Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Biology - Biodiversity
Încărcat de
www.bhawesh.com.npDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Biology - Biodiversity
Încărcat de
www.bhawesh.com.npDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Downloaded from:- www.bhawesh.com.
np
Downloaded from:- www.bhawesh.com.np
TAXONOMY
The taxonomy is the branch of biology, which deals with identification, naming, and
classification of organisms. The father of taxonomy is considered as Carolus Linnaeus.
Binomial Nomenclature
The system of giving scientific name to organisms by using two Latin words is called
binomial nomenclature. For example Rana tigrina (Frog). The first word represents genus
and the name is called generic name. The second word represents species and called
specific name. Some of the scientific names of organisms are given below.
Man Homo sapiens Lion Panthera
tigris
Onion Allium sepa Garlic Allium sativum
Potato Solanum tuberosum Rat Rattus rattus
Rules of binomial nomenclature
Scientific name should be in two Latin words.
The scientific name should be italicized.
Scientific name should be underlined in hand written script
The generic name should be started from capital letter and the specific name should
be started from small letter.
The scientific name of the two or more organisms should not be similar.
Two Kingdom System of Classification
Carolus Linnaeus divided the organisms into two kingdoms, the plant Kingdom and the
Animal Kingdom. This system was based on the characteristics of animals and the plants.
Plant Kingdom Animal Kingdom
The organisms of this kingdom are
autotrophic i.e. they bear chlorophyll
molecule
They have cellulosic cell wall around the
cell
The body is fixed at one place
They are less sensitive due to absence of
nervous system
Their reserved food material is starch
Centrosome is absent in the cell
Large vacuoles are present in the cells
The body is branched having definite
shape
The organisms of this kingdom are
heterotrophic i.e. they do not bear
chlorophyll
They don't have cellulosic cell wall in the cell
They show locomotion, not fixed organisms
They are highly sensitive due to presence of
nervous system
Their reserved food material is glycogen
The centrosome is present in the cell
Vacuoles are very small or absent
The body is compact having definite shape
Downloaded from:- www.bhawesh.com.np
Downloaded from:- www.bhawesh.com.np
Shortcomings of Two Kingdom System of Classification
The cell of bacteria consists of cell wall and it is heterotrophic. They show characters of
both plants and animals. The body of fungi is highly branched and cell has cell wall but
they are heterotrophic and the stored food is glycogen. Hence, they show both plant
and animal like characters. A kind of protozoan named Euglena contains chlorophylls
and shows locomotion. It also shows both plant and animal like characters.
Five Kingdom System of Classification
To include all the organisms, Robort H Whittaker in 1969 proposed a new system of
classification. In his system, the organisms are included in five kingdoms. They are
Monera, Protista, Fungi, Animalia, and Plantae. This system is based on cellular
complexity, body structure, and mode of nutrition.
General Characters
Kingdom Monera
This kingdom includes all the unicellular, microscopic, and prokaryotic organisms, which do not
contain a well-defined nucleus, the nuclear material is freely found in cytoplasm, they lack well-
developed cell organelles, they may be auto or heterotrophic Example: Bacteria and
Cyanobacteria
Kingdom Protista
This kingdom includes all the unicellular but eukaryotic organisms which are: auto or heterotrophic,
the cell contain well defined nucleus and cell organelles, all the vital activities are performed by
single cell, Example: Euglena, Volvox, Paramecium, Amoeba
Kingdom Fungi
This kingdom includes all the multicellular few are unicellular eukaryotic organisms, which are:
Heterotrophic that grows on decaying organic matter, achlorophyllous, branched body, do not
show locomotion, cell wall is made up of chitin, reserve food is glycogen. Example: Yeast, Mucor,
Mushroom.
Kingdom Animalia
This kingdom includes all the multicellular eukaryotic organisms, which are: heterotrophic that feeds
on autotrophic organisms through different way, show movement, no cell wall is present, reserve
food is glycogen, body is compact. Example: Rat, Pigeon, Frog
Kingdom Plantae
This kingdom includes all the multicellular eukaryotic organisms which are: autotrophic due to
having chlorophyll molecules for photosynthesis, cellulosic cell wall is present, reserve food is starch,
do not show locomotion, body is branced. Example: mustard, mango etc.
In this system the monera are thought to have originated at first. The protista are
originated from monera. From protista Fungi and animalia and plantae were evolved.
This shows a evolutionary relationship among five kingdoms. This relationship is called
phyllogenetic relationship. The evolutionary history of an organism is called phylogeny.
The classification based on the phyllogenetic relationship is called phylogenetic system
of classification.
Downloaded from:- www.bhawesh.com.np
Downloaded from:- www.bhawesh.com.np
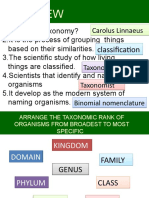
Taxonomic categories
There are different categories or
groups to classify or to include related
organisms in same group to make
easier for study are called taxonomic
categories.
Any category of the taxonomic
group of any rank is called taxon
(pleural-taxa)
Taxonomic Higherarchy
The arrangement of taxonomic categories based on the taxonomic rank is called
taxonomic higherarchy. The highest rank of the taxonomic categories is kingdom and
the lowest rank is species.
What is species or why species is called basic unit of taxonomy?
The species means group of individuals having very close relationship and they can
reproduce successfully. Below species, there is no any rank of taxonomic category.
Therefore, it is called basic unit of taxonomy, for eg. tigrina is the species of frog.
Genus: The group of two or more species having similarity in many characters is called
genus, for eg. Rana is the genus of frog.
Family: The group of two or more genus having similarity in many characters is called
family, for eg Ranidae is the family of frog.
Order: The group of two or more family having similarity in many characters is called order,
for eg Anura is the family of frog.
Division: The group of two or more orders having similarity in many characters is called
division, for eg Gnathostomata is the family of frog.
Class: The group of two or more divisions having similarity in many characters is called
class, for eg Amphibia is the family of frog.
Phylum: The group of two or more classes having similarity in many characters is called
Phylum, for eg Chordata is the family of frog.
Kingdom: The group of two or more phyla having similarity in many characters is called
kingdom, for eg Animalia is the family of frog.
Plant Animal
Kingdom
Division
Class
Series
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Series
Order
Family
Genus
Speceis
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- CH 03 BiodiversityDocument9 paginiCH 03 BiodiversityZain NoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hierarchical TaxonomicDocument24 paginiHierarchical TaxonomicJoedee NicolasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Notes For Medical EntranceDocument40 paginiBiology Notes For Medical EntranceNickOoPandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1st Year Notes Biology PDFDocument144 pagini1st Year Notes Biology PDFmrtweets67% (6)
- Classification of OrganismDocument35 paginiClassification of OrganismJnll JstnÎncă nu există evaluări
- ClassificationDocument39 paginiClassificationAl-Bien TadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1st Year Notes BiologyDocument144 pagini1st Year Notes BiologyAkbar Dad BabarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classification of Living OrganismsDocument29 paginiClassification of Living OrganismsOJ ICONICÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linnaeuss System of ClassificationDocument33 paginiLinnaeuss System of Classificationheartyjune.ortizo0610Încă nu există evaluări
- "Biodiversity" Is A Concise Form of "Biological Diversity" and Was Biodiversity Is The Occurrence of Diverse or Varied Forms of Living Beings WhichDocument11 pagini"Biodiversity" Is A Concise Form of "Biological Diversity" and Was Biodiversity Is The Occurrence of Diverse or Varied Forms of Living Beings Whichbrm1shubhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Five Kingdom SystemDocument8 paginiFive Kingdom SystemsanaullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample OnlyDocument6 paginiSample OnlySeb LlaveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taxonomy XI Final NewDocument5 paginiTaxonomy XI Final NewPrazwal RegmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classification of Living Organism G8Document5 paginiClassification of Living Organism G8Akeisha PascuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stages of Living ThingsDocument18 paginiStages of Living ThingsJay DansÎncă nu există evaluări
- Living World Class XiDocument32 paginiLiving World Class XivijithamuraliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes BiologyDocument144 paginiNotes BiologySrikanth VsrÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 2 2Document8 pagini4 2 2bejeweled1308Încă nu există evaluări
- TaxonomicDocument51 paginiTaxonomicAlvin OliverosÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2nd Jump ReportDocument17 pagini2nd Jump Reportzyan reyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acellular LifeDocument20 paginiAcellular LifeMinahil IlyasÎncă nu există evaluări
- PP27 Classification Systems UPDATEDDocument59 paginiPP27 Classification Systems UPDATEDnaledimonyela3Încă nu există evaluări
- Life VarityDocument23 paginiLife VaritySubhan ullah TutorialÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 - BiodiversityDocument8 paginiChapter 3 - BiodiversityShah SaqibÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Taxonomic Concept & Principles, Description, Nomenclature, Identification & ClassificationDocument28 paginiBasic Taxonomic Concept & Principles, Description, Nomenclature, Identification & ClassificationKaela Sophia AndalisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Notes (2) 1Document90 paginiBiology Notes (2) 1refilwesechele057Încă nu există evaluări
- Beta Monic Ai-MonicaiDocument6 paginiBeta Monic Ai-MonicaiJAYAKUMARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taxonomy Report PDFDocument18 paginiTaxonomy Report PDFjoreina ramosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classification - Taxonomy ReadingDocument7 paginiClassification - Taxonomy Readingapi-262368188Încă nu există evaluări
- Classification of Organisms: Name: Class: VII Date: Subject: ScienceDocument3 paginiClassification of Organisms: Name: Class: VII Date: Subject: ScienceShashi AgnihotriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biodiversity: The Origin of SpeciesDocument19 paginiBiodiversity: The Origin of Speciesnasrin banuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 7 SCDocument5 paginiChapter 7 SCapi-523871804Încă nu există evaluări
- PP27. Classification SystemsDocument44 paginiPP27. Classification SystemsThanyani MavhivhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classification of OrganismsDocument63 paginiClassification of OrganismsKim DahyunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Text 2 Classification of Living ThingsDocument3 paginiText 2 Classification of Living ThingsmisterxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kingdom Classification 3Document28 paginiKingdom Classification 3Merium FazalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology NotesDocument88 paginiBiology NotesKordell leydÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classification, Biodiversity & Conservation: Made by Zainah Jabr Grade: 12-ADocument10 paginiClassification, Biodiversity & Conservation: Made by Zainah Jabr Grade: 12-Azainah jabrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Living Organisms and SpeciesDocument2 paginiLiving Organisms and SpeciesmeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class Notes of CBSE 9Document8 paginiClass Notes of CBSE 9Tapas BanerjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBSE 11th Sample BIOLOGY 1Document17 paginiCBSE 11th Sample BIOLOGY 1ALEENA KANNIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diversity in Living Organisms Biodiversity-The Wide Variety of Living Organisms (Flora and Fauna) On Earth ConstitutesDocument6 paginiDiversity in Living Organisms Biodiversity-The Wide Variety of Living Organisms (Flora and Fauna) On Earth ConstitutesAAKASH JOONÎncă nu există evaluări
- HierarchyDocument4 paginiHierarchyBinazir RavanbakhshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Making Sense of Our Biological World: Lesson 3Document43 paginiMaking Sense of Our Biological World: Lesson 3Beng QuinnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taxonomy and Classification UpdateDocument40 paginiTaxonomy and Classification UpdateQuartermaster RobotÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03 TaxonomyDocument11 pagini03 TaxonomythinkiitÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8D Classification V3Document21 pagini8D Classification V3Cricket DavisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To 5 Kingdom Classification - Grade 8Document5 paginiIntroduction To 5 Kingdom Classification - Grade 8anirudhramesh289Încă nu există evaluări
- Class 9 Diversity in Living Organisms BiologyDocument8 paginiClass 9 Diversity in Living Organisms BiologyShweta ShuklaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review: Classification ClassificationDocument28 paginiReview: Classification ClassificationGerlie VelascoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animal KingdomDocument5 paginiAnimal KingdomEstrella RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 - Characteristics and Classification of Living ThingsDocument3 pagini1 - Characteristics and Classification of Living ThingsAvyay TopraniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Definition and Classification, Exemplification Text, Arado, BrettniaDocument5 paginiDefinition and Classification, Exemplification Text, Arado, BrettniaShiela JoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biological ScienceDocument21 paginiBiological Sciencehelperforeu100% (3)
- Additional: By: Group 1Document12 paginiAdditional: By: Group 1Wem Louie YapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Taxonomy: DiversityDocument12 paginiIntroduction To Taxonomy: DiversityRajesh Kumar GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handout For Week 6Document10 paginiHandout For Week 6Cheena Francesca LucianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviewer in BiologyDocument13 paginiReviewer in BiologyAldren BeliberÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taxonomy 1Document27 paginiTaxonomy 1Rouie john dizonÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Completely Different World of Protists - Biology Book for Kids | Children's Biology BooksDe la EverandThe Completely Different World of Protists - Biology Book for Kids | Children's Biology BooksÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economics Class 11 Unit 14-StatisticsDocument0 paginiEconomics Class 11 Unit 14-Statisticswww.bhawesh.com.npÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economics Class 11 Unit 13-Development-PlanningDocument0 paginiEconomics Class 11 Unit 13-Development-Planningwww.bhawesh.com.npÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economics Notes Class 11 All in OneDocument0 paginiEconomics Notes Class 11 All in Onewww.bhawesh.com.np85% (46)
- Economics Class 11 Unit 8-PovertyDocument0 paginiEconomics Class 11 Unit 8-Povertywww.bhawesh.com.npÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economics Class 11 Unit 9-IndustryDocument0 paginiEconomics Class 11 Unit 9-Industrywww.bhawesh.com.np100% (2)
- Economics Class 11 Unit 15 Collection of DATADocument0 paginiEconomics Class 11 Unit 15 Collection of DATAwww.bhawesh.com.npÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economics Class 11 Unit 12-Government-FinanceDocument0 paginiEconomics Class 11 Unit 12-Government-Financewww.bhawesh.com.npÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economics Class 11 Unit 2-Basic-Economic-IssuesDocument0 paginiEconomics Class 11 Unit 2-Basic-Economic-Issueswww.bhawesh.com.npÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economics Class 11 Unit 11-Foreign-TradeDocument0 paginiEconomics Class 11 Unit 11-Foreign-Tradewww.bhawesh.com.npÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economics Class 11 Unit 4-Economic-DevelopmentDocument0 paginiEconomics Class 11 Unit 4-Economic-Developmentwww.bhawesh.com.npÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economics Class 11 Unit 1 - Basic-Concept-Of-EconomicDocument0 paginiEconomics Class 11 Unit 1 - Basic-Concept-Of-Economicwww.bhawesh.com.np100% (5)
- Economics Class 11 Unit 5 Natural Resources of NepalDocument0 paginiEconomics Class 11 Unit 5 Natural Resources of Nepalwww.bhawesh.com.npÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economics Class 11 Unit 7-AgricultureDocument0 paginiEconomics Class 11 Unit 7-Agriculturewww.bhawesh.com.np0% (1)
- Economics Class 11 Unit 6-Human-ResourceDocument0 paginiEconomics Class 11 Unit 6-Human-Resourcewww.bhawesh.com.npÎncă nu există evaluări
- SLC - OPT Math - FunctionsDocument0 paginiSLC - OPT Math - Functionswww.bhawesh.com.np100% (1)
- Biology - Botany - Kingdom MoneraDocument0 paginiBiology - Botany - Kingdom Monerawww.bhawesh.com.npÎncă nu există evaluări
- SLC - OPT Math - PolynomialsDocument0 paginiSLC - OPT Math - Polynomialswww.bhawesh.com.npÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology - Zoology Unit 7 Detailed Study of FrogDocument0 paginiBiology - Zoology Unit 7 Detailed Study of Frogwww.bhawesh.com.npÎncă nu există evaluări
- SLC - OPT Math - Compound AnglesDocument0 paginiSLC - OPT Math - Compound Angleswww.bhawesh.com.np100% (1)
- Biology - Unit 4 Kingdom ProtistaDocument0 paginiBiology - Unit 4 Kingdom Protistawww.bhawesh.com.npÎncă nu există evaluări
- SLC - Compulsory Math - Time and WorkDocument0 paginiSLC - Compulsory Math - Time and Workwww.bhawesh.com.npÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology - Unit 9 Animal BehaviourDocument0 paginiBiology - Unit 9 Animal Behaviourwww.bhawesh.com.np100% (1)
- SLC - Compulsory Math - Area of Triangles and ParallelogramDocument0 paginiSLC - Compulsory Math - Area of Triangles and Parallelogramwww.bhawesh.com.npÎncă nu există evaluări
- SLC - Compulsory Math - Theorems From GeometryDocument0 paginiSLC - Compulsory Math - Theorems From Geometrywww.bhawesh.com.np100% (1)
- SLC - Compulsory Math - SETSDocument0 paginiSLC - Compulsory Math - SETSwww.bhawesh.com.npÎncă nu există evaluări
- SLC - Compulsory Math - Geometric DeductionDocument10 paginiSLC - Compulsory Math - Geometric Deductionwww.bhawesh.com.np0% (1)
- SLC - OPT Math - Arithmetic ProgressionDocument0 paginiSLC - OPT Math - Arithmetic Progressionwww.bhawesh.com.npÎncă nu există evaluări
- SLC - Opt Math - AllDocument0 paginiSLC - Opt Math - Allwww.bhawesh.com.np100% (1)
- SLC - Compulsory Math - Measurement of Areas & Volumes of Solid FiguresDocument0 paginiSLC - Compulsory Math - Measurement of Areas & Volumes of Solid Figureswww.bhawesh.com.np100% (1)
- SLC - Compulsory Math - Model Question - AllDocument29 paginiSLC - Compulsory Math - Model Question - Allwww.bhawesh.com.np75% (8)
- Chapter 1 PDFDocument48 paginiChapter 1 PDFresearch55Încă nu există evaluări
- Biology CH 17-Tree of Life and Classification Final VersionDocument42 paginiBiology CH 17-Tree of Life and Classification Final VersionIvy Dianne PascualÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Name: English in Biology: Organisms Have Several Levels of OrganizationDocument7 paginiCourse Name: English in Biology: Organisms Have Several Levels of OrganizationViễn PhúuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Micro CH 2b TaxonomyDocument80 paginiMicro CH 2b TaxonomyBernadette Joyce PascualÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taxonomic Nomenclature2Document18 paginiTaxonomic Nomenclature2zendamariesabinayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carolus LinnaeusDocument30 paginiCarolus Linnaeusummu atiqah maisaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Living World FinalDocument31 paginiThe Living World FinalSourajeet SahooÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03 XI Biology Question BankDocument240 pagini03 XI Biology Question BankAnonymous fn9zdHU7Încă nu există evaluări
- +1 Biology Chapter 1 PDFDocument22 pagini+1 Biology Chapter 1 PDFArjun v sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Micr 22 Lab ManualDocument226 paginiMicr 22 Lab ManualJulio CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is A HerbariumDocument5 paginiWhat Is A HerbariumnairaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Materi Taksotum Binomial NomenklaturDocument46 paginiMateri Taksotum Binomial NomenklaturSolihatun RodiyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Target: Pre-Medical-2023/neet/nurture/phase-I/internal Test-02/19.05.2021Document4 paginiTarget: Pre-Medical-2023/neet/nurture/phase-I/internal Test-02/19.05.2021Ananya BalajiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Med-RM Bot SP-1 Ch-3 The Living WorldDocument24 paginiMed-RM Bot SP-1 Ch-3 The Living Worldkrish masterjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Requisites in Developing Good Research TitleDocument2 paginiRequisites in Developing Good Research TitleJohnmichael IbrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taxonomy Classification 17Document27 paginiTaxonomy Classification 17Shayvon Clarke100% (1)
- Taxonomy and KeysDocument8 paginiTaxonomy and KeysJoshua SakalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Botanical Classification of VegetablesDocument4 paginiBotanical Classification of Vegetablesusha rani VeeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- LP (Classification of Living Thingsgroup)Document5 paginiLP (Classification of Living Thingsgroup)a.gayle1998Încă nu există evaluări
- Biology MSDocument6 paginiBiology MSalafaabdallah118Încă nu există evaluări
- Classification of Microbes Unit IIDocument66 paginiClassification of Microbes Unit IIjaskarn_jazz100% (1)
- G 6 Scintbk 2Document275 paginiG 6 Scintbk 2Bullet Rubia100% (1)
- Fossils NotesDocument7 paginiFossils NotesKate PerojaÎncă nu există evaluări
- IGCSE Biology Section 1 Lesson 1Document44 paginiIGCSE Biology Section 1 Lesson 1Zhuko Suko AdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diversity and ClassifictionDocument25 paginiDiversity and ClassifictionmiomodgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carl LinnaeusDocument3 paginiCarl LinnaeusKhalil Mae LabuyoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 - The Living World PDFDocument4 paginiChapter 1 - The Living World PDFChainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Living WorldDocument33 paginiLiving WorldShuryans MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- ZOOLOGY BasicsNotes PDFDocument10 paginiZOOLOGY BasicsNotes PDFknarasimhareddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Living World Class 11 Notes Biology Chapter 1Document13 paginiThe Living World Class 11 Notes Biology Chapter 1dharun0704Încă nu există evaluări