Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Bipol Better Known As Biodegradable Polymer
Încărcat de
Diana NguyenDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Bipol Better Known As Biodegradable Polymer
Încărcat de
Diana NguyenDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
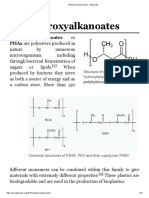
Bipol better known as Biodegradable Polymer, is a copolymer of PHB and PHV, produced through the bacteria Alcaligenes Europhus(
Cupriavidus necator). Alcaligenes Eutrophus is cultivated in a suitable medium. For it to proliferate it is than fed with a carbon based food substance such as fructose or glucose. Once proliferation is sufficient certain nutrients are restricted or removed, in the case of Alcaligenes Eutrophus nitrogen is removed. Because of the removal of nitrogen, which is an element for bacteria to proliferate, the bacteria stop dividing and start producing the polymer in cutoplasmic granules. The bacterial cell are than lysed, usually with detergent and the polymer is extracted and then purified. In the case of PHB ,the percentage of Poly(3HB ) in bacterial cells is normally low, from 1 to 30%, but under controlled fermentation conditions of carbon excess and nitrogen limitation, overproduction of polymer can be encouraged to produce yields of up to 80% of the dry cell weight.
Bipol has many similar properties to other polymers( polypropylene): Insoluble in water non toxic
strong thermoplastic Melting point is 140C- 180C resistant to chemical attack renewable biocompatible( medical applications) biodegradable( waste management)
Due to these properties Bipol can be used for disposable nappies, shampoo bottles, sutures( stitches), stents and bone plates. In the use of Bipol for these is that it is biodegradable, while many other plastic or polymers are not biodegradable or take a long time to breakdown. It is able to biodegrade as in PHA's they are produced from renewable resources( the A.eutrophus), their structures can be manipulated through genetic and physiological measures. PHA is blended and regulated with natural and or synthetic polymers which allow for the microbes to produce PHA degrading enzymes, short chains of PHA behave similarly to polypropylene thus having many similar properties. However Bipol is very expensive to produce as it requires technical expertise such as microbiologist, to further study and analyse the bacteria and also polymer extraction is a hard task as it does not always have enough yield. Recent discoveries for the use of Bipol is that Bipol could be used in genetic engineering, for example the genes that allow Alcaligenes Eutrophus to produce cytoplasmic granules when nitrogen is depleted, can be extracted from the bacteria and transferred to a more faster efficient bacteria such as E.coli bacteria which multiplies faster and allows for higher yield and easier extraction. Also the possibility of implanting this gene into plants such as potatoes and corn, thus instead of storing starch it would store polymer instead, however transgenic plants may not be sufficient due to costs, land coverage and the fact that plants may not grow if it only stores polymer as plants require other necessities to grow. Thus Bipol is a very useful biodegradable copolymer and with further research could replace polypropylene and be a greener substance to use instead of polypropylene.
By: Diana Nguyen
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- A Compilation of Ligno-Cellulose Feedstock and Related Research for Feed, Food and EnergyDe la EverandA Compilation of Ligno-Cellulose Feedstock and Related Research for Feed, Food and EnergyÎncă nu există evaluări
- BiopolDocument3 paginiBiopolJeffrey100% (2)
- Fungi and Lignocellulosic BiomassDe la EverandFungi and Lignocellulosic BiomassChristian P KubicekÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIOPOLDocument4 paginiBIOPOLLewis TranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biopol (PHA)Document1 paginăBiopol (PHA)Anna WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Bioplastic and Biopolymer ProductionDocument10 paginiUnesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Bioplastic and Biopolymer ProductionAliAliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Production of The Biopolymer: (Hydroxybutanoate)Document2 paginiProduction of The Biopolymer: (Hydroxybutanoate)Hemant KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Araújo Et Al.. 2020. Demonstration of The Ability of The Bacterial Polysaccharide FucoPol To Flocculate Kaolin SuspensionsDocument29 paginiAraújo Et Al.. 2020. Demonstration of The Ability of The Bacterial Polysaccharide FucoPol To Flocculate Kaolin SuspensionsAzb 711Încă nu există evaluări
- Hemant Kumar - Biopolymer ResearchDocument2 paginiHemant Kumar - Biopolymer ResearchHemant KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microbial Production of Biopolymers and Polymer PrecursorsDocument10 paginiMicrobial Production of Biopolymers and Polymer PrecursorsIJRASETPublicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Single-Cell Protein Single-Cell Protein (SCP) Refers To Edible Unicellular Microorganisms. The Biomass orDocument33 paginiSingle-Cell Protein Single-Cell Protein (SCP) Refers To Edible Unicellular Microorganisms. The Biomass orSiddhant SoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Salinivibrio SP PHAsDocument6 paginiSalinivibrio SP PHAsteacher.mireyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polyhydroxybutanoate (PHB) :: ProductionDocument1 paginăPolyhydroxybutanoate (PHB) :: ProductionRaymond MoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biotech Roject 1Document30 paginiBiotech Roject 1bhaskar VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 14.Applied-BioPlastic A Better-Mukti GilDocument6 pagini14.Applied-BioPlastic A Better-Mukti GilImpact JournalsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kanjan A Chump Ol 2013Document12 paginiKanjan A Chump Ol 2013Kaomi CarbajalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Production of Poly (3-Hydroxybutyrate) by Fed-Batch Culture of Filamentation-Suppressed Recombinant Escherichia ColiDocument5 paginiProduction of Poly (3-Hydroxybutyrate) by Fed-Batch Culture of Filamentation-Suppressed Recombinant Escherichia Coliapi-3743140Încă nu există evaluări
- 17 Microbial Biomass Protein: 17.1 Production and Properties of QuornDocument2 pagini17 Microbial Biomass Protein: 17.1 Production and Properties of Quornboladenieve63Încă nu există evaluări
- Fermentation of Lactose To Ethanol in Cheese WheyDocument13 paginiFermentation of Lactose To Ethanol in Cheese WheyVitor ArsenioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fermentation of Lactose To Ethanol in Cheese Whey Permeate and Concentrated Permeate by Engineered Escherichia ColiDocument12 paginiFermentation of Lactose To Ethanol in Cheese Whey Permeate and Concentrated Permeate by Engineered Escherichia ColijoelfloresanchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ijbt 4 (2) 186-193 PDFDocument0 paginiIjbt 4 (2) 186-193 PDFdian_2108Încă nu există evaluări
- The Overview of Fermentation ProcessesDocument29 paginiThe Overview of Fermentation ProcessesNur JannahÎncă nu există evaluări
- FermentationDocument27 paginiFermentationaqsaÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Recombinant Escherichia Coli Strain Tailored For The ProductionDocument6 paginiNew Recombinant Escherichia Coli Strain Tailored For The ProductionAndresMauricio MontesGonzalezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biocatalysts Based On Immobilized Cells of Microorganisms in The Production of Bioethanol and BiobutanolDocument6 paginiBiocatalysts Based On Immobilized Cells of Microorganisms in The Production of Bioethanol and BiobutanolYisela Escobar CortésÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polymers of 3-Hydroxyacids in Plants: Enea Rezzonico, Laurence Moire & Yves PoirierDocument6 paginiPolymers of 3-Hydroxyacids in Plants: Enea Rezzonico, Laurence Moire & Yves PoirierhafsaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abstract - Advance Microbial Treatment MethodologiesDocument3 paginiAbstract - Advance Microbial Treatment MethodologiesRicardo LandazuriÎncă nu există evaluări
- BT-SEC Unit-4Document12 paginiBT-SEC Unit-4sanmathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- E ColiDocument14 paginiE Coliopkbvjmn123Încă nu există evaluări
- Animal Feed Science and Technology: J. Apajalahti, K. VienolaDocument8 paginiAnimal Feed Science and Technology: J. Apajalahti, K. Vienolaamamùra maamarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development of EcoDocument9 paginiDevelopment of EcoARJYA ROYÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHA - Production Application and Its Bioremediation in EnvironmentDocument14 paginiPHA - Production Application and Its Bioremediation in EnvironmentKhan RavianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seminario 1-2022-1Document13 paginiSeminario 1-2022-1Elias Gerardo Pardo LlamoccaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant Molecular Farming For Recombinant Therapeutic ProteinsDocument61 paginiPlant Molecular Farming For Recombinant Therapeutic Proteinsnitin_star2010Încă nu există evaluări
- Metabolisme Mikrobia Rumen 1Document56 paginiMetabolisme Mikrobia Rumen 1Komang Doyle Savitri100% (2)
- Acido Lactico Hojarasca de MaizDocument34 paginiAcido Lactico Hojarasca de MaizAlex CárdenasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bioprcess Test 4Document5 paginiBioprcess Test 4Krish KÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHB Process 1998Document10 paginiPHB Process 1998mtlopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio PolDocument2 paginiBio PolArijit DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 1 Notes Biological Engineering PDFDocument17 paginiModule 1 Notes Biological Engineering PDFSantosh V HiremathÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2018) Finding of Novel Lactate Utilizing Bacillus Sp. YHY22 and Its Evaluation For Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) ProductionDocument9 pagini2018) Finding of Novel Lactate Utilizing Bacillus Sp. YHY22 and Its Evaluation For Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) Productionadmos0319Încă nu există evaluări
- PHA - PolyhydroxyalkanoatesDocument10 paginiPHA - PolyhydroxyalkanoatesMd. Shaharuk AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biopolymer Production Poblete CastroDocument11 paginiBiopolymer Production Poblete Castrosonia.diazÎncă nu există evaluări
- PhytoplasticDocument3 paginiPhytoplasticPradeepkumar MÎncă nu există evaluări
- AlgaeDocument10 paginiAlgaeRajiv BhattÎncă nu există evaluări
- Production of Poly (3-Hydroxybutyrate) From A Dairy Industry Wastewater Using Bacillus Subtilis EPAH18: Bioprocess Development and SimulationDocument9 paginiProduction of Poly (3-Hydroxybutyrate) From A Dairy Industry Wastewater Using Bacillus Subtilis EPAH18: Bioprocess Development and Simulationroseta0218Încă nu există evaluări
- BIOPOLDocument2 paginiBIOPOLLEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bioprocess TechnologyDocument22 paginiBioprocess Technologyfabianosir321Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit - Iii 3.0 Production of Secondary Metabolites 3.1.0 Production of AntibioticsDocument25 paginiUnit - Iii 3.0 Production of Secondary Metabolites 3.1.0 Production of AntibioticsBharathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- PPFM Presentation KarthikeyanDocument30 paginiPPFM Presentation KarthikeyanKarthikeyan Nanjappan100% (2)
- Fermentation: Metabolic BiodiversityDocument10 paginiFermentation: Metabolic BiodiversityEduar Moreno LondoñoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bacteriology Virology - Lec3 - 4 - FDocument6 paginiBacteriology Virology - Lec3 - 4 - FBrianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biopolymers in Textile IndustryDocument6 paginiBiopolymers in Textile IndustryAsim Kumar Roy ChoudhuryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biofloc Farming Technology Agriculture - Lyst3582Document8 paginiBiofloc Farming Technology Agriculture - Lyst3582venshmasuslaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 136-Article Text-761-1-10-20210107Document12 pagini136-Article Text-761-1-10-20210107Chronika Rati ManurungÎncă nu există evaluări
- BiopolymersDocument29 paginiBiopolymersAbdul BasitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rodrguez Contreras 2013Document10 paginiRodrguez Contreras 2013fernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bhuwal 2013Document10 paginiBhuwal 2013keysofiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nbs Fermentation Basics PDFDocument26 paginiNbs Fermentation Basics PDFsadatrafiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Still in Love With YouDocument0 paginiStill in Love With Youalissa33Încă nu există evaluări
- A Local EcosystemDocument13 paginiA Local EcosystemDiana NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Backcrosses and Test CrossesDocument2 paginiBackcrosses and Test CrossesDiana NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Photos Yn HeseDocument1 paginăPhotos Yn HeseDiana NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evolution and Natural SelectionDocument30 paginiEvolution and Natural SelectionDiana NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ext 1 Maths HSC Task 2 H Yrly 2009 With Solutions2Document28 paginiExt 1 Maths HSC Task 2 H Yrly 2009 With Solutions2Diana NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Examining Conflict in One DayDocument3 paginiExamining Conflict in One DayDiana NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Generic Course PlannerDocument1 paginăGeneric Course PlannerDiana NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group Fitness Timetable Whitlam Leisure CentreDocument1 paginăGroup Fitness Timetable Whitlam Leisure CentreDiana NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Youth Rapist Faces Adult Sentenc1Document1 paginăYouth Rapist Faces Adult Sentenc1Diana NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peace My BruddahDocument2 paginiPeace My BruddahDiana NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Task 3 BiatchDocument1 paginăEnglish Task 3 BiatchDiana NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hi ThereDocument3 paginiHi ThereDiana NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Look Up Definitions and Record in BooksDocument2 paginiLook Up Definitions and Record in BooksDiana NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hapiro Uses Metaphors To Emphasize The FantasyDocument3 paginiHapiro Uses Metaphors To Emphasize The FantasyDiana NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2005 2 Unit AnswersDocument6 pagini2005 2 Unit AnswersDiana NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Azula S Crown Turotial by FaeriedreamerDocument1 paginăAzula S Crown Turotial by FaeriedreamerDiana NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- For Whom The Bell Tolls Few Subjects Can Be Discussed With More Insightfulness and Curiosity Than DeathDocument4 paginiFor Whom The Bell Tolls Few Subjects Can Be Discussed With More Insightfulness and Curiosity Than DeathDiana NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluate The Effectiveness of The Domestic and International Legal Systems in Dealing With International CrimeDocument3 paginiEvaluate The Effectiveness of The Domestic and International Legal Systems in Dealing With International CrimeDiana NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surface Area and Rate of ReactionDocument1 paginăSurface Area and Rate of ReactionDiana NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Legal Studies Syllabus St6Document47 paginiLegal Studies Syllabus St6Diana NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Cosmic Engine - RAW INFODocument24 paginiThe Cosmic Engine - RAW INFODiana NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brief Summary of ChloroflurocarbonsDocument6 paginiBrief Summary of ChloroflurocarbonsDiana NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atwood AnalysisDocument2 paginiAtwood AnalysisDiana Nguyen67% (3)
- Evaluate The Effectiveness of The Criminal Trial Process in Achieving JusticeDocument4 paginiEvaluate The Effectiveness of The Criminal Trial Process in Achieving JusticeDiana Nguyen50% (2)
- Speeches Atwood 3Document2 paginiSpeeches Atwood 3Diana NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 © NSW Det 2009Document68 pagini1 © NSW Det 2009Diana NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Context: MAGARET ATWOOD (Handsmade Tale)Document1 paginăContext: MAGARET ATWOOD (Handsmade Tale)Diana Nguyen100% (1)
- Recombinant DNA Technology in Todays Medicine-BIO PROJECTDocument8 paginiRecombinant DNA Technology in Todays Medicine-BIO PROJECTavik sadhuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 23 RQDocument4 paginiChapter 23 RQMia MistypuffÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAFC Pharma™ - High-Potent API Manufacturing Through Fermentation TechnologyDocument2 paginiSAFC Pharma™ - High-Potent API Manufacturing Through Fermentation TechnologySAFC-GlobalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Notebook: 06.02 Bacteria: Key Questions and Terms Notes Contrasting Domains: Archaea and BacteriaDocument3 paginiBiology Notebook: 06.02 Bacteria: Key Questions and Terms Notes Contrasting Domains: Archaea and BacteriaKeara RaleighÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structure and Functions of Biological Molecules: at The End of The Lesson, You Are Expected ToDocument4 paginiStructure and Functions of Biological Molecules: at The End of The Lesson, You Are Expected ToFrancinne MartinÎncă nu există evaluări
- IB DP Biology 1.4 Membrane Transport QuestionDocument19 paginiIB DP Biology 1.4 Membrane Transport QuestionikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mangrove Sofe BookDocument145 paginiMangrove Sofe BookNurul Hikmah ZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Discovery and DevelopmentDocument28 paginiDrug Discovery and DevelopmentMirza Shaharyar BaigÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thesis Complete PDFDocument269 paginiThesis Complete PDFshjahsjanshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- En Qiagen Onestep RT PCR Kit HandbookDocument44 paginiEn Qiagen Onestep RT PCR Kit HandbookAlbino VelasquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cure For CancerDocument6 paginiCure For CancerSimanjuntak Sitombuk MarganaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet FermentationDocument5 paginiWorksheet FermentationRyan De AlloÎncă nu există evaluări
- UW Infectious Diseases + Microbiology Educational Objectives PDFDocument75 paginiUW Infectious Diseases + Microbiology Educational Objectives PDFDrbee10Încă nu există evaluări
- Diversity and Endemicity of Chilimo Forest, Central EthiopiaDocument4 paginiDiversity and Endemicity of Chilimo Forest, Central Ethiopiaasmeraamde21Încă nu există evaluări
- Bio Lesson PlanDocument38 paginiBio Lesson PlanLisa B Arnold100% (2)
- Cornell Notes CH 7Document2 paginiCornell Notes CH 7Aaron WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disinfectant Efficacy Study Final Amal AdelDocument47 paginiDisinfectant Efficacy Study Final Amal AdelYUSSIF MOHAMED ABDELRAOUFÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bacteria From PrescottDocument19 paginiBacteria From PrescottYekitaSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Congenital Nephrotic SyndromeDocument44 paginiCongenital Nephrotic Syndromeaad81kolrenmed50% (2)
- BCC - DNA Replication in Prokaryotes Lecture 20Document31 paginiBCC - DNA Replication in Prokaryotes Lecture 20AmyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Annelid ADocument52 paginiAnnelid AMohammad Sharifuddin SallehÎncă nu există evaluări
- SMK KUBONG STPM Trial 2010 BiologyDocument18 paginiSMK KUBONG STPM Trial 2010 BiologyWendy LohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cfasmsumain Fplereview2022 PhycologyDocument149 paginiCfasmsumain Fplereview2022 PhycologyPilihp Elessej Yaj NiuqidcidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Malaria ModulDocument18 paginiMalaria ModulcheiwinarnoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nitrate Reduction in Sulfate Reducing BacteriaDocument10 paginiNitrate Reduction in Sulfate Reducing BacteriaCatalinaManjarresÎncă nu există evaluări
- AQA Biology Predicted Paper 2Document27 paginiAQA Biology Predicted Paper 2Nimisha RejiÎncă nu există evaluări
- AGM 301 - Mid Sem QPDocument15 paginiAGM 301 - Mid Sem QPshubham100% (1)
- Scooby's Suggested Solutions For The 2014 VCE Biology Exam - Short AnswerDocument6 paginiScooby's Suggested Solutions For The 2014 VCE Biology Exam - Short AnswerRite10210Încă nu există evaluări
- Nucleotide MetabolismDocument89 paginiNucleotide Metabolismfeby ary annasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonDe la EverandSully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (103)
- The Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldDe la EverandThe Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (58)
- Hero Found: The Greatest POW Escape of the Vietnam WarDe la EverandHero Found: The Greatest POW Escape of the Vietnam WarEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (19)
- The Beekeeper's Lament: How One Man and Half a Billion Honey Bees Help Feed AmericaDe la EverandThe Beekeeper's Lament: How One Man and Half a Billion Honey Bees Help Feed AmericaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindDe la EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsDe la EverandA Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (242)
- Faster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestDe la EverandFaster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (28)
- Highest Duty: My Search for What Really MattersDe la EverandHighest Duty: My Search for What Really MattersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyDe la EverandReality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (24)
- 35 Miles From Shore: The Ditching and Rescue of ALM Flight 980De la Everand35 Miles From Shore: The Ditching and Rescue of ALM Flight 980Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (21)
- Pale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in SpaceDe la EverandPale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in SpaceEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (588)
- The End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellDe la EverandThe End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (80)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidDe la EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1395)
- System Error: Where Big Tech Went Wrong and How We Can RebootDe la EverandSystem Error: Where Big Tech Went Wrong and How We Can RebootÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationDe la EverandThe Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (46)
- Transformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelDe la EverandTransformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- How to Build a Car: The Autobiography of the World’s Greatest Formula 1 DesignerDe la EverandHow to Build a Car: The Autobiography of the World’s Greatest Formula 1 DesignerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (122)
- Dirt to Soil: One Family’s Journey into Regenerative AgricultureDe la EverandDirt to Soil: One Family’s Journey into Regenerative AgricultureEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (125)
- Mini Farming: Self-Sufficiency on 1/4 AcreDe la EverandMini Farming: Self-Sufficiency on 1/4 AcreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (76)
- The Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyDe la EverandThe Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fire on the Horizon: The Untold Story of the Gulf Oil DisasterDe la EverandFire on the Horizon: The Untold Story of the Gulf Oil DisasterÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansDe la EverandThe Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansÎncă nu există evaluări
- How to Build a Car: The Autobiography of the World’s Greatest Formula 1 DesignerDe la EverandHow to Build a Car: The Autobiography of the World’s Greatest Formula 1 DesignerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (54)
- The Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastDe la EverandThe Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (31)