Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Case Pres Drugs
Încărcat de
Glaizalyn Fabella TagoonTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Case Pres Drugs
Încărcat de
Glaizalyn Fabella TagoonDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
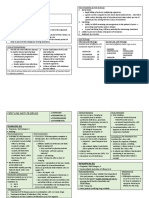
Drug Classification: Antipyretic Analgesic (nonopioid) Anti-inflammatory Antirheumatic Antiplatelet Salicylate NSAID
Pharmacologic action Analgesic and antirheumatic effects are attributable to aspirins ability to inhibit the synthesis of prostaglandins, important mediators of inflammation. Antipyretic effects are not fully understood, but aspirin probably acts in the thermoregulatory center of the hypothalamus to block effects of endogenous pyrogen by inhibiting synthesis of the prostaglandin
Indication Mild to moderate pain Fever Inflammatory conditions rheumatic fever, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis Reduction of risk of recurrent TIAs or stroke in males with history of TIA due to fibrin platelet emboli Reduction of risk of death or nonfatal MI in patients with history of infarction or unstable angina pectoris
Contraindication Contraindicated with allergy to salicylates or NSAIDs (more common with nasal polyps, asthma, chronic urticaria); allergy to tartrazine (cross-sensitivity to aspirin is common); hemophilia, bleeding ulcers, hemorrhagic states, blood coagulation defects, hypoprothrombine mia, vitamin K deficiency (increased risk of bleeding) Use cautiously with impaired renal function; chickenpox,
Side effect Nausea, GI upset, heartburn (take drug with food); easy bruising, gum bleeding (related to aspirins effects on blood clotting). Report ringing in the ears; dizziness, confusion; abdominal pain; rapid or difficult breathing; nausea, vomiting, bloody stools.
Nursing responsibility BLACK BOX WARNING: Do not use in children and teenagers to treat chickenpox or flu symptoms without review for Reyes syndrome, a rare but fatal disorder. Give drug with food or after meals if GI upset occurs. Give drug with full glass of water to reduce risk of tablet or capsule lodging in the esophagus. Do not crush, and ensure that patient does not chew SR preparations. Do not use aspirin that has a strong vinegarlike odor.
Name: Aspirin Dosage: ADULTS Minor aches and pains: 325650 mg q 4 hr. Arthritis and rheumatic conditions: 3.26 g/day in divided doses. Acute rheumatic fever: 58 g/day;
modify to maintain serum salicylate level of 1530 mg/dL. TIAs in men:1,300 mg/day in divided doses (650 mg bid or 325 mg qid). MI prophylaxis: 75 325 mg/day.
intermediary. Inhibition of platelet aggregation is attributable to the inhibition of platelet synthesis of thromboxane A2, a potent vasoconstrictor and inducer of platelet aggregation. This effect occurs at low doses and lasts for the life of the platelet (8 days). Higher doses inhibit the synthesis of prostacyclin, a potent vasodilator and inhibitor of platelet aggregation.
MI prophylaxis Unlabeled use: Prophylaxis against cataract formation with long-term use
influenza (risk of Reyes syndrome in children and teenagers); children with fever accompanied by dehydration; surgery scheduled within 1 wk; pregnancy (maternal anemia, antepartal and postpartal hemorrhage, prolonged gestation, and prolonged labor have been reported; readily crosses the placenta; possibly teratogenic; maternal ingestion of aspirin during late pregnancy has been associated with the following adverse fetal
WARNING: Institute emergency procedures if overdose occurs: Gastric lavage, induction of emesis, activated charcoal, supportive therapy.
Take extra precautions to keep this drug out of the reach of children; this drug can be very dangerous for children.
Use the drug only as suggested; avoid overdose. Avoid the use of other over-thecounter drugs while taking this drug. Many of these drugs contain aspirin, and serious overdose can occur.
Take the drug with food or after meals if GI upset occurs.
Do not cut, crush, or chew sustained-release products.
effects: low birth weight, increased intracranial hemorrhage, stillbirths, neonatal death); lactation.
Over-the-counter aspirins are equivalent. Price does not reflect effectiveness.
Drug Classification: Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) receptor antagonist Antiplatelet name:
Pharmacologic action Inhibits platelet aggregation by blocking ADP receptors on platelets, preventing clumping of platelets.
Indication Treatment of patients at risk for ischemic events history of MI, ischemic stroke, peripheral artery disease Treatment of patients with acute coronary syndrome
Contraindication Contraindicated with allergy to clopidogrel, active pathological bleeding such as peptic ulcer or intracranial hemorrhage, lactation. Use cautiously with bleeding disorders, recent surgery, hepatic impairment, pregnancy.
Side effect Dizziness, lightheadedness (this may pass as you adjust to the drug); headache (lie down in a cool environment and rest; OTC preparations may help); nausea, gastric distress (eat frequent small meals); prolonged bleeding (alert doctors, dentists of this drug use). Report skin rash, chest pain, fainting,
Nursing responsibility Provide small, frequent meals if GI upset occurs (not as common as with aspirin). Provide comfort measures and arrange for analgesics if headache occurs.
Generic Clopidogrel Brand Name: Plavix Dosages: ADULTS
Recent MI, stroke, or established peripheral arterial disease: 75 mg PO daily. Acute coronary
syndrome: 300 mg PO loading dose, then 75 mg/day PO with aspirin, given at a dose from 75325 mg once daily
severe headache, abnormal bleeding.
Drug Classification: -Anticoagulant -Low Molecular Weight Heparin GENERIC enoxaparin BRAND Lovenox NAME:
NAME:
Dosage: - DVT prophylaxis: 30 mg subcutaneously bid with initial dose soon as possible after surgery, not more than 24 hr after surgery. Continue thr oughout the postoperative period for 710 days; then 40 mg daily subcutaneously for
Pharmacol ogic action Lowmolecularweight heparin that inhibits thrombus and clot formation by blocking factor Xa, factor IIa, preventing the formation of clots.
Indication Prevention of DVT, which may lead to pulmonary embolism following hip replacement, knee replacement surgery, abdominal surgery Prevention of ischemic complications of unstable angina and nonQ-wave MI Treatment of DVT, pulmonary embolus with warfarin Prevention of DVT in medical patients who are at risk for thromboembolic complications due to severely restricted mobility during acute
Contraindication Contraindi cated with hype rsensitivit y to enoxap arin, heparin, pork products; severe thromboc ytopenia; uncontroll ed bleeding. Use cautiously with pregnanc y or lactation, history of GI bleed, spinal
Side effect bleeding. Fever, nausea, diarrhea, and fluid retention are common. Less commonly, enoxaparin can induce abnormal liver tests in the blood, suggesting mild damage to the liver, and a reduction in blood platelets and red blood cells. Mild local irritation, pain, hematoma, ecchymosis, and erythema may occur at the site of injection. Hypersensitivity reactions also may occur.
Nursing responsibility - Give drug as soon as possible after hip surgery, within 12 hr of knee surgery, and within 2 hr preoperatively for abdominal surgery. - Give deep subcutaneous injections; do not give enoxaparin by IM injection. - Administer by deep subcutaneous injection; patient should be lying down. Alternate between the left and right anterolateral and posterolater al abdominal wall. Introduce the whole length of the needle into a skin fold held between the thumb and forefinger; hold the skin fold throughout the injection. - Apply pressure to all injection sites after needle is withdrawn; inspect injection sites for signs of hematoma; do not massage injection sites. - Do not mix with other injections or infusions.
up to 3 wk may be used. -Patients undergoing abdominal surgery: 40 mg/day subcutaneously begun within 2 hr preoperatively and continued for 710 days. -Outpatient DVT treatment: 1 mg/kg subcutaneously q 12 hr. -Unstable angina and nonQ-wave MI: 1 mg/kg subcutaneously q 12 hr for 28 days. -Inpatient DVT treatment: 1.5 mg/kg subcutaneously once daily. -Prevention of DVT in high-risk medical patients: 40 mg/day subcutaneously for 611 days, has been used up to 14 days.
illnesses
tap, spinal/epi dural anesthesi a
- Store at room temperature; fluid should be clear, colorless to pale yellow. - Provide for safety measures (electric razor, soft toothbrush) to prevent injury to patient who is at risk for bleeding. - Check patient for signs of bleeding; monitor blood tests. - Alert all health care providers that patient is on enoxaparin. - Discontinue and initiate appropriate therapy if thromboembolic episode occurs despite enoxaparin therapy. .
Drug Classification: Beta- adrenergic
Pharmacologic action Unknown. A selective beta blocker that
Indication Hypertension Acute MI
Contraindication -Hypersensitive to drug.
Side effect -CV: hypotension -GI: nausea
and
Nursing responsibility -Always check patients apical pulse
blocking agents GENERIC NAME: Metoprolol HCL BRAND NAME: Lopressor
selectively blocks beta1 receptors; decreases cardiac output, peripheral resistance, and cardiac oxygen consumption; and depresses rennin secretion
Angina Pectoris
-Patient with sinus bradycardia, -cardiogenic shock and heart failure
vomiting -Respi: dyspnea -Skin: rash
-Monitor BP -Store drug at room temperature. -Inform patient about the side effects and adverse effects of the medication. -Advise patient to take it with meals. -Tell patient to report if he/she feels shortness of breath. -Tell patient That metoprolol is not advisable to breastfeeding mothers. -Advise not to withdrawn drug abruptly
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Music-Grade 7 Lesson PlanDocument3 paginiMusic-Grade 7 Lesson PlanGlaizalyn Fabella TagoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health Teaching Plan Area: Barangay Balong Bato San Juan City Topic: Diet For Hypertension and DiabetesDocument5 paginiHealth Teaching Plan Area: Barangay Balong Bato San Juan City Topic: Diet For Hypertension and DiabetesGlaizalyn Fabella TagoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluate Staff Nurse PerformanceDocument8 paginiEvaluate Staff Nurse PerformanceGlaizalyn Fabella Tagoon100% (8)
- Evaluation Tool For Oropharyngeal SuctioniingDocument2 paginiEvaluation Tool For Oropharyngeal SuctioniingGlaizalyn Fabella TagoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study - Prostate AdenocarcinomaDocument5 paginiDrug Study - Prostate AdenocarcinomaGlaizalyn Fabella TagoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Postpartum Discharge PlanDocument2 paginiPostpartum Discharge PlanGlaizalyn Fabella Tagoon75% (12)
- Assessment Tool For The Geriatric PatientDocument5 paginiAssessment Tool For The Geriatric PatientGlaizalyn Fabella Tagoon100% (1)
- Media PDFs April09IDDDocument4 paginiMedia PDFs April09IDDGlaizalyn Fabella TagoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oropharyngeal Suction ChecklistDocument4 paginiOropharyngeal Suction ChecklistGlaizalyn Fabella Tagoon50% (2)
- Aac-Rerc - Psu.edu Documents Fager Ped Rehab 2010 PDFDocument9 paginiAac-Rerc - Psu.edu Documents Fager Ped Rehab 2010 PDFGlaizalyn Fabella TagoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Journal PDFDocument5 paginiJournal PDFGlaizalyn Fabella TagoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surgical InstrumentsDocument4 paginiSurgical InstrumentsGlaizalyn Fabella TagoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- PATHODocument1 paginăPATHOGlaizalyn Fabella TagoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ebn PDFDocument9 paginiEbn PDFGlaizalyn Fabella TagoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- ABC Hypothethical CaseDocument6 paginiABC Hypothethical CaseGlaizalyn Fabella TagoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prob Prio - AbcDocument1 paginăProb Prio - AbcGlaizalyn Fabella TagoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Managing side effects of ChlorpromazineDocument7 paginiManaging side effects of ChlorpromazineGlaizalyn Fabella Tagoon100% (1)
- Neurogenic ShockDocument3 paginiNeurogenic ShockGlaizalyn Fabella TagoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Managing side effects of ChlorpromazineDocument7 paginiManaging side effects of ChlorpromazineGlaizalyn Fabella Tagoon100% (1)
- EBN - Chicken PoxDocument5 paginiEBN - Chicken PoxGlaizalyn Fabella TagoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Rate F BioDocument13 paginiRate F BiorahsreeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tuberculosis Treatment: General Principles and ApproachDocument24 paginiTuberculosis Treatment: General Principles and ApproachRahul PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study - Nalbuphine (Nubain)Document3 paginiDrug Study - Nalbuphine (Nubain)Maria Theresa BuscasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pantosec 40 Tab InnovaDocument30 paginiPantosec 40 Tab InnovaAnmol KudalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Find out what Galvus is and its uses, side effects and warningsDocument5 paginiFind out what Galvus is and its uses, side effects and warningsRadhakrishna KurupÎncă nu există evaluări
- Free Drug Bank GUIDE 1 PDFDocument76 paginiFree Drug Bank GUIDE 1 PDFRaouf Ra'fat Soliman100% (11)
- Pharmacology ReviewersDocument5 paginiPharmacology ReviewersNeisha Halil VillarealÎncă nu există evaluări
- PharmacogeneticsDocument12 paginiPharmacogeneticsSijan PoudelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complete Albendazole Information From DrugsDocument4 paginiComplete Albendazole Information From DrugselephantynoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mcaz QisDocument12 paginiMcaz QisthembaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stock Opname 2021 23-01-2022Document42 paginiStock Opname 2021 23-01-2022yunitacahyaniiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dosage Calculation Questions & AnswersDocument11 paginiDosage Calculation Questions & AnswersBlue FlashesÎncă nu există evaluări
- PH 1.13:BETA Blockers: Dr. Lavakumar S Professor Dept of Pharmacology SssmcriDocument31 paginiPH 1.13:BETA Blockers: Dr. Lavakumar S Professor Dept of Pharmacology SssmcriBeena ShajimonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Biopharmaceutic Considerations of A Drug DesignDocument89 pagini5 Biopharmaceutic Considerations of A Drug DesignImDanaBananaaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pidato HipertensiDocument2 paginiPidato HipertensiPutu Mita100% (1)
- Switching To-From AnticoagulantsDocument8 paginiSwitching To-From AnticoagulantsAlex AlxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stesolid® Rectal Tubes 5 MG and 10 MG: DiazepamDocument2 paginiStesolid® Rectal Tubes 5 MG and 10 MG: DiazepamYudha Arya IrawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Magnesium Sulfate for Eclampsia and Pre-EclampsiaDocument3 paginiMagnesium Sulfate for Eclampsia and Pre-EclampsiaSchyna Marielle VitaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- MEDICATION LISTDocument31 paginiMEDICATION LISTluis alberto silva caicedoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complete Drug FormularyDocument96 paginiComplete Drug FormularyRPh Krishna Chandra JagritÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inserto Allegra Pediatrico Cropped-MergedDocument2 paginiInserto Allegra Pediatrico Cropped-MergedPAUL MENDOZA FLORESÎncă nu există evaluări
- Td0221596enn 002Document48 paginiTd0221596enn 002Andrei BombardieruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology of Antipyretic DrugsDocument19 paginiPharmacology of Antipyretic DrugsPretty HiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inquiry Drugs: of Into The of andDocument4 paginiInquiry Drugs: of Into The of andlordhavok33Încă nu există evaluări
- UntitledDocument9 paginiUntitledMAHMCI ORDRÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.E.2-Caspofungin Guideline 2003Document3 pagini3.E.2-Caspofungin Guideline 2003damondouglasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anticholinergic DrugsDocument4 paginiAnticholinergic DrugsAmikyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Musculoskeletal PharmacologyDocument18 paginiMusculoskeletal PharmacologyBLEEMAGE100% (2)
- FurosemideDocument4 paginiFurosemideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Notes - Lec 20 - Antimycobacterial AgentsDocument14 paginiNotes - Lec 20 - Antimycobacterial AgentsChesmar MacapalaÎncă nu există evaluări