Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Assignment 3 3
Încărcat de
api-236083981Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Assignment 3 3
Încărcat de
api-236083981Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Assignment 3.
2
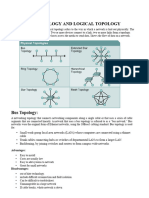
Topology is the mathematical study of shapes and spaces. It is a major area of mathematics concerned with the most basic properties of space, such as connectedness, continuity and boundary. It is the study of properties that are preserved under continuous deformations including stretching and bending, but not tearing or gluing. The five types of physical topology are: point to point, bus, star, ring or circular, mesh, and tree. Advantages: Star Topology Better performance: star topology prevents the passing of data packets through an excessive number of nodes. At most, 3 devices and 2 links are involved in any communication between any two devices. Although this topology places a huge overhead on the central hub, with adequate capacity, the hub can handle very high utilization by one device without affecting others. Isolation of devices: Each device is inherently isolated by the link that connects it to the hub. This makes the isolation of individual devices straightforward and amounts to disconnecting each device from the others. This isolation also prevents any non-centralized failure from affecting the network. Benefits from centralization: As the central hub is the bottleneck, increasing its capacity, or connecting additional devices to it, increases the size of the network very easily. Centralization also allows the inspection of traffic through the network. This facilitates analysis of the traffic and detection of suspicious behavior. Disadvantages: Star Topology High dependence of the system on the functioning of the central hub. Failure of the central hub renders the network inoperable. There is central server dependency. Expensive to purchase.
Advantages: Bus Topology Ease of installation. Simple and cheap. Minimizes the amount of cable needed to connect the network. Disadvantages: Bus Topology If the main cable fails, all the other sources will die. Reconfiguration, fault isolation and installation of new devices tend to be difficult since the network is designed to be most efficient during installation. The longer the distance covered by a signal along the shared communication line the greater the heat is produced due to energy being transformed to heat making the signal weaker the farther it travels. A fault along the shared communication line stops all transmissions in the network. Advantages: Tree Topology It is scalable. Secondary nodes allow more devices to be connected to a central node. Point to point connection of devices. Having different levels of the network makes it more manageable hence easier fault identification and isolation. Disadvantages: Tree Topology As more and more nodes & segments are added, the maintenance becomes difficult. Maintenance of the network may be an issue when the network spans a great area. Since it is a variation of bus topology, if the backbone fails, the entire network is crippled.
The 5-4-3 rule also referred to as the IEEE way (contrary to the Ethernet way) is a design guideline for Ethernet computer networks covering the number of repeaters and segments on shared-access Ethernet backbones in a tree topology. It means that in a collision domain there should be at most 5 segments tied together with 4 repeaters, with 3 segments containing active senders. Network Operating System refers to software that implements an operating system of some kind that is oriented to computer networking. For example, one that runs on a server and enables the server to manage data, users, groups, security, applications, and other. The two types of Network Operating Systems are peer to peer, and client to server.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Computer-Communication NetworksDe la EverandComputer-Communication NetworksJames S. MeditchÎncă nu există evaluări
- Star Topology: Types of Network Topologies Ethernet Local Area Networks RouterDocument4 paginiStar Topology: Types of Network Topologies Ethernet Local Area Networks RouterNishil VijayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bus TopologyDocument6 paginiBus Topologylea_eazeÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Computer Network Is A Group of Computer Systems and Other Computing Hardware Devices That Are Linked Together Through Communication Channels To Facilitate Communication and ResourceDocument7 paginiA Computer Network Is A Group of Computer Systems and Other Computing Hardware Devices That Are Linked Together Through Communication Channels To Facilitate Communication and Resource2nablsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 89492NW TopologiesDocument25 pagini89492NW TopologiesAbdur RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Difference Between Network TypologiesDocument6 paginiDifference Between Network Typologiesشمیم نازÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group Number:-3: Team Mates NamesDocument41 paginiGroup Number:-3: Team Mates NamesManish GautamÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is A Network Operating SystemDocument8 paginiWhat Is A Network Operating SystemJay-r MatibagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic NetworkingDocument8 paginiBasic NetworkingDavid Atoroyo SikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network Topologies: and Its TypesDocument19 paginiNetwork Topologies: and Its TypesJeff Clifford LuyahanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network Topology 1Document10 paginiNetwork Topology 1anonymousÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 3 PresentationDocument15 paginiGroup 3 PresentationRaymond PunoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study About Basic of Network (Topologies) and Types of network-LAN, Man, WanDocument11 paginiStudy About Basic of Network (Topologies) and Types of network-LAN, Man, WanAnonymous aQxekTRÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topology Networks g10Document6 paginiTopology Networks g10Julie BinwagÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02 TopologyDocument4 pagini02 TopologyHailay HadushÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network Topology: Presented by Susanta MaharanaDocument18 paginiNetwork Topology: Presented by Susanta Maharanasanyasi mahakhudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical 1Document24 paginiPractical 1harishpillai1994Încă nu există evaluări
- TopologyDocument11 paginiTopologyAdilet KenesovÎncă nu există evaluări
- TopologyDocument10 paginiTopologyAmeliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CN LAB FileDocument58 paginiCN LAB FileHEERAJÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network Systems & Protocols: Task 1Document12 paginiNetwork Systems & Protocols: Task 1qwerty2711Încă nu există evaluări
- Star TopologyDocument7 paginiStar TopologyadelenyamhuriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network TopologiesDocument6 paginiNetwork TopologiesTaimoor ZubairÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advantages of A Linear Bus TopologyDocument5 paginiAdvantages of A Linear Bus Topologynirav4042Încă nu există evaluări
- Network Topologies: Lecture # 2Document21 paginiNetwork Topologies: Lecture # 2Monika RehmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network TopologiesDocument9 paginiNetwork TopologiesshijinbgopalÎncă nu există evaluări
- CN - Assignment2Document14 paginiCN - Assignment2WhatsApp statusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network TopologyDocument13 paginiNetwork TopologySara AbidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topology 1Document2 paginiTopology 1mcsm-f18-055Încă nu există evaluări
- What Is Topology or Network Topology?Document25 paginiWhat Is Topology or Network Topology?Mimi Rubia AvilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Networks Toplogys1Document9 paginiComputer Networks Toplogys1ammapetÎncă nu există evaluări
- TLE ICT 10 - Network Topologies - Activity SheetDocument7 paginiTLE ICT 10 - Network Topologies - Activity SheetGioSanBuenaventuraÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Network TopologyDocument4 paginiWhat Is Network TopologyGoldy BatraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wireless 105Document6 paginiWireless 105Cristian Rene Orozco PerezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network TopologyDocument7 paginiNetwork TopologyJayvee Puntalba CalinogÎncă nu există evaluări
- Networking Is The Practice of Connecting Multiple Devices and Computers Together in Order To Share Resources and Communicate With Each OtherDocument3 paginiNetworking Is The Practice of Connecting Multiple Devices and Computers Together in Order To Share Resources and Communicate With Each Othermumo dannÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Network TopologyDocument5 paginiWhat Is Network TopologyRohit JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- This Article Tells About, Bus and Ring Topologies With Advantages and Disadvantages of EachDocument13 paginiThis Article Tells About, Bus and Ring Topologies With Advantages and Disadvantages of EachDesai MehulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Khawaja Fareed University of Engineering and Information Technology Rahim Yar KhanDocument5 paginiKhawaja Fareed University of Engineering and Information Technology Rahim Yar KhanTrusted Coins DealerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Architecture FileDocument49 paginiComputer Architecture FileFunsuk VangduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Topology and Logical TopologyDocument3 paginiPhysical Topology and Logical TopologyNO NameÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network PDFDocument66 paginiNetwork PDFq_riusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Networks: Unit 3Document18 paginiComputer Networks: Unit 3PRIYANKÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Network Topology: Name: Neel Patel School: DCPEMS Class: 11 Sub: IT Guided: Roshni Sundrani MamDocument16 paginiTypes of Network Topology: Name: Neel Patel School: DCPEMS Class: 11 Sub: IT Guided: Roshni Sundrani MamNeel PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network TopologyDocument10 paginiNetwork TopologyLegese TusseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Network BasicsDocument29 paginiComputer Network BasicsGOPI backbencherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Networking AssignmentDocument15 paginiNetworking AssignmentabcdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final ManDocument15 paginiFinal Manmr.irfanshaikh7686Încă nu există evaluări
- Presented by Vinay Shukla Cs 3rd Year: Guided By:-Sudhanshu NayakDocument23 paginiPresented by Vinay Shukla Cs 3rd Year: Guided By:-Sudhanshu NayakVinay ShuklaÎncă nu există evaluări
- May Cse 1Document9 paginiMay Cse 1الملاك الابيضÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced NetworkingDocument15 paginiAdvanced NetworkingdisgruntledattitudeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network Technology: M.S Raza MohamedDocument8 paginiNetwork Technology: M.S Raza Mohamedrazamohamed1Încă nu există evaluări
- Assignment - Ii: Computer NetworksDocument8 paginiAssignment - Ii: Computer NetworksAashish RaghunathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topology 3Document3 paginiTopology 3mcsm-f18-055Încă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Exemplar Standard - Module 2Document166 paginiLesson Exemplar Standard - Module 2Leu NameÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network TopologiesDocument23 paginiNetwork TopologiesdendenliberoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 8 Setting Up The NetworkDocument133 paginiLesson 8 Setting Up The NetworkLeu NameÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network Topology DiagramDocument7 paginiNetwork Topology DiagramSatvik SalatÎncă nu există evaluări
- MemunaDocument6 paginiMemunajallohadrahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geology of Johannesburg ReadingDocument2 paginiGeology of Johannesburg ReadingKavish DayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of Eye Patch, Eye Shield and Pressure Dressing To The EyeDocument2 paginiApplication of Eye Patch, Eye Shield and Pressure Dressing To The EyeissaiahnicolleÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4MA0 4H MSC 20140306Document14 pagini4MA0 4H MSC 20140306HaiqaPervezÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Evaluation of The Strength of Slender Pillars G. S. Esterhuizen, NIOSH, Pittsburgh, PADocument7 paginiAn Evaluation of The Strength of Slender Pillars G. S. Esterhuizen, NIOSH, Pittsburgh, PAvttrlcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Revolution OutlineDocument8 paginiIndustrial Revolution OutlineGeraldine GuarinÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Gingerbread Man-1 EnglishareDocument40 paginiThe Gingerbread Man-1 EnglishareamayalibelulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.1 Introduction To KennametalDocument40 pagini1.1 Introduction To KennametalVig PankajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 - Part 1 Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument43 paginiChapter 1 - Part 1 Introduction To Organic ChemistryqilahmazlanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 Occupational Safety Hazards in Food Service OperationsDocument14 paginiChapter 4 Occupational Safety Hazards in Food Service OperationsStraichea Mae TabanaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ESM-4810A1 Energy Storage Module User ManualDocument31 paginiESM-4810A1 Energy Storage Module User ManualOscar SosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6.003 Homework #12 Solutions: ProblemsDocument9 pagini6.003 Homework #12 Solutions: ProblemsSamu PacurucuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1943 Dentures Consent FormDocument2 pagini1943 Dentures Consent FormJitender ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2019 - High Levels of Polypharmacy in RheumatoidDocument7 pagini2019 - High Levels of Polypharmacy in RheumatoidGustavo ResendeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1 - Statistics ProbabilityDocument3 paginiAssignment 1 - Statistics ProbabilityAzel Fume100% (1)
- Syllabus (402050B) Finite Element Analysis (Elective IV)Document3 paginiSyllabus (402050B) Finite Element Analysis (Elective IV)shekhusatavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Developing Agility and Quickness (Etc.) (Z-Library) - 66Document2 paginiDeveloping Agility and Quickness (Etc.) (Z-Library) - 66guypetro6Încă nu există evaluări
- Penetration Test & Softening PointDocument7 paginiPenetration Test & Softening PointAli M. Chehadeh100% (4)
- Topik 3 - Hazard Di Air Selangor, Penilaian Risiko Langkah Kawalan Rev1 2020 090320Document59 paginiTopik 3 - Hazard Di Air Selangor, Penilaian Risiko Langkah Kawalan Rev1 2020 090320Nuratiqah SmailÎncă nu există evaluări
- Annie Ovenden Exibition 2017Document19 paginiAnnie Ovenden Exibition 2017Vitaliy ChuenkoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Charles Haanel - The Master Key System Cd2 Id1919810777 Size878Document214 paginiCharles Haanel - The Master Key System Cd2 Id1919810777 Size878Hmt Nmsl100% (2)
- Barium SulphateDocument11 paginiBarium SulphateGovindanayagi PattabiramanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sperm Count EvaluationDocument3 paginiSperm Count EvaluationGarry Kin CamarilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nurtured Womb e BookDocument22 paginiNurtured Womb e BookSteph's Desserts100% (1)
- Cho Gsas - Harvard 0084L 11462Document503 paginiCho Gsas - Harvard 0084L 11462Claudemiro costaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pediatric Gynecology BaruDocument79 paginiPediatric Gynecology BaruJosephine Irena100% (2)
- Course On Quantum ComputingDocument235 paginiCourse On Quantum ComputingAram ShojaeiÎncă nu există evaluări
- North Central Mindanao College: Maranding, Lala, Lanao Del NorteDocument8 paginiNorth Central Mindanao College: Maranding, Lala, Lanao Del NorteAnalyn FielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Cement Chemistry and Classification BY Dr.K.RainaDocument89 paginiIntroduction To Cement Chemistry and Classification BY Dr.K.Rainakishana ramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes in Pregnancy: Supervisor: DR Rathimalar By: DR Ashwini Arumugam & DR Laily MokhtarDocument21 paginiDiabetes in Pregnancy: Supervisor: DR Rathimalar By: DR Ashwini Arumugam & DR Laily MokhtarHarleyquinn96 DrÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Field-Effect Transistor - August 1972 Popular ElectronicsDocument5 paginiThe Field-Effect Transistor - August 1972 Popular Electronicsmac9papÎncă nu există evaluări