Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
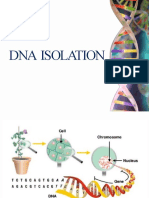
Dna Extraction
Încărcat de
Neo Mervyn MonahengTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Dna Extraction
Încărcat de
Neo Mervyn MonahengDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Faculty of Health and Wellness Sciences. BHSc.
Medical Laboratory Science Molecular Notes DNA extraction
DNA EXTRACTION
Department of Biomedical Sciences 1 Cytogenetics 29th April 2013
http://www.enotes.com/dna-isolation-methods-reference/dna-isolation-methods Application: Isolation of DNA is needed for genetic analysis, which is used for scientific, medical, or forensic purposes. Scientists use DNA in a number of applications, such as introduction of DNA into cells and animals or plants, or for diagnostic purposes. In medicine the latter application is the most common. On the other hand, forensic science needs to recover DNA for identification of individuals (for example rapists, petty thieves, accident, or war victims), paternity determination, and plant or animal identification. Interfering substances: Presence of proteins, lipids, polysaccharides and some other organic or inorganic compounds in the DNA preparation can interfere with DNA analysis methods, especially with polymerase chain reaction (PCR). They can also reduce the quality of DNA leading to its shorter storage life. Common samples from which DNA can be extracted: Sources for DNA isolation are very diverse. Basically it can be isolated from any living or dead organism. Common sources for DNA isolation include whole blood, hair, sperm, bones, nails, tissues, blood stains, saliva, buccal (cheek) swabs, epithelial cells, urine, paper cards used for sample collection, bacteria, animal tissues, or plants. Principles in DNA extraction A number of commercial DNA purification kits use the same principles. Lysis solutions contain: sodium chloride; tromethamine (also known as Tris), which is a buffer to retain constant pH Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), which binds metal ions Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), which is a detergent. A common enzyme used in DNA extraction is Proteinase K. Collection of the isolated DNA The Basic steps in DNA extraction 1. Cell disruption or lysis to release the cellular DNA. This can be mechanical (sonicating or grinding), or by chemical means. 2. Membrane lipids are removed by detergents. 3. Enzyme removal of proteins using proteases. 4. Removal of RNA with RNase. 5. Precipitation of the DNA can be done with alcohol ethanol or isopropanol. (DNA is insoluble in these alcohols- DNA can be resolubilised in pure water or a slightly alkaline buffer) 6. The removal of Mg2+ and Ca2+ cations will prevent enzymes such as DNase from degrading the isolated DNA.
Faculty of Health and Wellness Sciences. BHSc. Medical Laboratory Science Molecular Notes DNA extraction
Department of Biomedical Sciences 2 Cytogenetics 29th April 2013
Quantity of DNA recovered A Diploid Cell contains approximately 6 pg of DNA Sperm contains approximately 3 pg of DNA The average WBC of an adult is 5 - 10 X 106 cells per ml of blood. Therefore, the theoretical recovery of DNA per ul of blood is 30 - 60 ng The RFLP procedure on requires a minimum of 50 ng of high molecular weight double stranded DNA. The PCR reactions call for on average 1 ng of DNA (single or double stranded). Quantitation of recovered DNA A tabletop spectrophotometer called a nanodrop uses 2ul for quantification. Nucleic acids absorb light at a wavelength of 260nm. When a 260 nm light source shines on a DNA sample, the light that passes through can be measured, and the amount of light absorbed can be measured. For double stranded DNA, an optical density (OD) of 1 at 260 nm correlates to a DNA concentration of 50ng/ul. Therefore the DNA concentration can be calculated from the optical density reading. NB A blank of purified water or the buffer without DNA should be used as an internal quality control measure ie to get a zero reading when there is no DNA present.
Methods: Organic (Phenol-Chloroform) Extraction Non-Organic (Proteinase K and Salting out) Chelex (Ion Exchange Resin) Extraction FTA Paper (Collection, Storage, and Isolation) Silica Based (Silica exchange resin- Qiagen) Magnetic Beads (see diagram on next page) The use of magnetic beads can be automated, increases throughput, can remove amplification inhibitors, uses no hazardous chemicals. The principle underlying magnetic bead procedures involves attracting DNA to magnetic beads, holding the beads in place using a magnetized source, such as a rack or tube holder, and washing away other components of the sample. Invitrogen's ChargeSwitch Technology (CST) involves the use of magnetic beads whose surface bears a charge that can be switched based on the pH of the surrounding buffer environment. At low pH, the beads are positively charged, attracting the negatively charged DNA molecules and allowing proteins and contaminants to be removed by washing. The ChargeSwitch Forensic DNA Purification Kit includes: Lysis buffer Magnetic beads Proteinase K Purification buffer Wash buffer Elution buffer
Faculty of Health and Wellness Sciences. BHSc. Medical Laboratory Science Molecular Notes DNA extraction
Department of Biomedical Sciences 3 Cytogenetics 29th April 2013
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pagini6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- NTSE Question Bank & Solutions (Complete Syllabus) PDFDocument7 paginiNTSE Question Bank & Solutions (Complete Syllabus) PDFSaksham50% (2)
- Activity 3 - Dna IsolationDocument4 paginiActivity 3 - Dna IsolationMemeowwÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineered Nanopores for Bioanalytical ApplicationsDe la EverandEngineered Nanopores for Bioanalytical ApplicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dna ExtractionDocument21 paginiDna ExtractionXian LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1-Internal Heat GainDocument15 pagini1-Internal Heat GainWunNa100% (1)
- Preventing Cavitation Damage in Liquid Ring PumpsDocument6 paginiPreventing Cavitation Damage in Liquid Ring Pumpshimadri.banerji60Încă nu există evaluări
- Spectrophotometric Determination of The Concentration and Purity of DNA of Musa Acuminata Through Nucleic Acid IsolationDocument7 paginiSpectrophotometric Determination of The Concentration and Purity of DNA of Musa Acuminata Through Nucleic Acid IsolationWynona Genesis G. BasilioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ce Foundtn Manual Edited PDFDocument30 paginiCe Foundtn Manual Edited PDFNeo Mervyn Monaheng67% (6)
- Lab-2 Genet Ic DNA Isolation Methods-1Document27 paginiLab-2 Genet Ic DNA Isolation Methods-1Samyak ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dna Extraction MethodsDocument63 paginiDna Extraction MethodsSimranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dna:rna ExtractionDocument15 paginiDna:rna ExtractionEleeyaah Tan100% (1)
- The Rapid & Non-Enzymatic Isolation of DNA From The Human Peripheral Whole Blood Suitable For GenotypingDocument16 paginiThe Rapid & Non-Enzymatic Isolation of DNA From The Human Peripheral Whole Blood Suitable For GenotypingWabilal PurnamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Isolation of DNA From Animal TissuesDocument10 paginiIsolation of DNA From Animal TissuesAnura BandaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Step 1: Cell LysisDocument8 paginiStep 1: Cell LysisWennielyn SanchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dna IsolationDocument58 paginiDna IsolationTitisPudyatikaDestyaAndiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nucleic Acid (DNA) ExtractionDocument2 paginiNucleic Acid (DNA) ExtractionAbrar 111Încă nu există evaluări
- Nucleic Acid Genetic: Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Is ADocument11 paginiNucleic Acid Genetic: Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Is ATushar GulatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dna Extraction ProtocolDocument4 paginiDna Extraction Protocolelizabethafrifa7Încă nu există evaluări
- Lab Report 4Document13 paginiLab Report 4Farah TubasiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical - Ii Lab in Molecular BiologyDocument96 paginiPractical - Ii Lab in Molecular BiologyNaruto UzumakiÎncă nu există evaluări
- DNA IsolationDocument20 paginiDNA IsolationYiğit ArslanÎncă nu există evaluări
- GCT 1Document58 paginiGCT 1Wajid KhattakÎncă nu există evaluări
- DNAzolR A Reagent For The Rapid Isolation of GenomDocument5 paginiDNAzolR A Reagent For The Rapid Isolation of GenomGabriela Daniela Sandoval GámezÎncă nu există evaluări
- DNA ExtractionDocument56 paginiDNA ExtractionZain YaqoobÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dna Barcoding and FingerprintingDocument53 paginiDna Barcoding and Fingerprintingian clyds christian sanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 13 DNA ExtractionDocument21 paginiWeek 13 DNA ExtractionUmer FarooqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Literature Review On Dna ExtractionDocument4 paginiLiterature Review On Dna Extractionc5nazs86100% (1)
- Nucleic Acid PreparationDocument6 paginiNucleic Acid PreparationDemetrio BenitezÎncă nu există evaluări
- DNA Extraction: DNA Isolation Is A Routine Procedure To CollectDocument3 paginiDNA Extraction: DNA Isolation Is A Routine Procedure To CollectAli Akand AsifÎncă nu există evaluări
- DNA ExtractionDocument3 paginiDNA ExtractionsujithasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Molecular Biology Part IIDocument29 paginiPractical Molecular Biology Part IIDr. Gurumurthy D MÎncă nu există evaluări
- University of Poonch RawalakotDocument18 paginiUniversity of Poonch RawalakotAbdul qadeerÎncă nu există evaluări
- DNA IsolationDocument12 paginiDNA Isolationhirenkumar bhalaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Extracción de DNA A Partir de Muestras de Sangre CoaguladaDocument5 paginiExtracción de DNA A Partir de Muestras de Sangre CoaguladaManuel Alejandro Castro GarcíaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rich Text Editor FileDocument10 paginiRich Text Editor Filezara janeÎncă nu există evaluări
- DNA Isolation / ExtractionDocument5 paginiDNA Isolation / Extractionangeldust803sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Extraction MethodsDocument18 paginiExtraction MethodsNived K KÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant PathologyDocument14 paginiPlant PathologySudip NeupaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Detection of Genes in Fungi by PCR Amplification and Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisDocument12 paginiThe Detection of Genes in Fungi by PCR Amplification and Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisAnsah Samuel SafoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 06 Laporan Genetika DNA ISOLATIONDocument5 pagini06 Laporan Genetika DNA ISOLATIONhananÎncă nu există evaluări
- RDNA Lect Lecture Notes Mid Sem BTech IDDDocument146 paginiRDNA Lect Lecture Notes Mid Sem BTech IDDarpna sjsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dna Extraction DissertationDocument6 paginiDna Extraction DissertationWhatShouldIWriteMyPaperOnUK100% (1)
- Module II - HybridizationDocument13 paginiModule II - HybridizationAnanya SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Simplified Universal Genomic DNA Extraction ProtDocument8 paginiA Simplified Universal Genomic DNA Extraction ProtAlessandroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dna Extraction ThesisDocument5 paginiDna Extraction Thesistiffanyyounglittlerock100% (2)
- Tatie Molecular Genetics Write UpDocument11 paginiTatie Molecular Genetics Write UpYOLANDA NYARADZO MUPITAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ex. 5 DNA Extraction PDFDocument3 paginiEx. 5 DNA Extraction PDFAlyssa Pauline PalacioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genomic Dna Isolation From Human Whole Blood Samples by Non Enzymatic Salting Out MethodDocument2 paginiGenomic Dna Isolation From Human Whole Blood Samples by Non Enzymatic Salting Out MethodamandbhaskarÎncă nu există evaluări
- DNA Extraction From MeatDocument25 paginiDNA Extraction From Meatnoor saqibÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Does DNA Extraction InvolveDocument2 paginiWhat Does DNA Extraction InvolveSuneel Kumar Jaipal SKÎncă nu există evaluări
- DNA Extraction PostLabDocument3 paginiDNA Extraction PostLabNasser Manungka SabandalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio 3A Lab: DNA Isolation and The Polymerase Chain Reaction ObjectivesDocument7 paginiBio 3A Lab: DNA Isolation and The Polymerase Chain Reaction Objectivesazura_zfÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanved Mol B Assignment - ClareDocument10 paginiAdvanved Mol B Assignment - Clareizakobia1Încă nu există evaluări
- Dna Isolation From e Coli ProtocolDocument5 paginiDna Isolation From e Coli ProtocolMegh Raj BhattÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nucleic Acid Isolation, Analysis and Visualization L2 27-10-2020Document26 paginiNucleic Acid Isolation, Analysis and Visualization L2 27-10-2020Tanveer KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- DNA Sample Collection and PreservationDocument9 paginiDNA Sample Collection and PreservationDr Lalit Chandravanshi (SUSAH Associate Professor)Încă nu există evaluări
- Duhok Polytechnic University: Shekhan Technical College of HealthDocument27 paginiDuhok Polytechnic University: Shekhan Technical College of HealthNechir Zaxoy100% (1)
- Genomic Report MRIN 2015Document15 paginiGenomic Report MRIN 2015Jessica AdhykaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biological Macromolecule: Nucleic Acid: Melissa Caitlin RedcobladoDocument9 paginiBiological Macromolecule: Nucleic Acid: Melissa Caitlin RedcobladoJhon Raphael JimenezÎncă nu există evaluări
- To Have A Closer Look and Examine at The DNA Molecule and Extract Our Own DNA Using Buccal CellDocument10 paginiTo Have A Closer Look and Examine at The DNA Molecule and Extract Our Own DNA Using Buccal CellLim Zi XuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- mb502 P Assignments Solution by MeRRyDocument5 paginimb502 P Assignments Solution by MeRRyaimenjavaid965Încă nu există evaluări
- BT 403+mod III+NKJ+Lecture+ 2 DNA+Isolation 2011Document8 paginiBT 403+mod III+NKJ+Lecture+ 2 DNA+Isolation 2011tulibhawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thesis On Dna ExtractionDocument8 paginiThesis On Dna Extractionafcmunxna100% (2)
- Js 190 - Dna Extraction MethodsDocument56 paginiJs 190 - Dna Extraction MethodsKelvin LeongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Botha 2 Comparative Aquatic Toxicity of - Gold NanoparticlesDocument8 paginiBotha 2 Comparative Aquatic Toxicity of - Gold NanoparticlesNeo Mervyn MonahengÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Blood Covenant: by Mindena SpurlingDocument33 paginiThe Blood Covenant: by Mindena SpurlingNeo Mervyn MonahengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gulumian SAJS 2012Document9 paginiGulumian SAJS 2012Neo Mervyn MonahengÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Review On Nanomaterials For Environmental RemediationDocument35 paginiA Review On Nanomaterials For Environmental RemediationNeo Mervyn MonahengÎncă nu există evaluări
- SKEPP 2011 Nanomaterials - in - REACH - Report - 15082011 PDFDocument239 paginiSKEPP 2011 Nanomaterials - in - REACH - Report - 15082011 PDFNeo Mervyn MonahengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Youth Volunteering in Africa The Case of The Au Youth Volunteers CorpsDocument12 paginiYouth Volunteering in Africa The Case of The Au Youth Volunteers CorpsNeo Mervyn MonahengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Caps Fet - Life Sciences - GR 10-12 Web - 2636Document82 paginiCaps Fet - Life Sciences - GR 10-12 Web - 2636Neo Mervyn Monaheng50% (2)
- Mathematics 1 Tutorials 2017Document66 paginiMathematics 1 Tutorials 2017Neo Mervyn MonahengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap2 Power Point PresentationDocument74 paginiChap2 Power Point PresentationNeo Mervyn MonahengÎncă nu există evaluări
- DR McCormick Academic Essay Notes February 2017Document9 paginiDR McCormick Academic Essay Notes February 2017Neo Mervyn MonahengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Joint and by Products 2016Document20 paginiJoint and by Products 2016Neo Mervyn MonahengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Manual Converted Final 2017Document43 paginiPractical Manual Converted Final 2017Neo Mervyn MonahengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 6 Handout 3 Poster GM CropsDocument1 paginăClass 6 Handout 3 Poster GM CropsNeo Mervyn MonahengÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 CytoUserGuide 6.0Document134 pagini2 CytoUserGuide 6.0Neo Mervyn MonahengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bachelor of CommerceDocument1 paginăBachelor of CommerceNeo Mervyn MonahengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 1 Handout 2 Topics in Nanobt Poster Biotech TimelineDocument1 paginăClass 1 Handout 2 Topics in Nanobt Poster Biotech TimelineNeo Mervyn MonahengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Promylocytic LeukaemiaDocument2 paginiAcute Promylocytic LeukaemiaNeo Mervyn Monaheng100% (1)
- 9LHDocument1 pagină9LHNeo Mervyn MonahengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 1 Handout 3 Topics in Nanobtposter Traditional BiotechDocument1 paginăClass 1 Handout 3 Topics in Nanobtposter Traditional BiotechNeo Mervyn MonahengÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Citizen - Laboratory Scientist Degree Created - 25 OctoberDocument1 paginăThe Citizen - Laboratory Scientist Degree Created - 25 OctoberNeo Mervyn MonahengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Density Functional TheoryDocument3 paginiDensity Functional TheoryNeo Mervyn MonahengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Developmental Delay (DD) or Intellectual Disability (ID) Testing AlgorithmDocument1 paginăDevelopmental Delay (DD) or Intellectual Disability (ID) Testing AlgorithmNeo Mervyn Monaheng100% (1)
- Dr. Johnson Segment 2 Lecture NotesDocument3 paginiDr. Johnson Segment 2 Lecture NotesNeo Mervyn MonahengÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Nicodemus Visits Jesus) : Presented by Sermons 4 Kids Featuring The Art of Henry MartinDocument10 pagini(Nicodemus Visits Jesus) : Presented by Sermons 4 Kids Featuring The Art of Henry MartinNeo Mervyn MonahengÎncă nu există evaluări
- MSC in Clinical Epidemiology Course Outline 2015Document24 paginiMSC in Clinical Epidemiology Course Outline 2015Neo Mervyn MonahengÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBL ExhibitDocument1 paginăCBL ExhibitNeo Mervyn MonahengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ye Are GodsDocument2 paginiYe Are GodsNeo Mervyn MonahengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Workflow 2Document3 paginiWorkflow 2Neo Mervyn MonahengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lateral Deflection of Tall BuildingsDocument4 paginiLateral Deflection of Tall BuildingsAshnaBeeslallÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bitumat TopsealDocument5 paginiBitumat TopsealsathiyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Process Calculations: Autumn 2021Document23 paginiChemical Process Calculations: Autumn 2021Ujjwal AnandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effect of Lime and Phosphorus Fertilizer On Acid Soil Properties and Sorghum Grain Yield and Yield Components at Assosa in Western EthiopiaDocument9 paginiEffect of Lime and Phosphorus Fertilizer On Acid Soil Properties and Sorghum Grain Yield and Yield Components at Assosa in Western EthiopiaPremier PublishersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ce140 PS 3 PDFDocument1 paginăCe140 PS 3 PDFAydinAkhtarpour100% (1)
- PG 91Document1 paginăPG 91Shahruzi MahadzirÎncă nu există evaluări
- BEIKE - Tripod Catalogue 2014Document30 paginiBEIKE - Tripod Catalogue 2014BaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Algorithms For Chemical Computations (Acs Symposium Series No 46)Document157 paginiAlgorithms For Chemical Computations (Acs Symposium Series No 46)sairama786Încă nu există evaluări
- Summary 4º ESO - Unit 3 - Genetic Information and Nucleic AcidsDocument89 paginiSummary 4º ESO - Unit 3 - Genetic Information and Nucleic AcidsPILARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daftar Pustaka: Reactor Design, John Wiley & Sons Inc., USADocument4 paginiDaftar Pustaka: Reactor Design, John Wiley & Sons Inc., USASyariful Maliki NejstaršíÎncă nu există evaluări
- AT 0 Lab Report PDFDocument7 paginiAT 0 Lab Report PDFerlanggasulaiman90Încă nu există evaluări
- CL 0100 CH 2 X 50 ML CL 0500 CH 4 X 125 ML: in Vitro Diagnostic Medical DeviceDocument1 paginăCL 0100 CH 2 X 50 ML CL 0500 CH 4 X 125 ML: in Vitro Diagnostic Medical DeviceBPG ServiceÎncă nu există evaluări
- 22 6Document13 pagini22 6Francisco M. RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Properties of Gelatins From Skins of Fish - Black Tilapia (Oreochromis Mossambicus) and Red Tilapia (Oreochromis Nilotica)Document4 paginiProperties of Gelatins From Skins of Fish - Black Tilapia (Oreochromis Mossambicus) and Red Tilapia (Oreochromis Nilotica)Rizky Febrian SatrianiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gs11m12a01 01e PDFDocument38 paginiGs11m12a01 01e PDFDhirender DagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Texture 160203172810Document28 paginiTexture 160203172810NainaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Charmaine,,,,,Anlytical ChemistryDocument8 paginiCharmaine,,,,,Anlytical ChemistryMarlougen BranzuelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antimicrobial Activity and Chemical Composition of Essential Oil FromDocument9 paginiAntimicrobial Activity and Chemical Composition of Essential Oil FromTrần Thuý QuỳnhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemicals Zetag MSDS Inverse Emulsion Zetag 8849 FS - 0710Document6 paginiChemicals Zetag MSDS Inverse Emulsion Zetag 8849 FS - 0710PromagEnviro.comÎncă nu există evaluări
- (PDF) a General LC-MS - MS Method for Monitoring Potential Β-Lactam Contamination in Drugs and Drug-Manufacturing SurfacesDocument16 pagini(PDF) a General LC-MS - MS Method for Monitoring Potential Β-Lactam Contamination in Drugs and Drug-Manufacturing SurfacessppÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thin CylinderDocument5 paginiThin CylinderAngshuman BhardwajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shjohntec 2008218115733800771Document36 paginiShjohntec 2008218115733800771Kristin NgoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Incorporation of Waste Plastic in Asphalt Binders To Improve TheirDocument9 paginiIncorporation of Waste Plastic in Asphalt Binders To Improve TheirSandor ManesesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problemas Geotecniafree1Document46 paginiProblemas Geotecniafree1Dickey Design100% (3)
- Temperature Dependence and ZTC Bias Point Evaluation of Sub 20nm Bulk Multigate DevicesDocument16 paginiTemperature Dependence and ZTC Bias Point Evaluation of Sub 20nm Bulk Multigate DevicesYgor AguiarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monel K500 PDFDocument6 paginiMonel K500 PDFOZAIRTRADELINKÎncă nu există evaluări
- FLSolutions Operation ManualDocument250 paginiFLSolutions Operation ManualCooordinación Metrologia Nutermía sasÎncă nu există evaluări