Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
1.1 Calculations PDF
Încărcat de
Willium ThomasTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
1.1 Calculations PDF
Încărcat de
Willium ThomasDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chemistry: Topic 1.
1 Calculations
Calculating No. of Moles:
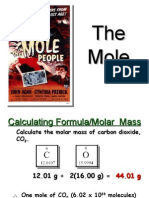
There are 3 ways to calculate the number of moles (depending on the information given): 1. Moles (of a substance) = given mass in grams/Ar or Mr 2. Moles (in a solution) = concentration x (volume in cm/1000) 3. Moles (of a gas) = volume in cm/24000cm
Empirical Formula
Gives you the moles of each atom and the ratio of moles 1. Divide given percentage/mass by r.a.m 2. Divide each answer by the smallest answer 3. If ratios are not whole numbers, multiply each answer by a small integer Example: A compound contains 39.13% carbon, 52.17% oxygen and 8.70% hydrogen. Calculate the empirical formula. Step 1 (divide by r.a.m) Carbon: 39.13/12 = 3.26 Oxygen: 52.17/16 = 3.25 Hydrogen: 8.70/1 = 8.70 Step 2 (divide by smallest) Carbon: 3.26/3.25 = 1 Oxygen: 3.25/3.25 = 1 Hydrogen: 8.70/3.26 = 2.66 Step 3 (multiply all by small integer) Carbon: 1 x 3 = 3 Oxygen: 1 x 3 = 3 Hydrogen: 2.66 x 3 = 8 .:. Empirical formula is C3H8O3
Molecular Formula
To find the molecular formula we need to use the molecular formula mass and the empirical formula mass. Molecular formula mass = empirical formula mass x an integer
Create PDF with GO2PDF for free, if you wish to remove this line, click here to buy Virtual PDF Printer
Example: A hydrocarbon with Relative Molecular Mass (Mr) of 28gmol-1 has the following composition: carbon 85.7% and hydrogen 14.3%. Calculate the hydrocarbons molecular formula. Step 1 (find empirical formula mass) Carbon: 85.7/12 = 7 Hydrogen: 14.3/1 = 14.3 Carbon: 7/7 = 1 Hydrogen: 14.3/7 = 2 .:. Empirical formula = CH2 .:. Empirical formula mass = 12 + 2 = 14g Step 2 (multiply empirical formula mass by an integer) So, we know that: Mr = 28gmol-1 Empirical formula mass = 14g So we need to find which integer multiplies 14 to give 28 .:. 2 x 14 = 28 .:. Multiply empirical formula ratios by 2 .:. Molecular formula = C2H4
Gas Calculations
Remember that 1 mole of any gas occupies 24000cm (24dm) at room temperature and pressure. Moles of a gas = volume of gas in cm/24000cm Example: Calculate the number of moles of H2 in 240cm of the gas. Moles = 240/24000 = 10-2 moles Volume of a gas = number of moles x 24000
Create PDF with GO2PDF for free, if you wish to remove this line, click here to buy Virtual PDF Printer
Example: What is the volume of 5.6 x 10-2 moles of chlorine molecules? Volume = 0.0056 x 24000 = 134.4cm Example: Calculate the volume of 10g of hydrogen gas. Moles = 10/2 = 5 moles Volume = 5 x 24000 = 120000cm = 120dm Example: Calculate the mass of 1000cm of carbon dioxide. Moles = 1000/24000 = 4.17 x 10 -2 Mass = 0.0417 x 44 = 1.8g
Volumetric Analysis
Calculations involving solutions. Can be measured as moldm-3 or gdm-3 Concentration = moles/volume (in dm) Example: What is the molarity of a solution in moldm-3 of NaOH which contains 4g of NaOH in 250cm of solution? NaOH (Mr) = 40 Moles = 4/40 = 0.1 .:. 0.1/0.25 = 0.4moldm-3
Kyoto -
Create PDF with GO2PDF for free, if you wish to remove this line, click here to buy Virtual PDF Printer
Create PDF with GO2PDF for free, if you wish to remove this line, click here to buy Virtual PDF Printer
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Chem1 2 - Calculations 1Document8 paginiChem1 2 - Calculations 1api-247243068Încă nu există evaluări
- The Mole & Avogadro's ConstantDocument16 paginiThe Mole & Avogadro's ConstantKamran ArshadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.2 The Mole Con220the20mole20conceptDocument14 pagini4.2 The Mole Con220the20mole20conceptjessy cahÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Mole Concept ExplainedDocument12 paginiThe Mole Concept ExplainedVictor OkosunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Cheat SheetDocument3 paginiChemistry Cheat SheetgaarryÎncă nu există evaluări
- As Chemistry Unit 1 NotesDocument71 paginiAs Chemistry Unit 1 NotesUmer Mohammed100% (2)
- Formula, Equations and MolesDocument4 paginiFormula, Equations and MolesyasinrÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 24 Calculations and Chemical ReactionsDocument14 pagini1 24 Calculations and Chemical ReactionsSabina SabaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Molar Gas Volume in Calculations, Moles, Gas Volumes and Avogadro's LawDocument7 paginiThe Molar Gas Volume in Calculations, Moles, Gas Volumes and Avogadro's LawkushanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculations Involving The Mole.: You Must Learn This and Be Able To Apply It in CalculationsDocument7 paginiCalculations Involving The Mole.: You Must Learn This and Be Able To Apply It in CalculationsRohaya MeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculating A and Percent Abundance Example 1: Boron Has Two Naturally Occurring IsotopesDocument9 paginiCalculating A and Percent Abundance Example 1: Boron Has Two Naturally Occurring IsotopesJessica DobrinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moles and Mole CalculationsDocument14 paginiMoles and Mole CalculationsAhmadElgindyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quick Notes: Relative Atomic MassDocument20 paginiQuick Notes: Relative Atomic Massanwar9602020Încă nu există evaluări
- CHEMISTRY PROBLEMSDocument22 paginiCHEMISTRY PROBLEMScarlÎncă nu există evaluări
- QuizDocument4 paginiQuizsololexzibÎncă nu există evaluări
- IGCSE Chemistry - CalculationsDocument27 paginiIGCSE Chemistry - CalculationsChemistryKlipz100% (14)
- Principles-of-chem-STOICHIOMETRY-pptDocument41 paginiPrinciples-of-chem-STOICHIOMETRY-pptshirayuki_sanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mol Concepts and Calculation of ChemicalDocument7 paginiMol Concepts and Calculation of ChemicalMuna LasenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculate chemical reaction yieldsDocument20 paginiCalculate chemical reaction yieldsPhi NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantitative Composition of CompoundsDocument3 paginiQuantitative Composition of CompoundsJoy CrisostomoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap 7 Mole and Chemical CompositionDocument36 paginiChap 7 Mole and Chemical CompositionAnthony AraizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ChemTeam - Combustion Analysis - Problems 1 - 10Document12 paginiChemTeam - Combustion Analysis - Problems 1 - 10David KabuyaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emp Formula Given Mass Data - HTML PDFDocument6 paginiEmp Formula Given Mass Data - HTML PDFesn_kÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry 1.2 NotesDocument13 paginiChemistry 1.2 NotescheeheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculating Chemical QuantitiesDocument2 paginiCalculating Chemical Quantitiesloli XxxxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 Chemical Calculations Calculat PDFDocument37 paginiChapter 5 Chemical Calculations Calculat PDFAbdullah Sabry AzzamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 1 - Topic 3 Lecture 4 (The Mole Concept)Document23 paginiModule 1 - Topic 3 Lecture 4 (The Mole Concept)Yvonne RagguettÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moles and Stoich-07 PDFDocument16 paginiMoles and Stoich-07 PDFNabila Hanim100% (1)
- 1.2 NotesDocument15 pagini1.2 NotesCallie Jia LiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap1 StoichiometryDocument42 paginiChap1 StoichiometryAndré QianÎncă nu există evaluări
- MARTINEZ Ideal Gas and Polytropic ProblemDocument25 paginiMARTINEZ Ideal Gas and Polytropic Problemyeng botz0% (1)
- Composition Stoichiometry ProblemsDocument51 paginiComposition Stoichiometry ProblemsIsabel Velan ViernesÎncă nu există evaluări
- WuzibDocument2 paginiWuzibJammellia WilliamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Fixed Quantity of Gas at 21Document8 paginiA Fixed Quantity of Gas at 21nonoytagupa3Încă nu există evaluări
- 1ST 2ND Quarter - Problems Gen ChemDocument7 pagini1ST 2ND Quarter - Problems Gen ChemJayebriel YabutÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 3 StoichiometryDocument45 paginiLecture 3 StoichiometryAndrew LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 1Document9 paginiProblem 1Prince Isaiah JacobÎncă nu există evaluări
- '16-'17-1T-CHEM 5 PtsDocument21 pagini'16-'17-1T-CHEM 5 PtsLorenz BerroyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Titration LabDocument4 paginiTitration Labsanique peterkinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revision of KS4 Calculations in Chemistry For KS5 WorksheetDocument6 paginiRevision of KS4 Calculations in Chemistry For KS5 WorksheetniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet Revision Calculations ks5Document6 paginiWorksheet Revision Calculations ks5James YangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Important Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th Mole Concept and Stoichiometry ADocument6 paginiImportant Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Aspurohit1991100% (1)
- Atkkkkkkkk BaruuuuuDocument29 paginiAtkkkkkkkk BaruuuuuSavira AÎncă nu există evaluări
- ChemTeam - Assorted Gas Law Problems 26-50Document13 paginiChemTeam - Assorted Gas Law Problems 26-50Koh Jiun AnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Set - Ideal Gas LawDocument12 paginiProblem Set - Ideal Gas LawJakie UbinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 9 - The Mole (Part-1)Document3 paginiChapter 9 - The Mole (Part-1)Mihika ShethÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHEM115 Chapt3Document41 paginiCHEM115 Chapt3Abdullah JadidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 2 StoichiometryDocument52 paginiLecture 2 StoichiometryHiep NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3Document7 paginiChapter 3Shafiqah SamsuriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 2 NotesDocument15 paginiTopic 2 NotesrehanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2011 Stoichiometry Test MEMODocument4 pagini2011 Stoichiometry Test MEMOJackson MakgolengÎncă nu există evaluări
- MATTER (1.2 Mole Concept)Document102 paginiMATTER (1.2 Mole Concept)Nor AfidahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stoich AnsDocument23 paginiStoich AnsNaze TamarayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Percent Composition of CompoundsDocument15 paginiPercent Composition of CompoundsAlicia M. GordonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Composition of Substances and SolutionsDocument20 paginiComposition of Substances and SolutionsBante yamiral WondimeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap 9: The Mole (Part 1)Document5 paginiChap 9: The Mole (Part 1)Atif Baloch28Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 10 - Chemical QuantitiesDocument44 paginiChapter 10 - Chemical Quantitiesapi-256257174Încă nu există evaluări
- As Practical 14 - Indirect Enthalpy ChangeDocument3 paginiAs Practical 14 - Indirect Enthalpy ChangeWillium ThomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- As Practical 13 - Direct Enthalpy Change 2Document1 paginăAs Practical 13 - Direct Enthalpy Change 2Willium ThomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- SIIIP Awards EoI FormDocument2 paginiSIIIP Awards EoI FormWillium ThomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revision Time ExampleDocument9 paginiRevision Time Exampleabdee95Încă nu există evaluări
- User data with names and passwordsDocument2 paginiUser data with names and passwordsWillium Thomas0% (1)
- Srilanka Exams Edexcel Important Notice MathematicsDocument2 paginiSrilanka Exams Edexcel Important Notice MathematicsWillium ThomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5090 O/L Biology Classified PDFDocument2 pagini5090 O/L Biology Classified PDFWillium Thomas100% (1)
- Frog has 2 legs and a queen girlfriendDocument1 paginăFrog has 2 legs and a queen girlfriendWillium ThomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research TopicsDocument7 paginiResearch TopicsWillium ThomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chess Problems For You..Document19 paginiChess Problems For You..Willium ThomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Secondary Education 1Document16 paginiSecondary Education 1Willium ThomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Female Reproductive SysDocument3 paginiFemale Reproductive SysWillium ThomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mid Year ExaminationDocument25 paginiMid Year ExaminationJue MayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tribology of PolymersDocument8 paginiTribology of Polymerssuman AcharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- IB MYP Chemistry Topic Coverage Map by ConceptDocument6 paginiIB MYP Chemistry Topic Coverage Map by ConceptSiddhant ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Absolute Virtual Instrument TCHDocument6 paginiAbsolute Virtual Instrument TCHNAdreaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vmts Jee Full Test 5 Question Paper & Answer KeyDocument14 paginiVmts Jee Full Test 5 Question Paper & Answer Keyharshit pandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Predicting Products of Chemical Reaction PDFDocument1 paginăPredicting Products of Chemical Reaction PDFJennifer LomboyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liquid - Liquid ExtractionDocument27 paginiLiquid - Liquid ExtractionRob LadrillonoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CM1401 NotesDocument33 paginiCM1401 NotesTeo Jia Ming NickolasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Process Design of Cooling Towers PDFDocument36 paginiProcess Design of Cooling Towers PDFFELIPE DURANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Driving Equilibria: Dean-Stark Trap: Science Education CollectionDocument2 paginiDriving Equilibria: Dean-Stark Trap: Science Education CollectionLJ RBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Burners HandbookDocument47 paginiIndustrial Burners HandbookLeydi HernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Incinerator Bms Training July 2015Document33 paginiIncinerator Bms Training July 2015mir_zarrarÎncă nu există evaluări
- EPA Method 3101Document3 paginiEPA Method 3101skrim240Încă nu există evaluări
- Cathodic Protection Installation DetailsDocument12 paginiCathodic Protection Installation Detailsaldeto71Încă nu există evaluări
- Zirconium Information Center Zirconium Information Center Properties, Applications and Research Properties, Applications and ResearchDocument6 paginiZirconium Information Center Zirconium Information Center Properties, Applications and Research Properties, Applications and ResearchLai Wei KhangÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Law of Thermodynamics Updated Summer 2021Document15 paginiFirst Law of Thermodynamics Updated Summer 2021Khalid Mohamed AbdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- FAQDocument6 paginiFAQSoma Shekar LÎncă nu există evaluări
- PEk 3Document10 paginiPEk 3Rajesh ChowdhuryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Determination of Indiactor Constant of Bromocresol GreenDocument3 paginiDetermination of Indiactor Constant of Bromocresol GreenShouvik MitraÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Perfect Tool For Teaching Laboratories and Routine AnalysisDocument2 paginiThe Perfect Tool For Teaching Laboratories and Routine Analysisvsinisa1Încă nu există evaluări
- Microstructural Evolution and Strengthening in 17-4 PH Stainless Steel after Long-Term AgingDocument10 paginiMicrostructural Evolution and Strengthening in 17-4 PH Stainless Steel after Long-Term AgingjlplazaolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit10 Fruit BatteryDocument4 paginiUnit10 Fruit BatteryZyrine Geneta DiodocoÎncă nu există evaluări
- GAC Regeneration Via FentonDocument235 paginiGAC Regeneration Via FentonNelson EnviromatchÎncă nu există evaluări
- Out PDFDocument211 paginiOut PDFAbraham RojasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air Cycle Refrigeration SystemsDocument12 paginiAir Cycle Refrigeration SystemsginupaulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flashcards - Equilibrium in Chemistry FlashcardsDocument5 paginiFlashcards - Equilibrium in Chemistry Flashcardskitty2911Încă nu există evaluări
- Flow CoefficientDocument1 paginăFlow Coefficienthml2827Încă nu există evaluări
- Test Bank For Organic Chemistry Structure and Function 6th Edition VollhardtDocument15 paginiTest Bank For Organic Chemistry Structure and Function 6th Edition Vollhardtverawinifredtel2Încă nu există evaluări
- QwertyDocument3 paginiQwertyAaron AldoverÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 Question Bank Welding EngineeringDocument5 paginiUnit 1 Question Bank Welding EngineeringSayiram GÎncă nu există evaluări