20 20 60 40 66 42.5
***added
LOCATION Operating rooms First room (far end of a section of piping and all individual branches to rooms) Second room (on a section of piping) Each additional room (on a section of piping) b Emergency rooms First outlet 2nd&3rd 4--12 13--20 21--40 40 & up Trauma rooms First room (far end of a section of piping and all individual branches to rooms) Second room (on a section of piping) Each additional room (on a section of piping) Delivery rooms First room (far end of a section of piping and all individual branches to rooms) Second room (on a section of piping) Each additional room (on a section of piping) Recovery rooms 1--8 outlets 9--12 13--16 and up ICU rooms CCU rooms Other spaces such as Patient rooms (Medical and surgical)(beside outlets) First outlet 2nd&3rd 4--12 13--20 21--40 40 & up Labor rooms Sometimes one outlet/bed First outlet 2nd&3rd 4--12 13--20 21--40 40 & up Nurseries First outlet 2nd&3rd 4--12 13--20 21--40 40 & up Special care nurseries First outlet 2nd&3rd 4--12 13--20 21--40 40 & up Dyalisis First outlet 2nd&3rd 4--12 13--20 21--40 40 & up Anesthesia work rooms First outlet 2nd&3rd 4--12 13--20 21--40 40 & up MRI First outlet 2nd&3rd 4--12 13--20 21--40 40 & up CT-Scan
PER ROOM 50 30 20
PER OUTLET
PER BED
NUMBER OF OUTLETS 2/room
TOTAL 50 30 40
2/bed
1/bed 100 100 75 50 33 25 6 12 51 30 69 23 120 120 382.5 150 227.7 57.5
First outlet 2nd&3rd 4--12 13--20 21--40 40 & up Endoscopy rooms First outlet 2nd&3rd 4--12 13--20 21--40 40 & up
100 100 75 50 33 25 100 100 75 50 33 25
20 10 10 10 10 10 20 10 10 10 10 10 1/room
20 0 0 0 0 0 40 0 0 0 0 0
Where Oxygen is used to power fluidicaly controlled anesthesia ventilators, increase LPM volume by 40% All outlets in the emergency dept. (area) should have 100% simultaneous use factors c Where Oxygen is used to power fluidically controlled ventilators, volume should be 40 LPM d Simultaneous-use factor for other spaces: the first outlet on the end section of piping 20 LPM, 100% use factor. For additional outlets on the section of piping 10 LPM with the use-factors used in the above table.
b
Then you get
2450.2
LPM of Oxygen
NITROUS OXIDE
SIMULTA NEOUS USE VOLUME, LPM/ FACTOR ROOM 30 20 15 20 20 20 15 20 15
LOCATION First operating room (far end of piping and all individual branches to operating rooms Second operating room (on a section of piping) Each additional operating rom (on a section of piping) Delivery rooms Emerency rooms Trauma rooms Aneshtesia work room Plaster (fracture room) Endoscopy room
1 1 2
TOTAL 30 20 30 0 0 80 15 20 15
4 1 1 1
Then you get
210
LPM of Nitrous Oxide
Go to
GO TO FINAL COMPARAISON SHEET
Project No. TK0191 Sheet No. of Checked by
Date 15/1/2002 Computed by Y.G. Approved by
Mechanical & Industrial Department CAIRO - EGYPT Subject Medical Gases CFM estimation Building Adapazari Hosptial
Project No. TK0191 Sheet No. of Checked by
Date 15/1/2002 Computed by Y.G. Approved by
PPDG
CFM COMPRESSED AIR VACUUM OXYGEN NITROUS OXIDE LPM
67.20 200.00 86.53 7.42
1902.89 5663.37 2450.20 210.00
Oxygen Tank Calculations
Go to
Schedule of Equipment Pipe Sizing
Mechanical & Industrial Department CAIRO - EGYPT Subject Oxygen tank capacity and reserve Building King Hussein Hospital
Project No. J0274 Sheet No. of Checked by
Date 30/11/2003 Computed by Y.G. Approved by
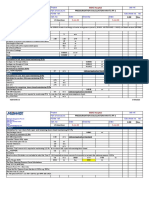
Total number of beds =
269
beds
Following the Practical plumbing guide for bulk systems: Allow 500 cu.ft/bed/month+reserve manifold for one day supply: # of beds*500= 134500 cu.ft/month 156.3953 cu.ft/momth Final Tank capacity
Convert to liquid status= The reserve for one day is: montn reserve/30= 4483.333 1 cylinder= 244 # of cylinders= 18.37432 so 20
cu.ft./day cu.ft so cylinders cylinders
Go to
Schedule of Equipment Pipe Sizing
Mechanical & Industrial Department CAIRO - EGYPT Subject Schedule of equipment Building Adapazari Hosptial
Project No. TK0191 Sheet No. of Checked by
Date 15/1/2002 Computed by Y.G. Approved by
Medical Vacuum Unit Column NO. 1 Unit NO. System served Medical Vacuum Building Hospital Floor Basement Room Specification type Pressure (mm Hg) Capacity l/s per unit Quantity Packaged duplex 381 45 1
Medical Compressed Air Unit Column NO. 1 Unit NO. System served Medical Air Building Hospital Floor Basement Room Reciprocating packaged oilSpecification type less Quadraplex Discharge pressure Kpa 345 Capacity l/s per unit 20 Quantity 1
L/S is the expanded flow at 510 mm Hg
Oxygen Tank Calculations
Go to
Pipe Sizing
Mechanical & Industrial Department CAIRO - EGYPT Subject Pressure loss/100 ft calculations Building Adapazari Hospital Oxygen Distance to the farthest outlet Taking fittings and elbows into accounts Converting to ft 697.18 ft
DESIGN CALCULATION SHEET
Project No. TK0191 Sheet No. of Checked by
Date 15/1/2002 Computed by Y.G. Approved by
170 m 170 m x 1.25 = 212.5 m
If 697.18 shouldn't exceed 5 PSI of total pressure drop Then the pressure drop per 100 ft will be 0.7172 .7 PSI/100ft Pressure drop = 34.85892 PSI
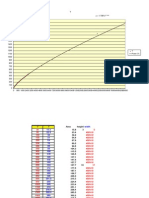
LPM
50 250 500 1500 2500 4000 7500 15000 25000 50000
1/2 0.04 0.99
3/4 0.11 0.45
in 1-1/4
1-1/2
2-1/2
0.11 0.95
0.3 0.83
0.34 0.88
0.2 0.71
0.22 0.89
0.35 0.98
0.23 0.92
Vacuum Distance to the farthest outlet Taking fittings and elbows into accounts Converting to ft 697.18 ft 170 m 170 m x 1.25 = 212.5 m
If 697.18 shouldn't exceed 4 in Hg Then the pressure drop per 100 ft will be 0.5737 Pressure drop across pipe = 14.9352 PSI
1 8 15 30 50 100 175 250 450 700 1000 3/4 0.02 0.76 1 0.2 0.6 1-1/4 1-1/2 in 2 2-1/2
.6 in Hg
3 4 5 6
0.18 0.68
0.3 0.74
CFM
0.2 0.76
0.24 0.7
0.3 0.58
0.13 0.45
0.13 0.3
0.1 0.24
Sizing the Vacuum pump discharge piping to the roof
3/4 CFM 325 1 1-1/4 1-1/2 2 2-1/2 3 4 5 in
Medical air Distance to the farthest outlet Taking fittings and elbows into accounts Converting to ft 697.18 ft 170 m 170 m x 1.25 = 212.5 m
If 697.18 shouldn't exceed 5 in Hg Then the pressure drop per 100 ft will be 0.7172
in 1-1/4
.7 PSI/100ft
CFM
5 20 40 90 140 250 400 750 1600
1/2 0.3
3/4 0.03 0.69
1 0.2 0.8
1-1/2
2-1/2
0.18 0.93
0.41 1
0.27 0.85
0.33 0.84
0.27 0.94
0.22 1
Nitrous Oxide
Distance to the farthest outlet Taking fittings and elbows into accounts Converting to ft 356.79 ft
87 m 87 m x 1.25 = 108.75 m
If 356.79 shouldn't exceed 5 in Hg Then the pressure drop per 100 ft will be 1.4014
in 1-1/4
1 PSI/100ft
1/2
3/4
1-1/2
2-1/2
LPM
50 250 500 1500 2500 4000 7500 15000 25000 50000
0.04 0.99
0.11 0.45
0.11 0.95
0.3 0.83
0.34 0.88
0.2 0.71
0.22 0.89
0.35 0.98
0.23 0.92
Oxygen Tank Claculations
Go to
Schedule of Equipment
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Medical Gas Pipeline SizingDocument6 paginiMedical Gas Pipeline Sizingnini26100% (3)
- Medical Gases CalculationsDocument14 paginiMedical Gases CalculationsNghiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Gas DesignDocument8 paginiMedical Gas Designwetchkrub100% (1)
- IJM Calculation For Lift Lobby (Fire Lift)Document6 paginiIJM Calculation For Lift Lobby (Fire Lift)MFaiz RHamiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Gas CalculationDocument11 paginiMedical Gas CalculationfaizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Medical Gas System of Assiut I PDFDocument97 paginiDesign of Medical Gas System of Assiut I PDFWalmick Santos100% (2)
- Central Medical Gas Systems 24506901708Document9 paginiCentral Medical Gas Systems 24506901708PrestoneKÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stair Case PressurisationDocument5 paginiStair Case Pressurisationsardarmkhan100% (1)
- Design StepsDocument4 paginiDesign StepsAvk Sanjeevan100% (3)
- ASHRAE Duct Noise Vs VelocityDocument1 paginăASHRAE Duct Noise Vs Velocityasdthu75% (4)
- When Sizing A Water Storage Tank For Exclusive Fire Protection UseDocument4 paginiWhen Sizing A Water Storage Tank For Exclusive Fire Protection UsemengineeringÎncă nu există evaluări
- Smoke Extraction System Sample CalculationDocument5 paginiSmoke Extraction System Sample Calculationsmcsaminda100% (3)
- Hvac in Hospitals (Ot)Document11 paginiHvac in Hospitals (Ot)anmol100% (1)
- Vevtilation Calculation For The Transformer RoomDocument2 paginiVevtilation Calculation For The Transformer Roomgutmont100% (9)
- EXHAUST FAN Static Pressure CalculationDocument15 paginiEXHAUST FAN Static Pressure CalculationCarlo Santi Bayabay0% (1)
- Automatic Duct SizingDocument4 paginiAutomatic Duct SizingSudhir KulkarniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grille Sizing ChartDocument1 paginăGrille Sizing Chartirfanbaig3688% (8)
- Ventilation Calculator ASHRAE 62 - 2 Existing HousesDocument23 paginiVentilation Calculator ASHRAE 62 - 2 Existing HousesSharon Lambert67% (3)
- Smoke Evacuation System CalculationsDocument3 paginiSmoke Evacuation System Calculationsamo3330100% (4)
- Medical Gas OutletsDocument48 paginiMedical Gas OutletsIrvin Bradford Dee100% (1)
- Medical Gas Vaccum Piping SystemDocument56 paginiMedical Gas Vaccum Piping Systemssgjmlim67% (3)
- Pressure Loss Calculation SheetDocument6 paginiPressure Loss Calculation Sheetchuyen.reeÎncă nu există evaluări
- CAL-03 - Staircase Pressurization CalculationDocument4 paginiCAL-03 - Staircase Pressurization CalculationAbdul Sami100% (1)
- Template Hose Reel CalculationDocument3 paginiTemplate Hose Reel CalculationMFaiz RHamira100% (7)
- All NFPA TablesDocument24 paginiAll NFPA TablesKhyle Laurenz DuroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Smoke Ventilation Calculations - M TowerDocument4 paginiSmoke Ventilation Calculations - M TowerMaaz Junaidi80% (5)
- Medical Gas System PDFDocument7 paginiMedical Gas System PDFk1l2d3Încă nu există evaluări
- Calculation of Smoke Spilled SystemDocument2 paginiCalculation of Smoke Spilled SystemMFaiz RHamira100% (1)
- Pressurization BSIDocument3 paginiPressurization BSIRaja Antony100% (3)
- Stair Case Pressurization Calculation - Class ADocument8 paginiStair Case Pressurization Calculation - Class ALarry Bea100% (4)
- Car Park Calc.Document1 paginăCar Park Calc.hasanadel88100% (1)
- Smoke Manag. Ex. Fan Calc.Document2 paginiSmoke Manag. Ex. Fan Calc.Mahmoud NmiesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stairwell Lift Pressurization CalculationsDocument31 paginiStairwell Lift Pressurization CalculationsKarthikeyan SankarrajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Duct Area Diagram and Area Calculation FormulaDocument49 paginiDuct Area Diagram and Area Calculation FormulaSanthosh Kumar75% (4)
- Medical Gas Piping Design-Part1Document4 paginiMedical Gas Piping Design-Part1Gage Floyd Bitayo100% (2)
- Full Sprinkler SpecificationDocument22 paginiFull Sprinkler Specificationmakmak9100% (1)
- Kitchen Equipments From AshraeDocument2 paginiKitchen Equipments From AshraeJeffy Shannon100% (9)
- Smoke Ventilation CalculationDocument8 paginiSmoke Ventilation CalculationroinbanerjiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Residential Fire Sprinkler CalculationDocument3 paginiResidential Fire Sprinkler CalculationCarlo Santi BayabayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Gas System StandersDocument152 paginiMedical Gas System StandersROMARU 2010Încă nu există evaluări
- Staircase Pressurisation Calculation Rev-04Document36 paginiStaircase Pressurisation Calculation Rev-04Anish KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ventilation Calculation 1 PDFDocument5 paginiVentilation Calculation 1 PDFGior GioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sizing Medical Gas PipingDocument6 paginiSizing Medical Gas PipingYoke Shu100% (1)
- Template Wet Riser CalculationDocument4 paginiTemplate Wet Riser CalculationMFaiz RHamira100% (1)
- Guide To Smoke Extraction in BuildingsDocument76 paginiGuide To Smoke Extraction in BuildingsKc Hon100% (2)
- Stair Pressurization CalculationDocument9 paginiStair Pressurization CalculationHaymanot BaynesagnÎncă nu există evaluări
- M'Sia Fire Stair Pressurization SampleDocument10 paginiM'Sia Fire Stair Pressurization Samplenim_gourav1997Încă nu există evaluări
- Food Court's Kitchens VentilationsDocument1 paginăFood Court's Kitchens VentilationsSudhir KulkarniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Gas Piping SpecDocument22 paginiMedical Gas Piping Specvvg100% (1)
- BS7074Document1 paginăBS7074Anonymous BJ9omOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stair Pressurization CalculationDocument2 paginiStair Pressurization Calculationnaruto256100% (1)
- BR258 Design Approaches For Smoke Control in Atrium BuildingsDocument70 paginiBR258 Design Approaches For Smoke Control in Atrium BuildingsGan Yi Zhe100% (6)
- 2 Smoke Calculation r4.Document11 pagini2 Smoke Calculation r4.muhammed sabir v aÎncă nu există evaluări
- Smoke Management Calculation Method - SeeniDocument2 paginiSmoke Management Calculation Method - SeenisathakkumalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stair Case Pressurization FAN - OmarDocument2 paginiStair Case Pressurization FAN - OmarDesigner Forever100% (1)
- Air Conditioning System Design CalculationDocument12 paginiAir Conditioning System Design Calculationmattcmwong67% (3)
- Air 4 Bar PlantDocument7 paginiAir 4 Bar PlantAbu ZakaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SHRM Cu01 Fcu SMDocument228 paginiSHRM Cu01 Fcu SMWai LaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- VersaFlow Coriolis 100 Mass Flow Sensor Specifications, 34-VF-03-09Document20 paginiVersaFlow Coriolis 100 Mass Flow Sensor Specifications, 34-VF-03-09Javier Alejandro QuingaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GEA ATEX CatalogueDocument18 paginiGEA ATEX CataloguebracioÎncă nu există evaluări
- ss4-3 Ajmal PDFDocument37 paginiss4-3 Ajmal PDFsitehabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steel Design 3 ConnectionsDocument208 paginiSteel Design 3 Connectionssitehab100% (2)
- DeplasmanDocument40 paginiDeplasmansitehabÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Model 1Document1 pagină1 Model 1sitehabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beam CalculatorDocument113 paginiBeam CalculatorEbert Joel Paico AmayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Malzeme Cetveli̇Document1 paginăMalzeme Cetveli̇sitehabÎncă nu există evaluări
- FaultDocument18 paginiFaultsitehab0% (1)
- Poles PDFDocument82 paginiPoles PDFsitehabÎncă nu există evaluări
- RC13 Torsion1Document20 paginiRC13 Torsion1Edward van MartinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Selection of Main CB & Branch CBDocument34 paginiSelection of Main CB & Branch CBمعن قطاونهÎncă nu există evaluări
- ShortCircuitCurrentCalculation IscDocument28 paginiShortCircuitCurrentCalculation IscsitehabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thuyõt Minh Týnh To N Kõt CêuDocument11 paginiThuyõt Minh Týnh To N Kõt CêusitehabÎncă nu există evaluări
- R.C Hollow Beam Under Pure Torsion PDFDocument37 paginiR.C Hollow Beam Under Pure Torsion PDFsitehabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earthmat DesignDocument6 paginiEarthmat DesignPavan KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laminate InertiaDocument1 paginăLaminate InertiasitehabÎncă nu există evaluări
- 45' Pole Shop Drawing PDFDocument1 pagină45' Pole Shop Drawing PDFsitehabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Load CalculationDocument274 paginiElectrical Load Calculationsitehab77% (22)
- 021 040 20TR Ae 14114 PDFDocument1 pagină021 040 20TR Ae 14114 PDFsitehabÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 - Precast Concrete Structures-Students PDFDocument17 pagini8 - Precast Concrete Structures-Students PDFsitehabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fixed Bas by MariamDocument5 paginiFixed Bas by MariamsitehabÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5.1 Design of Sanitary Wastewater Manholes - 1456Document4 pagini5.1 Design of Sanitary Wastewater Manholes - 1456sitehab100% (2)
- ACI 318 08 Rec Sec MX Q Torsion Design Rev06 02 May 2013Document9 paginiACI 318 08 Rec Sec MX Q Torsion Design Rev06 02 May 2013sitehabÎncă nu există evaluări
- COT (C 1)Document106 paginiCOT (C 1)sitehabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Besign of Fixed Base: Staining ActionsDocument9 paginiBesign of Fixed Base: Staining ActionssitehabÎncă nu există evaluări
- 021 040 20TR Ae 14112 PDFDocument1 pagină021 040 20TR Ae 14112 PDFsitehabÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 - Bearing of Bored PileDocument8 pagini01 - Bearing of Bored PilesitehabÎncă nu există evaluări
- , m Hệ số khi (m) bằngDocument2 pagini, m Hệ số khi (m) bằngsitehabÎncă nu există evaluări
- 00 Columns 3DDocument25 pagini00 Columns 3DsitehabÎncă nu există evaluări
- 00 Columns DtronDocument2 pagini00 Columns DtronsitehabÎncă nu există evaluări
- 00 Columns DtronDocument2 pagini00 Columns DtronsitehabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Major Neurological Syndromes PDFDocument260 paginiMajor Neurological Syndromes PDFVirlan Vasile Catalin100% (1)
- Hazop PDFDocument18 paginiHazop PDFLuiz Rubens Souza Cantelli0% (1)
- A Study On Customer Satisfaction Towards: Ankur 2018-19Document10 paginiA Study On Customer Satisfaction Towards: Ankur 2018-19Pubg GamerÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDF 20221013 211252 0000Document1 paginăPDF 20221013 211252 0000Meann جرابيللوÎncă nu există evaluări
- STS CRFDocument38 paginiSTS CRFYosoy LomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engl7 Q4 W4 Determining-Accuracy Villanueva Bgo Reviewed-1Document18 paginiEngl7 Q4 W4 Determining-Accuracy Villanueva Bgo Reviewed-1johbaguilatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shaolin 18 Lohan HandsDocument9 paginiShaolin 18 Lohan HandsHero Gmr JonesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Construction of Magic Soak Pit With Locally Available Materials and Economical DesignDocument4 paginiConstruction of Magic Soak Pit With Locally Available Materials and Economical DesignInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maternity Benefit-Employer's ObligationsDocument20 paginiMaternity Benefit-Employer's ObligationsSonika BhatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laboratory Result Report: Requested Test Result Units Reference Value Method ImmunologyDocument1 paginăLaboratory Result Report: Requested Test Result Units Reference Value Method ImmunologyYaya ZakariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A 58 Year Old Client Is Admitted With A Diagnosis of Lung CancerDocument9 paginiA 58 Year Old Client Is Admitted With A Diagnosis of Lung CancerNur SanaaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Estimation of Blood GlucoseDocument3 paginiEstimation of Blood Glucosepodcast gazalÎncă nu există evaluări
- D-Ox Benefits of Hydrogen WaterDocument10 paginiD-Ox Benefits of Hydrogen WaterGabi Del RosarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Varsity 39Document254 paginiThe Varsity 39cosmin_bloju8997Încă nu există evaluări
- The Miracle of ChocolateDocument10 paginiThe Miracle of ChocolateAmanda YasminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Social Work MaterialDocument214 paginiSocial Work MaterialBala Tvn100% (2)
- AishwaryaDocument52 paginiAishwaryamohitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Identifikasi Dan Prevalensi Nematoda Saluran Pencernaan Kuda Lokal (Equus Caballus) Di Kecamatan Moyo Hilir SumbawaDocument7 paginiIdentifikasi Dan Prevalensi Nematoda Saluran Pencernaan Kuda Lokal (Equus Caballus) Di Kecamatan Moyo Hilir SumbawaBeebli PuchaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uganda Dental Association Journal November 2019Document36 paginiUganda Dental Association Journal November 2019Trevor T KwagalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wellness at SeaDocument9 paginiWellness at SeaRam Niwas ChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Word Structure (MT)Document19 paginiBasic Word Structure (MT)leapphea932Încă nu există evaluări
- Chevron Phillips Chemical Company Issued Sales SpecificationDocument1 paginăChevron Phillips Chemical Company Issued Sales SpecificationSarmiento HerminioÎncă nu există evaluări
- FA Form No2-Visa Application FormDocument1 paginăFA Form No2-Visa Application FormacademydonutÎncă nu există evaluări
- Murawski 2009Document6 paginiMurawski 2009Sofia Valeria MonrealÎncă nu există evaluări
- Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion and Mechanisms of Action of AflatoxinsDocument3 paginiAbsorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion and Mechanisms of Action of AflatoxinsMaya Innaka ArhayuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inc Tnai IcnDocument7 paginiInc Tnai IcnDeena MelvinÎncă nu există evaluări
- CP of Dexterous ConsultantsDocument12 paginiCP of Dexterous ConsultantsDipankar GhoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bellavista 1000 Technical - SpecificationsDocument4 paginiBellavista 1000 Technical - SpecificationsTri DemarwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- EDC Annual ReportDocument433 paginiEDC Annual ReportAngela CanaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nina Fay Calhoun Award - Intl RelationsDocument5 paginiNina Fay Calhoun Award - Intl RelationsAltrusa International of Montrose COÎncă nu există evaluări