Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Torefaksi
Încărcat de
rifkasyaputriTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Torefaksi
Încărcat de
rifkasyaputriDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Utilization of Municipal Solid Waste into Environmentally Friendly Solid Fuel by Torrefaction Process
Utilization of municipal solid waste (MSW) directly as a fuel has many obstacles, both technical and non-technical. Kendala teknis di antaranya adalah kandungan air yang tinggi, densitas energi yang rendah serta komponen yang heterogen dan bentuk yang beragam. Technical constraints include the high water content, low energy density and the components that a heterogeneous and diverse forms. Sedangkan kendala non-teknis adalah berupa bau busuk dan potensi sumber bibit penyakit.While non-technical constraints are a bad smell and the potential source of germs. Various constraints caused improper waste used as fuel. Conversely, if the waste management applied the right technology it will get two benefits at once, i.e., reduced significantly the amount of MSW and alternative fuel produced from garbage. Salah satu teknologi pengolahan sampah yang menjanjikan yang dapat menghasilkan bahan bakar padat adalah torefaksi.One of the MSW processing technologies that promises that can produce solid fuel is torrefaction. Torefaksi merupakan proses perlakuan panas pada temperatur tertentu (untuk biomassa biasanya antara 200-300 o C), yang dilakukan pada tekanan atmosfer tanpa kehadiran oksigen. Torrefaction is a heat treatment process at a given temperature (for biomass is usually between 200-300oC), which performed at atmospheric pressure in absence of oxygen. Torefaksi pada biomassa berhasil meningkatkan densitas energinya dan memperbaiki karakteristiknya sebagai bahan bakar.On biomass torrefaction managed to increase its energy density and improve its characteristics as a fuel. Torefaksi pada biomassa kayu berhasil menaikkan nilai kalornya dan menyisakan energi sampai 90% [1]. Wood biomass torrefaction successful in raising the value of energy density and leaving up to 90%. Di samping itu, sifat-sifat pembakaran kayu hasil torefaksi menghasilkan asap yang lebih sedikit dibandingkan dengan kayu yang tidak ditorefaksi [2]. In addition, the combustion properties of wood torrefaction produced less smoke than the wood that was not torrefied.Hariadi dkk. Torrefaction on non-biomass materials, namely peat, successfully raise heating value (HHV) to the equivalent of coal sub bituminous C to high volatile C bituminous classification ASTM D 388. The objectives of this study to get the kind of waste components which can be improved fuel quality through the torrefaction process and get torrefaction temperature and residence time to produce maximum heating value.
Study on municipal solid waste in city of Bandung, Indonesia, shows that the largest mass fraction of MSW is organic component, which is 42%. The results are also informed that the mass fraction of MSW that can be used as fuel reaches 75%, after which 25% utilized by scavengers. This indicates that if in the waste management applied the right technology it will get two benefits at once, ie, reduced significantly the amount of waste and produced fuel from waste. Theoretically, the heat power generated from MSW in Bandung can reach 91.5 MW. Berdasarkan jenis materialnya, sampah padat perkotaan secara umum dapat dikelompokan menjadi dua komponen utama, yakni komponen organik dan anorganik.Based on the type of material, municipal solid waste in general can be grouped into two main components, namely organic and inorganic components.Dalam kaitannya dengan bahan bakar, komponen sampah tersebut dapat dibagi menjadi dua kelompok, yaitu komponen yang bisa dimanfataakan sebagai bahan bakar dan komponen yang tidak bisa dimanfaatkan sebagai bakar. Di samping itu, dalam prakteknya di lapangan, komponen sampah juga dapat dipisahkan menjadi dua kelompok, yakni komponen yang diambil oleh pemulung dan yang ditinggalkan. In terms of fuel, the waste components can be divided into two groups, namely the components that can be utilized as a fuel and components that cannot be utilized as fuel. In addition, in practice in the field, waste components can also be separated into two groups, the components taken by scavengers and the abandoned. Untuk pengujian torefaksi sampah ini, sampel pengujian dipilih berdasarkan pertimbangan kriteria pengelompokan di atas, yakni komponen yang bisa dimanfaatkan sebagai bahan bakar dan tidak diambil oleh pemulung.In InIn the waste torrefaction, testing samples were chosen based on consideration of the above grouping criteria, i.e., components that can be utilized as a fuel and not taken by scavengers. Dari komponen organik, sampel yang dipilih sebagai spesimen pengujian adalah sampah halaman (daun) dan sisa makanan (nasi), sedangkan dari komponen anorganik dipilih plastik bukan daur ulang, yakni plastik kemasan makanan dan minuman serta karet sintetikFrom the organic component, the sample is selected as the test specimen is garbage yard (leaves) and food residues (rice), while the inorganic component is selected from plastic non-recycled, the plastic packaging of food and beverages as well as synthetic rubber.
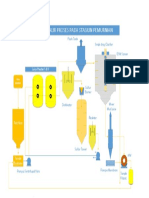
Waste torrefaction ePengujian torefaksi sampah ini dilakukan di Laboratorium Termodinamika PPAU-IR ITB menggunakan reaktor torefaksi skala bangku yang ada yang menggunakan media uap panas lanjut.EExperiment was conducted in Thermodynamics Laboratory PPAU-IR ITB using a bench-scale torrefaction reactor using superheated steam media. Massa awal dan ukuran spesimen tidak sama untuk setiap sampel, tergantung pada jenisnya.Initial mass and size of the specimens are not the same for each sample, depending on the type and density. Masing-masing sampel diuji secara terpisah dengan dua variasi temperatur dan waktu tinggEach sample tested separately with two variations of temperature and resident time of torrefaction. Variasi temperatur sama untuk semua spesimen, yakni 250 dan 300 C. Sedangkan untuk waktu tinggal, variasi pertama juga sama untuk semua spesimen, yakni 60 minit, dan variasi kedua adalah lamanya waktu yang diperlukan untuk mencapai laju penurunan massa konstanTT Temperature variation is same for all specimens, i.e. 250 and 300C. While residence time, the first variation is the same for all specimens, which is 60 minutes, and the second variation is the length of time required to start the asymptotic mass loss. Solid product of waste torrefaction Produk padat hasil torekasi sampah secara fisik umumnya sama dengan produk torefaksi biomassa, yakni berwarna hitam keabu-abuan dan bersifat rapuh.results are physically similar to products of biomass torrefaction, namely black-gray in color and are fragile. Torrefaction products from all components of the waste like this character, except for the first type of plastic (plastic-1), gray color mixed with white. Material padat hasil torefaksi plastik dan karet lebih keras dibandingakn hasil torefaksi daun dan sisa makananSolid material results in plastic and rubber torrefaction harder than torrefaction results of leaves and food residues. Profiles of solids mass loss of the various components of the waste samples showed the same pattern, namely the rate of mass loss is relatively rapid at the beginning of the process, then slowed down and eventually tend to be asymptotic. For the same sample components with the temperature varying process, as visible on the leaves and food residues, the time taken until a constant mass of solid value more quickly to higher temperatures of torrefaction. Waktu yang dibutuhkan sampai massa padatan cenderung berharga konstan pada proses torefaksi daun adalah sekitar 20 menit untuk temperatur 300 C dan 25 menit untuk temperatur 250 C. Sedangkan untuk sisa makanan, waktu yang dibutuhkan adalah sekitar 25 menit untuk temperatur 300 C dan 35 menit untuk temperatur 250 C. Hasil ini sejalan dengan hasil percobaan torefaksi biomassa yang sudah banyak dilakukan, di mana pada temperatur proses yang lebih tinggi, laju penurunan massa padatan lebih cepat.The time needed to tend to a solid mass at a constant value of leaves torrefaction process is about 20 and 25 minutes for the torrefaction temperature 300C and 250C respectively. As for the food residue, the time required is approximately 25 and 35 minutes for the torrefaction temperature 300C and 250C respectively. Pada plastik jenis kedua, material padat yang tersisa adalah aluminium foil saja, yakni sekitar 20%.In the second type of plastic, the remaining solid material is aluminum foil, namely approximately 20%. Hal ini mungkin disebabkan karena material plastik yang ada pada sampel plastik-2 ini didominasi oleh zat volatil ringan sehingga semuanya habis menguap ketika ditorefaksi. This is probably because the plastic material on a plastic sample-2 is dominated by light volatile matters that evaporate when they torrefied. Aluminium foil bukan material yang bisa dibakar sehingga produk torefaksi dari jenis plastik-2 ini tidak bisa dipakai
sebagai bahan bakar. Aluminum foil is not combustible so that torrefaction products from plastic type-2 cannot be used as fuel. Sebagaimana telah disebutkan di atas, proses torefaksi pada plastik-1 dan karet menyebabkan ia meleleh dan melengket pada wadah spesimen.TTTThe torrefaction process of plastic-1 and the rubber causing it to melt and cling to the specimen container. Pori-pori wadah yang tertutup menyebabkan tekanan aliran uap pada permukaan bawah wadah (alas) menjadi besar sehingga mempengaruhi hasil pengukuran massa spesimen yang diambil setiap saat. The closed pores of the container caused the flow of steam pressure on the lower surface of the container (base) to be large and it affects the results of specimen mass loss measurements. Conclusions of the research are: 1. Dari beberapa jenis komponen sampah padat perkotaan yang dijadikan sampel dalam penelitian ini, hanya dua komponen saja yang bisa ditorefaksi yaitu daun dan sisa makananFrom several types of municipal solid waste components that are selected to be sampled in this study, only two components that can be torrefied, namely the leaves and food residue. Torefaksi pada plastik kemasan makanan instan (plastik-1) dan karet sintetik tidak bisa dilakukan karena material komponen ini meleleh dan melengket pada wadah spesimen sehingga pengukuran massa selama proses tidak akurat.Torrefaction on instant food packaging plastic (plastic-1) and synthetic rubber could not be done because this component materials to melt and cling to the specimen container so that the measurement of the mass during the process is not accurate. Sedangkan torefaksi pada plastik kemasan minuman instan (plastik-2) hanya menyisakan material padat yang tidak bisa dibakar (aluminium foil). Whereas in the torrefaction on plastic packaging instant drinks (plastic-2) leaving only a dense material that cannot be burned (aluminum foil). 2. Nilai kalor maksimum poduk torefaksi daun diperoleh pada temperatur proses 300 C dan waktu tinggal 20 minit, yakni sebesar 5397 kkal/kg, atau mengalami kenaikan sebesar 27% dibandingkan nilai kalor awalThe maximum heating value of the product of leaves torrefaction obtained at a process temperature 300C and resident time 20 minutes, namely 5397 kcal/kg, or an increase of 27% compared to the calorific value of raw material. 3. Nilai kalor maksimum poduk torefaksi sisa makanan diperoleh pada temperatur proses 250 C dan waktu tinggal 30 minit, yakni sebesar 6889 kkal/kg, atau mengalami kenaikan sebesar 46% dibandingkan nilai kalor awal.The maximum heating value of the product of food residues torrefaction obtained at a process temperature 250C and resident time 30 minutes, namely 6889 kcal/kg, or an increase of 46% compared to the calorific value of raw material. 4. Dari berbagai variasi temperatur proses dan waktu tinggal torefaksi, nilai kalor yang dihasilkan tidak mempunyai perbedaan yang signifikan, yaitu berselisih antara 0,0301 untuk daun dan 0,01-0,04 untuk sisa makanan, dari nilai kalor maksimum untuk masing-masing sampel.From the variations of process temperature and resident time, calorific value produced no significant difference from the maximum heating value for each sample, which is at variance among 0,03-01 and 0,01-0,04 for leaves and food residues respectively.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Malaysia Sewerage Industry Guideline Volume 4Document295 paginiMalaysia Sewerage Industry Guideline Volume 4Asiff Razif100% (13)
- Final Draft IpapDocument46 paginiFinal Draft IpapShelai Lucero100% (2)
- Flow Diagram Sulphuric Acid PlantDocument3 paginiFlow Diagram Sulphuric Acid PlantAnisa SudarmajiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prediction of Deactivation Rates and Mechanisms of Reforming CatalystsDocument2 paginiPrediction of Deactivation Rates and Mechanisms of Reforming CatalystsSarahEkaPutriDarlismawantyaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project of HR Practices of Coca Cola Company in Gujranwala: Gift Business School GujranwalaDocument37 paginiProject of HR Practices of Coca Cola Company in Gujranwala: Gift Business School Gujranwalabajwa122100% (4)
- Travis County vs. IRma Gomez, Uriel Castro and Mustang Kimbro Estates, LLCDocument9 paginiTravis County vs. IRma Gomez, Uriel Castro and Mustang Kimbro Estates, LLCAnonymous Pb39klJÎncă nu există evaluări
- Utility Systems in Chemical EngineeringDocument28 paginiUtility Systems in Chemical EngineeringAndrianPratamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proposal KP HolcimDocument27 paginiProposal KP HolcimPutu Trisnayadhi DharmawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- NG Lube Long Life SeriesDocument2 paginiNG Lube Long Life SeriesSoetopo Awaluddin100% (1)
- Analysis of The Adsorption Process and of Desiccant Cooling SystemsDocument155 paginiAnalysis of The Adsorption Process and of Desiccant Cooling SystemsRajesh VyasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yulianti Sampora, Yenni Apriliany Devy, Dewi Sondari, Dan Athanasia Amanda Septevani. 2020. Simultaneous Pretreatment ProceDocument9 paginiYulianti Sampora, Yenni Apriliany Devy, Dewi Sondari, Dan Athanasia Amanda Septevani. 2020. Simultaneous Pretreatment ProceAdhan AkbarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iron and SteelDocument6 paginiIron and SteelkhansaaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Penggunaan Energi Di Industri Pulp Dan Kertas: Aspek Teknologi Dan LingkunganDocument10 paginiPenggunaan Energi Di Industri Pulp Dan Kertas: Aspek Teknologi Dan LingkunganRudy surya 08Încă nu există evaluări
- Problems and Suggestions of Conveyor SystemsDocument2 paginiProblems and Suggestions of Conveyor SystemsHari Haran0% (1)
- Natural gas analysis inlet outlet absorberDocument121 paginiNatural gas analysis inlet outlet absorberAyu permata sariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ocw Chapter 4Document48 paginiOcw Chapter 4Agam HanasichulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- UTS OPM I Bukit 2017Document1 paginăUTS OPM I Bukit 2017Muhammad Fikri PratamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.3 Boiler OperationDocument23 pagini1.3 Boiler OperationLydia RupidaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Sumber Ta FixDocument55 paginiData Sumber Ta FixWanda YunitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mesin Thermoforming VakumDocument8 paginiMesin Thermoforming Vakumeeng khoiriyah100% (1)
- Makalah Termodinamika IIIDocument33 paginiMakalah Termodinamika IIIdata laptop asusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patent Pabrik Phenyl Ethyl AlcoholDocument6 paginiPatent Pabrik Phenyl Ethyl AlcoholFaizhal DimazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lampiran PerhitunganDocument15 paginiLampiran PerhitunganAchmadJa'farShodiqShahabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neraca Massa Dan Neraca Panas Ball Mill (Revisi FIXED)Document18 paginiNeraca Massa Dan Neraca Panas Ball Mill (Revisi FIXED)astrianyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lampiran 3. Flow Chart PKS PTPN II Pagar MerbauDocument2 paginiLampiran 3. Flow Chart PKS PTPN II Pagar MerbauIra SinagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GHS Poster - Merck OldDocument1 paginăGHS Poster - Merck Oldqwerty uiopÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polivinyl Alcohol Factory DesignDocument163 paginiPolivinyl Alcohol Factory DesignDizaichaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Soal Turbin Uap LengkapDocument4 pagini10 Soal Turbin Uap Lengkaptoys deeÎncă nu există evaluări
- MEBERC PhyChemDocument122 paginiMEBERC PhyChemJames Ivan Palanas RotorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrochemical Degradation of Remazol Red RB 133 Using Sacrificial ElectrodesDocument23 paginiElectrochemical Degradation of Remazol Red RB 133 Using Sacrificial ElectrodesGlobal Research and Development ServicesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Centrifugal compressor performance optimizationDocument27 paginiCentrifugal compressor performance optimizationDea Amelia100% (1)
- Risky Septian Proposal KP PT Salim Ivomas Pratama TBKDocument12 paginiRisky Septian Proposal KP PT Salim Ivomas Pratama TBKRisky SeptianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Downterm ADocument2 paginiDownterm Awiyatmi0% (1)
- KR3543-Lecture 2-VLE and Flash Calculation 20192020 - Revised-20190912065536 PDFDocument66 paginiKR3543-Lecture 2-VLE and Flash Calculation 20192020 - Revised-20190912065536 PDFNatasha Mgt JoharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laporan Pati TermodifikasiDocument16 paginiLaporan Pati TermodifikasiFery HaidirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Engineering Projects Can Be Divided Into Three TypesDocument25 paginiChemical Engineering Projects Can Be Divided Into Three Typestrungson1100% (1)
- Zhang Yie Zien. High-Rate Mesophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Palm Oil Mill Effluent (POME) PDFDocument6 paginiZhang Yie Zien. High-Rate Mesophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Palm Oil Mill Effluent (POME) PDFZainul Fikri TampengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neraca Energi Dengan Reaksi KimiaDocument5 paginiNeraca Energi Dengan Reaksi Kimiaaulia utamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ruzicka CP Estimation MethodDocument11 paginiRuzicka CP Estimation MethodAndreea Cristina PetcuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jurnal Penting REAKTOR PDFDocument8 paginiJurnal Penting REAKTOR PDFGilang PerdanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Satuan SiDocument40 paginiSatuan Siaisyah sri lestari100% (1)
- GR ControlDocument15 paginiGR ControlSastra Diharlan BaharÎncă nu există evaluări
- BOILER EFFICIENCYDocument11 paginiBOILER EFFICIENCYWisnu Jati NugrohoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rustic Wood Toy Manufacturing Cash Flow AnalysisDocument2 paginiRustic Wood Toy Manufacturing Cash Flow AnalysispratitatriasalinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Silica Plastic BlockDocument5 paginiSilica Plastic Blockdharshini deivasigamaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teknik Reaksi Kimia I: by HaryantoDocument23 paginiTeknik Reaksi Kimia I: by HaryantoHarymsl MslÎncă nu există evaluări
- B. Lampiran Neraca EnergiDocument70 paginiB. Lampiran Neraca EnergihilnimahraniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multiple Hearth Furnaces B3Document3 paginiMultiple Hearth Furnaces B3Ossy DewintaÎncă nu există evaluări
- New agitated reactor and heat exchanger installation cost estimateDocument2 paginiNew agitated reactor and heat exchanger installation cost estimateDiego MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mesin Pengolah Susu Kedelai Kapasitas 30 Kilogram PerjamDocument6 paginiMesin Pengolah Susu Kedelai Kapasitas 30 Kilogram PerjamruslysmgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tugas Kelas A Termodinamika Industri KimiaDocument1 paginăTugas Kelas A Termodinamika Industri KimiaayatbimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sealing Gasket (ENKA)Document6 paginiSealing Gasket (ENKA)Apras TyoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tugas 1 Perancangan Alat ProsesDocument6 paginiTugas 1 Perancangan Alat ProsesAldo HoseaÎncă nu există evaluări
- tmp7F33 TMPDocument11 paginitmp7F33 TMPFrontiersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plagiarism Checker X analyzes report on advance stop line designDocument22 paginiPlagiarism Checker X analyzes report on advance stop line designMuhamad Ichsan YogaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parameter Menghitung Temperatur Kalorik (Caloric Temperatur, TDocument4 paginiParameter Menghitung Temperatur Kalorik (Caloric Temperatur, TRiski Maulana100% (1)
- Water Treatment Process OptimizationDocument36 paginiWater Treatment Process OptimizationmasnawatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sintesis Nanoselulosa Dari Tongkol Jagung Dengan Perlakuan Hidrolisis Kimia Dan HomogenisasiDocument68 paginiSintesis Nanoselulosa Dari Tongkol Jagung Dengan Perlakuan Hidrolisis Kimia Dan HomogenisasimustikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagram alir proses pemurnian tebuDocument1 paginăDiagram alir proses pemurnian tebuFadhillah UÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chlorine: International Thermodynamic Tables of the Fluid StateDe la EverandChlorine: International Thermodynamic Tables of the Fluid StateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Waste Plastic Conversion into Chemical Product Like NaphthaDocument6 paginiWaste Plastic Conversion into Chemical Product Like NaphthasodgoweisjdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jurnal Mahasiswa D-IV Teknik Mesin Produksi dan Perawatan Vol. XX, No. XX, Bulan Tahun: Pengaruh Jenis Plastik dan Temperature Reaktor Terhadap Volume Minyak Hasil PirolisisDocument8 paginiJurnal Mahasiswa D-IV Teknik Mesin Produksi dan Perawatan Vol. XX, No. XX, Bulan Tahun: Pengaruh Jenis Plastik dan Temperature Reaktor Terhadap Volume Minyak Hasil PirolisisWahyu RohmantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Artikel KusekDocument6 paginiArtikel KuseksuryadimalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zhu 2004Document11 paginiZhu 2004ERIKO DARMAWANÎncă nu există evaluări
- JadwalDocument1 paginăJadwalrifkasyaputriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prosedur KOBALDocument5 paginiProsedur KOBALrifkasyaputriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Narrative Story Passed On by Mary MDocument1 paginăNarrative Story Passed On by Mary MrifkasyaputriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Korean Viruses in SMADADocument2 paginiKorean Viruses in SMADArifkasyaputriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calon NegarawanDocument2 paginiCalon NegarawanrifkasyaputriÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Origin of ElementsDocument4 paginiThe Origin of ElementsrifkasyaputriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tugas Sejarah " ": Peradaban Lembah Sungai NilDocument1 paginăTugas Sejarah " ": Peradaban Lembah Sungai NilrifkasyaputriÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Get Biochemichal InformationDocument13 paginiHow To Get Biochemichal InformationrifkasyaputriÎncă nu există evaluări
- LemakDocument54 paginiLemakrifkasyaputriÎncă nu există evaluări
- PP MTKDocument1 paginăPP MTKrifkasyaputriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Korean Viruses in SMADADocument2 paginiKorean Viruses in SMADArifkasyaputriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dange TugasDocument15 paginiDange TugasrifkasyaputriÎncă nu există evaluări
- JSDEWES 0385 M V 02 VerelderDocument18 paginiJSDEWES 0385 M V 02 VerelderZavaleta RedlerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Green Arch PDFDocument19 paginiGreen Arch PDFKishore RajaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enviromail 65 - Adsorbable Organic Halides AOX - May 2013Document2 paginiEnviromail 65 - Adsorbable Organic Halides AOX - May 2013fisheriesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taipei 101Document7 paginiTaipei 101Chan Won SiewÎncă nu există evaluări
- Epec 3606 Control Unit: Technical DocumentDocument49 paginiEpec 3606 Control Unit: Technical DocumentJoao SilvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Current AffairsDocument135 paginiCurrent AffairsSri KanthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Camp Ensign HistoryDocument167 paginiCamp Ensign HistoryCAP History Library100% (1)
- Paper Product Price QuotationDocument6 paginiPaper Product Price QuotationVipin SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- StudentDocument101 paginiStudentHarsha Samagara0% (1)
- DVR Evix Er-401Document82 paginiDVR Evix Er-401SaimonK100% (1)
- Abraham AynekugnemDocument85 paginiAbraham AynekugnemBerihu GirmayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Leopard General and in Stal Tion InformationDocument18 paginiLeopard General and in Stal Tion InformationChandrasekhar SonarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Xt2052y2asr GDocument1 paginăXt2052y2asr GjoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Invoice 1 (Plumbing Ababil)Document1 paginăInvoice 1 (Plumbing Ababil)Ragul KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of Precast Building System DesignDocument7 paginiAnalysis of Precast Building System Designshashank adigaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blue Forest Resorts-Project ReportDocument13 paginiBlue Forest Resorts-Project ReportIcarus Builders And Developers Pvt. Ltd67% (3)
- A Proposed 3-Storey Municipal HallDocument14 paginiA Proposed 3-Storey Municipal Hallvictorvarias25Încă nu există evaluări
- Serbuk Albedo PDFDocument4 paginiSerbuk Albedo PDFM Sahidna AlbarkanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non-Biodegradable Waste Disposal MethodsDocument5 paginiNon-Biodegradable Waste Disposal MethodsAnnu KambleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Letter For Swach BhartDocument3 paginiLetter For Swach Bhartsumit mundliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- August 5-9 2019 CapDev Formulation Steps and ToolsDocument83 paginiAugust 5-9 2019 CapDev Formulation Steps and ToolsJerome Ogawan100% (1)
- Aswad - Table of ContentsDocument1 paginăAswad - Table of ContentsMahbub BhuiyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technology: Machine Reliability. The Early YearsDocument7 paginiTechnology: Machine Reliability. The Early Yearsdaniel adamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Roxol Bioenergy Corporation energy problems and solutionsDocument9 paginiRoxol Bioenergy Corporation energy problems and solutionsAldren Delina RiveraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corn Starch Bags Replace Plastic with Renewable MaterialDocument68 paginiCorn Starch Bags Replace Plastic with Renewable MaterialAryanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Axial-Fan AC-HyBlade EN PDFDocument48 paginiAxial-Fan AC-HyBlade EN PDFСергей КолесниковÎncă nu există evaluări