Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Loci in Two Dimension
Încărcat de
kalkultaDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Loci in Two Dimension
Încărcat de
kalkultaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
1
LOCI IN TWO DIMENSION
1. Mark the intersection point(s) of the loci. Locus I:A point M moves in such a way that it is equidistant from lines PR and SQ. Locus II:A point N moves in such a way that TN = 0.6 cm.
2. in the diagram below, ABC is an equilateral triangle. Points X,Y and Z are the midpoints of Ab, BC and AC respectively. Using a pencil and ruler draw the locus of point P which moves in the triangle and is always equidistant from lines AB and BC
A Y X Z
3. The diagram below shows a square ABCD of side 4cm. Constuct the locus of points P which moves in the square and is always 4 cm from point C.
Diagram 3 in the answer space shows four squares, PKJN, KQLJ , NJMS and JLRM. W, X and Y are three moving points in the diagram. (a)W moves such that it is equidistant from the straight lines PS and QR. By using the letters in the diagram, state the locus of W. (b)On the diagram, draw (i)the locus of X such that XJ = JN, (ii)the locus of Y such that its distance from point Q and point S are the same. (c)Hence, mark with the symbol all the intersections of the locus of X and the locus of Y. Answer: (a) (b) (i) ,(ii) (c)
Diagram 3
Diagram 4 in the answer space shows a square PQRS drawn on a grid of equal squares with sides of 1 unit. M, X and Y are three moving points in the diagram. (a)M is the point which moves such that its distances from point Q and point S are the same. By using the letters in the diagram, state the locus of M. (b)On the diagram, draw (i)The locus for the point X that is constantly 5 units from the line QR. (ii)The locus for the point Y that is constantly 7 units from the point R. (c)Hence, mark with the symbol the intersection of the locus of X and the locus of Y. Answer: (a) (b) (i) , (ii) (c)
Diagram 4
Diagram 5 in the answer space shows a square PQRS drawn on a grid of equal squares with sides of 1 unit. W, X and Y are three moving points in the diagram. (a)W is the point which moves such that it Is equidistant from the straight line PQ and PS. By using the letters in the diagram, state the locus of W. (b)On the diagram, draw (iii)the locus for the point X that is constantly 5 units from the point P. (iv)the locus for the point Y that is constantly 4 units from the point QR. (c)Hence, mark with the symbol the intersection of the locus of X and the locus of Y. Answer: (a) (b) (i) , (ii) (c)
Diagram 5
(a)
Diagram 6 shows a rhombus MNOP. N M
Diagram 6
X is a moving point in the rhombus such that it is always equidistant from the straight lines PM and PO. By using the letters in diagram, state the locus of X. (b) Diagram 7 in the answer space shows a regular hexagon ABCDEF. Y and Z are two moving points in the hexagon. On diagram 7, draw the locus of Y such that YD = DE , (i) the locus of Z such that it is equidistant from point B and point F. (ii) Hence, mark with the symbol the intersection of the locus Y and the locus of Z. Answer: (a) (b) (c)
A B
(c)
(i) , (ii)
E Diagram 7
Diagram 8 in the answer space shows a circle with centre O, drawn on a grid of equal squares with sides of 1 unit. AOB a diameter of the circle. X , Y and Z are three moving points inside the circle. (a)X is the point which moves such that it is constantly 3 units from the point O. Describe fully the locus of X. (b)On Diagram 8, draw (i)The locus of the point Y which moves such that its distance is constantly 2 units from the line AB. (ii) The locus of point Z which moves such that it is equidistant from the point A and the point B . (c)l Hence, mark with the symbol the intersection of the locus of Y and the locus of Z.
Answer: (a) (b) (i), (ii) (c)
Diagram 8
Diagram 9 in the answer space shows an isosceles triangle PQR drawn on a grid of equal squares with sides of 1 unit . X and Y are two moving points inside the triangle PQR. (a) On Diagram 9 , draw (i) the locus of point X which moves such that its distance is constantly 6 units from the point Q. (ii) the locus of point Y which moves such that its distance is constantly 3 units from line PQ. (b) Hence, mark with the symbol the intersection of the locus of X and the locus of Y.
Answer: (a) (i), (ii) (b)
Diagram 9
10
Diagram 10 in the answer space shows a squares KLMN with sides of 6 units drawn on a grid of equal squares with sides of 1 units . X, Y and Z are three moving points inside the square. (a)Z is the point which moves such that it is always equidistant from point K and point M. Using the letters in Diagram 10, state the locus of X. (b)On Diagram 10, draw (i)lthe locus of point Y which moves such that it is always equidistant from the straight line KL and KN. (ii)the locus of the point Z which moves such that its distance is constantly 2 units from the point P. (c)Hence, mark with the symbol Z. Answer: (a) (b) (i),(ii) (c) the intersection of the locus of Y and the locus of
Diagram 10
11
Diagram 11 in the answer space shows a quadriateral PQRS drawn on a grid of equal squares with sides of 1 unit. l W , X and Y are three moving points inside the quadriateral PQRS. (a)W is the point which moves such that it is always equidistant from point Q and point S. By using the letters in Diagram 11 , state the locus of W. (b)On the Diagram 11, draw (i)the locus of the point X such that it is always 6 units from point P. (ii)the locus of the point Y which moves such that its distance is constantly 3 units from the line PQ. (c)Hence, mark with the symbol the intersection of the locus of X and the locus of Y. Answer: (a) (b) (i) , (ii)
Diagram 11
9 12 the figure shows a rhombus.
H
(a) X is a moving point in the rhombus such that XF = XH. by using the letter in the figure, state the locus of X. (b) Y is another moving point that equidistant from FE and FG (i) Construct the loci of X and Y on the figure (ii) Mark the intersection of the two loci with symbol
13.
The figure shows a straight line,PQ
(a) Construct, on the figure (i) The locus of appoints, L, which moves such it is always 2cm from points P, (ii) The locus of a point, M, which moves such that it is always 2.5 cm from point Q. (b) Mark all the intersections of the two loci with the letter S
10
14
In the diagram, PQRS is a circle with centre O and radius 1.5 cm. Mark the points which are 1.5 cm from O and also equidistant from P and R with symbol
Q O
11
15
Diagram in the answer space shows two squares, JKNP and KLMN, each with sides 4 cm. X, V and Z are three moving points in the diagram. (a) X moves such that it is equidistant from the straight lines JP and LM. By using the letters in the diagram, state the locus of X. (b) On the diagram, draw (i) the locus of Y such that YN = 3 cm, (ii) the locus of Z such that ZP = ZJ. (c) Hence, mark with the symbol x for all the intersections of the locus of V and the locus of Z.
Answer: (a) (b) (i), (ii) (c)
12
16
Diagram in the answer space shows a right-angled triangle PQR. X, Y and Z are three moving points in the diagram (a) X moves such that it is equidistant from point P and point R. By using letters in the diagram, state the locus of X. (b) On the diagram, draw (i) the locus of Y such that PR = QR, (ii) the locus of Z such that it is always 4 cm from Q. (c) Hence, mark with the symbol x for all the intersections of the locus of V and the locus of Z.
Answer: (a) (b) (i), (ii) (c)
13
17
Diagram in the answer space shows four squares, AQPT QBRP TPSD and PRCS drawn on a grid of equal squares with sides 1 unit. V, W and X are three moving points in the diagram. (a) V moves such that it is equidistant from the straight lines AB and DC. By using the letters in the diagram, state the locus of V. (b) On the diagram, draw (i) the locus of point W that is constantly 4 units form the line AD, (ii) the locus of point X that is constantly 6 units from point D. (c) Hence, mark with the symbol x for all the intersections of the locus of W and the locus of X.
Answer: (a) (b) (i), (ii) (c)
14
18
Diagram in the answer space shows a rectangle JKLM drawn on a grid of equal squares with sides 1 unit. T, X and Y are three moving points in the diagram. (a) T is the point which moves such that its distance from point M and L are the same. By using the letters in the diagram, state the locus of T. (b) On the diagram, draw (i) the locus of X such that XL =7 units, (ii) the locus of Y such that the perpendicular distance of V from the line KL is always 4 units. (c) Hence, mark with the symbol x for all the intersections of the locus of X and the locus of V.
Answer: (a) (b)
15
19
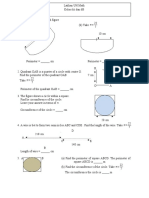
The figure shows a rectangle.
2cm
4 cm
(a) Construct, on the figure (i) The locus of a points, P, which moves such that it is always 2 cm from the vertex B. (ii) The locus of a points, Q, which moves such that its perpendicular distance from the side BC is always 1 cm (b) Mark all the intersections of the loci with the letter M
16
20
The figure shows a rectangles, PQRS.
5 cm
3 cm
(a) Construct the locus of a points, L, that moves such that its perpendicular distance from the diagonal PR and QS is always the same (b) Describe the locus constructed in (a)
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Chapter 15 I Trigonometry II StudentDocument41 paginiChapter 15 I Trigonometry II StudentAngie Kong Su MeiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ADD MATHS Progressions FORM 5Document6 paginiADD MATHS Progressions FORM 5Cik NursharwaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moem Math OlympiadDocument15 paginiMoem Math OlympiadamitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Locus, Geometrical Construction and TransformationDocument10 paginiLocus, Geometrical Construction and TransformationJason CookÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form 3 - Chapter 12Document7 paginiForm 3 - Chapter 12ayobsmkdbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bab6 Mathf2Document2 paginiBab6 Mathf2cikguanuar100% (1)
- PNUAT Numerical SkillsDocument10 paginiPNUAT Numerical SkillsRhonel Galutera100% (1)
- Add Maths F4 Topical Test 5 (BL)Document3 paginiAdd Maths F4 Topical Test 5 (BL)hanifah100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Significant Figures (Form 4)Document13 paginiChapter 1 - Significant Figures (Form 4)Yeap Lay Tin100% (4)
- Solving Simultaneous Equations GraphicallyDocument5 paginiSolving Simultaneous Equations GraphicallyJoel GrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Latihan Penjelmaan PMRDocument10 paginiLatihan Penjelmaan PMRMamat Firdaus100% (1)
- OCR (MEI) Core 1 - January 2011Document16 paginiOCR (MEI) Core 1 - January 2011Joel GrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 9 Basic PolygonsDocument8 paginiChapter 9 Basic PolygonsJu WenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maths ExerciseDocument4 paginiMaths ExercisechenziuleiiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter11 - Lines and Planes in 3DDocument6 paginiChapter11 - Lines and Planes in 3DHayati Aini AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bab11 Mathf2Document2 paginiBab11 Mathf2cikguanuarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 33 Angles Parallel-Lines2Document8 pagini33 Angles Parallel-Lines2Joel GrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Symmetry Question'sDocument12 paginiSymmetry Question'sAira HabibÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 8 Math Test Preparation - Indices and Standard FormDocument2 paginiGrade 8 Math Test Preparation - Indices and Standard FormAntonius LukitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circle TheoremDocument2 paginiCircle TheoremCarole ThamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maths PMR Past Year Questions CollectionDocument0 paginiMaths PMR Past Year Questions CollectionSin YeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6 - Coordinate GeometryDocument19 paginiChapter 6 - Coordinate GeometryshahrulkamilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Area of sectors and arcs GCSE maths worksheetDocument8 paginiArea of sectors and arcs GCSE maths worksheetDespina NestoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- ProgressionsDocument23 paginiProgressionsHayati Aini AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standard FormDocument14 paginiStandard FormJohari Ibrahim100% (1)
- Form 3 Revision Exercise on Laws of IndicesDocument52 paginiForm 3 Revision Exercise on Laws of IndicesLi Ann ChungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Set Pt3 Zon Keramat TerkiniDocument24 paginiSet Pt3 Zon Keramat TerkiniChe Mohd SaribuwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1st Mid-Term Test (Add Maths f4)Document5 pagini1st Mid-Term Test (Add Maths f4)Jarnice Ling Yee ChingÎncă nu există evaluări
- MATHS FORM 2 ALGEBRADocument18 paginiMATHS FORM 2 ALGEBRAAh Cheong100% (1)
- Extra Exercises - Express and SpecialDocument26 paginiExtra Exercises - Express and Specialdmal88Încă nu există evaluări
- Calculating lengths and angles from right trianglesDocument3 paginiCalculating lengths and angles from right trianglesihsanjayatrainingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form 2 Maths Circle 11 (Test)Document4 paginiForm 2 Maths Circle 11 (Test)chaiseng yongÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPM MATHS: Transformations & AreasDocument8 paginiSPM MATHS: Transformations & AreasNg Lay HoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modul 7 PDF July 13 2009 9 39 PM 129kDocument15 paginiModul 7 PDF July 13 2009 9 39 PM 129kSin YeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Add Maths F4 Topical Test 6 (E)Document4 paginiAdd Maths F4 Topical Test 6 (E)HANIFAHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circle Questions Based On Examination FormatDocument10 paginiCircle Questions Based On Examination FormatSmktt LakerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form 2 Math Chapter 10Document4 paginiForm 2 Math Chapter 10Lywee Neo75% (4)
- Y10 Mye Paper 2 2022Document11 paginiY10 Mye Paper 2 2022Let's hit 100k sub without any videosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics Geometrical Constructions SubjectiveDocument3 paginiMathematics Geometrical Constructions SubjectivenadzulkipliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math F2 Ujian 3 K1Document4 paginiMath F2 Ujian 3 K1compeilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1: Number Bases: Value of The DigitDocument7 paginiChapter 1: Number Bases: Value of The DigitJiajia LauÎncă nu există evaluări
- IndicesDocument1 paginăIndicescekminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Year 8 Pathway A Homework 025Document4 paginiYear 8 Pathway A Homework 025yasin gulamhussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Secondary 2 Normal (A) Mathematics Test 2 Algebraic Fractions, Equations and Inequalities 1 HourDocument7 paginiSecondary 2 Normal (A) Mathematics Test 2 Algebraic Fractions, Equations and Inequalities 1 HourHira HassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics Form 3 Chapter 8 LociDocument15 paginiMathematics Form 3 Chapter 8 LociFrancesca CheeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solving Math Problems from PFS/MATHEMATICS/PT3/2015 ExamDocument16 paginiSolving Math Problems from PFS/MATHEMATICS/PT3/2015 ExamAnonymous NRauXdoGÎncă nu există evaluări
- PermutationsDocument4 paginiPermutationsMall Singh BhullarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Done Circular MeasureDocument12 paginiDone Circular MeasureSharvinder SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standard Form Exam QuestionsDocument4 paginiStandard Form Exam Questionsmarsila2Încă nu există evaluări
- Quiz 1Document2 paginiQuiz 1Jiajia LauÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maths F4 Final Year Examination 17Document5 paginiMaths F4 Final Year Examination 17CIKGU Rahmat NazriÎncă nu există evaluări
- F3 Math C1 PMR QuestionsDocument1 paginăF3 Math C1 PMR QuestionsGee LengÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Maths) (Chung Cheng High School (Yishun) ) (4E5N) (Preliminary Examination 2) (2012) (Paper 1 Original)Document17 pagini(Maths) (Chung Cheng High School (Yishun) ) (4E5N) (Preliminary Examination 2) (2012) (Paper 1 Original)linnbrownie100% (1)
- Indices & Standard Form F2 2013Document8 paginiIndices & Standard Form F2 2013Juan Chee WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ol Mock 2019 575 Math p2 2019 - 1Document14 paginiOl Mock 2019 575 Math p2 2019 - 1Alphonsius WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE07P1E - Set 1 - FinalDocument19 paginiCE07P1E - Set 1 - Finalapi-3858963Încă nu există evaluări
- Maths Form 2Document22 paginiMaths Form 2HaziraAzlyÎncă nu există evaluări
- LocusDocument10 paginiLocusIlyana HaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Loci 1Document4 paginiLoci 1Ai ChooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Loci in Two Dimensions (P2)Document6 paginiLoci in Two Dimensions (P2)f_puadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Loci in Two DimensionDocument7 paginiLoci in Two DimensionSathis KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 48-th Czech and Slovak Mathematical Olympiad 1999: Category ADocument1 pagină48-th Czech and Slovak Mathematical Olympiad 1999: Category AAli HüseynovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geometry Worksheet Name - Inequalities in One Triangle Date - PeriodDocument2 paginiGeometry Worksheet Name - Inequalities in One Triangle Date - Periodmayonaissedelight smoothieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Task 3 AnswersDocument5 paginiTask 3 AnswersCristan DomingoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math 5 Q3 Week 3Document10 paginiMath 5 Q3 Week 3ANGELICA MARIE CONAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applications of Triangle CongruenceDocument2 paginiApplications of Triangle CongruenceDane Hern'zÎncă nu există evaluări
- Set 10 Shape and SpaceDocument13 paginiSet 10 Shape and SpaceKhairul Risor LegacyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 5 Geometry: Choose Correct Answer(s) From The Given ChoicesDocument3 paginiClass 5 Geometry: Choose Correct Answer(s) From The Given ChoicesKomal TagraÎncă nu există evaluări
- MensurationDocument22 paginiMensurationBlessy BobanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sec 2 Math Admiralty Sec Sa2 2013.textmarkDocument25 paginiSec 2 Math Admiralty Sec Sa2 2013.textmarkkutaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PolygonDocument25 paginiPolygonKumuthini ManiyamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ellipse Hyperbola - Formula Sheet - MathonGoDocument15 paginiEllipse Hyperbola - Formula Sheet - MathonGoASHISH NAIK100% (1)
- MATH PreDocument6 paginiMATH PreJHONCRIS GAMBOAÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Hsgs - Edu.vn) Inequalities - Marathon PDFDocument35 pagini(Hsgs - Edu.vn) Inequalities - Marathon PDFNguyen Huu QuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Latihan UH Math Kelas 6A dan 6BDocument14 paginiLatihan UH Math Kelas 6A dan 6BDitya Dwi AndariÎncă nu există evaluări
- AIME Solutions MortemEtInteritum BoleDocument6 paginiAIME Solutions MortemEtInteritum BoleAbhishek JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- AssigmentDocument5 paginiAssigmentshafahat aliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answer Key For Math 4 Q3 - Module 7 - Week 7Document2 paginiAnswer Key For Math 4 Q3 - Module 7 - Week 7Jimuel AngelÎncă nu există evaluări
- MATHS Summative Assessment Set 2 - 31 Questions on HRK Mathematics TestDocument8 paginiMATHS Summative Assessment Set 2 - 31 Questions on HRK Mathematics Testnewtonfogg123Încă nu există evaluări
- Problem 1: SolutionDocument7 paginiProblem 1: SolutionJongho KoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic College Mathematics 2nd Edition Miller Solutions Manual 1Document51 paginiBasic College Mathematics 2nd Edition Miller Solutions Manual 1christopher100% (41)
- Ellipse AnswerDocument2 paginiEllipse AnswerXhyllieght VœuxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculate volumes and surface areas of common solidsDocument17 paginiCalculate volumes and surface areas of common solidssam_raunayÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSEC June 2013 Mathematics P1Document11 paginiCSEC June 2013 Mathematics P1Tamera GreenÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCERT Books For Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 TrianglesDocument44 paginiNCERT Books For Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 TrianglesHashya BalarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigo 1 Class Test (MS)Document5 paginiTrigo 1 Class Test (MS)Madhu SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adobe Scan 24 Nov 2023Document17 paginiAdobe Scan 24 Nov 2023vidhya associateÎncă nu există evaluări
- APMO Problem Ans Solution PDFDocument213 paginiAPMO Problem Ans Solution PDFS.M.A NahianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crystal classes and symbolsDocument1 paginăCrystal classes and symbolsIlham Malik Ja'farÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maths Form 2 NotesDocument144 paginiMaths Form 2 NotesHila KipsÎncă nu există evaluări