Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Electro Chemistry
Încărcat de
seekforheavenDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Electro Chemistry
Încărcat de
seekforheavenDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
A2
ELECTRO-CHEMISTRY
Q1 (a) What do you understand by the term standard electrode potential?
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
(b) The following cell was set up between a copper electrode and an unknown metal
electrode M2+(aq) /M(s). The standard cell potential was found to be 0.76 V, and the copper
foil was the positive electrode.
(i) Use the Data Booklet to calculate the standard electrode potential of the
M2+(aq) /M(s) system.
...................................................................................................................................................
(ii) Draw an arrow over the voltmeter symbol in the above diagram to show the
direction of electron flow through the voltmeter.
(iii) Predict the outcomes of the following situations. Describe what you might see and write
ionic equations for any reactions that occur.
I A rod of metal M is dipped into a solution of 1 moldm3 CuSO4.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
II Dilute sulphuric acid is added to a beaker containing a powdered sample of metal M.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
(c) Because of its increased scarcity, cheaper copper ornaments are no longer made from
the solid metal, but from iron that has been copper plated.
(i) Complete the following diagram showing the set-up for a copper electroplating
process. Show clearly the polarity (+/) of the power source, and suggest a suitable
electrolyte.
ZAHID IQBAL WARRAICH
0333-4200541
A2
ELECTRO-CHEMISTRY
(ii) A current of 0.500 A is passed through the electroplating cell. Calculate the time required
to deposit a mass of 0.500 g of copper on to the ornament.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
(June 2003)
Q2 Although standard electrode potentials are measured for solutions where the
concentrations of ions are 1.0 mol dm3, cells used as sources of battery power tend to
operate with more concentrated solutions. This question concerns the electrode reactions
involved in the hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell and the lead-acid car battery.
(a) In the hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell, H2(g) and O2(g) are fed onto two inert electrodes
dipping into NaOH(aq).
(i) Use the Data Booklet to calculate E ocell for this reaction.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
(ii) Construct an equation for the overall reaction.
...................................................................................................................................................
(iii) By using one of the phrases more positive, more negative or no change, deduce the
effect of increasing [OH(aq)] on the electrode potential of
the left hand electrode ............................................................................................................
the right hand electrode ..........................................................................................................
(iv) Hence deduce whether the overall Ecell is likely to increase, decrease or remain the
same, when [OH(aq)] increases. Explain your answer.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
(v) Suggest one other reason why a high [NaOH(aq)] is used in the fuel cell.
...................................................................................................................................................
ZAHID IQBAL WARRAICH
0333-4200541
A2
ELECTRO-CHEMISTRY
(b) In the cells of a lead-acid car battery the following reactions take place.
(i) Use the Data Booklet to calculate E ocell for this reaction.
...................................................................................................................................................
(ii) Construct an equation for the overall reaction.
...................................................................................................................................................
The electrolyte in a lead-acid cell is H2SO4(aq). Most of the Pb2+(aq) ions that are produced
at the electrodes are precipitated as the highly insoluble PbSO4(s).
(iii) Construct an equation for the overall cell reaction in the presence of H2SO4.
...................................................................................................................................................
(iv) By considering the effect of decreasing [Pb2+(aq)] on the electrode potentials of the
cathode and the anode, deduce the effect of the presence of H2SO4(aq) in the
electrolyte on the overall Ecell.
State whether the Ecell will increase, decrease or remain the same.
Overall Ecell will .........................................................................................................................
Explain your answer.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
(June 2010 P41)
Q3 The electrolytic purification of copper can be carried out in an apparatus similar to the
one shown below.
The impure copper anode contains small quantities of metallic nickel, zinc and silver,
together with inert oxides and carbon resulting from the initial reduction of the copper ore
with coke. The copper goes into solution at the anode, but the silver remains as the metal
and falls to the bottom as part of the anode sludge. The zinc also dissolves.
(a) (i) Write a half equation including state symbols for the reaction of copper at the anode.
...................................................................................................................................................
(ii) Use data from the Data Booklet to explain why silver remains as the metal.
...................................................................................................................................................
(iii) Use data from the Data Booklet to predict what happens to the nickel at the anode.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
ZAHID IQBAL WARRAICH
0333-4200541
A2
ELECTRO-CHEMISTRY
(iv) Write a half equation including state symbols for the main reaction at the cathode.
...................................................................................................................................................
(v) Use data from the Data Booklet to explain why zinc is not deposited on the cathode.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
(vi) Suggest why the blue colour of the electrolyte slowly fades as the electrolysis proceeds.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
(b) Most of the current passed through the cell is used to dissolve the copper at the anode
and precipitate pure copper onto the cathode. However, a small proportion of it is wasted in
dissolving the impurities at the anode which then remain in solution.When a current of 20.0 A
was passed through the cell for 10.0 hours, it was found that 225 g of pure copper was
deposited on the cathode.
(i) Calculate the following, using appropriate data from the Data Booklet.
number of moles of copper produced at the cathode
number of moles of electrons needed to produce this copper
number of moles of electrons that passed through the cell
(ii) Hence calculate the percentage of the current through the cell that has been
wasted in dissolving the impurities at the anode.
(c) Nickel often occurs in ores along with iron. After the initial reduction of the ore with coke,
a nickel-iron alloy is formed.Use data from the Data Booklet to explain why nickel can be
purified by a similar electrolysis technique to that used for copper, using an impure nickel
anode, a pure nickel cathode, and nickel sulfate as the electrolyte. Explain what would
happen to the iron during this process.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
(Nov 2010 P41)
ZAHID IQBAL WARRAICH
0333-4200541
A2
ELECTRO-CHEMISTRY
Q4 (a) What is meant by the term standard electrode potential, SEP?
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
(b) Draw a fully labelled diagram of the apparatus you could use to measure the SEP of the
Fe3+ / Fe2+ electrode.
(c) The reaction between Fe3+ ions and I ions is an equilibrium reaction.
(i) Use the Data Booklet to calculate E CELL the for this reaction.
...................................................................................................................................................
(ii) Hence state, with a reason, whether there will be more products or more reactants at
equilibrium.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
(iii) Write the expression for Kc for this reaction, and state its units.
An experiment was carried out using solutions of Fe3+(aq) and I(aq) of equal
concentrations. 100 cm3 of each solution were mixed together, and allowed to reach
equilibrium.
The concentrations at equilibrium of Fe3+(aq) and I2(aq) were as follows.
(iv) Use these data, together with the equation given in (c), to calculate the concentrations
of Fe2+(aq) and I(aq) at equilibrium.
(v) Calculate the Kc for this reaction.
(June 2013 P43)
ZAHID IQBAL WARRAICH
0333-4200541
A2
ELECTRO-CHEMISTRY
Q5 (a) The diagram below shows an incomplete experimental set-up needed to measure the
Ecell of a cell composed of the standard Cu2+/Cu electrode and an Ag+/Ag electrode.
(i) State the chemical composition of
solution A, .................................................................................................................................
electrode B. ...............................................................................................................................
(ii) Complete the diagram to show the whole experimental set-up.
(b) The above cell is not under standard conditions, because the [Ag+] in a saturated solution
of AgCl is much less than 1.0 mol dm3. The Eelectrode is related to [Ag+] by the following
equation.
(i) Use the Data Booklet to calculate the E cell if the cell was operating under standard
conditions.
In the above experiment, the Ecell was measured at +0.17V.
(ii) Calculate the value of Eelectrode for the Ag+/Ag electrode in this experiment.
...................................................................................................................................................
(iii) Use equation 1 to calculate [Ag+] in the saturated solution.
(c) (i) Write an expression for Ksp of silver sulfate, Ag2SO4, including units.
Ksp = .................................................................... units .............................................................
Using a similar experimental set-up to that illustrated opposite, it is found that [Ag+] in a
saturated solution of Ag2SO4 is 1.6102 mol dm3.
(ii) Calculate the value of Ksp of silver sulfate.
(Nov 2012 P42)
ZAHID IQBAL WARRAICH
0333-4200541
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Analytical Chemistry PDFDocument14 paginiAnalytical Chemistry PDFSamer EhabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inorganic Chem 2Document68 paginiInorganic Chem 2yvg95100% (1)
- Reaction Kinetics 2Document8 paginiReaction Kinetics 2yvg95Încă nu există evaluări
- Reaction KineticsDocument37 paginiReaction KineticsDaisyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transition Metals TestDocument12 paginiTransition Metals Testpaulcampbell37Încă nu există evaluări
- F325 Lattice EnthalpyDocument12 paginiF325 Lattice EnthalpyDoc_Croc100% (1)
- Business Revision Notes 1AS1Document6 paginiBusiness Revision Notes 1AS1Piran UmrigarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydroxy CompoundsDocument7 paginiHydroxy CompoundsahumanbeinginearthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Reactions O Level NotesDocument22 paginiChemical Reactions O Level Notesveryveryhappyfeet100% (1)
- Percentage Obtained by Trainee-EXAM Sample Prep: Employees A B C Total % Practical TrainingDocument3 paginiPercentage Obtained by Trainee-EXAM Sample Prep: Employees A B C Total % Practical Trainingdesireeann2014100% (1)
- Organic ReactionsDocument16 paginiOrganic Reactionsyie_793Încă nu există evaluări
- EXAMINER TIPS For Mastering IGCSE ChemistryDocument6 paginiEXAMINER TIPS For Mastering IGCSE ChemistryAnand Kumar100% (1)
- Relationship between metal reactivity and carbonate decompositionDocument3 paginiRelationship between metal reactivity and carbonate decompositionZou JunyiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mod 4 Revision Guide 10 Synthetic RoutesDocument2 paginiMod 4 Revision Guide 10 Synthetic RoutesdufraiscÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topical Mock Chemistry QuestionsDocument294 paginiTopical Mock Chemistry QuestionsMichael Mike100% (1)
- Gravimetric Analysis of Iron PDFDocument3 paginiGravimetric Analysis of Iron PDFEmrico Luiz PerezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section A: Mcqs Halogen DerivativesDocument11 paginiSection A: Mcqs Halogen DerivativesBint A. Qadir100% (1)
- CHM2 Group2 and Group7 QDocument25 paginiCHM2 Group2 and Group7 Qareyouthere92Încă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Atp XTH Igcse 28-06-2021Document7 paginiChemistry Atp XTH Igcse 28-06-2021Encrpyt Is PlayingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edexcel IGCSE ChemistryDocument11 paginiEdexcel IGCSE ChemistrySamuel Muabia Plānet0% (1)
- Basic-Rules On MCQDocument8 paginiBasic-Rules On MCQponak001Încă nu există evaluări
- Mce Igcse Chemistry PPT c05Document30 paginiMce Igcse Chemistry PPT c05Aysha Minhas100% (1)
- Identification of Ions and GasesDocument5 paginiIdentification of Ions and GasesJobelle Aleli Perez EhinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 14.hydroxyl Compounds Lecture NotesDocument22 pagini14.hydroxyl Compounds Lecture Notesgeoboom12100% (4)
- KSP Calcium Hydroxide C12!4!13Document7 paginiKSP Calcium Hydroxide C12!4!13Nazihah Moomoo50% (2)
- 2011 H2 Chem SRJC Prelim Paper 2 Suggested AnswersDocument15 pagini2011 H2 Chem SRJC Prelim Paper 2 Suggested AnswersonnoezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2nd Chap QnbankDocument21 pagini2nd Chap QnbankVishnu SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9701 TP4 Alkenes v2.0Document38 pagini9701 TP4 Alkenes v2.0charlesma123Încă nu există evaluări
- Updated Applied Chemistry Programme on CatalysisDocument54 paginiUpdated Applied Chemistry Programme on CatalysisRajatSonkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Solubility RulesDocument1 paginăThe Solubility RuleslvicencioaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Holiday Homework on Pollution Types, Causes, Effects and ControlDocument13 paginiChemistry Holiday Homework on Pollution Types, Causes, Effects and ControlKhushmeetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Determining Concentrations of Sodium Hydroxide and Carbonate in a MixtureDocument13 paginiDetermining Concentrations of Sodium Hydroxide and Carbonate in a MixtureOliver QuekÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Step by Step Guide To Exam SuccessDocument16 paginiThe Step by Step Guide To Exam SuccessTinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro to MS Examples - Functional GroupsDocument5 paginiIntro to MS Examples - Functional GroupsMohamed DahmaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- High School Science Teachers Training Program (Bangalore)Document4 paginiHigh School Science Teachers Training Program (Bangalore)Amby GovindÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro To Organic ChemistryDocument5 paginiIntro To Organic Chemistryyvg95Încă nu există evaluări
- IGCSE Chemistry Revision GuideDocument20 paginiIGCSE Chemistry Revision GuidekarlabrooksÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aqa Chemistry Student Guide 2 Inorganic and Organic Chemistry 1 9781471843693 1471843696 CompressDocument89 paginiAqa Chemistry Student Guide 2 Inorganic and Organic Chemistry 1 9781471843693 1471843696 CompressSumayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ionic Bonding 4. Bonding: Evidence For The Existence of IonsDocument9 paginiIonic Bonding 4. Bonding: Evidence For The Existence of IonsAnastasia ErshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pink and Purple Colored People Illustrations Online Class Etiquette Education PresentationDocument15 paginiPink and Purple Colored People Illustrations Online Class Etiquette Education Presentationpps ipaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Online Class RulesDocument12 paginiOnline Class RulesKate Evangelista100% (1)
- Understanding Oxidation Numbers Through Electronegativity and Partial ChargesDocument14 paginiUnderstanding Oxidation Numbers Through Electronegativity and Partial ChargesEricÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5070 Teacher Guide (For Examination From 2023)Document30 pagini5070 Teacher Guide (For Examination From 2023)IQRA SOHAIL100% (1)
- Qualitative Analysis: Tip: in Order To Identify An Unknown Salt, It MustDocument11 paginiQualitative Analysis: Tip: in Order To Identify An Unknown Salt, It MustFarrel LeroyÎncă nu există evaluări
- School AssemblyDocument2 paginiSchool AssemblyRising the screen Generations100% (1)
- Metals and Non-Metals ExtractionDocument8 paginiMetals and Non-Metals ExtractionvibhorxpandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aliphatic Organic SynthesisDocument30 paginiAliphatic Organic SynthesisrationalwikiÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Row Transition MetalsDocument39 paginiFirst Row Transition MetalsArielle LewisÎncă nu există evaluări
- WaterDocument40 paginiWateryooÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5070 w10 QP 42Document16 pagini5070 w10 QP 42Shahnawaz MemonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uses and Manufacture of Sulphuric AcidDocument23 paginiUses and Manufacture of Sulphuric AcidLalitha KurumanghatÎncă nu există evaluări
- House Rules For Virtual ClassroomDocument2 paginiHouse Rules For Virtual ClassroomEunice Ortile100% (1)
- 2020 2021 Professional Development Plan.Document2 pagini2020 2021 Professional Development Plan.Regine Grace OligarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polymers Homework1 1Document4 paginiPolymers Homework1 1mike100% (1)
- MSC 305 Principles of Teaching and LearningDocument148 paginiMSC 305 Principles of Teaching and LearningVouchsiem MaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electro ChemistryDocument13 paginiElectro ChemistryRameenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.4.3 Discovery of The ElectronDocument31 pagini4.4.3 Discovery of The ElectronMozammel AnowarÎncă nu există evaluări
- BondingDocument14 paginiBondingMuizzudin AzaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- P3 10 Motor EffectDocument58 paginiP3 10 Motor EffectHiruni FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic structure and bondingDocument4 paginiAtomic structure and bondingMalak ShokryÎncă nu există evaluări
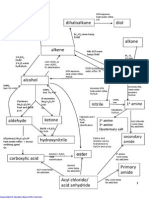
- Organic Chemistry A Levels A2Document44 paginiOrganic Chemistry A Levels A2seekforheaven100% (1)
- Knockhardy Bonding PowerpointDocument84 paginiKnockhardy Bonding Powerpointjakester349Încă nu există evaluări
- Redox ReactionsDocument55 paginiRedox ReactionsseekforheavenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrode PotentialDocument31 paginiElectrode PotentialseekforheavenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 95996-2014-Syllabus Cambridge SyllabusDocument90 pagini95996-2014-Syllabus Cambridge Syllabusaline_lin_2Încă nu există evaluări
- 9701 Y13 SyDocument104 pagini9701 Y13 SySaaqo QasimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry BES 2013 SyllabusDocument102 paginiChemistry BES 2013 SyllabusseekforheavenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Materials of Chemistry A Levels A2Document9 paginiDesign and Materials of Chemistry A Levels A2seekforheavenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic StructureDocument14 paginiAtomic StructurerosestrikesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Knockhardy Bonding PowerpointDocument84 paginiKnockhardy Bonding Powerpointjakester349Încă nu există evaluări
- 2014 Syllabus Update A-Level ChemistryDocument1 pagină2014 Syllabus Update A-Level ChemistryseekforheavenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2014 Syllabus Update A-Level ChemistryDocument1 pagină2014 Syllabus Update A-Level ChemistryseekforheavenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic StructureDocument14 paginiAtomic StructurerosestrikesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 95996-2014-Syllabus Cambridge SyllabusDocument90 pagini95996-2014-Syllabus Cambridge Syllabusaline_lin_2Încă nu există evaluări
- (ELECS2) Exp5 - Class A and Class B Power Amplifier - The GWAPINGSDocument12 pagini(ELECS2) Exp5 - Class A and Class B Power Amplifier - The GWAPINGSFrodolfre Reginald LazoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ece206l SyllDocument7 paginiEce206l SyllBlaze MooreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Temperature Compensated Battery State-Of-Charge (Soc) Table 1.1Document8 paginiTemperature Compensated Battery State-Of-Charge (Soc) Table 1.1Nadeem MirzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ATS2M1-1-16A-230VDocument2 paginiATS2M1-1-16A-230Vmariam fekiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Leakage Inductance Determination For Transformers With Interleaving of WindingsDocument5 paginiLeakage Inductance Determination For Transformers With Interleaving of WindingsLRHENGÎncă nu există evaluări
- Miniature Circuit BreakersDocument78 paginiMiniature Circuit BreakersIndera ArifiantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7011a 6-10kva SpecsDocument10 pagini7011a 6-10kva SpecsOscar MorenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Datasheet 74192Document7 paginiDatasheet 74192phongbui135100% (3)
- Extended Life Computer Grade CapacitorDocument2 paginiExtended Life Computer Grade CapacitorАндрей ПоляковÎncă nu există evaluări
- LAC 65.1 Load Cell Amplifier ModuleDocument2 paginiLAC 65.1 Load Cell Amplifier ModulerngÎncă nu există evaluări
- Telecom-02-00022-V2Document21 paginiTelecom-02-00022-V2husam hamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thesis On Power Quality Improvement Using DstatcomDocument5 paginiThesis On Power Quality Improvement Using DstatcomheatherricedesmoinesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Company Introduction (ILJIN Electric) 2009 LatestDocument43 paginiCompany Introduction (ILJIN Electric) 2009 Latestgabriel_petre2001Încă nu există evaluări
- Battery CatalogDocument86 paginiBattery CatalogGayfuckingfaceÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAMS 101 Ways To Use Your Signal Generator 1959Document130 paginiSAMS 101 Ways To Use Your Signal Generator 1959Wasim KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part 1 General Electrical Specification v4Document15 paginiPart 1 General Electrical Specification v4godspower brunoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual Ricoh Af InstDocument21 paginiManual Ricoh Af Instanon_748411981Încă nu există evaluări
- Vortex Plus Technical Manual 011117 - 2 PDFDocument31 paginiVortex Plus Technical Manual 011117 - 2 PDFNam NguyễnÎncă nu există evaluări
- DatasheetDocument3 paginiDatasheetHamza AbbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- TdaDocument7 paginiTdaΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣΠΑΝΑΓΟΣÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optical Mineralogy: Lab 14 - Fall, 2012 Biaxial Interference FiguresDocument13 paginiOptical Mineralogy: Lab 14 - Fall, 2012 Biaxial Interference Figuressagnik royÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power System Operation and Control NotesDocument61 paginiPower System Operation and Control Notesanon_613151744100% (1)
- Tv21usp Ee PDFDocument1 paginăTv21usp Ee PDFodilonsouzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cold-Junction-Compensated K-Thermocouple-to-Digital Converter (0°C To +1024°C)Document8 paginiCold-Junction-Compensated K-Thermocouple-to-Digital Converter (0°C To +1024°C)Виктор АнатольевичÎncă nu există evaluări
- Megometro KyoritsuDocument1 paginăMegometro KyoritsuRafael AlvarezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Ic Design TutorialDocument4 paginiDigital Ic Design Tutorialkrishna kanthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vol02 Tab02Document212 paginiVol02 Tab02cphcricriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Potential TransformerDocument9 paginiPotential TransformerofjeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nanochemistry Characterization AFM SEMDocument6 paginiNanochemistry Characterization AFM SEMRoshni GhaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical and Computer - Electronics, Controls, and Communications CBT Exam SpecificationsDocument3 paginiElectrical and Computer - Electronics, Controls, and Communications CBT Exam SpecificationsJorge GuerreroÎncă nu există evaluări