Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Guidelines For Formulation of Project Proposals For Hand Made Paper
Încărcat de
Ramesh BobbaDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Guidelines For Formulation of Project Proposals For Hand Made Paper
Încărcat de
Ramesh BobbaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
10/30/13
Guidelines for Formulation of Project Proposals for Hand Made Paper
Guidelines for Formulation of Project Proposals for Hand Made Paper
Introduction Ever since man has been on earth he has made use of the materials around him. As numbers increased the need to communicate became apparent and language was born. Inevitably people began to look for ways both of preserving their ideas and culture and of passing information to others without having to meet face to face. The written word had arrived. The Egyptians started with papyrus in 4000 B.C . but true paper made from indivudual fibres did not appear until about 105 A.D. when the C hinese made some from mulberry flex, hemp and cotton, Tsai Lun who made paper from mulberry is considered the father of paper. However there archeological evidence shows that people were writing letter in India on paper made from cotton that has been well beaten together in 327 A.C . Handmade paper making is one such village industry that originated before independence when all village industries took part in swadeshi movement under the inspiration of Mahatma Gandhi. Handmade paper units can be as small as of 50 kg per day. It would be within the reach to set up such unit at many places. This would not only help in increasing the production of paper but also bring uplift of the weaker section of the society. The raw material for making hand made paper could be cotton linter, tailor cuttings, hosiery waste, bast fiberes (jute/ hemp etc), wheat straw, rice straw, bagasse, cotton stalk, grasses, waste paper etc. These raw materials are easily available in villages. The technology for making handmade paper includes simplicity of operation, low cost of installation and the same equipment can produce any and many varieties of hand made paper. This industry has the privilege or exemption from excise duty and have no restriction on the use of electric power What is paper and board? Paper is generally defined as a single ply, flat material, varying in density and material content according to end use. Paper is a cellulose material amended with different additives, which form a cohesive sheet with desirable paper qualities. Paper can be made from many different plants, which contain adequate amounts of cellulose fibres. Board is defined as a multiply bound material, which normally has a greater density than the paper. The cellulose, in the strong and durable form of elongated tubular fibres is the basic substance of paper. Paper can be made from many different plants which contain adequate amount of cellulose fibres. How paper is made? In paper manufacturing the fibrous portion of the plants are reduced to pulp by chemical or biological action followed by mechanical process of grinding. Paper is made by deposition, from a dilute water suspension of pulp, an even layer of cellulose fibre on fine screen that permits the water to drain through but retains the intermingled particles of cellulose. This layer of fibres, removed from the screen and finally pressed and dried, becomes a sheet with cohesive strength and associated properties that we recognize as paper. The characteristic quality of the paper produced depends on the colour, length, diameter, flexibility, strength and other related properties of the fibres used. Fibres used in paper making Seed hair fibre- cotton, silk-cotton, hemp, jute, flex etc. Stem fibre - corn, sugarcane, bamboo, straw etc. Leaf fibre aloe fibre, pineapple leaf fibre, palm etc. Fruit fibre coconut Wood fibre spruce, cedar, maple etc. Waste papers shredded currency waste, office records, press cuttings etc. The principal factors that determine whether a plant shall or shall not be used in manufacture of paper are suitability of fibre, dependability of supply, cost of collection, transportation and preparation and tendency to deteriorate in storage. Paper Characteristics & Paper products The range of paper and board products can be classified into types and grades: types relate to the paper or board machine design, and the grades are the function of the end use of the product and the choice of materials. The types, grades and uses of papers manufacture depending on its fibre characteristics such as strength and optical characteristics, processing methods and type of paper machines and their configuration. The types of paper or board can vary according to end- use. There are four distinct grades of paper and board. Machine glazed (M.G.) paper and Board This grade of paper or board is obtained by pressing the moist material firmly against the surface of a drying calender. The moist paper adheres to the cylinder surface until it is dry enough for separation. Creped papers The M.G. machine can be used to produce creped paper. This can be done with addition of a scraping blade, which removes the paper from the cylinder before it is dry enough for natural separation. The most important area of paper application are as writing paper, cards, boards etc. (Newsprint, coated printing & writing, un-coated printing &
capart.nic.in/scheme/guidelines_hand_paper_frame.html 1/4
10/30/13
Guidelines for Formulation of Project Proposals for Hand Made Paper
writing, tissue & sanitary, packaging & industries and boards etc.) The social, intellectual and industrial progress of a modern society is interwoven with the usage of paer and paperboards. The global paper industry is capital intensive and resource based. Paper manufacture is one of the most energy intensive industrial processes. In India, total indigenous production of paper and paper products are 4.1 million tons in 1999-2000 by 380 paper mills. The current per capita consumption of paper in India is 3.8 kg. and is expected to more than double at 7.9 kg paper and paper products will increase at a rate of 5% at every phase of human development. The hand made paper production is an age-old process in India. At present there are about 435 units producing 12,000 MT of paper, board and paper fancy items by providing employment to 7000 persons. The usual paper making process in a mill is highly polluting. The black liquor generated by pulping, bleach and boiler emission are great problem for the paper industry, while hand made paper (HMP) making is based on a clean process with negligible or very litter pollution. Thus HMP industry is a sunrise industry with a remarkable increase of about 150% in annual production. The Holistic Approach In Paper Production By MCRC Shri AMM Murugappa C hettiar Research C enter (MC RC ), C hennai was established in 1977 with a division engaged in research on photosynthesis and energy at Tharamani, C hennai 600 113. MC RC has developed energy efficient papers from alternative cellolosic material. MC RC paper technology aimed to bridge the gaps in conventional paper making processes. It is environment friendly; pollution free and does not lead to depletion of natural resources. Thus paper as a product essential to provide literacy, education and information, which in turn demands the process of technology development and this development centres on environment issues like deforestation and pollution problem. Thus there is a great demand to develop new technologies to produce paper without disturbing trees, forests and environment. MC RC use various raw materials like Banana stem, waste-cotton, matgrass, bagasse and other agricultural residues like palmarosea grass. No sodium hydroxide is used in manufacture and natural dyes are used for colouring. Thus MC RC eco-friendly paper technology has been experimented successfully as commercial enterprises. The paper produces is being used for different purposes by converting the paper into paper products. Objectives The main focus of the project should be Motivation, Training, Information dissemination, Technical and Financial assistance for setting up of eco-friendly paper processing centres in the rural areas. Eligibility Voluntary Organisation working in rural areas with a legal status of a society registered for 3 years under Societies Registration Act XXI, 1860 or any corresponding state Act or a Trust registered under Indian Trust Act, 1882 or the C haritable and Religious Trusts Act, 1920 will be eligible for financial assistance subject to the condition that: The The The The VO VO VO VO should should should should have a nationalised Bank or Post Office A/c for last three years. be working in rural areas, even if the Hqrs. are in urban area. possess Permanent Account Number (PAN) of Income Tax Department. not be under funding restriction.
Preparation and submission of project proposal The project proposal should be prepared on the lines of the format prescribed by C APART. The objectives of the proposal should be precise and well defined indicating the likely benefits to be derived and specified the category of beneficiary. The action programmes and method of implementation of the activities should be as detailed as possible and clear outlining the work allocation and time schedule of each activity. Two copies of the project proposal complete in all respects with organizational profile, certified photocopy of Memorandum and Bye-laws and Registration C ertificate, Audited Statement of Accounts, Annual Report, Bank/Post Office Accounts of last three years and Permanent Account Number of the Organization should be forwarded to C APART Regional C ommittees for project costing upto 20 lakhs and projects with a budget above this are to be forwarded to the Head Quarters in New Delhi. Service requirements 1. Water 1000 lit./ day 2. Power 80 H.P. 3. Building 2,000 sq. ft. 4. Drying shed 3000 sq. ft. 5. Employment 20 persons/ shift Methodology and process of manufacturing Hand Made Paper C ellulosic materials like waste cotton, waste banana stem, mat grass, Palmarosa grass and other agriculture residues are to be collected. These materials have to be collected from different villages. Mixed fibres raw materials
capart.nic.in/scheme/guidelines_hand_paper_frame.html 2/4
10/30/13
Guidelines for Formulation of Project Proposals for Hand Made Paper
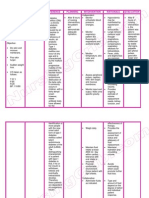
are sorted out to remove any non fibrous and metallic portion. Cutting Sorted fibrous raw material is cut into small pieces (1-3 cm). A handmade chaff cutter can be used for this purpose. Dusting/ washing The cut pieces are dusted and washed to remove dust and dirt particles. The dusting can be done by mechanical duster or by beating the material by hand. Digestion The fibrous raw materials are cooked with caustic soda for 2-3 hours in mild steel vessel (Digester). The pulp is then washed thoroughly with water to get rid of traces of alkali and dissolved matter Pulping The strips are then put into a treatment vessel and processed with microbes. The bio treated strips are then fed into a beater along with water and sized additives to form a pulp type mixture. This unbleached pulp may need to be treated with non-polluting bleaching agents. The chemicals (rosin and alum) and colour may be added to improve the pulp quality as per requirement. VAT processing The pulp mixture is spread on a net, which enables the water present to settle down and form a paper sheet. These paper sheets are blotted on a woolen/ gada cloth. Similarly other paper sheets are also mounted and eventually all the sheets are collected in a heap. Cylinder Mould Processing C ards and boards are processed through cylinder mould machine for pulp formation on to the wire-mesh and then in cylinder mould drum. Sun light drying Water is drawn out from these sheets with the help of a hydraulic press and then these sheets are detached for the cloth and left to dry in sun light. Calendering After drying these sheets are passed through two heavy rollers or and calendering in between two metal sheets for polishing the papers or boards. Cutting Lastly the sheet is cut to the required size and shape as required for marketing. The paper thus made can be further converted into bags, box, files and pads etc. depending on the order to be received to the unit. Three production units can supply 25% of paper and cards to the conversion unit. Depending on the market order the unit can operate on converting paper into various products. Equipments The equipments and machines required includes (i) Rag C hoppers (ii) Beaters (iii) Pulp tanks (iv) calendar machines (v) Agitators (vi) Hydraulic Press (vii) C ylinder mould, vat power driven machine etc. Economics For producing, 40 tonnes of hand made paper annually the capital investment required is about Rs. 4 lakhs and the working capital Rs. 1.25 lakhs. The unit is expected to earn a profit of Rs. 1 lakhs per year and employ 20 persons. The project proposal may be submitted under ARTS format to the Regional C ommittees of C APART. C ollection of cellulosic material Sorting out for quality control Beater pulping processing with water (30 minutes) Sizing with natural additives (rosin, Alum, C hina clay, Talcum power) C ylinder mould processing Vat processing (VAT/ AUTOVAT method) Paper boards/ sheets Blotting on C loth Sun light drying Screw pressing Paper cutting C alendering/ polishing
capart.nic.in/scheme/guidelines_hand_paper_frame.html 3/4
10/30/13
Guidelines for Formulation of Project Proposals for Hand Made Paper
Packaging Market supply Production conservation Market supply Advantages of MCRC s Process in Paper Making In conventional paper making process, cellulose is obtained from trees (deforestation) after chemical and mechanical treatment with the result that only 30-40% of the stating material is useful for paper making, whereas in MC RC paper process 85-90% of cellulose is obtained from tree usufructs, followed by microbial/ mechanical pulping by using non polluting additives and dyes from natural sources. The advantages of MCRC s paper making technology is outlined as below: Technology Souorce Raw material Percentage of raw available for paper Treatment Energy Water (M)/ tonne Effluent PRODUC T C onventional papers Tree C ellulose 35 Mechanical/ chemical High 1000 Pollution C hemical treated MC RC papers Tree usufructs C ellulose 85-90 Microbial/ mechanical Low 25 Pollution free Green Product
material
Project Viability/ Cost Benefit Analysis Production capacity 100 kg/ day (3 ton/ month) Employment (regular) 20 women/ shift E.B. Power 80 HP Water 1000 L/day Project cost Rs. 100,000 Building 3000 sq. ft. drying shed & 2000 sq. ft. working space with thatched roof are required. Expenditure Raw material (a) (Banana stem, cotton, agri residues Rs. 1300.00 130 kg / day @ Rs. 10/ kg.) (b) Additives (True wax, Talcum powder, Rs. 260.00 Starch & Alum:(for 130 kg. raw material @ Rs. 2 kg. (c) Labour; skilled (trained) 6 persons @ Rs. 60) Rs. 360.00 (d) Power charges (80 HP, 40 units @ Rs. 5) (e) Transport, maintenance, overheads & administration Rs. 100.00 Total production cost / 100 kg. paper Rs. 2,200.00 100 kg. paper. Expected sale (Rs. 40/kg.) of 100 kg. Rs. 4,000.00 Net income day Rs.1,780.00
Depending upon the hand made papers design and thickness the sale value may increase. If the conversion of paper into products like greeting cares, visiting cards paper bags and office files may add the sale value of the papers produced. Contact Agencies 1. Any of KVIC units in the region. 2. Dr. Vatsala, MC RC , Turanani, C hennai 3. Dr. H. Sudershan, VGKK, BR Hills, C hamraj Nagar (Distt.), Karnataka. 4. Aurobindo Ashram, Auroville, Pondicherry.
capart.nic.in/scheme/guidelines_hand_paper_frame.html
4/4
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Ms-09-Development of A Paper Recycling ProcessDocument7 paginiMs-09-Development of A Paper Recycling ProcesshidaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Papermaking From Recycled Materials, Including Pop-up Greeting Cards With Circuitry.De la EverandPapermaking From Recycled Materials, Including Pop-up Greeting Cards With Circuitry.Încă nu există evaluări
- Handmade Papermaking in IndiaDocument8 paginiHandmade Papermaking in IndiajopaudecruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sustainable Innovations in Recycled TextilesDe la EverandSustainable Innovations in Recycled TextilesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maulana Azad National Institute of Technology (A Institute of National Importance) BHOPAL-462007Document24 paginiMaulana Azad National Institute of Technology (A Institute of National Importance) BHOPAL-462007Prakhar KulshreshthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handbook of Paper and Paperboard Packaging TechnologyDe la EverandHandbook of Paper and Paperboard Packaging TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction (1) Pfr...... - 113301Document47 paginiIntroduction (1) Pfr...... - 113301Rani JaiswalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sustainable Innovations in Textile Chemical ProcessesDe la EverandSustainable Innovations in Textile Chemical ProcessesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper Making ProcessDocument16 paginiPaper Making ProcessWinwin07Încă nu există evaluări
- Environmental Footprints of Recycled PolyesterDe la EverandEnvironmental Footprints of Recycled PolyesterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Usreenidhipapaers ReportDocument13 paginiUsreenidhipapaers ReporttriumphswamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Detailed Project Report ON Handmade Paper Manufacturing & Conversion UnitDocument38 paginiA Detailed Project Report ON Handmade Paper Manufacturing & Conversion UnitNaga PrabhasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ecofriendly ProductionofpaperproductsDocument11 paginiEcofriendly Productionofpaperproductsmikaela.pagatpatanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper BagsDocument36 paginiPaper BagsSagar Shinde100% (3)
- Ms 09 DevelopmentofapaperrecyclingprocessDocument7 paginiMs 09 DevelopmentofapaperrecyclingprocessHarsh PawarÎncă nu există evaluări
- StudyReport Paper Recycling Research Philippines - Work ResultsDocument40 paginiStudyReport Paper Recycling Research Philippines - Work ResultsMora Joram89% (9)
- TOPIC 15 Paper (Note)Document7 paginiTOPIC 15 Paper (Note)Kaynine KikoÎncă nu există evaluări
- TNPLDocument34 paginiTNPLpriyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PapermakingDocument13 paginiPapermakingoyadieyeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Index: TopicDocument36 paginiIndex: TopicAliArababadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eco-Friendly Handmade Paper Making: Shri AMM Murugappa Chettiar Research CentreDocument0 paginiEco-Friendly Handmade Paper Making: Shri AMM Murugappa Chettiar Research CentreAnand RasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ecofriendly ProductionofpaperproductsDocument11 paginiEcofriendly ProductionofpaperproductsMarylyn MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bplan Paper RecyclingDocument18 paginiBplan Paper RecyclingSwathi Bollineni100% (1)
- History: Paper Making ProcessDocument4 paginiHistory: Paper Making Processxebelab379Încă nu există evaluări
- Paper No.: 12 Paper Title: Food Packaging Technology Module - 05: Paper and Paper Based Packaging MaterialsDocument10 paginiPaper No.: 12 Paper Title: Food Packaging Technology Module - 05: Paper and Paper Based Packaging MaterialsTrishitman DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper Mill PDFDocument39 paginiPaper Mill PDFpgn.exl0% (1)
- PRP Final File According To The Irslan AkramDocument20 paginiPRP Final File According To The Irslan AkramarslanakramrajputÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handout 4C - DiagramDocument4 paginiHandout 4C - DiagramHong NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review Related Literature YawwasDocument74 paginiReview Related Literature Yawwassherfa abdusalamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper StoryDocument2 paginiPaper StoryHans MooreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Make Your Own PaperDocument4 paginiMake Your Own PaperfembarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper Vending MachineDocument67 paginiPaper Vending MachineLawrenze Morales78% (9)
- Project On Cost Analysis of Setting Up A Waste Paper Recycling UnitDocument15 paginiProject On Cost Analysis of Setting Up A Waste Paper Recycling UnitPrakhar KulshreshthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synopsis Diploma in Mechanical Engineering: 1) Name of The StudentDocument8 paginiSynopsis Diploma in Mechanical Engineering: 1) Name of The StudentRushikesh PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2Document11 paginiChapter 2MarkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business Plan - Paper RecyclingDocument6 paginiBusiness Plan - Paper RecyclingSuemi CansinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Report On Kraft Paper From Waste Paper (20 TPD)Document7 paginiProject Report On Kraft Paper From Waste Paper (20 TPD)EIRI Board of Consultants and PublishersÎncă nu există evaluări
- AsdDocument3 paginiAsdTrần Quốc HuyÎncă nu există evaluări
- AvinashDocument72 paginiAvinashsaikripa121Încă nu există evaluări
- Sample Innovation PaperDocument22 paginiSample Innovation PaperMelcorr N. MontesclarosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research About Paper RecyclingDocument7 paginiResearch About Paper Recyclingxoopgxplg100% (1)
- Business Plan, Paper Recycling PlantDocument22 paginiBusiness Plan, Paper Recycling PlantSucesor66650% (4)
- Chapter One: Plant Design and Economics Project For Fifth Year Chemical Engineering Students On Waste Paper RecyclingDocument28 paginiChapter One: Plant Design and Economics Project For Fifth Year Chemical Engineering Students On Waste Paper RecyclingAwokeÎncă nu există evaluări
- PapTile Inc. - ABSTRACTDocument2 paginiPapTile Inc. - ABSTRACTJaycee SalazarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ielts ReadingDocument2 paginiIelts ReadingTolkynÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summer Training ReportDocument81 paginiSummer Training ReportAmitTewariJr.Încă nu există evaluări
- StudyReport Paper Recycling Research Philippines - Work Results PDFDocument40 paginiStudyReport Paper Recycling Research Philippines - Work Results PDFMjhaz Chua MelgarejoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper Mill READYDocument85 paginiPaper Mill READYagility dreamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- With A Very Bright Morning To One and All Respected Sir and All My Dear Friends Gathered HereDocument13 paginiWith A Very Bright Morning To One and All Respected Sir and All My Dear Friends Gathered HereLakshyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper Recycling Research ch1.3Document6 paginiPaper Recycling Research ch1.3Dela Torre, Emilio Joseph N.Încă nu există evaluări
- Case Study 3 PDFDocument33 paginiCase Study 3 PDFSrinu KakolluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter - I: 1.1. About The StudyDocument32 paginiChapter - I: 1.1. About The StudyAjay VickyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assingnment Individual: Nama: No Pelajar: Kod Kursus: Mkt539 (Brand Management) Semester 4 Pensyarah MissDocument13 paginiAssingnment Individual: Nama: No Pelajar: Kod Kursus: Mkt539 (Brand Management) Semester 4 Pensyarah Missalviana andrewÎncă nu există evaluări
- PAPER Work Life Balance of Employees at Karanja Industries PVT LTD BidarDocument12 paginiPAPER Work Life Balance of Employees at Karanja Industries PVT LTD BidarDr Bhadrappa HaralayyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper Industry Project Report Full ProjectDocument49 paginiPaper Industry Project Report Full ProjectManjula Ashok100% (2)
- Paper Recycling: Academic Reading Strides Ielts TrainingDocument2 paginiPaper Recycling: Academic Reading Strides Ielts TrainingStrides for EnglishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper MacheDocument2 paginiPaper MacheAkiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper & PulpDocument22 paginiPaper & Pulplorenavila401Încă nu există evaluări
- DAIRY FARM (BUFFALO) PROJECT REPORT FOR BANK LOAN - Animal Husbandry PDFDocument8 paginiDAIRY FARM (BUFFALO) PROJECT REPORT FOR BANK LOAN - Animal Husbandry PDFRamesh Bobba58% (19)
- Mini Dairy Model Project For Ten Animal UnitsDocument6 paginiMini Dairy Model Project For Ten Animal Unitssuresh6265Încă nu există evaluări
- Fluidized Bed CombustionDocument57 paginiFluidized Bed CombustionRamesh Bobba100% (1)
- (I) Heat Transfer - Yunus ÇengelDocument935 pagini(I) Heat Transfer - Yunus ÇengelRamesh Bobba92% (13)
- Variables in The EquationDocument3 paginiVariables in The EquationfiharjatinÎncă nu există evaluări
- IBDP Physics Oxford David - Homer Course Ebook 4th Edition-2014 CH-1Document27 paginiIBDP Physics Oxford David - Homer Course Ebook 4th Edition-2014 CH-1Milek Anil KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ssi-199-22 D Vikran Dolphin Rev.1Document2 paginiSsi-199-22 D Vikran Dolphin Rev.1ANGEL ANTONIO GUTIERREZ CONTRERASÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gulfpub Wo 201805Document81 paginiGulfpub Wo 201805Patricia.PÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformational and Charismatic Leadership: The Road Ahead 10th Anniversary EditionDocument32 paginiTransformational and Charismatic Leadership: The Road Ahead 10th Anniversary Editionfisaac333085Încă nu există evaluări
- Designing The Workplace For CollaborationDocument17 paginiDesigning The Workplace For Collaborationmas zak danielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Forensics ReportDocument7 paginiComputer Forensics ReportMatias IacobuzioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sequence Analytical and Vector Geometry at Teaching of Solid Geometry at Secondary SchoolDocument10 paginiSequence Analytical and Vector Geometry at Teaching of Solid Geometry at Secondary SchoolJuan S. PalmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inner DriveDocument51 paginiInner DriveShaurya VajhulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Watt AC-DC Converters: FeaturesDocument3 paginiWatt AC-DC Converters: FeatureskofidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Etymological Wordplay in Ovid's Pyramus and ThisbeDocument5 paginiEtymological Wordplay in Ovid's Pyramus and Thisbeignoramus83Încă nu există evaluări
- Sagan WaltzDocument14 paginiSagan WaltzKathleen RoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- April FoolDocument179 paginiApril FoolrogeraccuraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intercostal Drainage and Its ManagementDocument36 paginiIntercostal Drainage and Its ManagementAnusha Verghese67% (3)
- Have Been Tried From Time To Time," As Churchill Famously Said (Third Paragraph) "?Document25 paginiHave Been Tried From Time To Time," As Churchill Famously Said (Third Paragraph) "?Aditya ThakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Declaration of Absence of Conflict of InterestDocument1 paginăDeclaration of Absence of Conflict of InterestJvhelcoronacondat CondatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan Diabetes Mellitus Type 1Document2 paginiNursing Care Plan Diabetes Mellitus Type 1deric85% (46)
- Tugas Farmasi Klinis: Feby Purnama Sari 1802036Document9 paginiTugas Farmasi Klinis: Feby Purnama Sari 1802036Feby Purnama SariÎncă nu există evaluări
- AWANA Handbook 2010-2011Document8 paginiAWANA Handbook 2010-2011carriepratchard100% (1)
- BRB Personal Care Cost Effictive Guide Formulation Edition 2019Document28 paginiBRB Personal Care Cost Effictive Guide Formulation Edition 2019Abdulrahman HamdanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Extension of MDRRMO OfficeDocument12 paginiExtension of MDRRMO OfficeJustin YuabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus EM1Document2 paginiSyllabus EM1Tyler AnthonyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evelyn Arizpe - Teresa Colomer - Carmen Martínez-Roldán - Visual Journeys Through Wordless Narratives - An International Inquiry With Immigrant Children and The Arrival-Bloomsbury Academic (2014)Document290 paginiEvelyn Arizpe - Teresa Colomer - Carmen Martínez-Roldán - Visual Journeys Through Wordless Narratives - An International Inquiry With Immigrant Children and The Arrival-Bloomsbury Academic (2014)Lucia QuirogaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cot 4 Mapeh (Health)Document15 paginiCot 4 Mapeh (Health)RELYN LUCIDOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fire and IceDocument11 paginiFire and IcelatishabasilÎncă nu există evaluări
- File Server Resource ManagerDocument9 paginiFile Server Resource ManagerBùi Đình NhuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Philippines and Singapore Trade Relations and Agreements: 1. What Leads To Said Agreement?Document11 paginiPhilippines and Singapore Trade Relations and Agreements: 1. What Leads To Said Agreement?Ayrah Erica JaimeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Python Versus Matlab: Examples in Civil EngineeringDocument32 paginiPython Versus Matlab: Examples in Civil EngineeringNiranjanAryan100% (1)
- Mechanical Energy Storage: Created by Nick StroudDocument24 paginiMechanical Energy Storage: Created by Nick StroudAli ShazanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PriceDoxy 09 September 2011Document56 paginiPriceDoxy 09 September 2011Elena OltuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0De la EverandScaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0Evaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on AI, Analytics, and the New Machine AgeDe la EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on AI, Analytics, and the New Machine AgeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (69)
- Generative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewDe la EverandGenerative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (2)
- The Toyota Way (Second Edition): 14 Management Principles from the World's Greatest ManufacturerDe la EverandThe Toyota Way (Second Edition): 14 Management Principles from the World's Greatest ManufacturerEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (121)
- SYSTEMology: Create time, reduce errors and scale your profits with proven business systemsDe la EverandSYSTEMology: Create time, reduce errors and scale your profits with proven business systemsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (48)
- Blue Ocean Strategy, Expanded Edition: How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition IrrelevantDe la EverandBlue Ocean Strategy, Expanded Edition: How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition IrrelevantEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (387)
- Lean Thinking: Banish Waste and Create Wealth in Your Corporation, 2nd EdDe la EverandLean Thinking: Banish Waste and Create Wealth in Your Corporation, 2nd EdEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (17)
- Sales Pitch: How to Craft a Story to Stand Out and WinDe la EverandSales Pitch: How to Craft a Story to Stand Out and WinEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (2)
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)De la EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (11)
- Systems Thinking: A Guide to Strategic Planning, Problem Solving, and Creating Lasting Results for Your BusinessDe la EverandSystems Thinking: A Guide to Strategic Planning, Problem Solving, and Creating Lasting Results for Your BusinessEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (80)
- The Ruler's Guide: China's Greatest Emperor and His Timeless Secrets of SuccessDe la EverandThe Ruler's Guide: China's Greatest Emperor and His Timeless Secrets of SuccessEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (14)
- Strategic Analytics: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewDe la EverandStrategic Analytics: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (46)
- The Prosperity Paradox: How Innovation Can Lift Nations Out of PovertyDe la EverandThe Prosperity Paradox: How Innovation Can Lift Nations Out of PovertyEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (5)
- Artificial Intelligence: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewDe la EverandArtificial Intelligence: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (104)
- How to Grow Your Small Business: A 6-Step Plan to Help Your Business Take OffDe la EverandHow to Grow Your Small Business: A 6-Step Plan to Help Your Business Take OffEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (62)
- A New Way to Think: Your Guide to Superior Management EffectivenessDe la EverandA New Way to Think: Your Guide to Superior Management EffectivenessEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (18)
- The 10X Rule: The Only Difference Between Success and FailureDe la EverandThe 10X Rule: The Only Difference Between Success and FailureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (289)
- 2022-2023 Price Action Trading Guide for Beginners in 45 MinutesDe la Everand2022-2023 Price Action Trading Guide for Beginners in 45 MinutesEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (4)
- How to Grow Your Small Business: A 6-Step Plan to Help Your Business Take OffDe la EverandHow to Grow Your Small Business: A 6-Step Plan to Help Your Business Take OffEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Harvard Business Review Project Management Handbook: How to Launch, Lead, and Sponsor Successful ProjectsDe la EverandHarvard Business Review Project Management Handbook: How to Launch, Lead, and Sponsor Successful ProjectsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (16)
- Play Bigger: How Pirates, Dreamers, and Innovators Create and Dominate MarketsDe la EverandPlay Bigger: How Pirates, Dreamers, and Innovators Create and Dominate MarketsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (73)
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on Managing Yourself, Vol. 2De la EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on Managing Yourself, Vol. 2Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (11)
- Elevate: The Three Disciplines of Advanced Strategic ThinkingDe la EverandElevate: The Three Disciplines of Advanced Strategic ThinkingEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (3)
- How to Write Effective Policies and Procedures: The System that Makes the Process of Developing Policies and Procedures EasyDe la EverandHow to Write Effective Policies and Procedures: The System that Makes the Process of Developing Policies and Procedures EasyEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- HBR Guide to Setting Your StrategyDe la EverandHBR Guide to Setting Your StrategyEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (18)
- Strategy Skills: Techniques to Sharpen the Mind of the StrategistDe la EverandStrategy Skills: Techniques to Sharpen the Mind of the StrategistEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5)
- Better, Simpler Strategy: A Value-Based Guide to Exceptional PerformanceDe la EverandBetter, Simpler Strategy: A Value-Based Guide to Exceptional PerformanceEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (13)
- Learn and Understand Business AnalysisDe la EverandLearn and Understand Business AnalysisEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (31)