Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Day 1
Încărcat de
MRose SerranoDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Day 1
Încărcat de
MRose SerranoDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
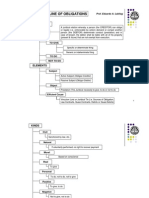
Credit Transactions Atty. Luis Alfonso Llaguno 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9.
Commodatum Mutuum Deposits Guaranty Surety Mortgage Chattel and Real Pledge Concurrence and Preference of Credit - Someone got insolvent - Liabilities more than his assets - Rules (Law provides order in payment) 10. Insolvency Law There are special laws governing other topics Ex: Chattel Mortgage Law Property Registration Decree. Homework: Law on Commodatum (1933-1952) Obligation and Contracts Obligation : to give(Real) to do or not do. ( Personal) Sources of Obligations To Give: Something To Do: Personal (Not subject to specific performance.) Determinate Indeterminate In case of loss (importance) Unilateral Obligation (( Donation) To accept or not.) Reciprocal (One Legal Source) // Non reciprocal ( Different Source) Bilateral Obligation They have obligation to each other. DELAY: DEMAND + LAPSE OF TIME - Time if someone has breached his contract.
Exceptions
Sources of Damages Fraud ( INCIDENTAL / CAUSAL) Negligence ( It can be waived) Delay Contravention of the Tenor of the Obligation (Obligor did not perform the obligation needed) - He did something else. - He violated the contract Force Majeure Types Pure Conditional ( Future and Uncertain & Past and Unknown) - Retroacts from the moment the obligation is constituted. - Resolutory Condition and Suspensive Consdition - Sole will of one of the parties (Potestative ) VOID - Eg. Death by Malaria Period - Happening of the event at some determinate time - It will definitely happen - Resolutory Condition and Suspensive Consdition - E. g. Death of a Person - For the benefit of both the D and C Joint and Solidary - Extent of Liability 2/more creditors or debtors - Solidary : Commodatum (Tort/ Employers) Obligation of Penal Clause Modes of Extinguishment 1. Payment (Complete) Ds excuse: Substantial Compliance in good faith : the C will reduce his obligation 3rd Party Payment Not Know: Delagacion : Up to the extent he is benefited (Beneficial Reimbursement)
Know: will assume the rights of the creditor. (Expromission) Legal Tender : Excludes Promissory notes and Checks ( Unless encashed) Special Forms of Payment 1. Dation in Payment : Initial : load with security delivery of the object 2. Application of Payments: Indebted by D to C (Not Consolidated) - Most onerous debts - All equal (Proportionally) 3. Payment by Cession (No longer used now a days because of Law of Insolvency) 4. Tender and Consignation 5. Loss: Change in the nature of the obligation to be delivered. - Cannot be invoked as a ground especially if its Generic. - Illegal, goes out of commerce, rebus sic instantibus 6. Condonation/ Remission 7. Confusion / Merger of Rights H&W (separation of property regime ) -> died Promissory Note Scenario D-> PN ->C->E->D (Grocery Items) 8. Compensation 9. Novation : Intent by the parties to extinguish the old obligation and change to a new one. Mortgage (Accessory Contract) x-D -> Z | y-C Mortgagor Contracts Meeting of the minds Offer: ( Complete and Certain) + Acceptance : Absolute = Performance of a Contracts Types of Contracts
1. Consensual Contract ( No need for Document ( Meeting of the Minds) Eg. Sales 2. Real Contracts: add something up ( Another element is added because of the Nature ( Delivery) Eg. Loan, Mutuum, Deposit, Commodatum, Pledge Meeting of the Minds + Delivery 3. Formal / Solemn contracts : Form for public policy. Consent = fraud Eg. Partnership of Real property, Donation + Acceptance, Chattel Mortgage (Must be registered) Five Principles of Contracts 1. Consensuality 2. Uninanimity 1306 (Can stipulate on anything) 3. Relativity (1311) : Contracts are binding upon the parties only. - Binding to the assigns, successors and heirs. - Exception: Commodatum 4. Obligatoriness: (1159) Contracts are the law of force between the parties. 5. Mutuality (Interest) 1308: The validity or enforceability cannot be left to the will of the parties. Types of Contracts Valid Voidable (within 4 Years) may be ratified Rescissible Contracts 1380 (Economic Prejudice) -> Resolution vs. 1191 - Creditor is not a party of the contract can sue for the rescission of the contract. - 4 Years - Can be ratified Unenforceable - 2 or more persons are incapacitated. - Agent goes beyond his authority - Statute of Frauds ( Procedural-> Substantive Laws)
o Defense can be waived o Failure to object; the court will still try the case. o Partial execution. Void An element is missing Element is illegeal Impossible Laws declare it void. Sale of animal with contagious disease. (Does not Prescribe) 3rd parties can assail Reformation : 10 Years from Cause of Action
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- ASS 5-Reviewer in Midterm Law On Obligations and ContractsDocument9 paginiASS 5-Reviewer in Midterm Law On Obligations and ContractsRev Richmon De ChavezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contract Law Chapter 8 NotesDocument6 paginiContract Law Chapter 8 NotesDavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Civrev TLCDocument13 paginiCivrev TLCAdrian BernardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ESSENTIAL ELEMENTS OF CONTRACTSDocument14 paginiESSENTIAL ELEMENTS OF CONTRACTSErika ApitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NOTES - Dec 7Document3 paginiNOTES - Dec 7cmv mendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cause and ObjectDocument30 paginiCause and ObjectAlmineÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACCLAW4 Incomplete ReviewerDocument3 paginiACCLAW4 Incomplete ReviewerAggi Rayne Sali BucoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Midterm Reviewer in BLDocument17 paginiMidterm Reviewer in BLRev Richmon De ChavezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contracts Art. 1305 - Art. 1317 Not All Agreements Are Contracts All Contracts Are AgreementsDocument24 paginiContracts Art. 1305 - Art. 1317 Not All Agreements Are Contracts All Contracts Are AgreementsDIOMARIS C. BASIOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contracts Notes General Provision ARTICLES 1305-1314Document6 paginiContracts Notes General Provision ARTICLES 1305-1314Maria Cristina Moreno PootÎncă nu există evaluări
- CONTRACTS (Arts. 1305-1317.) General ProvisionsDocument20 paginiCONTRACTS (Arts. 1305-1317.) General ProvisionsAlmineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oblicon Reviewer PDFDocument22 paginiOblicon Reviewer PDFKrisha BodiosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contracts Atty CasemDocument211 paginiContracts Atty CasemJonathan Japson LarozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ContractDocument10 paginiContractKyrah Angelica DionglayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accountancy Review Center (ARC) of The Philippines IncDocument8 paginiAccountancy Review Center (ARC) of The Philippines IncLouiseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obligations and Contract HandoutsDocument34 paginiObligations and Contract HandoutsSandra LobatonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Commercial Law EssentialsDocument17 paginiCommercial Law EssentialsrahulroycgÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 REVIEW NOTES ON CONTRACTS, OBLIGATIONS & DAMAGESDocument22 pagini1 REVIEW NOTES ON CONTRACTS, OBLIGATIONS & DAMAGESJanetGraceDalisayFabrero100% (1)
- Without Advance Notice To The BorrowerDocument2 paginiWithout Advance Notice To The BorrowerDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes ForDocument10 paginiNotes ForRufhyne DeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- ContractsDocument7 paginiContractsmallaripijjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contracts W/o VoidDocument24 paginiContracts W/o VoidmallaripijjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Law and ObligationDocument12 paginiLaw and ObligationMa. Ermina Mae CelestraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contracts General Provisions: Coverage of DiscussionsDocument19 paginiContracts General Provisions: Coverage of DiscussionsAmie Jane MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ContractDocument47 paginiContract2245151Încă nu există evaluări
- The Law of Contracts in 40 CharactersDocument1 paginăThe Law of Contracts in 40 CharactersKelsey100% (7)
- Module 1 - Topic No. 1 - Part9Document10 paginiModule 1 - Topic No. 1 - Part9Limuel MacasaetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Notes On Law On Contracts Revised 09Document17 paginiLecture Notes On Law On Contracts Revised 09JanetGraceDalisayFabrero100% (3)
- ObliCOn - Overview of ContractsDocument49 paginiObliCOn - Overview of ContractsAizen IchigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- MODULE DWCC - Obligation and Contracts Part3 OnlineDocument8 paginiMODULE DWCC - Obligation and Contracts Part3 OnlineCharice Anne VillamarinÎncă nu există evaluări
- RFBT ReviewersDocument13 paginiRFBT ReviewersRose MarieÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9 - Discharge & RemediesDocument4 pagini9 - Discharge & RemediesBeren RumbleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Civil Law Review 2 (Dean Villagonzalo)Document8 paginiCivil Law Review 2 (Dean Villagonzalo)Shine BillonesÎncă nu există evaluări
- ContractDocument10 paginiContractCeline CabreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Law School Survival Guide (Volume I of II) - Outlines and Case Summaries for Torts, Civil Procedure, Property, Contracts & Sales: Law School Survival GuidesDe la EverandLaw School Survival Guide (Volume I of II) - Outlines and Case Summaries for Torts, Civil Procedure, Property, Contracts & Sales: Law School Survival GuidesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contracts - Law 3Document28 paginiContracts - Law 3Aiziel OrenseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handout For ContractsDocument20 paginiHandout For ContractsLeane MarcoletaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Salient Points on Obligations and Contracts (Module 1Document4 paginiSalient Points on Obligations and Contracts (Module 1KN IT SOLUTIONÎncă nu există evaluări
- True. If He Committed An Act Na ExemptedDocument10 paginiTrue. If He Committed An Act Na ExemptedRegine LangrioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oblicon Diagrams - LabitagDocument74 paginiOblicon Diagrams - LabitagDigoy Esguerra100% (3)
- Business Law ContractsDocument10 paginiBusiness Law ContractsSabi HuddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discussion 3.1Document5 paginiDiscussion 3.1jenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contracts-Red 2Document167 paginiContracts-Red 2Gio Gonzales100% (2)
- Business Law EssentialsDocument109 paginiBusiness Law Essentialskamalpreetkaur_mba100% (1)
- Prelim Oblicon AnswerDocument25 paginiPrelim Oblicon Answerscrrbd467Încă nu există evaluări
- Contracts NotesDocument30 paginiContracts NotesJarelle Kate De GuzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obligations and ContractsDocument10 paginiObligations and ContractsCee HonasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obligations and Contracts 2Document6 paginiObligations and Contracts 2JpagÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Contract General ProvisionDocument3 pagini1 Contract General ProvisionVic BalmadridÎncă nu există evaluări
- CONTRACTS | 193Document208 paginiCONTRACTS | 193Twish BarriosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Law On ContractsDocument48 paginiLaw On ContractsElissa Pagulayan100% (2)
- General Provisions of Contract LawDocument5 paginiGeneral Provisions of Contract LawCandypopÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4) Special Modes of PaymentDocument15 pagini4) Special Modes of PaymentAndrea Gural De GuzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- BA 9207 Legal AspectsDocument55 paginiBA 9207 Legal Aspectsvasanth777Încă nu există evaluări
- Discharge of Contract LawDocument8 paginiDischarge of Contract LawAbi abiramiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contract Law ApuntesDocument4 paginiContract Law ApuntesVerónica Rueda PuyanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 3 Lesson 3 Laws On Obligations and ContractsDocument11 paginiModule 3 Lesson 3 Laws On Obligations and ContractsGerstene Reynoso MaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Self-Help Guide to the Law: Contracts and Sales Agreements for Non-Lawyers: Guide for Non-Lawyers, #5De la EverandThe Self-Help Guide to the Law: Contracts and Sales Agreements for Non-Lawyers: Guide for Non-Lawyers, #5Încă nu există evaluări
- The 5 Elements of the Highly Effective Debt Collector: How to Become a Top Performing Debt Collector in Less Than 30 Days!!! the Powerful Training System for Developing Efficient, Effective & Top Performing Debt CollectorsDe la EverandThe 5 Elements of the Highly Effective Debt Collector: How to Become a Top Performing Debt Collector in Less Than 30 Days!!! the Powerful Training System for Developing Efficient, Effective & Top Performing Debt CollectorsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Soccer (Football) Contracts: An Introduction to Player Contracts (Clubs & Agents) and Contract Law: Volume 2De la EverandSoccer (Football) Contracts: An Introduction to Player Contracts (Clubs & Agents) and Contract Law: Volume 2Încă nu există evaluări
- Joint AffidavitDocument2 paginiJoint AffidavitMRose SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lyceum of The Philippines: Court-Annexed MediationDocument2 paginiLyceum of The Philippines: Court-Annexed MediationMRose SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rule 78 Letters Testamentary and of AdministrationDocument3 paginiRule 78 Letters Testamentary and of AdministrationMRose SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- DateDocument1 paginăDateMRose SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Legal PaperDocument1 paginăLegal PaperMRose Serrano0% (1)
- Midterms& Sem ScheduleDocument1 paginăMidterms& Sem ScheduleMRose SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Estate TaxDocument6 paginiEstate TaxMRose SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- II Causes of ActionDocument2 paginiII Causes of ActionMRose SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter IIIDocument1 paginăChapter IIIMRose SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Outline Evidence.2014Document9 paginiCourse Outline Evidence.2014trishortizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adobe Photoshop Serial NumbersDocument1 paginăAdobe Photoshop Serial NumbersMRose SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Affidavit of No Land HoldingDocument1 paginăAffidavit of No Land HoldingMRose SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- TaxationDocument19 paginiTaxationMRose SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- My Home Address ... 1723 Riane Ln. Houston, TX 77049....Document1 paginăMy Home Address ... 1723 Riane Ln. Houston, TX 77049....MRose SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- April 28, 2014 - ADRDocument24 paginiApril 28, 2014 - ADRMRose SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Estate TaxDocument6 paginiEstate TaxMRose SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Legal ResearchDocument3 paginiLegal ResearchMRose SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tax1 CaseDigest NemoDocument14 paginiTax1 CaseDigest NemoMRose SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alaban+vs +caDocument2 paginiAlaban+vs +caMRose SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Torts Reviewer (Gianna - Ranx.tina - Gi.sam - Katz.alex - Emjo.didy)Document102 paginiTorts Reviewer (Gianna - Ranx.tina - Gi.sam - Katz.alex - Emjo.didy)MRose SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Public International Law (Finals) XI: International Protection For Human RightsDocument5 paginiPublic International Law (Finals) XI: International Protection For Human RightsMRose SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Torts Additional DigestDocument3 paginiTorts Additional DigestMRose SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Women and Children - Reaction PaperDocument3 paginiWomen and Children - Reaction PaperMRose SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Celedonio P. Gloria and Antonio Barredo For Petitioner. Jose G. Advincula For RespondentsDocument34 paginiCeledonio P. Gloria and Antonio Barredo For Petitioner. Jose G. Advincula For RespondentsMRose SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- SuccessionDocument286 paginiSuccessionMRose Serrano100% (2)
- Martha Rose C. Serrano - Court Reaction PaperDocument3 paginiMartha Rose C. Serrano - Court Reaction PaperMRose SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Torts Additional DigestDocument3 paginiTorts Additional DigestMRose SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Women and Children Atty. June AmbrosioDocument4 paginiWomen and Children Atty. June AmbrosioMRose SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Political Rights of Women in Philippine ContextDocument16 paginiThe Political Rights of Women in Philippine ContextMRose SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reaction Paper WomenDocument2 paginiReaction Paper WomenMRose SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Administrative Code of 1987Document14 paginiAdministrative Code of 1987Neill Matthew Addison OrtizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Illegality Defence NotesDocument1 paginăIllegality Defence NotesElenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Designer Basket, Inc. Vs Air Sea TransportDocument8 paginiDesigner Basket, Inc. Vs Air Sea TransportPeter PiperÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus - 2012-13 Civil Procedure (Avena)Document22 paginiSyllabus - 2012-13 Civil Procedure (Avena)Renz RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conflicts of Law All Cases (Digest)Document35 paginiConflicts of Law All Cases (Digest)paul2574100% (2)
- Conflicts of Laws - Case Digests (Contractual Relations)Document5 paginiConflicts of Laws - Case Digests (Contractual Relations)Hazelmer FernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rules 6 10Document77 paginiRules 6 10cmv mendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Republic vs. CastellviDocument13 paginiRepublic vs. CastellviJohn Edward Kenneth Macawili RagazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- JACA vs. PEOPLEDocument2 paginiJACA vs. PEOPLEAbigail TolabingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Validity of Customs Personnel Order ChallengedDocument57 paginiValidity of Customs Personnel Order ChallengedPAMELA PARCEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class Note On Contract LawDocument11 paginiClass Note On Contract LawMustafizur Rahman Deputy ManagerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Privileged Mitigating Rather Than Just OrdinaryDocument7 paginiPrivileged Mitigating Rather Than Just OrdinaryPortia WynonaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liability LawDocument3 paginiLiability LawCarina MariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BailDocument40 paginiBailLyana Sulaiman100% (1)
- Disclaimer:: Code of Civil Procedure, 1908Document1 paginăDisclaimer:: Code of Civil Procedure, 1908KartikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trade and Investment v. Phil. Veterans BankDocument8 paginiTrade and Investment v. Phil. Veterans BankCZARINA ANN CASTROÎncă nu există evaluări
- UCD Property Law II Adverse PossessionDocument6 paginiUCD Property Law II Adverse PossessionPaul O'Dea100% (2)
- Ereneta Vs BezoreDocument4 paginiEreneta Vs BezoreAbigail DeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- NPC vs Court of Appeals and ECI - Damages from typhoon-induced floodingDocument7 paginiNPC vs Court of Appeals and ECI - Damages from typhoon-induced floodingTris LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 525A CJ2 Performance TablesDocument20 pagini525A CJ2 Performance TablesErnani L AssisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Framework Civil ProcedureDocument6 paginiFramework Civil ProcedureRayner AbuegÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tan Boon Bee V JarencioDocument2 paginiTan Boon Bee V JarencioPeperoniiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operating Agreement of BTF, LLCDocument7 paginiOperating Agreement of BTF, LLCjsconrad12Încă nu există evaluări
- Vfp. Vfpia and The VMDCDocument28 paginiVfp. Vfpia and The VMDCPrincess Trisha Joy UyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expert Travel v. CADocument15 paginiExpert Travel v. CARedge DionisioÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Limitation Act, 1908 PDFDocument92 paginiThe Limitation Act, 1908 PDFMimi mekiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adversepossesionofimmprop Judgement 07 Aug 2019Document60 paginiAdversepossesionofimmprop Judgement 07 Aug 2019roshankaziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ayala Investments Vs CA GR No. 118305, February 12, 1998Document2 paginiAyala Investments Vs CA GR No. 118305, February 12, 1998Loisse VitugÎncă nu există evaluări
- Construction Law Study NotesDocument9 paginiConstruction Law Study NotesJazzmondÎncă nu există evaluări
- Williams v Carwardine Case SummaryDocument8 paginiWilliams v Carwardine Case SummaryBhumika M ShahÎncă nu există evaluări