Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Moving Man - Velocity Time Graphs
Încărcat de
spreemouseDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Moving Man - Velocity Time Graphs
Încărcat de
spreemouseDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
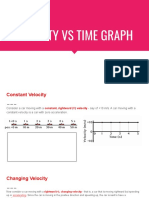
Moving Man - Velocity vs.
Time Graphs
Teacher Pages
Prior Knowledge The students should know:
How to make a line graph The basic unit of measure for distance is the meter and for speed it is meters per second. What is meant by the term slope of a line.
Activity & Simulation InstructionsThis assignment is intended as an assignment the students will complete outside of class either at home or in a library. That the 0m point where the moving man is located is an arbitrary point and all distance measurements will be made from that point. That the positive and negative values on the position graph represent the direction the man moves from the 0m point. To close the acceleration graphs the students need to click on this symbol, located in the upper right hand corner of the acceleration graph Give the students a descriptive vocabulary to use in their description of a graph. For example; Description of Samples of descriptive phrases Direction Moving from ____ to ___ Moving away from Moving towards observer observer Speed Standing still Moving slow Moving fast Learning Goals The students will: Develop a general knowledge of Velocity vs. Time graphs and Distance vs. Time graphs o What graphs of a person standing still would look like o What graphs of a person moving away from an observer at a constant speed would look like. o What graphs of a person moving towards an observer at a constant speed would look like. o How differences in speed appear on the graphs
Moving Man - Velocity vs. Time Graphs
Student Pages
Background Remember graphs are not just an evil thing your teacher makes you create, they are a means
of communication. Graphs are a way of communicating by using pictures and since a picture is worth a thousand words knowing how to make and interpret graphs will save you a lot of writing.
Learning Goals The students will:
Develop a general knowledge of Velocity vs. Time graphs and Distance vs. Time graphs o What graphs of a person standing still would look like o What graphs of a person moving away from an observer at a constant speed would look like. o What graphs of a person moving towards an observer at a constant speed would look like. o How differences in speed appear on the graphs Screen 1
Procedure Do the following activity using this web site
http://www.colorado.edu/physics/phet/simulations-base.html Then click on The Moving Man
1. Getting started. After The Moving Man is open leave the position graph and the velocity graph open but close the acceleration graph. Your screen should look like screen 1. 2. Making observations. By either clicking on the man or the slider cause the man to move back and forth and observe what shows up on the graphs. Using the axis provided below make sketches of Distance vs. Time and Velocity vs. Time graphs for the actions described next to each axis. A man moving from 0 to 10 at a slow steady pace.
10
Distance (m) Distance (m) Distance (m)
10
Velocity (m/s)
Time (s)
5 0
5 0
-5 -10 10 5 0
-5 -10 10
Time (s)
A man moving from 0 to 10 at a fast pace.
Velocity (m/s)
-5 -10
Time (s)
5 0
-5 -10
Time (s)
A man standing still at 4m
10 5 0
Time (s)
10
Velocity (m/s)
5 0
-5 -10
-5 -10
Time (s)
Moving Man - Velocity vs. Time Graphs
A man moving from 0 to 10 at a fast pace the moving back to 0 at a slow pace.
10
Distance (m) Distance (m) Distance (m)
10
Velocity (m/s)
Time (s)
5 0
5 0
-5 -10 10 5 0
-5 -10 10
Time (s)
A man moving from 0 to -10 at a fast pace the moving back to 0 at a slow pace.
Velocity (m/s)
-5 -10
Time (s)
5 0
-5 -10
Time (s)
A man moving from 10 to 0 at a fast pace.
10 5 0
Time (s)
10
Velocity (m/s)
5 0
-5 -10
-5 -10
Time (s)
Apply what you learned. Look at the Distance vs. Time graph below and for the different parts of the graph that are marked by the dotted lines make the corresponding Velocity vs. Time graph directly below each part.
10
-5 -10 10
Velocity
Distance Velocity
5 0 5 0 -5 -10
Time
Time
Time
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Formal Homework Assignment 1 - This Assignment, and Other "Formal Homework Assignment"s, Are Graded.Document24 paginiFormal Homework Assignment 1 - This Assignment, and Other "Formal Homework Assignment"s, Are Graded.mhm000666100% (5)
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDe la EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (10)
- The Moving Man Simulation Lab 2013-08-19Document4 paginiThe Moving Man Simulation Lab 2013-08-19sk112Încă nu există evaluări
- Moving ManDocument4 paginiMoving Manapi-341972466Încă nu există evaluări
- Newton PairsDocument8 paginiNewton PairssasikumaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moving Man - Distance Time Graph Student VersionDocument4 paginiMoving Man - Distance Time Graph Student VersionRashid AlbinaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moving Man - Velocity vs. Time Graphs: Background - Lab Write-Up - Learning Goals ProcedureDocument2 paginiMoving Man - Velocity vs. Time Graphs: Background - Lab Write-Up - Learning Goals ProcedurereynandcpcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motion: Speed and Velocity: Resource ID#: 51000 Primary Type: Lesson PlanDocument9 paginiMotion: Speed and Velocity: Resource ID#: 51000 Primary Type: Lesson PlanJuloura PastorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Charisma B Moving Man Phet LessonDocument7 paginiCharisma B Moving Man Phet Lessonapi-255910104Încă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 3: Kinematics of Human MotionDocument5 paginiExperiment 3: Kinematics of Human MotionKamylle Consebido67% (3)
- One Dimensional Kinematics - Chapter OutlineDocument55 paginiOne Dimensional Kinematics - Chapter OutlineAnonymous GTCOMvÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER 3-Kinematics PDF ModuleDocument17 paginiCHAPTER 3-Kinematics PDF ModuleLesther James CastroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2, Linear Motion (Sec. 1)Document23 paginiChapter 2, Linear Motion (Sec. 1)FullyFaltooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phet The Moving Man SimulationDocument4 paginiPhet The Moving Man Simulationapi-341972466100% (1)
- Write Down The Effect It Has OnDocument4 paginiWrite Down The Effect It Has OnMadhumika ThammaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Write Down The Effect It Has OnDocument4 paginiWrite Down The Effect It Has OnWave NewÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is My Acceleration?: From Doug Porter, NEAT, Rising Sun, IndianaDocument2 paginiWhat Is My Acceleration?: From Doug Porter, NEAT, Rising Sun, IndianaMa Lourdes MangahasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inquiry Physics of 01sampleDocument0 paginiInquiry Physics of 01sampleQusthalaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity Sheet Week 3-4 3rd QTRDocument7 paginiActivity Sheet Week 3-4 3rd QTRMarian Anion-GauranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Object Is in When Its From Another Object Is Movement Depends On Your Point ofDocument28 paginiAn Object Is in When Its From Another Object Is Movement Depends On Your Point ofWelfredo Jr YuÎncă nu există evaluări
- S2!3!01 - Distance Time Graphs - SimulationDocument8 paginiS2!3!01 - Distance Time Graphs - SimulationChathunikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- University Physics Lab: Purpose of The ExperimentDocument29 paginiUniversity Physics Lab: Purpose of The ExperimentdaisyhendersonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motion Graphs-Good-S CaesarDocument31 paginiMotion Graphs-Good-S CaesarNYL BRIAN BUISER100% (1)
- Moving Man SimulationDocument12 paginiMoving Man SimulationAlexa AquinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- مذكرة شرح Physics - فيزياء لغات للصف الاول الثانوى لمدارس اللغات-الامتحان التعليمىDocument20 paginiمذكرة شرح Physics - فيزياء لغات للصف الاول الثانوى لمدارس اللغات-الامتحان التعليمىRania Gamal Fouad100% (1)
- Velocity Lesson Plan: Part 1, "Wet" LabDocument7 paginiVelocity Lesson Plan: Part 1, "Wet" LabGerlieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Velocity Lesson Plan: Part 1, "Wet" LabDocument7 paginiVelocity Lesson Plan: Part 1, "Wet" LabGerlie VelascoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kinema TicsDocument32 paginiKinema TicsMatthew Brian UbacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Report FinalDocument7 paginiLab Report Finalapi-301890166Încă nu există evaluări
- The Meaning of Shape For A P-T GraphDocument7 paginiThe Meaning of Shape For A P-T Graphcpverma2811Încă nu există evaluări
- Physics NotesDocument34 paginiPhysics NotesKeerthana SubramaniamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Describing and Measuring MotionDocument22 paginiDescribing and Measuring MotionRenz Dela Cruz ArellanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motion PPT (Summary)Document23 paginiMotion PPT (Summary)Helmiyanto IsmoyoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 9: D-T & V-T GraphsDocument5 paginiLesson 9: D-T & V-T Graphsmajji satishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro To Force and MotionDocument26 paginiIntro To Force and MotionErnesto GullodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motion Notes Part 3Document2 paginiMotion Notes Part 3api-247084136Încă nu există evaluări
- Velocity Acceleration Lab PDFDocument6 paginiVelocity Acceleration Lab PDFUltramixÎncă nu există evaluări
- Speed and VelocityDocument6 paginiSpeed and VelocityHien DuongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To KinematicsDocument11 paginiIntroduction To KinematicsMax SaubermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in GRAPHING MOTIONDocument6 paginiA Detailed Lesson Plan in GRAPHING MOTIONabbyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Moving Man Acceleration Simulation Lab 2013-08-19Document5 paginiThe Moving Man Acceleration Simulation Lab 2013-08-19sk112Încă nu există evaluări
- Kinematics-Rejhan MehmedovicDocument10 paginiKinematics-Rejhan MehmedovicPepic FarisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics of Everyday Phenomena A Conceptual Introduction To Physics 8th Edition Griffith Solutions ManualDocument25 paginiPhysics of Everyday Phenomena A Conceptual Introduction To Physics 8th Edition Griffith Solutions ManualDianaMartinygrb100% (40)
- 101 Motion in A Straight LineDocument5 pagini101 Motion in A Straight LinemonalisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Velocity Lesson Plan: Part 1, "Wet" LabDocument7 paginiVelocity Lesson Plan: Part 1, "Wet" LabqweerÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1d Motion Homework 1Document6 pagini1d Motion Homework 1h07d16wn100% (1)
- Force and Motion ContentDocument24 paginiForce and Motion Contentravichandra dasariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rate of Change Mcr4uDocument5 paginiRate of Change Mcr4uapi-443869667Încă nu există evaluări
- IGCSE - Physics - Lesson Plan 1 - Movement and PositionDocument4 paginiIGCSE - Physics - Lesson Plan 1 - Movement and PositionHoracio FerrándizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics LearningDocument107 paginiPhysics LearningcutejhomzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Distance Vs Time GraphsDocument4 paginiDistance Vs Time GraphsMercedes DolendoÎncă nu există evaluări
- M2L6 Velocity-Time GraphDocument40 paginiM2L6 Velocity-Time GraphJoma Guerra ina moÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seminar Lesson PlanDocument18 paginiSeminar Lesson PlanNo one KnowsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Key Ideas: Section 1 MotionDocument25 paginiKey Ideas: Section 1 Motionapi-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Forces and Motion Speed 2019 7P1.1Document42 paginiForces and Motion Speed 2019 7P1.1Andrew nateÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Moving Man: Distance, Displacement, Speed & Velocity: Background - Learning GoalsDocument6 paginiThe Moving Man: Distance, Displacement, Speed & Velocity: Background - Learning GoalsKiara NorwoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Walkthelineassignment Ivywhittaker DemingDocument2 paginiWalkthelineassignment Ivywhittaker Demingapi-340387682Încă nu există evaluări
- Go!Motion Calculus ModelingDocument6 paginiGo!Motion Calculus ModelingSarah JarnaginÎncă nu există evaluări
- Graphing PP For WebsiteDocument20 paginiGraphing PP For Websiteapi-261802313Încă nu există evaluări
- Teacher's Notes: Gradients On GraphsDocument52 paginiTeacher's Notes: Gradients On GraphsItz TeyyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pivot Interactives Motion Graphs of Positive and Negative AccelerationDocument2 paginiPivot Interactives Motion Graphs of Positive and Negative AccelerationSophiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 121-Ch3 Revised Fall 2013Document12 pagini121-Ch3 Revised Fall 2013Swarnav BanikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energy Skate Park Basics HTML 5 Phet Lab PrelabDocument4 paginiEnergy Skate Park Basics HTML 5 Phet Lab PrelabspreemouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agenda Feb 23rd, 2015Document1 paginăAgenda Feb 23rd, 2015spreemouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test - Data Structure and Algorithm - Flashcards - Quizlet Par 3Document4 paginiTest - Data Structure and Algorithm - Flashcards - Quizlet Par 3spreemouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- This Is A Text: (Event Time)Document2 paginiThis Is A Text: (Event Time)spreemouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- EXIT SLIP Name: - Date: - BlockDocument1 paginăEXIT SLIP Name: - Date: - BlockspreemouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- For Further Information On Modeling: South Jersey Modeling Institutein Physics, Chemistry, and BiologyDocument3 paginiFor Further Information On Modeling: South Jersey Modeling Institutein Physics, Chemistry, and BiologyspreemouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Number Bases WorksheetDocument4 paginiNumber Bases WorksheetspreemouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agenda 04 29 b3bDocument9 paginiAgenda 04 29 b3bspreemouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Do Now:: Write How You Connect To Today's Quote in Your NotebooksDocument12 paginiDo Now:: Write How You Connect To Today's Quote in Your NotebooksspreemouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bank Day Rubric EdittedDocument3 paginiBank Day Rubric EdittedspreemouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Do Now:: April 7, 2014Document6 paginiDo Now:: April 7, 2014spreemouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis: 1an Introduction To Gamma Ray SpectrumDocument6 paginiAnalysis: 1an Introduction To Gamma Ray SpectrumspreemouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Graphing Exponential FunctionsDocument11 paginiGraphing Exponential FunctionsspreemouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agenda 04 29 B3aDocument4 paginiAgenda 04 29 B3aspreemouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Do Now:: Write How You Connect To Today's Quote in Your NotebooksDocument12 paginiDo Now:: Write How You Connect To Today's Quote in Your NotebooksspreemouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agenda 04 08 b1 b2Document6 paginiAgenda 04 08 b1 b2spreemouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Student LedConferencePacket CSDocument1 paginăStudent LedConferencePacket CSspreemouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Work ? (In Physics)Document20 paginiWhat Is Work ? (In Physics)spreemouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agenda 04 24 b1 b2Document4 paginiAgenda 04 24 b1 b2spreemouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Do Now:: April 3, 2014Document8 paginiDo Now:: April 3, 2014spreemouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bahamas CIDDocument16 paginiBahamas CIDspreemouse100% (1)
- Agenda 04 28 b1 b2Document9 paginiAgenda 04 28 b1 b2spreemouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agenda 04 10 b1 b2Document3 paginiAgenda 04 10 b1 b2spreemouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agenda 04 07 B3aDocument3 paginiAgenda 04 07 B3aspreemouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Do Now:: April 7, 2014Document6 paginiDo Now:: April 7, 2014spreemouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Do Now:: April 8, 2014Document6 paginiDo Now:: April 8, 2014spreemouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agenda 03 31 b1 b2Document7 paginiAgenda 03 31 b1 b2spreemouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agenda 04 10 b1 b2Document3 paginiAgenda 04 10 b1 b2spreemouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Do Now:: April 8, 2014Document3 paginiDo Now:: April 8, 2014spreemouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multiple Sources Vialogues Quizlets: Synthesize InformationDocument3 paginiMultiple Sources Vialogues Quizlets: Synthesize InformationspreemouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sajc h2 Physics Summary Notes (All Topics)Document43 paginiSajc h2 Physics Summary Notes (All Topics)AjathShatruRajuÎncă nu există evaluări
- AB C D E: Direction of MovementDocument2 paginiAB C D E: Direction of MovementKamrul Hasan SagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Caculation Step MotorDocument10 paginiCaculation Step MotorIgnacio LascurainÎncă nu există evaluări
- MasteringPhysics - Assignment 5 - Forces Part OneDocument6 paginiMasteringPhysics - Assignment 5 - Forces Part OneStrange Sht100% (1)
- Work and Energy Practice QuestionsDocument3 paginiWork and Energy Practice QuestionsApex InstituteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamics of Rigid Bodies-Lecture 1Document4 paginiDynamics of Rigid Bodies-Lecture 1Jaya Mae Mañago0% (1)
- JEE Mains Q.bank Circular MotionDocument63 paginiJEE Mains Q.bank Circular MotionTapankumar Sanyal50% (4)
- Free Falling ObjectsDocument18 paginiFree Falling ObjectsLauro DelarosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motion of Charged ParticleDocument27 paginiMotion of Charged ParticleGurvir SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circular Motion Problems: Kinematic: A V R ADocument7 paginiCircular Motion Problems: Kinematic: A V R AAshley De Leon100% (1)
- 2019 Book PrinciplesOfMechanicsDocument179 pagini2019 Book PrinciplesOfMechanicsJimena OrthÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLL Science 8 Q1 2022 2023Document12 paginiDLL Science 8 Q1 2022 2023Hakimah C. CauntonganÎncă nu există evaluări
- NSO Class 11 PCM Solved Sample PaperDocument10 paginiNSO Class 11 PCM Solved Sample PaperMurtaza LokhandwalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics 101: Fall 2003 Session - General InformationDocument4 paginiPhysics 101: Fall 2003 Session - General InformationMAnohar KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics430 Lecture23Document17 paginiPhysics430 Lecture23André LuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Set ForceAndAccelerationV01Document2 paginiProblem Set ForceAndAccelerationV01Benedick Jayson P. Marti100% (1)
- Universal Gravitation LawDocument11 paginiUniversal Gravitation Lawanurag3069Încă nu există evaluări
- Dynamics & Statics: Previous Year Questions From 2020 To 1992Document17 paginiDynamics & Statics: Previous Year Questions From 2020 To 1992Subhay kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inverse Dynamics PDFDocument8 paginiInverse Dynamics PDFNaško JanežÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gravitation 150820160911 Lva1 App6892 PDFDocument22 paginiGravitation 150820160911 Lva1 App6892 PDFAshutosh Kumar SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parul University: Subject: PHYSICS Semester: I - Academic Year 2017-18Document1 paginăParul University: Subject: PHYSICS Semester: I - Academic Year 2017-18Trilok AkhaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uploads545454543371chapter 6 Practice Problems Review and Assessment 2 .PDF 2Document28 paginiUploads545454543371chapter 6 Practice Problems Review and Assessment 2 .PDF 2shers xtrustxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Em Ut5Document17 paginiEm Ut5david josephÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 KinematicDocument11 paginiChapter 2 KinematicTutor_KLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fortnightly Sub Test-1A (C-9) Phase-I - Science (14-05-2021)Document4 paginiFortnightly Sub Test-1A (C-9) Phase-I - Science (14-05-2021)I AM KIM TAEHYUNG50% (2)
- Analisis Distribusi Kecepatan Dan Sedimen Pada Tikungan 55° Saluran Terbuka Tampang Segi EmpatDocument8 paginiAnalisis Distribusi Kecepatan Dan Sedimen Pada Tikungan 55° Saluran Terbuka Tampang Segi EmpatIsmorel IsmorelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spectrum Physics - May 2016Document100 paginiSpectrum Physics - May 2016Popovici DraganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Single VS Double Leg Countermovement Jump TestsDocument8 paginiSingle VS Double Leg Countermovement Jump TestsGiselle Andrea Naranjo VillateÎncă nu există evaluări