Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
H Appm 2013
Încărcat de
api-239280915Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
H Appm 2013
Încărcat de
api-239280915Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
2013.
M32
Coimisin na Scrduithe Stit State Examinations Commission
__________________________
LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2013
___________________________
APPLIED MATHEMATICS HIGHER LEVEL
___________________________
FRIDAY, 21 JUNE MORNING, 9.30 to 12.00
____________________________
Six questions to be answered. All questions carry equal marks. A Formulae and Tables booklet may be obtained from the Superintendent. Take the value of g to be 98 m s 2 . Marks may be lost if necessary work is not clearly shown.
____________________________________
Page 1 of 6
1.
(a)
A ball is thrown vertically upwards with a speed of 441 m s 1 . Calculate the time interval between the instants that the ball is 392 m above the point of projection.
(b)
A lift ascends from rest with constant acceleration f until it reaches a speed v. It continues at this speed for t1 seconds and then decelerates uniformly to rest with deceleration f. The total distance ascended is d, and the total time taken is t seconds. Draw a speed-time graph for the motion of the lift. 1 (ii) Show that v = f (t t1 ) . 2 4d (iii) Show that t1 = t 2 . f (i)
2.
(a)
Two cars, A and B, travel along two straight roads which intersect at an angle . Car A is moving towards the intersection at a uniform speed of 9 m s 1 . Car B is moving towards the intersection at a uniform speed of 15 m s 1 . At a certain instant each car is 90 m from the intersection and approaching the intersection.
(i) (ii)
Find the distance between the cars when B is at the intersection. If the shortest distance between the cars is 36 m, find the value of . P
(b)
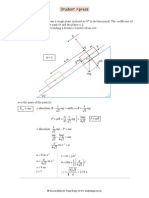
An aircraft P, flying at 600 km h 1 , sets out to intercept a second aircraft Q, which is a distance away in a direction west 30 south, and flying due east at 600 km h 1 . Find the direction in which P should fly in order to intercept Q. Q
30
600 600
Page 2 of 6
3.
(a)
A particle is projected from a point on horizontal ground. The speed of projection is u m s 1 at an angle to the horizontal. The range of the particle is R and the maximum height reached by the particle is
2u 2 sin cos . g Find the value of .
R 4 3
(i) (ii)
Show that R =
(b)
1 to the horizontal. 2 A particle is projected up the plane with initial speed u m s 1 at an angle to the inclined plane. A plane is inclined at an angle tan 1 The plane of projection is vertical and contains the line of greatest slope. Find the value of that will give a maximum range up the inclined plane.
4.
(a)
Two particles of masses 6 kg and 7 kg are connected by a light inextensible string passing over a smooth light fixed pulley which is fixed to the ceiling of a lift. The particles are released from rest. Find the tension in the string (i) when the lift remains at rest (ii) when the lift is rising vertically with constant g acceleration . 8 6 6 7
(b)
A light inextensible string passes over a smooth fixed pulley, under a movable smooth pulley of mass m3 , and then over a second smooth fixed pulley. A particle of mass m1 is attached to one end of the string and a particle of mass m2 is attached to the other end. The system is released from rest. Find the tension in the string in terms of m1 , m2 and m3 .
m1
m3
m2
Page 3 of 6
5.
(a)
A smooth sphere A, of mass 3m, moving with speed u, collides directly with a smooth sphere B, of mass 5m, which is at rest. The coefficient of restitution for the collision is e. Find
(i) (ii)
the speed, in terms of u and e, of each sphere after the collision the value of e if the magnitude of the impulse imparted to each sphere as a result of the collision is 2mu.
(b)
A ball is dropped on to a table and it rises after impact to one-quarter of the height of the fall.
(i)
Find the value of the coefficient of restitution between the ball and the table.
If sheets of paper are placed on the table the coefficient of restitution decreases by a factor proportional to the thickness of the paper. When the thickness of the paper is 25 cm it rises to only one-ninth of the height of the fall.
(ii)
Find the value of the coefficient of restitution between the ball and this thickness of paper.
(iii) What thickness of paper is required in order that the rebound will be one-sixteenth of the height of the fall?
6.
(a)
A rectangular block of wood of mass 20 kg and height 2 m floats in a liquid. The block experiences an upward force of 400d N, where d is the depth, in metres, of the bottom of the block below the surface. Find
(i) (ii)
2m d
value of d when the block is in equilibrium the period of the motion of the block if it is pushed down 03 m from the equilibrium position and then released. A
(b)
A vertical rod BA, of length 4l, has one end B fixed to a horizontal surface with the other end A vertically above B. The ends of a light inextensible string, of length 4l, are fixed to A and to a point C, a distance 2l below A on the rod. A small mass m kg is tied to the mid-point of the string. It rotates, with both parts of the string taut, in a horizontal circle with uniform angular velocity .
(i) (ii)
4l
Find the tension in each part of the string in terms of m, l and . At a given instant both parts of the string are cut. Find the time (in terms of l ) which elapses before the mass strikes the horizontal surface. Page 4 of 6
7.
(a)
Two forces 5 N and 12 N are inclined at an angle as shown in the diagram. They are balanced by a force of 15 N. Find the acute angle .
5N
12 N 15 N B
(b)
Two uniform rods AB and BC, of length 1 and weight W, are hinged at B and rest in equilibrium on a smooth horizontal plane. A weight W is attached to AB at a distance b from A as shown in the diagram. A light inextensible string AC of length 2q prevents the rods from slipping.
(i) (ii)
2q
Find the reaction at A and the reaction at C. Show that the tension in the string is q (1 + b ) W 2 1 q2 .
8.
(a)
Prove that the moment of inertia of a uniform circular disc, of mass m and 1 radius r , about an axis through its centre perpendicular to its plane is mr 2 . 2
(b)
A uniform circular lamina, of mass 8m and radius r, can turn freely about a horizontal axis through P perpendicular to the plane of the lamina. Particles each of mass m are fixed at four points which are on the circumference of the lamina and which are the vertices of square PQRS. The compound body is set in motion. Find
(i) (ii)
the period of small oscillations of the compound pendulum the length of the equivalent simple pendulum.
Page 5 of 6
9.
(a)
V1 cm3 of liquid A of relative density 08 is mixed with V 2 cm3 of liquid B of relative density 09 to form a mixture of relative density 088.
The mass of the mixture is 044 kg. Find the value of V1 and the value of V 2 .
(b)
Liquid C of relative density 08 rests on liquid D of relative density 12 without mixing. A solid object of density floats with part of its volume in liquid D and the remainder in liquid C. 2a . The fraction of the volume of the object immersed in liquid D is a Find the value of a.
10.
(a)
If x2 dy 7 = 0 dx
and y = 1 when x = 7, find the value of y when x = 14 .
(b)
A particle starts from rest at O at time t = 0. It travels along a straight line with acceleration ( 24t 16 ) m s 2 , where t is the time measured from the instant when the particle is at O. Find
(i) (ii)
its velocity and its distance from O at time t = 3 the value of t when the speed of the particle is 80 m s 1 .
(c)
Water flows from a tank at a rate proportional to the volume of water remaining in the tank. The tank is initially full and after one hour it is half full. After how many more minutes will it be one-fifth full?
Page 6 of 6
Blank Page
Blank Page
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- H Appm 2011Document8 paginiH Appm 2011api-239280915Încă nu există evaluări
- H Appm 2007Document8 paginiH Appm 2007api-239280915Încă nu există evaluări
- 2014 Applied Maths Higher Level QuestionsDocument5 pagini2014 Applied Maths Higher Level Questionss_nimalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iit Jee Model Paper 4Document14 paginiIit Jee Model Paper 4studysteps.in67% (3)
- Free Assignment & DPP Physics Centre of MassDocument13 paginiFree Assignment & DPP Physics Centre of MassApex Institute92% (12)
- DPP Nlm-IiDocument8 paginiDPP Nlm-IiMohammed Aftab Ahmed0% (1)
- IIT JEE - Rotation Motion (MAINS)Document6 paginiIIT JEE - Rotation Motion (MAINS)yashsodhaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- P0IITU05 - Rotational Motion QnsDocument7 paginiP0IITU05 - Rotational Motion QnsxTERMINATOR007Încă nu există evaluări
- Physics: V and V Respectively, Then V V V V V VDocument8 paginiPhysics: V and V Respectively, Then V V V V V VPawan PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rigid Body Dynamics Type 2 PART 2 of 3 ENGDocument21 paginiRigid Body Dynamics Type 2 PART 2 of 3 ENGRavi YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 June M2Document6 pagini10 June M2Mohammed Mohammed Al HassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moving Axis Rotation Cases - 37Document6 paginiMoving Axis Rotation Cases - 37Dhruv KuchhalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part - I: Subjective Questions: Section (A) : Calculation OF Centre of MassDocument26 paginiPart - I: Subjective Questions: Section (A) : Calculation OF Centre of MassBalaji Classes washimÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15 M2 June 2005Document5 pagini15 M2 June 2005Remy ChaplaisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Sheet WPEDocument9 paginiPractice Sheet WPENaveen JaferÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iit Model Paper 7Document19 paginiIit Model Paper 7studysteps.in100% (1)
- 5086 - 0801 M2 January 2008 (6 Files Merged)Document33 pagini5086 - 0801 M2 January 2008 (6 Files Merged)POk TAngÎncă nu există evaluări
- USAPhO Problems (2007-2014)Document311 paginiUSAPhO Problems (2007-2014)Science Olympiad Blog95% (19)
- Mechanics Revision PaperDocument16 paginiMechanics Revision PapersagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 Phy - Set B Ut-2Document4 pagini11 Phy - Set B Ut-2dikshachoud44Încă nu există evaluări
- Jee Main Mock Test PaperDocument52 paginiJee Main Mock Test PapermanojÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0a.specimen M3Document4 pagini0a.specimen M3Margarita SatrakiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circular and Work EnergyDocument18 paginiCircular and Work EnergyArmaan AspirantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irp DPP No3Document4 paginiIrp DPP No3Shivam JaggiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1978 Applied Maths Higher Level Questions 1Document4 pagini1978 Applied Maths Higher Level Questions 1dawnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics (Jee Advanced)Document8 paginiPhysics (Jee Advanced)PranavMachingal100% (1)
- Phy 01Document212 paginiPhy 01Varsha Dange100% (1)
- 2013 Jee-Advanced Model Paper-1Document19 pagini2013 Jee-Advanced Model Paper-1Uttej Arendkar A33% (3)
- STPM 2014 Trial p1 Set 2 Q & ADocument17 paginiSTPM 2014 Trial p1 Set 2 Q & Achoichiang100% (1)
- 1121 Final 1R S205Document5 pagini1121 Final 1R S205Prabaharan GunarajahÎncă nu există evaluări
- SQP Hy 11 2022 23Document13 paginiSQP Hy 11 2022 23It's all About fitnessÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iit PaceDocument19 paginiIit PaceabhishekjanjalkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- NL CQ 6 SSPDocument4 paginiNL CQ 6 SSPGokul NathÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02 PhysicsDocument14 pagini02 PhysicsSaikatSenguptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Bitsat 2010 Sample Test 2Document7 paginiPhysics Bitsat 2010 Sample Test 2Abhay Kumar NayakÎncă nu există evaluări
- IIT-JEE 2012 Physics QuestionsDocument8 paginiIIT-JEE 2012 Physics QuestionsmonikakatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- DPP WpeDocument6 paginiDPP WpeMohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- JUNE-2014 Further Maths MechanicsDocument3 paginiJUNE-2014 Further Maths MechanicsBunkweh BertusÎncă nu există evaluări
- GRM M M GR M GRM M GRM: Section - A: (Physics)Document22 paginiGRM M M GR M GRM M GRM: Section - A: (Physics)pskphyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Paper IDocument12 paginiPhysics Paper IMOHAMMED ASIF100% (3)
- Physics Old Exam With Solutions 051Document11 paginiPhysics Old Exam With Solutions 051poker100% (1)
- Physics (Question Paper) AITS 24 SHIFT 1Document7 paginiPhysics (Question Paper) AITS 24 SHIFT 1Saravanan BÎncă nu există evaluări
- 24-12 IIT Nurtre AdvancedDocument3 pagini24-12 IIT Nurtre AdvancedAnkur GoyalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jee Main Part Test 1Document13 paginiJee Main Part Test 1Mohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 Physics SPDocument4 pagini11 Physics SPvikas vyasÎncă nu există evaluări
- JEE Main Sample PaperDocument13 paginiJEE Main Sample PaperAnweshaBose100% (1)
- Er. Shravan Katiyar: Physics For Iit-Jee (Main & Advanced)Document4 paginiEr. Shravan Katiyar: Physics For Iit-Jee (Main & Advanced)ShreyanshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics & ChemistryDocument15 paginiPhysics & ChemistryDexterMorgan007Încă nu există evaluări
- PHYSICSDocument21 paginiPHYSICSdishugirdhar08100% (1)
- DPP - Impulse & MomentumDocument6 paginiDPP - Impulse & MomentumMohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- GCE Mech M1 M5 Specimen Paper MkschemeDocument46 paginiGCE Mech M1 M5 Specimen Paper MkschemeAlbert RlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter - 5 - Centre of MassDocument16 paginiChapter - 5 - Centre of MassMohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2De la EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Evaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3De la EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Evaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (1)
- A Complete Course in Physics ( Graphs ) - First EditionDe la EverandA Complete Course in Physics ( Graphs ) - First EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 Collisions Page 1Document5 pagini4 Collisions Page 1api-239280915Încă nu există evaluări
- 22 April 2013 09:33: 3. Projectiles Page 1Document3 pagini22 April 2013 09:33: 3. Projectiles Page 1api-239280915Încă nu există evaluări
- 27 April 2015 12:58: 3. Projectiles Page 1Document4 pagini27 April 2015 12:58: 3. Projectiles Page 1api-239280915Încă nu există evaluări
- 26 March 2014 13:41: 3. Projectiles Page 1Document4 pagini26 March 2014 13:41: 3. Projectiles Page 1api-239280915Încă nu există evaluări
- Newton 2007Document3 paginiNewton 2007api-239280915Încă nu există evaluări
- Solutions ch10Document14 paginiSolutions ch10api-239280915Încă nu există evaluări
- 2013 Ms AppmDocument28 pagini2013 Ms Appmapi-239280915Încă nu există evaluări
- Solutions ch03Document18 paginiSolutions ch03api-239280915Încă nu există evaluări
- INMOTC 2020 Problem SetDocument7 paginiINMOTC 2020 Problem SetShamim AkhtarÎncă nu există evaluări
- GeometryDocument20 paginiGeometrySshivam Anand100% (1)
- A. Directions: Read and Analyze The Questions Carefully. Choose The Letter of The Correct AnswerDocument2 paginiA. Directions: Read and Analyze The Questions Carefully. Choose The Letter of The Correct AnswerEricka CabalunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4037 s05 QP 2Document8 pagini4037 s05 QP 2mstudy123456Încă nu există evaluări
- Riemannian ManifoldsDocument8 paginiRiemannian ManifoldsJorge Dueñas PamplonaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 12 Mean Value TheoremsDocument20 paginiUnit 12 Mean Value TheoremsChandradeep Reddy TeegalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 30 1 1 Maths StandardDocument11 pagini30 1 1 Maths StandardJharana MohantyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematical Tripos: Complete Answers Are Preferred To FragmentsDocument21 paginiMathematical Tripos: Complete Answers Are Preferred To FragmentsKrishna OochitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endterm Algebra 2019 TT01Document1 paginăEndterm Algebra 2019 TT01khang nguyễnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Mechanics of MaterialsDocument8 paginiChapter 1 - Introduction To Mechanics of MaterialsHoney ChuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Upang Cea Common Bes025 p3Document69 paginiUpang Cea Common Bes025 p3Jairo OntongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math WD Solns 3Document23 paginiMath WD Solns 3Chemuel Mardie G. Obedencio100% (6)
- Mathematics Grade 11 Revision Memo Term 2_2024Document29 paginiMathematics Grade 11 Revision Memo Term 2_2024mariamofokengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steel Tables by R Agor, Birla Publications PDFDocument97 paginiSteel Tables by R Agor, Birla Publications PDFankitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sumi E B.compressedDocument127 paginiSumi E B.compressedabelmil123Încă nu există evaluări
- FirstSemLectureNotes CourseMaterial 2016 17Document46 paginiFirstSemLectureNotes CourseMaterial 2016 17Naveen KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exp 3 Balancing of Rotating MassesDocument13 paginiExp 3 Balancing of Rotating MassesBikash Choudhuri100% (2)
- The Mathematical IntelligencerDocument4 paginiThe Mathematical Intelligencerpepitperez8266Încă nu există evaluări
- Jmo 2003Document2 paginiJmo 2003Dr Shyam Sundar AgrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- STEM - Pre-Calculus CG PDFDocument5 paginiSTEM - Pre-Calculus CG PDFQuinnie Anne CarreonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch.1 Complex NumbersDocument28 paginiCh.1 Complex NumbersKaren Chong YapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quaternions, Torsion and The Physical Vacuum Theories of M. Sachs and G. Shipov ComparedDocument8 paginiQuaternions, Torsion and The Physical Vacuum Theories of M. Sachs and G. Shipov ComparedOdessa FileÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculation of AreaDocument13 paginiCalculation of AreaEmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Euclidean Distance Matrix AnalysisDocument14 paginiEuclidean Distance Matrix AnalysisVictoria LiendoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review of Vector Algebra (Ch-7) Multivariate CalculusDocument14 paginiReview of Vector Algebra (Ch-7) Multivariate CalculusSubrat BarikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summative Test in Mathematics 9 (Quadratic Functions)Document4 paginiSummative Test in Mathematics 9 (Quadratic Functions)william felisilda100% (1)
- CPPDocument8 paginiCPPMitesh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- WebAssign Calc HWDocument12 paginiWebAssign Calc HWTahera AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- The 7 Crystal SystemsDocument9 paginiThe 7 Crystal SystemsJuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 05 One Dimensional Kinematics NotesDocument28 paginiTopic 05 One Dimensional Kinematics NotesRukiezillaÎncă nu există evaluări