Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Female Pelvis
Încărcat de
Annapurna DangetiDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Female Pelvis
Încărcat de
Annapurna DangetiDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
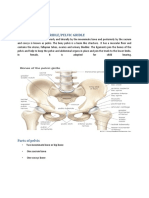
Female pelvis: The female pelvis (gynaecoid pelvis) is well adapted for childbearing by nature.
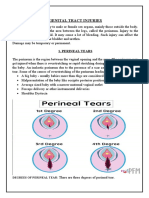
The gynaecoid pelvis has the characteristics giving rise to no difficulties in childbirth with a normal size baby. The size and shape of the female pelvis is the most important factor during childbearing and childbirth. Fetal head makes certain movements during its descent through pelvis so that the smallest diameter of the fetal head is easily brought to the largest diameter of the bony pelvis. Pelvic bones: Pelvic is made up of four bones 1. Two innominate (nameless) bones or hipbones. . !ne sacrum. ". !ne coccy#. I. Two Innominate bones are made up of three 1. Ilium the large flared out part. $liac crest as upper border %oncave border is iliac fossa &nterior superior iliac spine &nterior inferior iliac spine Posterior superior iliac spine Posterior inferior iliac spine 2. Ischium the thick lower part. &cetabulum $schial tuberosity $schial spine' location in relation to fetal head( ie.( above ())( below (*) or at (zero station) +reater sciatic ,otch' e#tends from sacro iliac -oint to ischial spine .esser /ciatic ,otch' e#tends from ischial spine to ischial tuberosity !bturator foramen' passage of pelvic nerve fibres 3. Pubic bone forms the anterior part. $nferior rami of Pubic bone (a) /uperior rami of pubic bone (b) /ymphysis pubis (a*b)' $t is formed at the -unction of two pubic bones. /ub pubic angle' angle between the inferior rami of the pubic bone. II. Sacrum $t is a wedge shaped bone consists of five fused vertebrae. /acral promontory' pro-ects inwards /acro iliac -oint 0ings of /acrum or &la of /acrum 1ollow of the /acrum' concave III. Coccyx
$t is a vestigial tail consists of four fused vertebrae forming a small triangular bone. $t is articulated with the sacrum %occy# moves backward during childbirth
Pelvic oints /ymphysis Pubis /acroiliac -oint /acro cocc#ygial -oint Pelvic !i"aments $nterpubic ligament /acroiliac ligament /acro cocc#ygial ligament /acrospinous ligament /acrotuberous ligament $nterspinous ligament $ntertuberous ligament
!an#mar$s o% the Pelvis The true pelvis is the bony canal through which fetus must pass during birth. $t consists of' 1. 2rim . %avity ". !utlet I. &rim &nterior border' Pubic bone Posterior border' /acral promontory and ala of the sacrum .ateral border' $liac bones 2rim of the pelvis consisits of' o /acral promontory o &la of the sacrum o /acro iliac -oint o $leopectineal line o $leopubic eminence o Pectineal line o Pubic tubercle o Pubic %rest o /ymphysis pubis 'iameters o% the &rim 1. (nterior posterior #iameter &natomical3 True con-ugate (11cm) ' e#tends from the sacral promontory to symphysis pubis !bstetrical con-ugate (14cm) ' e#tends from sacral promontory to 1. 5cm below the symphysis pubis 6iagnal con-ugate (1 cm) ' e#tends from sacral promontory to inferior border of symphysis pubis 2. )bli*ue #iameter 7ight !bli8ue diameter (1 cm) ' e#tends from 7t. /acroiliac -oint to .t. sacroiliac -oint. .eft !bli8ue diameter (1 cm) ' e#tends from 7t. /acroiliac -oint to .t. sacroiliac -oint. 3. Transverse #iameter Farthest points in the ileopectineal lines (1"cm).
.ongest diameter
II. Cavity
&nterior border' /ymphysis pubis Posterior border' /acral hollow .ateral border' /oft tissues &s it is round in shape( all diameters measure 1 cms.
III. )utlet 1. &natomical !utlet $t consisits of the lower border of all bones and sacro tuberous ligament. (&natomical outlet) 9 (pelvic strait) : !bstetrical outlet Pelvic strait consists of lower border of symphysis pubis( sacro cocc#ygial -oint and sacro ischial spine. . !bstetrical !utlet a. &ntero posterior diameter (1"cm)' ;#tends from inferior border of the symphysis pubis to the sacro coccy#gial -oint. b. !bli8ue diameter 7ight !bli8ue diameter (1 cm) ' e#tends from 7t. /acro spinous ligament to !bturator foramen .eft !bli8ue diameter (1 cm) ' e#tends from .t. /acro spinous ligament to !bturator foramen Transverse diameter (11cm) ' between the ischial spines. Types o% Pelvis 1. +ynaecoi# pelvis <ost suitable for childbirth 0ider brim $schial spines are blunt /ub pubic angle is =4> 2. (nthropoi# pelvis !val in shape Transverse diameter is shorter /een in tall women with narrow shoulders /ub pubic angle more than =4> 3. (n#roi# pelvis 1eart shaped brim &nterior posterior diameter is shorter Transverse diameter is wider %hildbirth is difficult ,. Platypelloi# pelvis ?idney shaped &nterior posterior diameter is smaller Transverse diameter is wider -uscles o% the pelvic %loor Super%icial muscles o %orpus cavernosa o $schiocavernosa o 2ulbocavernosa o Transverse perineal o ;#ternal sphinter ani 'eep -uscles
o o o
$schioco#ygeous muscle $leoco#ygeous muscle Puboco#ygeous
The Fetal S$ull (ntero.posterior #iameters o% the %etal hea# Suboccipito bre"matic) =.5cm e#tends from the nape of the neck to the centre of the bregma Suboccipito.%rontal) 14cm e#tends from the nape of the neck to the anterior end of the anterior fontanelle )ccipito.%rontal) 11.5cm e#tends from the occipital eminence to the root of the nose (glabella) -ento.vertical) 1".5cm e#tends from the mid point of the chin to the highest point on the saggital suture Submento. vertical) 11.5cm e#tends from the -unction of the floor of the mouth and neck to the highest point on the saggital suture Submento. bre"matic) =.5cm e#tends from -unction of the floor of the mouth and neck to the centre of the bregma. The transverse #iameters concerne# with the mechanism o% labour are
&iparietal #iameter) =.5cm( it e#tends between two parietal eminences Super.subparietal) @.5cm( it e#tends from a point placed below one parietal eminence to a point placed above the other parietal eminence of the opposite side &i.temporal #iameter) @cm(it is the distance between the antero)inferior ends of the coronal suture &i.mastoi# #iameter)A.5cm( it is the distance between the tips of the mastoid processes
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Microbiology MnemonicsDocument17 paginiMicrobiology MnemonicsAnnapurna Dangeti100% (2)
- Lower LimbDocument9 paginiLower LimbCrishu Razvi100% (4)
- Pediatrics MnemonicsDocument11 paginiPediatrics MnemonicsAnnapurna Dangeti100% (1)
- Emergency Medicine MnemonicsDocument18 paginiEmergency Medicine MnemonicsAnnapurna Dangeti100% (1)
- Chad Waterbury's ProgramsDocument34 paginiChad Waterbury's ProgramsBen Gibson100% (3)
- Biochemistry MnemonicsDocument20 paginiBiochemistry MnemonicsAnnapurna Dangeti100% (1)
- Physical Examination MnemonicsDocument11 paginiPhysical Examination MnemonicsAnnapurna Dangeti100% (1)
- MseDocument52 paginiMseAnnapurna DangetiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Logan Christopher - Secrets of The HandstandDocument61 paginiLogan Christopher - Secrets of The HandstandChouk Meta100% (3)
- Genital Tract InjuriesDocument24 paginiGenital Tract InjuriesManisha ThakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gastroenterology MnemonicsDocument10 paginiGastroenterology MnemonicsAnnapurna DangetiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Female PelvisDocument4 paginiFemale Pelvisvarshasharma05100% (1)
- Assignment On Neurological AssessmentDocument20 paginiAssignment On Neurological AssessmentSumandeep KaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internal Medicine MnemonicsDocument23 paginiInternal Medicine MnemonicsAnnapurna Dangeti0% (1)
- Cervical SpondylosisDocument26 paginiCervical SpondylosisAditya Anandito100% (2)
- Birth InjuriesDocument24 paginiBirth InjuriesGayathri R100% (1)
- Genetics MnemonicsDocument7 paginiGenetics MnemonicsAnnapurna Dangeti100% (1)
- Physiological Changes of Pregancy. NEW VERSION-For BSC Nursing StudentsDocument107 paginiPhysiological Changes of Pregancy. NEW VERSION-For BSC Nursing StudentsKripa Susan100% (2)
- MINOR DISORDERS OF PREGNANCY FinalDocument6 paginiMINOR DISORDERS OF PREGNANCY FinalChedupLepcha100% (7)
- Placental ExaminationDocument13 paginiPlacental ExaminationAnuradha Maurya50% (2)
- Seminar ON: Baby Friendly Hospital InitiativeDocument7 paginiSeminar ON: Baby Friendly Hospital InitiativeUmairah BashirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiology MnemonicsDocument18 paginiCardiology MnemonicsAnnapurna Dangeti100% (1)
- Bishop ScoreDocument21 paginiBishop ScoreShivam MalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obs Vaginal ExaminationDocument15 paginiObs Vaginal Examinationaparna shamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neck Pain, Cervical Radiculopathy, and Cervical MyelopathyDocument11 paginiNeck Pain, Cervical Radiculopathy, and Cervical MyelopathyAhmad Shakir100% (1)
- Anatomy MnemonicsDocument63 paginiAnatomy MnemonicsAnnapurna DangetiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maternal Pelvis Fetal Skull PDFDocument13 paginiMaternal Pelvis Fetal Skull PDFAnuradha Maurya100% (2)
- Female PelvisDocument18 paginiFemale PelvisNeelofur Ibran Ali100% (1)
- Female PelvisDocument7 paginiFemale PelvissubashikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fetal Skull and Maternal PelvisDocument28 paginiFetal Skull and Maternal PelvisAshwanee Jharia0% (1)
- Physiology of LabourDocument40 paginiPhysiology of LabourShubhi VaivhareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seminar On Female Pelvis and Pelvic FloorDocument11 paginiSeminar On Female Pelvis and Pelvic FloorJasmin SabnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uterine Malformations PDFDocument6 paginiUterine Malformations PDFsaritha OrugantiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neurology MnemonicsDocument26 paginiNeurology MnemonicsAnnapurna DangetiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ob EmergenciesDocument58 paginiOb Emergenciessanthiyasandy100% (1)
- Today Is The Big DayDocument9 paginiToday Is The Big DayAnnapurna DangetiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scientific Research Journal of India (SRJI) Vol - 2, Issue - 1, Year - 2013Document59 paginiScientific Research Journal of India (SRJI) Vol - 2, Issue - 1, Year - 2013Dr. Krishna N. SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prolonged Labour: Mrs. Shwetha Rani C.MDocument24 paginiProlonged Labour: Mrs. Shwetha Rani C.MSanthosh.S.U100% (1)
- 13 Genital Tract InjuriesDocument100 pagini13 Genital Tract InjuriesRana Vandana100% (1)
- Physiology and Management of 1St Stage of LabourDocument5 paginiPhysiology and Management of 1St Stage of LabourSucharita PandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physiology of 1st Stage of LaborDocument134 paginiPhysiology of 1st Stage of LaborVijith.V.kumar50% (2)
- Fetal Skull and Maternal PelvisDocument28 paginiFetal Skull and Maternal PelvisJawed HakeemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Managament of The 2nd Stage of LabourDocument53 paginiManagament of The 2nd Stage of LabourJSeashark100% (1)
- Augmentation of LabourDocument45 paginiAugmentation of LabourLamnunnem HaokipÎncă nu există evaluări
- Puerperium and Its Management 1Document35 paginiPuerperium and Its Management 1Elvis100% (2)
- Displacement of UtreusDocument13 paginiDisplacement of UtreusswethashakiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cephalo Pelvic Disproportion (CPD) & Contracted PelvisDocument45 paginiCephalo Pelvic Disproportion (CPD) & Contracted Pelvisbinipsamuel250% (1)
- Embryology MnemonicsDocument5 paginiEmbryology MnemonicsAnnapurna DangetiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanism of LabourDocument18 paginiMechanism of LabournamithaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-V Standardized and Non-Standardized Tests: Meaning, Characteristics, Objectivity, Validity, Reliability, Usability, Norms, Construction of TestsDocument11 paginiUnit-V Standardized and Non-Standardized Tests: Meaning, Characteristics, Objectivity, Validity, Reliability, Usability, Norms, Construction of TestsAnnapurna Dangeti100% (1)
- Unit-V Standardized and Non-Standardized Tests: Meaning, Characteristics, Objectivity, Validity, Reliability, Usability, Norms, Construction of TestsDocument11 paginiUnit-V Standardized and Non-Standardized Tests: Meaning, Characteristics, Objectivity, Validity, Reliability, Usability, Norms, Construction of TestsAnnapurna Dangeti100% (1)
- Assignment5 - Female PelvisDocument7 paginiAssignment5 - Female PelvispriyankaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument34 paginiEctopic Pregnancyannu panchalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bony Pelvis & Fetal SkullDocument130 paginiBony Pelvis & Fetal SkullSalman KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Minor Disorders of Newborn and Its ManagementDocument3 paginiMinor Disorders of Newborn and Its Managementarun26198891% (11)
- Abortion PP TDocument42 paginiAbortion PP TDivya ToppoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preventive Obstetrics PDFDocument25 paginiPreventive Obstetrics PDFAnju MargaretÎncă nu există evaluări
- Independent Nurse PractitionerDocument14 paginiIndependent Nurse PractitionerKarishma Shroff100% (1)
- 3rd Stage of LabourDocument10 pagini3rd Stage of LabourBhawna JoshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Normal Labour: 4 Mbbs Class Esut College of Medicine 2013Document77 paginiNormal Labour: 4 Mbbs Class Esut College of Medicine 2013nonny100% (1)
- Mechanism of LabourDocument10 paginiMechanism of LabourMithlesh Dewangan100% (4)
- Management of Woman During First Stage of Labour Management of Woman During First Stage of LabourDocument21 paginiManagement of Woman During First Stage of Labour Management of Woman During First Stage of LabourKinjal Vasava67% (3)
- Nephrology MnemonicsDocument5 paginiNephrology MnemonicsAnnapurna DangetiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uterine MalformationsDocument6 paginiUterine MalformationssubashikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maternal, Morbidity, Mortality and Fertility RatesDocument18 paginiMaternal, Morbidity, Mortality and Fertility Ratesmadhu.BÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment of Intrauterine Fetal Well BeingDocument11 paginiAssessment of Intrauterine Fetal Well Beingsagi mu100% (1)
- A Midwife in My Pocket: Pregnancy, Birth, and Life with a New Baby, Told as It Really IsDe la EverandA Midwife in My Pocket: Pregnancy, Birth, and Life with a New Baby, Told as It Really IsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physiology of Normal LabourDocument29 paginiPhysiology of Normal LabournamitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management of LabourDocument16 paginiManagement of LabourAlbert MusinguziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagnostic Modalities in PregnancyDocument11 paginiDiagnostic Modalities in PregnancyRavina Patel100% (1)
- Bleeding in Early PregnancyDocument25 paginiBleeding in Early PregnancyAnnapurna DangetiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stages of Labour: First StageDocument37 paginiStages of Labour: First StageJude Martin100% (1)
- Genital Tract InjuriesDocument19 paginiGenital Tract InjuriesMarvella Nongkhar100% (1)
- Postpartum Hemorrhage (PPH) : Prakash Thakulla InternDocument38 paginiPostpartum Hemorrhage (PPH) : Prakash Thakulla InternPrakash ThakullaÎncă nu există evaluări
- High Risk Labour FinalDocument60 paginiHigh Risk Labour FinalSusan HepziÎncă nu există evaluări
- HydramniosDocument31 paginiHydramniosSpandana DepuruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contracted PelvisDocument13 paginiContracted PelvisCuteness Romney100% (1)
- Puerperal SepsisDocument45 paginiPuerperal SepsisKalo kajiÎncă nu există evaluări
- AbortionsDocument99 paginiAbortionsAGERI PUSHPALATHAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Procedure Assignment For ManagementDocument7 paginiProcedure Assignment For ManagementPatel Amee100% (1)
- Pelvis: The Pelvis/Bony Gridle/Pelvic GridleDocument18 paginiPelvis: The Pelvis/Bony Gridle/Pelvic GridlepreezaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 - Applied AnatomyDocument46 pagini2 - Applied AnatomyKholoud KholoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Landmarks of PelvisDocument21 paginiLandmarks of Pelvisangel panchalÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER TWO ANATOMY OF FEMALE PELVIS AND PhysiologyDocument62 paginiCHAPTER TWO ANATOMY OF FEMALE PELVIS AND PhysiologyabyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Breastfeeding PositionsDocument2 paginiBreastfeeding PositionsAnnapurna DangetiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Get Some Now": in Ascending Resistor Value OrderDocument5 paginiGet Some Now": in Ascending Resistor Value OrderAnnapurna DangetiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychiatric EmergenciesDocument25 paginiPsychiatric EmergenciesAnnapurna DangetiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine System IntroductionDocument5 paginiEndocrine System IntroductionAnnapurna DangetiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Nursing PracticeDocument4 paginiAdvanced Nursing PracticeAnnapurna DangetiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Community Health Nursing-IIDocument4 paginiCommunity Health Nursing-IIAnnapurna DangetiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Signs in ObgyDocument2 paginiSigns in ObgyAnnapurna DangetiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscoskeletal SystemDocument5 paginiMuscoskeletal SystemJeevikaGoyalÎncă nu există evaluări
- JAAOS - Volume 03 - Issue 06 November 1995Document53 paginiJAAOS - Volume 03 - Issue 06 November 1995kenthepaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Levers in Musculoskeletal SystemDocument22 paginiLevers in Musculoskeletal SystemGlenn JohnstonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomic Aspects of Vaginal Eversion After Hysterectomy Delancey PDFDocument12 paginiAnatomic Aspects of Vaginal Eversion After Hysterectomy Delancey PDFANA ROSA HERNANDEZ HERNANDEZÎncă nu există evaluări
- ATLS 1.0 Mar 2018Document65 paginiATLS 1.0 Mar 2018Mahfilza MayubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hand Therapy NotesDocument2 paginiHand Therapy NotesPhillip Voglis0% (1)
- Ligamentos de La ManoDocument9 paginiLigamentos de La ManoEnrique Maturana SepulvedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2011 Physiotherapy Management of An Infant With Bilateral Congenital Talipes Equino VarusDocument5 pagini2011 Physiotherapy Management of An Infant With Bilateral Congenital Talipes Equino VarusPuput HarefaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hanakep 2 Neck SC Ii 2020Document47 paginiHanakep 2 Neck SC Ii 2020Hana AdivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscular System MindmapDocument1 paginăMuscular System MindmapMayeliz UrvinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Support Movement and LocomotionDocument13 paginiSupport Movement and LocomotionMuhammad AbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Frozen Shoulder Home ExercisesDocument5 paginiFrozen Shoulder Home ExercisesJörgen PuisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Poster Case Report Jecky Edited 2 (Final)Document1 paginăPoster Case Report Jecky Edited 2 (Final)Johannes CordeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biomechanical Determinants of Performance and Injury Risk During Cutting. A Performance-Injury ConflictDocument16 paginiBiomechanical Determinants of Performance and Injury Risk During Cutting. A Performance-Injury ConflictJuani CantellanosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tendon Exercises Alexander Zass Samson IronDocument7 paginiTendon Exercises Alexander Zass Samson IronpeebeepeesanjuÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Literature Review On De-Quervain's TenosynovitisDocument12 paginiA Literature Review On De-Quervain's TenosynovitisfricaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asthi Dhatu - Ayurveda and Modern Perspective: World Journal of Pharmaceutical and Medical ResearchDocument5 paginiAsthi Dhatu - Ayurveda and Modern Perspective: World Journal of Pharmaceutical and Medical ResearchKirti SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fractures of The Tibial PlafondDocument21 paginiFractures of The Tibial PlafondCamila FontechaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Posi 2Document19 paginiPosi 2Cathleen Drew TuazonÎncă nu există evaluări
- HeightDocument4 paginiHeightThiện Nhân NguyễnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dutton Chapter 24 The Temporomandibular JointDocument47 paginiDutton Chapter 24 The Temporomandibular JointdralismÎncă nu există evaluări
- Morris Iain - Basic KarateDocument49 paginiMorris Iain - Basic KarateBruno LeonardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Examination of Neck Pain According To CyriaxDocument33 paginiClinical Examination of Neck Pain According To CyriaxSahana ChowdhuryÎncă nu există evaluări