Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Chapter 1 CRM Strategic Imperatives PDF
Încărcat de
shivam007Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chapter 1 CRM Strategic Imperatives PDF
Încărcat de
shivam007Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
CRM The Stra ategic Imperatives
Session Coverag ge
Explosion of CRM in Marke eting and IT Enablers for the Growth of CRM Criticality of Customer Rela ationships Why Businesses Should A Adopt CRM? Implementing p g CRM
2
Explosion p of CRM in Marketing g & IT
Academics as well as practi itioners Conferences Journals Special Issues Associations & Forums Centers for CRM IT Solutions Siebel, E.piph hany, Oracle, SAP, Sage CRM, Microsoft Dynamics, SugarC CRM, Salesforce
Relationship p Management g
Relationships
Enterprise
Customer (Internal)
Cust tomer (Interm mediary)
Customer (Shareholder)
Enablers for the Growth of CRM
Emergence of service economy e economy, Emergence of market ec conomy, Global orientation of bus sinesses, and Aging population of the economically advanced economies
Acquiring, Retaining and Growing Customers What CRM Is About!
Customer
Customers needs can be situatio onal in nature. Customers needs are dynamic an nd can change over time, as well. Customers needs often correlate e with customer value. The most fundamental human ne eeds are psychological. There is no single best way to diff ferentiate customers by their needs. needs
Acquiring, Retaining and Growing G Customers.
Understand what they want Give what they want Give them at the right time and right place Deliver what is promised
Acquiring
Retaining Customers.
Keep the customer happy Building re elationships Constant communication c Remember r the little things o Business With Easy To Do
Acquiring
Ret taining
Acquiring
Growing Customers.
Keep value propositions g genuine Establishing meaningful & profitable relationships p trust level Build up Treat Customer Fairly
Acquiring
Growing
Enablers for the Growth of CRM ---1
Emergence E of f service i ec conomy
60-80% of GDP of develo oped nations >50% 50% in i I India di greater customer orie entation in services due to simultaneity / inseparab bility Services early adopters of f CRM
hotels, , airlines, , banking, g, financial fi services, , telecom and retailing. g
10
Enablers for the Growth of CRM----2
Emergence E of f market k t economy
Deregulation of indust tries across the world in the 90s
banking, telecommunica ations, broadcasting and airlines
Market oriented economy y necessitated customer focus and boosted the importance of CRM.
11
Enablers for the Growth of CRM ---3
Global Gl b l orientation i t ti of f bus b sinesses i
National markets to a borderless world / regional world Emergence of trading blocks b WTO helped create a global g orientation for firms Firms need stronger customer orientation to tap opportunities pp in new ma arkets while defending g their home markets.
12
Enablers for the Growth of CRM ----4
Aging A i population l ti of f th the economically i ll advanced d d economies i
Opportunities for wellness, financial well being, safety, security & recreation Slowed markets for traditiona al goods & services designed for a younger population Grow by increasing share share of wallet wallet & not through growth growth of markets stomers to meet changing needs Understanding of existing cus through h h suitable bl products d and d services.
13
Criticality y of Cus stomer Relationships p
Non-traditional N t diti l competit tit tion, ti Market maturity, and Misalignment between revenue and profits.
14
Criticality y of Cus stomer Relationships p
Non-traditional N t diti l competition titi
New entrants from outside th he industry Reliance in telecom, , Kingf gfisher in Airlines Substitute technology Digital Cameras, VoIP Supplier as a competitor Customer as a competitor labels Store labels s Private labels,
Incumbents forced to be relationship oriented to retain customers & protect from no on-traditional on traditional competitors.
15
Criticality y of Cus stomer Relationships p
Market M k t maturity t it
From capacity creation to o capacity utilization in developed markets Growth in emerging markets like l India and China. Understanding customers criti ical to success in these markets
diff differences in i customer t ne eeds, d cultural, lt l social, i l economic i and d also l regulatory environments.
Market maturity forcing firms s to be more customer-oriented
to retain their customers in th heir home markets and to attract customers in emerg ging markets.
16
Criticality y of Cus stomer Relationships p
Market M k t maturity t it
Firms from develope ed countries rely on repeat customers in domestic markets
17
Criticality y of Cus stomer Relationships p
Misalignment Mi li t between b t revenue and d profits fit
Inefficiencies through cus stomer subsidization Distribution Di t ib ti of f revenue es is i exponential, ti l while hil costs t distributed linearly with customer c size Revenues sharply skew wed from largest to smallest customers, while costs de ecline more gradually A small number of highly g yp profitable customers subsidise a large number of non-prof fitable customers
18
Customer Revenu ues & Costs
UNIT/$
COST
REVENUES
BIGGEST
CUSTOM MERS
SMALLEST
19
Criticality y of Cus stomer Relationships p
Misalignment Mi li t between b t reven nue and d profits fit
In retail markets, profit ma argins higher in large accounts and heavy users AT&T in August 1998
Was losing money on app proximately 25 million of its 70 million residential customers. customers 25 million customers - No long distance call or value added services. US $6 per month on custome er support. US $72 a year on each h of f the these 25 mn customers. t
20
Customer Revenu ues & Costs
NONTRADITIONAL COMPETITION CUSTO OMER RELATIO ONSHIP MANAGEMENT CUSTOMER NSACTION TRAN MAN NAGEMENT
UNIT/$
CUSTOMER OUTSOURCING MANAGEMENT
COST
REVENUES
BIGGEST
CUSTOM MERS
SMALLEST
21
Why y Businesses s Should Adopt p CRM?
Demand D d side id
rising customer expectations
Supply side
Technological advances & Declining costs of ICT reduce barriers to adoption of technology led CRM initi iatives.
22
Why y Businesses s Should Adopt p CRM? 1
Rising Ri i customer t expecta tations ti
increasing affluence in th he emerging economies, Greater G t awareness d due t to media di explosion, l i and d Increasing customer diver rsity.
23
Why y Businesses s Should Adopt p CRM?
Increasing affluence in the emerging e economies economies,
Large Middle Class in India and a China Demanding and quality consc cious. Markets - from a sellers to a buyers b market Professional class with greater global awareness and influence.
Can afford and are willing g to p pay y for better and customized p products and services. Nuclear families & double in ncome Traditional homemaking g acti ivities like cooking, g cleaning g and childcare being outsourced to service providers. p Boosts service economy Services force a higher custo omer orientation.
24
Why y Businesses s Should Adopt p CRM?
Greater G t awareness due d to to media di explosion l i
Explosion in the tradition nal media like the newspapers and televisions as well new media m like cable television and the internet
TV homes has remained stable s at about 100 million in the US in the last decade eloping countries It has exploded in the deve
China (341 mn), mn) India (~100 mn) and Brazil (44 mn)
Has raised customer aspira ations as well as expectations
25
Why y Businesses Should S Adopt p CRM?
Increasing I i customer t dive di ersity it
Mass marketing practices s fail with customers who are diverse in their lifestyles lifestyles, age, age income and ethnicity US
ethnic pluralism is increa asing as some minority groups like the Hispanic, Afro-American and the Asian are growing rapidly
Diversity y increases the e diversity y in demand and expectations.
26
Why y Businesses Should S Adopt p CRM?
Technological T h l i l advances d
27
Why y Businesses Should S Adopt p CRM?
Technological T h l i l advances d
Production
CAD/CAM CAD/CAM, JIT, JIT FMS Dell, Toyota
Distribution
Computer Aided Logistics (CALS) & scanner technology allow faster response - replenish hment with fewer stock-outs.
28
Why y Businesses Should S Adopt p CRM?
Technological advances
Facilitation
E-commerce E commerce technologies s connect enterprise with suppliers & customers Facilitates commercial as well w informational exchange Direct Services at a lower cost & Dis-intermediation
Consumption
Personalized consumptio on by co-opting customers as coproducers e.g. Dell Desire for instant gratif fication drives businesses to provide access to products anytime e and anywhere e.g. banks
29
Implementing p g CR RM
Developments in IT IT, data wa arehousing and data mining makes it possible for firms to t maintain 1-to-1relationships with their key customers. Challenges in selecting and implementing i technology intensive CRM solutions
top management commitment t, change management, developing customer centric processes, p integrating with legacy system ms, identifying and establishing pe erformance metrices, and evaluation of return on invest tments
30
Implementing p g CR RM
M Market-related k t l t d capabili bili iti ities t maintain to i t i customer t relationships for competi itive advantage
R Relationship l ti hi orientation i t ti must m t pervade d the th mindset, i d t values, l and norms of the organiza ation. Deepening knowledge of f customers and putting it to work throughout the organizati ion. Key yp processes must be in nternally y integrated g and externally y aligned with the corresp ponding processes of the firms customers.
31
Success of CRM in nitiatives
Process oriented strategic approach
3 elements e e e ts of o market-related a et e ated capability to maintain relationships with most valuable customers for competitive advantage. Relationship Orientation Keep deepening knowledge of customers and use it Key processes must be internally integrated and externally aligned with corresponding processes of firms customers.
Link the Operational, informational & organisational components of CRM. CRM
Delineate the challenges p formation, of Customer Relationship governance, performance evaluation and evolution.
32
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 101 Kickass QuotesDocument10 pagini101 Kickass QuotesbbionicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Copyright and IP quiz answersDocument2 paginiCopyright and IP quiz answersATTY. R.A.L.C.Încă nu există evaluări
- CH 5 Audit-Planning MCQDocument3 paginiCH 5 Audit-Planning MCQEhab hoba0% (1)
- RBC Case StudyDocument20 paginiRBC Case StudyRangan Majumder100% (2)
- PWAL - Technical Proposal On AuditDocument63 paginiPWAL - Technical Proposal On AuditOlufemi MoyegunÎncă nu există evaluări
- CRM Explained: What is Customer Relationship ManagementDocument205 paginiCRM Explained: What is Customer Relationship ManagementAbhimaurya50% (2)
- QMS 9001-2015 Internal Auditor Training Presentation PDFDocument17 paginiQMS 9001-2015 Internal Auditor Training Presentation PDFRuy MouraÎncă nu există evaluări
- RBC's Customer Profitability and CRM StrategyDocument25 paginiRBC's Customer Profitability and CRM StrategyRangan Majumder100% (1)
- 309 012 Evolution of CRMDocument14 pagini309 012 Evolution of CRMviomshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- No Sales, No Sleep: The $10 billion transform sales process to help corporate bankers and financial services salespeople win big transactions fasterDe la EverandNo Sales, No Sleep: The $10 billion transform sales process to help corporate bankers and financial services salespeople win big transactions fasterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Professional Services AgreementDocument4 paginiProfessional Services AgreementvaleriuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impact of CRM in TelecomDocument4 paginiImpact of CRM in TelecomMridul SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lighting Design ConsiderationsDocument42 paginiLighting Design Considerationsshivam007Încă nu există evaluări
- Infosys Spend AnalysisDocument10 paginiInfosys Spend AnalysisVikram Pratap SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muczynski Three Preludes: G. Schirmer, IncDocument4 paginiMuczynski Three Preludes: G. Schirmer, IncPyero Talone100% (7)
- Royal Bank of CanadaDocument18 paginiRoyal Bank of CanadaShruti VinyasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answerdash CaseDocument9 paginiAnswerdash CaseDishank Khimani100% (5)
- Customer Relationship ManagementDocument56 paginiCustomer Relationship Managementsnehachandan91Încă nu există evaluări
- BPO ServiceDocument33 paginiBPO ServiceAkhil VartakÎncă nu există evaluări
- A new era of Value Selling: What customers really want and how to respondDe la EverandA new era of Value Selling: What customers really want and how to respondÎncă nu există evaluări
- Samsung Group History and Rise as a Global ConglomerateDocument41 paginiSamsung Group History and Rise as a Global Conglomeratekrupamayekar100% (2)
- Supply Chain Finance Summit: 4th AnnualDocument9 paginiSupply Chain Finance Summit: 4th AnnualFrancois Donatien De SadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Web-Based Church Management SystemDocument60 paginiWeb-Based Church Management SystemSamuel AdielaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lighting Basics: From Nature's Light to Modern Artificial SourcesDocument64 paginiLighting Basics: From Nature's Light to Modern Artificial Sourcesshivam007Încă nu există evaluări
- Relationship Marketing: Course Code: 210-PM Faculty: Soumya Dutta GuptaDocument72 paginiRelationship Marketing: Course Code: 210-PM Faculty: Soumya Dutta GuptasoumyodguptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 Conceptual Foundations of CRM PDFDocument34 paginiChapter 2 Conceptual Foundations of CRM PDFshivam007Încă nu există evaluări
- introduction_to_crmDocument25 paginiintroduction_to_crmthakkurnikita51Încă nu există evaluări
- Customer Relationship Management of Birla Sun LifeDocument72 paginiCustomer Relationship Management of Birla Sun LifepraveenworlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Customer Relationship Management of Birla Sun LifeDocument72 paginiCustomer Relationship Management of Birla Sun LifeTarun NarangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Customer Relationship Management: Strategic Application of ItDocument62 paginiCustomer Relationship Management: Strategic Application of ItNishant KoolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Customer Relationship Management: Strategic Application of ItDocument52 paginiCustomer Relationship Management: Strategic Application of ItShipra SrivastavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Customer Relationship Management: An Introduction to CRM Concepts and StrategiesDocument30 paginiCustomer Relationship Management: An Introduction to CRM Concepts and StrategiesNavdeeshSharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is CRM 1Document12 paginiWhat Is CRM 1Ambuj RaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Retailer's Guide To: Supply Chain ManagementDocument28 paginiA Retailer's Guide To: Supply Chain ManagementVarun AgarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM)Document47 paginiCustomer Relationship Management (CRM)ponnusamysudhakarÎncă nu există evaluări
- CRM 101Document25 paginiCRM 101sayansambitÎncă nu există evaluări
- CRM Conceptual FoundationDocument37 paginiCRM Conceptual Foundationvinayche100% (1)
- IT Industry Scenario, Scope, Emerging TrendsDocument21 paginiIT Industry Scenario, Scope, Emerging TrendsErnesto BatesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Ijamh 1031 NN SharmaDocument4 pagini2 Ijamh 1031 NN SharmaedfwÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hilton Hotels Gains Competitive Edge with OnQ CRM SystemDocument17 paginiHilton Hotels Gains Competitive Edge with OnQ CRM Systemtechiegennext50% (2)
- CRMDocument8 paginiCRMdownload4artÎncă nu există evaluări
- IT Industry CRM Guide to Managing Customer RelationshipsDocument4 paginiIT Industry CRM Guide to Managing Customer RelationshipssubhashonaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Emergence of CRM Practice: Customer Relationship ManagementDocument101 paginiThe Emergence of CRM Practice: Customer Relationship Managementroushanijha123Încă nu există evaluări
- CH 01Document27 paginiCH 01Ankur PrabhakarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Customer Relationship Management (CRM)Document25 paginiIntroduction To Customer Relationship Management (CRM)Ruby JaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- CRM in Banking - How ICICI Bank implemented Salesforce CRMDocument36 paginiCRM in Banking - How ICICI Bank implemented Salesforce CRMKaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- SM PPT RBCDocument20 paginiSM PPT RBCAnkita KumariÎncă nu există evaluări
- CRM White PaperDocument5 paginiCRM White PaperdrajdÎncă nu există evaluări
- CRM - 1Document37 paginiCRM - 1srishti sharma.ayush1995Încă nu există evaluări
- First Direct: Branchless BankingDocument26 paginiFirst Direct: Branchless BankingNikita RunwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paradigm Shift in MarketingDocument16 paginiParadigm Shift in Marketingpinku_thakkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 CRM in B2C Markets PDFDocument27 paginiChapter 5 CRM in B2C Markets PDFshivam007100% (1)
- A Project On:: Customer Relationship Management (CRM)Document20 paginiA Project On:: Customer Relationship Management (CRM)nnjhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CRM Architecture WhitepaperDocument22 paginiCRM Architecture Whitepaperequitytrader100% (1)
- 1st Ch-Concept and Context of CRMDocument49 pagini1st Ch-Concept and Context of CRMnitish07singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Distribution Strategies in US Retail BankingDocument8 paginiDistribution Strategies in US Retail BankingtekmohitÎncă nu există evaluări
- CromaDocument52 paginiCromaHimanshu SachdevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Importance of CRM Activities in Real Estate IndustryDocument4 paginiImportance of CRM Activities in Real Estate IndustryAnanth KarthikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rethinking Marketin G: Group 8Document20 paginiRethinking Marketin G: Group 8TankaKoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENTDocument17 paginiCUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENTRavi Ramachandran RÎncă nu există evaluări
- E-Commerce: From B2C to B2B and BeyondDocument37 paginiE-Commerce: From B2C to B2B and BeyondTruong Quang ThaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CRM in InsuranceDocument18 paginiCRM in InsurancePramila ChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Achieving Customer Management Excellence in Emerging Markets ChannelDocument8 paginiAchieving Customer Management Excellence in Emerging Markets ChannelKeshav talwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- CRM in Service Sector Kiran UploadDocument27 paginiCRM in Service Sector Kiran UploadBalakrishna NutulapatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CRM Industry LandscapeDocument26 paginiCRM Industry LandscapeAdityaHridayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emerging CRM Concepts and the Need for Customer Relationship ManagementDocument14 paginiEmerging CRM Concepts and the Need for Customer Relationship ManagementanikethroyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBIS From Functional View PointDocument12 paginiCBIS From Functional View Pointmaba2610Încă nu există evaluări
- Case RCBDocument76 paginiCase RCBSaurabh KatariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- View On Cognizant StrategyDocument30 paginiView On Cognizant Strategysiddarthaprasad587100% (1)
- Simplified Digital Marketing, Customers and OutreachDe la EverandSimplified Digital Marketing, Customers and OutreachÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Customer Catalyst: How to Drive Sustainable Business Growth in the Customer EconomyDe la EverandThe Customer Catalyst: How to Drive Sustainable Business Growth in the Customer EconomyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CUSTOMER CENTRICITY & GLOBALISATION: PROJECT MANAGEMENT: MANUFACTURING & IT SERVICESDe la EverandCUSTOMER CENTRICITY & GLOBALISATION: PROJECT MANAGEMENT: MANUFACTURING & IT SERVICESÎncă nu există evaluări
- Is The Luminous Flux of A Lamp in Relation ToDocument3 paginiIs The Luminous Flux of A Lamp in Relation Toshivam007Încă nu există evaluări
- LLFY-Step by Step in DIALux With OSRAM LEDsDocument30 paginiLLFY-Step by Step in DIALux With OSRAM LEDsAbdulyekini Ahmadu100% (1)
- VHDL ProblemsDocument1 paginăVHDL Problemsshivam007Încă nu există evaluări
- Priority EncoderDocument11 paginiPriority Encodershivam007Încă nu există evaluări
- Lect - 6 & 7 Logic GatesDocument29 paginiLect - 6 & 7 Logic Gatesshivam007Încă nu există evaluări
- ELCOMA Presentation To GLA April 24 2013Document27 paginiELCOMA Presentation To GLA April 24 2013shivam007Încă nu există evaluări
- L-17 (NKK) (Ie) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document9 paginiL-17 (NKK) (Ie) ( (Ee) Nptel)generalclimaticÎncă nu există evaluări
- Decision Matrix Analysis WorksheetDocument1 paginăDecision Matrix Analysis Worksheetshivam007Încă nu există evaluări
- QM TECHNIQUE LectureDocument18 paginiQM TECHNIQUE Lectureshivam007Încă nu există evaluări
- VHDL Lecture Slides PDFDocument90 paginiVHDL Lecture Slides PDFshivam007Încă nu există evaluări
- Lect - 5 Boolean AlgebraDocument45 paginiLect - 5 Boolean Algebrashivam007100% (2)
- Lect 7k-MapDocument78 paginiLect 7k-Mapshivam007Încă nu există evaluări
- Lect - 1Document33 paginiLect - 1shivam007Încă nu există evaluări
- Lect - 2Document28 paginiLect - 2shivam007Încă nu există evaluări
- Lec 8 CounterDocument76 paginiLec 8 Countershivam007Încă nu există evaluări
- Lect - 3 & 4Document45 paginiLect - 3 & 4shivam007Încă nu există evaluări
- Lec 7 Sequential ContDocument10 paginiLec 7 Sequential Contshivam007Încă nu există evaluări
- Lec 6 Sequential AnalysisDocument42 paginiLec 6 Sequential Analysisshivam007Încă nu există evaluări
- Decoders & MuxDocument69 paginiDecoders & Muxshivam007Încă nu există evaluări
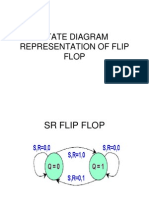
- Lec 4 STATE DIAGRAM REPRESENTATION OF FLIP FLOPDocument5 paginiLec 4 STATE DIAGRAM REPRESENTATION OF FLIP FLOPshivam007Încă nu există evaluări
- Bresenhams AlgorithmDocument15 paginiBresenhams AlgorithmIAGPLSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec 3 Asynchronous Flip-Flop InputsDocument9 paginiLec 3 Asynchronous Flip-Flop Inputsshivam007Încă nu există evaluări
- Conversion Between Flip Flop PDFDocument4 paginiConversion Between Flip Flop PDFshivam007Încă nu există evaluări
- 3D Transform PDFDocument15 pagini3D Transform PDFshivam007Încă nu există evaluări
- Latches & Flip FlopDocument28 paginiLatches & Flip Flopshivam007Încă nu există evaluări
- Arithmetic CircuitsDocument69 paginiArithmetic Circuitsshivam007100% (2)
- 3D Viewing Transform PDFDocument37 pagini3D Viewing Transform PDFshivam007Încă nu există evaluări
- 3D ViewingDocument22 pagini3D ViewingTurgay BatbatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intellectual Property Rights and TripsDocument14 paginiIntellectual Property Rights and TripsViswas1000Încă nu există evaluări
- D5548 373465-1Document3 paginiD5548 373465-1Luisa Fernanda Quiceno GiraldoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form and Application Object Guide 7 6Document660 paginiForm and Application Object Guide 7 6valeryvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report On Employee Communications and ConsultationDocument29 paginiReport On Employee Communications and Consultationakawasaki20Încă nu există evaluări
- Seven Keys For Successful Domain Portfolio Management: White PaperDocument12 paginiSeven Keys For Successful Domain Portfolio Management: White PaperSeema ThakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cost Allocation, Customer-Profitability Analysis, and Sales-Variance AnaylsisDocument17 paginiCost Allocation, Customer-Profitability Analysis, and Sales-Variance AnaylsisKelvin John RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Decisions Involving Alternative ChoicesDocument3 paginiDecisions Involving Alternative ChoicesHimani Meet JadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- This Is The Most Important Word When It Comes To Relationship MarketingDocument6 paginiThis Is The Most Important Word When It Comes To Relationship MarketingluvijoquicoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Swiss IT Loyalty Program Drives RevenueDocument4 paginiSwiss IT Loyalty Program Drives Revenuealan_boscoÎncă nu există evaluări
- IS 441 Exam SummeryDocument3 paginiIS 441 Exam SummeryIsuru De Silva0% (1)
- Vendor Registration FormDocument2 paginiVendor Registration FormmarksahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business Associates (Freelancer) in Mumbai: Smart4talent-Mumbai, MaharashtraDocument9 paginiBusiness Associates (Freelancer) in Mumbai: Smart4talent-Mumbai, MaharashtraAnkitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- India's Premier Coal Industry EventDocument8 paginiIndia's Premier Coal Industry EventmahantmtechÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rooms DivisionDocument19 paginiRooms Divisionনিয়াজ মাহমুদÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tata Docomo's STP and 4Ps Marketing MixDocument4 paginiTata Docomo's STP and 4Ps Marketing MixKt ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study MIS1 (Updated 092012)Document69 paginiCase Study MIS1 (Updated 092012)Trần Tiến100% (1)
- Etsi Guide On IprsDocument18 paginiEtsi Guide On IprsMaulik PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reply To EnquiryDocument16 paginiReply To EnquiryLalaPuspitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Smart Business Solutions Naming GuidelinesDocument4 paginiSmart Business Solutions Naming GuidelinespopatrajkumarÎncă nu există evaluări