Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Digestive System-1
Încărcat de
elinandreaTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Digestive System-1
Încărcat de
elinandreaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
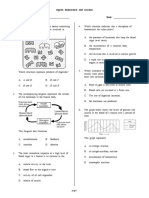
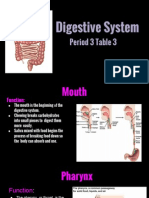
Digestive System Functions Mastication 1) Take in food.
- breaks large food particles into smaller parts 2) Break down food - increases efficiency of digestion because of 3) Absorb nutrients digestive enzymes 4) Eliminate wastes Salivary Glands Histology of the Digestive Tract - mixture of serous and mucous fluids - digestive tract mouth to the anus - tongue, palate, cheeks, and lips - Three pairs of large compound alveolar glands: Tunics o Parotid glands o Mucosa Serous glands Innermost tunic Surface of the second upper Mucous epithelium molar Lamina propria loose o Submandibular glands connective tissue Produce more serous than Muscularis mucosae thin mucous smooth layer o Sublingual glands o Submucosa Smallest of the three paired Outside the mucosa glands Thick layer of loose connective Produce mucous secretions tissue containing nerve, blood - Saliva 1 liter per day; contains salivary vessels, and small glands amylase (digestive enzyme) Submucosal plexus regulates - Mucin proteoglycan that gives lubricating secretion of glands quality to secretions o Muscularis - Regulated by autonomic nervous system, with Inner layer of circular smooth parasympathetic stimulation muscle and an outer layer of Esophagus longitudinal smooth muscle - muscular tube lined with moist stratified Myenteric plexus controls squamous epithelium motility transports food from the pharynx to the o Serosa or adventitia stomach Oral Cavity - upper esophageal sphincter superior end of - mouth the esophagus - connects to the pharynx through a space called - lower esophageal sphincter lower end of the fauces esophagus; - Divided into two regions: Swallowing o Vestibule space between lips or - Three phases: cheeks and the teeth or gums o Voluntary phase o Oral cavity medial to the teeth Bolus is formed and pushed by Lips and Cheeks the tongue to the oropharynx - for mastication and speech o Pharyngeal phase help manipulate food Reflex that is initiated when a Palate and Palatine Tonsils bolus stimulates tactile - for swallowing receptors in the oropharynx - prevents food from passing into the nasal cavity o Esophageal phase Tongue 5-8 seconds - moves the food in the mouth for proper pharynx to stomach mastication peristalsis (contraction and - major sensory organ for taste and major organ relaxation of esophagus) for speech Stomach Teeth Secretions of the stomach - 32 teeth - gastric juice - for mastication
food is mixed with the gastric juice forming chime - mucus lubricates and protects epithelial cells from damaging effect of acidic chime and pepsin - hydrochloric acid pH of 2 in the stomach - Pepsinogen o Precursor of the enzyme pepsin - Peptide two tor more amino acids united by a peptide bond - Regulation of stomach secretion: o Cephalic Phase Prepares stomach to receive food o Gastric phase Greatest volume of gastric secretions Presence of food in the stomach o Intestinal phase Entrance of chyme to the duodenum of small intestine stimulates neural and hormonal mechanisms that inhibit stomach secretions Reduces acidity of chyme Vomiting - reversed peristalsis - ejection of the stomachs contents Small Intestine 1) Duodenum o simple columnar epithelium cells absorptive cells goblet cells granular cells endocrine cells 2) Jejunum and Ileum - major sites of nutrient absorption Secretions of the Small intestines - mucus protects against digestive enzymes and acids - digestive enzymes (disaccharides and peptidase) are bound to the intestinal walls - Peptidase break the peptide bond in proteins to form amino acids - Disaccharidases break down disaccharides such as maltose and isomaltose, into monosaccharides - chemical or tactile irritation, vagal stimulation, and secretin stimulates intestinal secretion.
Movement of The Small Intestine - Segmental contractions o propagated for short distances o mix secretions from small intestines, pancreas, and liver with ingested materials which promotes their digestion and absorption - peristaltic contractions o proceed along the length of the intestine for variable distances to cause the chyme to move along the intestine Liver and Gallbladder Liver - largest internal organ of the body Gallbladder - stores bile Funcitons of the Liver 1) Bile production o produces 600-1000mL of bile a day o bile neutralizes and dilutes gastric acid and emulsifies fats 2) Storage - Hepatocytes remove sugar from the blood and store it in the form of glycogen - Hepatocytes help control blood sugar levels 3) Nutrient Interconversion 4) Detoxification 5) Phagocytosis 6) Synthesis Bile Transport 1) bile canaliculi collect bile from hepatocytes and join small hepatic ducts in the portal triads 2) Small hepatic ducts converge to form the right and left hepatic ducts, which exit the liver. 3) The cystic duct from the gallbladder joins the common hepatic duct. 4) The cystic duct from the gallbladder joins the common hepatic duct to form the common bile duct. 5) The common bile duct and pancreatic duct join the hapatopancreatic ampulla which opens into the duodenum at the major duodenal papilla. Gallbladder and Bile Storage - the gallbladder is a small sac on the inferior surface of the liver - gallbladder stores and concentrates bile Regulation of Bile Secretion and Release 1) secretin increases bile secretion. 2) Cholecystokinin stimulates gallbladder contraction and relaxation of sphincters of bile duct and hepatopancreatic ampulla.
Pancreas - pancreatic islets o produce inculin and glucagon Pancreatic Secretions - exocrine secretions - Pancreatic juice o Produced by small pancreatic ducts and contains bicarbonate ions o Enzymatic component is produced by the acini and contains enzymes that digest carbohydrates and lipids and porteins Regulation of Pancreatic Secretions - secretin stimulates release of aqueous component which neutralizes acidic chyme - cholecystokinin stimulates secretion of enzymatic component and relaxation of the sphincters of the pancreatic duct and hepatopancreatic ampulla - parasympathetic stimulation increases, and sympathetic stimulation decreases, secretion of the enzymatic component. -
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Biology Summary NotesDocument5 paginiBiology Summary NotesNoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mod 4 Revision Guide 1 Reaction Kinetics AQA A2 ChemistryDocument5 paginiMod 4 Revision Guide 1 Reaction Kinetics AQA A2 Chemistryviyas07Încă nu există evaluări
- BPH First Year Curriculum of Purbanchal UniversityDocument48 paginiBPH First Year Curriculum of Purbanchal Universityseo167Încă nu există evaluări
- Biology A2 Snab CourseworkDocument120 paginiBiology A2 Snab CourseworkIshwarya SivakumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enzymes (AS Level Bio)Document23 paginiEnzymes (AS Level Bio)DrMufaddal RampurwalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory System Revision PackDocument59 paginiCirculatory System Revision PackChinmayee TKÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8Cc Getting Oxygen EPSDocument44 pagini8Cc Getting Oxygen EPSZak Remtulla100% (1)
- Week 6 Integumentary WorksheetDocument2 paginiWeek 6 Integumentary WorksheetAthia ZamanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembranDocument3 paginiMovement of Substances Across The Plasma MembranNorshamsiah SamsudinÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Human Body SystemsDocument104 paginiThe Human Body Systemsapi-126624159Încă nu există evaluări
- Pollution Is The Introduction of Contaminants Into A Natural Environment That Causes Instability, DisorderDocument16 paginiPollution Is The Introduction of Contaminants Into A Natural Environment That Causes Instability, DisorderJassi Layal100% (2)
- Biology NotesDocument6 paginiBiology NotesElizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- OCR Biology F211 Cells, Exchange and Transport Revision NotesDocument4 paginiOCR Biology F211 Cells, Exchange and Transport Revision Notes24wrightphilip100% (1)
- Yr 7 Vocab ReproductionDocument2 paginiYr 7 Vocab ReproductionfghfjffgfgjfgfjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary Sheets: Going For Gold!Document2 paginiSummary Sheets: Going For Gold!chan myae100% (1)
- Human Body Systems Study GuideDocument1 paginăHuman Body Systems Study Guideapi-323449449Încă nu există evaluări
- 8A Food and DigestionDocument20 pagini8A Food and DigestionPoornimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework 7 J23.Document15 paginiHomework 7 J23.mauoshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- IGCSE Answers Chapters 01 05Document7 paginiIGCSE Answers Chapters 01 05María Eugenia MolteniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Composition of The CellDocument132 paginiChemical Composition of The Cellazfdin100% (3)
- Worksheet in BloodDocument12 paginiWorksheet in BloodBryan Mae H. DegorioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 6 - Musculoskeletal and Nervous SystemsDocument20 paginiLesson 6 - Musculoskeletal and Nervous Systemsapi-307592530Încă nu există evaluări
- IGCSE Biology NotesDocument50 paginiIGCSE Biology NotesRumaisa AbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9aa Environmental Variation VLE V3Document32 pagini9aa Environmental Variation VLE V3syztqÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8A Summary SheetDocument2 pagini8A Summary Sheetishaan surapaneniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marking Schemes For Topic 1,2 Stafford PapersDocument57 paginiMarking Schemes For Topic 1,2 Stafford PapersSuha AbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell MembraneDocument49 paginiCell MembraneKristen KonradÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transport in Plants HandoutDocument5 paginiTransport in Plants HandoutAsawni McDowellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Questions Outcome 5Document7 paginiQuestions Outcome 5doaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answers Outcome 5Document4 paginiAnswers Outcome 5doaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2010 Till 2021Document1.914 pagini2010 Till 2021Wael TareqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio Factsheet: The Kidney: Excretion and OsmoregulationDocument4 paginiBio Factsheet: The Kidney: Excretion and OsmoregulationjesvinjesvinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Regents Homeostasis and EnzymesDocument5 paginiRegents Homeostasis and Enzymesapi-3031203990% (1)
- Biology Key TermsDocument3 paginiBiology Key TermsIshra ChaudhryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Igcse Biology Digestion Revision GuideDocument3 paginiIgcse Biology Digestion Revision Guideapi-255623302Încă nu există evaluări
- Practical 2Document2 paginiPractical 2Dr.CharinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 2 - The Digestive SystemDocument25 paginiLesson 2 - The Digestive Systemapi-268442191Încă nu există evaluări
- 8a Food Digestion Science QuizDocument42 pagini8a Food Digestion Science QuizahmerjamilÎncă nu există evaluări
- IGCSE Biology Transport in Humans SummaryDocument63 paginiIGCSE Biology Transport in Humans SummaryClarissa Muliawan100% (1)
- 3.2 Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins WORDDocument6 pagini3.2 Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins WORDCaitlin Barrett100% (1)
- Sexual Reproduction in Human Beings (Part 1)Document40 paginiSexual Reproduction in Human Beings (Part 1)puspita8967628Încă nu există evaluări
- HSBDocument12 paginiHSBjemima MillsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digestive System PowerpointDocument19 paginiDigestive System Powerpointapi-277974939Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 TestDocument5 paginiUnit 1 Testapi-485795043Încă nu există evaluări
- What Is Variation and What Are Its Causes?: Key Words Key WordsDocument35 paginiWhat Is Variation and What Are Its Causes?: Key Words Key WordsPatrick AbidraÎncă nu există evaluări
- As Biology - Edexcel - Unit 1 - Lifestyle, Transport, Genes and HealthDocument21 paginiAs Biology - Edexcel - Unit 1 - Lifestyle, Transport, Genes and HealthWarusha KanchanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 8 Integrated Science Week 2 Lesson 2Document5 paginiGrade 8 Integrated Science Week 2 Lesson 2Balram HaroldÎncă nu există evaluări
- VariationDocument33 paginiVariationdejla67Încă nu există evaluări
- Reference: Essentials For Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb, EDocument11 paginiReference: Essentials For Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb, EAnnalei GagnéÎncă nu există evaluări
- Characteristics of Living Things CellsDocument13 paginiCharacteristics of Living Things CellsFrances FlynnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Domain Kingdom PhylumDocument74 paginiDomain Kingdom PhylumRia PerezÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Transport System IB Qq'sDocument12 paginiThe Transport System IB Qq'sJohn OsborneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 8 The Reproductive System Bilingual EducationDocument13 paginiUnit 8 The Reproductive System Bilingual EducationAntonio PrietoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Workshop About The Heart and Cardiac CycleDocument4 paginiWorkshop About The Heart and Cardiac CycleLina Mafla100% (1)
- Biology Revision Notes: Topic 7 Run For Your Life: Slow Twitch MusclesDocument18 paginiBiology Revision Notes: Topic 7 Run For Your Life: Slow Twitch MusclesDontÎncă nu există evaluări
- BiologyDocument39 paginiBiologyAnna MontiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- PCAT Test Prep Biology Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 3 of 4: PCAT Exam Study GuideDe la EverandPCAT Test Prep Biology Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 3 of 4: PCAT Exam Study GuideEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- Chemistry of Cell Review: Quick Review Notes Chapter 2De la EverandChemistry of Cell Review: Quick Review Notes Chapter 2Încă nu există evaluări
- Wholesale Product List - Us: Essential Oil SinglesDocument3 paginiWholesale Product List - Us: Essential Oil SinglesAngelo José Niño Bello100% (1)
- Burning Passion - A Mated LovestoryDocument111 paginiBurning Passion - A Mated LovestoryAnata Dake79% (14)
- What Makes A Person BeautifulDocument2 paginiWhat Makes A Person BeautifulHarish RaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Culinary Herbs & Spices 1D100Document4 paginiCulinary Herbs & Spices 1D100Radosław KwiecińskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subimal Mishra - EczematousDocument3 paginiSubimal Mishra - EczematousGregory Eleazar D. AngelesÎncă nu există evaluări
- BethelDocument4 paginiBethelbawihpuiapaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy of Larynx: Dr. Prashant YarlagaddaDocument24 paginiAnatomy of Larynx: Dr. Prashant YarlagaddaregisterpyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy Lecture Notes DigestiveDocument9 paginiAnatomy Lecture Notes DigestiveKenneth dela CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Admedika DiagnosaDocument143 paginiAdmedika Diagnosadiawima100% (1)
- 16 Back Spinal CordDocument27 pagini16 Back Spinal CordAnonymous lsnDTjvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Midterm Exam EssayDocument2 paginiMidterm Exam EssayJohn Drex CustodioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument14 paginiReproduction in PlantsAsif AyazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory System Anaphy LabDocument15 paginiRespiratory System Anaphy LabNicoleTrishiaDeparineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spatium ParapharyngeumDocument1 paginăSpatium ParapharyngeumMarina ČovićÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rabbit: Scientific Name:oryctolagus CuniculusDocument10 paginiRabbit: Scientific Name:oryctolagus CuniculusJefferson BeraldeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomical PositionsDocument39 paginiAnatomical PositionsWaqar AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy of The Female PelvisDocument60 paginiAnatomy of The Female PelvisMignot AnileyÎncă nu există evaluări
- StabilityDocument21 paginiStabilityDrYashvi ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dogs - Reading Comprehension For KidsDocument2 paginiDogs - Reading Comprehension For KidsPrimary Leap.co.uk100% (3)
- Gosner A Simplified Table For Staging Anuran Embryos and Larvae With Notes On IdentificationDocument9 paginiGosner A Simplified Table For Staging Anuran Embryos and Larvae With Notes On IdentificationjegarciapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stud ContractDocument2 paginiStud Contractapi-26366049567% (3)
- The Beagle Club - History of The BreedDocument3 paginiThe Beagle Club - History of The Breedapi-284176376Încă nu există evaluări
- The Cyatheaceae of PeruDocument35 paginiThe Cyatheaceae of PerudavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kavita Cheating On Her Husband Posted OnDocument22 paginiKavita Cheating On Her Husband Posted Onsanjay975100% (3)
- Skeletal System PowerpointDocument40 paginiSkeletal System PowerpointMugabi Fahad100% (1)
- HohohohohohohohohohoDocument37 paginiHohohohohohohohohohoKaraokeÎncă nu există evaluări
- The KOVA Glasstic Slide10Document2 paginiThe KOVA Glasstic Slide10Bety NuñezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Harry Potter - The Woes of Dumbledore's ArmyDocument18 paginiHarry Potter - The Woes of Dumbledore's ArmyNaveen AmarasingheÎncă nu există evaluări