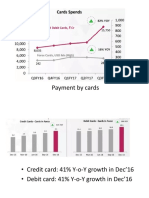
Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Governance
Încărcat de
cvramannaDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Governance
Încărcat de
cvramannaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Governance and Good Governance
Government: It is a critical and inseparable element of the state It is a responsible state for administration through various institutions to ensure a better society and improved lives of citizens. In the course of administration, the government creates a relationship between its various institutions and citizens. The nature of this relationship depends the nature of the state, e.g.,. Whether it is a military state, autocratic state, democratic state, or any other form Governance: Governance- Not Static but dynamic in nature Who govern and How well- Means Governance Definition of the exercise of economic, political and administrative UNDP authority to manage a country's affairs at all levels and by which states promote social cohesion and integration, and ensure the well-being of their population In General Focus on effective interaction between government, Market, Civil Society and Cooperative Endeavour to realize desire outcome Quality of government increase Significant position of citizens- Collective participation in decision making reform in the governing process for better and improved policy outcome Encompass Effectiveness of state, Government, Market and Community Encompass Political, Social and Economic Aspect of the governing system Definition for Reduction of the role of the State in economic activities as Market well as the promotion of the role of the market. Economy Definition As the set of guiding principles to improve and strengthen during period the capacity of the recipient countries towards better and of effective implementation of development initiatives. Globalisation Broad Independent Judiciary Concern Accountability Active Public participation- Not just as passive consumer Ensure Citizen right Empowering people Responsiveness Strong Civil Society including press
Civil Servants imbued with professional Ethos
Distinct Aspect of Governance
Form of political Regime
Process by which authority is excercised for managment of a country's economic and social resources Capacity of government to design, formulate and implement policies
Rule of Law: Police, Judiciary Regulatory burden: Policies that make market unfriendly
Control of Corruption
Measures for Governance by World Bank
Effectiveness of government: Competence bureaucracy and public delivery Service Instability and Violence
Voice and Accountability
Efficiency: a measure of how economically resources are used to produce the intended results
Effectiveness:
Subsidiarity: the principles that decision making should t&e place at the level that is most appropriate for a particular issue
Transparency and Access to information
Sustainability: Measures governance and its quality by International Fund for Agricultural Development
Inclusiveness and Equalty
Accountability:
Participation
Adherence to the rule of the law: the principle that every member of a society, even a ruler, must follow the law
Good Governance: Good governance would promote and ensure development. Sound economic policies and democratic institutions that are responsive to people's needs are instrumental for sustained economic growth, poverty eradication, and employment generation. This unit deals in detail with governance and development 1989: World Bank: Sub Sahara Africa- From crisis to Sustained growth Need for Good Governance
Good Governance- Sound development management Having four dimension or components Public Sector Managment- Civil Service reforms (ARC) and involvement of Privet Sectore (PPP model) A legal framework for devdelopment to ensure working of Market Ensure Accountability through Various institution and Mechanism
Ensuring transparency and Access to information Governance and Development: Inter relationship Development- Efforts to make for increasing per Capita income and improving standard living and well-being of society (including health, education, sanitation, safe drinking water, employment opportunity etc.) The term development is closely related to process of Governance. The Centre point of Both Development and governance is offering benefit to people. Both are complement each other. Development bears fruit in presence of good governance. Good governance ensure people participation in decision making process related to development programme. The participation of people in development initiatives truly reflects the empowerment of people.
According to Asian Development Bank (ADB), the four key areas of interrelationship between governance and development.
Accountability Transparency Participation Predictability
The United Nations General Assembly 2005 World Summit outcome envisaged that "good governance is essential for sustainable development
Sound Economic Policy Solid Democratic institution responsive to need of People Improved infrastructure
Sustained economic growth,
Basis for
Poverty eradication and employment creation; Peace and security, Domestic stability, Respects for human rights, including the right to development, the rule of law, gender equality and market oriented policies
Features of Good Governance:
The Challenges for Good Governance: 1) Political and Administrative aspects 2) Aspects in general
legal framework based on the rule of law and independenceof judiciary to protect human rights, secure social justice
need of cooperation among government and civil society organizations
A sound administrative system should lead to efficiency and effectiveness
freedom of associations and participation by various religious, social, economic and cultural and professional groups in the process of govenpnce Political accountability: acceptability of the political system by the people, and regular elections to legitimize the exercise of political power
Political and Administrative aspects
Freedom of information: needed for farmulation of public policies, decision- making, monitoring and evaluation of good performance.
Bureaucratic accountability: ensuring a system to monitor and control the performance of government offices and officials, in relation to quality of services, efficiency and misuse of discretionary power.
Violation of Human rights Criminalisatio n of politics
Poorly empowered grassroots democratic institutions
Centralisation of power and authority
Poor coordination among the political, administrative and community levelorganizations and institutions
Aspects in General
Corruption at various levels
Poor participation of disadvantaged in decision making process.
Weak legislators with criminal records, poor knowledge about development issues and low level of education
Poor people's participation in development processes
Delay in delivery of judicial decisions
Attributes of Good Governance: Attributes Rightsizing government function Greater use of information technology and management techniques Delegation, ethics and participation Ensuring Accountability Institutional reforms To identify and Care functions that cant performed by market such as law and order, security, Social service, Creating infrastructure, macroeconomic management autonomous regulatory agencies with quasi-judicial powers, in order to ensure that the functioning of private units evolving better systems of record keeping, movement of files, space utilization, and the adoption of other available means of automation make public offices more effective and efficient through computerized information system Simplification of office procedures, standardization of job output, and introduction of appraisal by result efficiency cum performance audit would ensure greater accountability Performance budgeting delegation and devolution of authority and responsibility adherence to clearly defined ethical standards process of consultation and participation in decision making Through institutional Framework and establishing accountability mechanism such as public accountable committee, executive accountability to parliament Right to information (RTI) Act Changing policy and programmes; improving administrative effectiveness; solving personal problems; countering pressures and threats from outside organizations. empowerment of citizens in general and vulnerable section in particular empowerment of grass root functionaries dispersal of politico-administrative power privatization, contracting out and removing delays and rigidity in public organizations Technology up gradation (introducing information technology), incorporating modern techniques of management to ensure effectiveness and efficiency capacity building of public institutions (training of civil servants) and transparency and openness in public organizations
Decentralization Delegation Democratization De-bureaucrazation Others ways
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Wipro. Order To Cash PDFDocument11 paginiWipro. Order To Cash PDFcvramannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Screenshot 2023-12-28 at 10.42.55 AMDocument1 paginăScreenshot 2023-12-28 at 10.42.55 AMcvramannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DEMONITISATIOONDocument3 paginiDEMONITISATIOONcvramannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SecurityDocument56 paginiSecuritycvramannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- India - Us Relations, HFCS, Westinghouse Deal, Nuclear Liability, GettnpDocument10 paginiIndia - Us Relations, HFCS, Westinghouse Deal, Nuclear Liability, GettnpcvramannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kashmir Issue: What Is Main ProblemDocument1 paginăKashmir Issue: What Is Main ProblemcvramannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Always Remember A Few Things Before and While You Are Inside The HallDocument1 paginăAlways Remember A Few Things Before and While You Are Inside The HallcvramannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Approved Annual Programme 2014Document1 paginăApproved Annual Programme 2014Kiran KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydraulic Structures For Flow Diversion & StorageDocument30 paginiHydraulic Structures For Flow Diversion & StorageIanleft9100% (1)
- Answer WritingDocument5 paginiAnswer WritingcvramannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SC Strikes Down 8 (4) of RPA: Eg: Russia Is India's Best Strategic Partner But Fairs Poor in Trade, US Is 2Document3 paginiSC Strikes Down 8 (4) of RPA: Eg: Russia Is India's Best Strategic Partner But Fairs Poor in Trade, US Is 2cvramannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Full TextDocument6 paginiFull TextAtul ThakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- 14th-Strenthening Financial MGTDocument27 pagini14th-Strenthening Financial MGTgopichand456Încă nu există evaluări
- Print Article-DetailsDocument2 paginiPrint Article-DetailscvramannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Rule Against Multiplicity and Child PornoDocument3 paginiRule Against Multiplicity and Child PornoHouston Criminal Lawyer John T. FloydÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organisational Behaviour - II India Yamaha Motors Interim PPT (Download To View Full Presentation)Document28 paginiOrganisational Behaviour - II India Yamaha Motors Interim PPT (Download To View Full Presentation)mahtaabkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Potential Nursing Diagnosis Problem Fdar / NCP: Activity # 2Document2 paginiPotential Nursing Diagnosis Problem Fdar / NCP: Activity # 2Karl KiwisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Second Unit Test 2022: Radha Madhav Public School BareillyDocument4 paginiSecond Unit Test 2022: Radha Madhav Public School BareillyRaghav AgarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- FS 1 Activity 3.3Document6 paginiFS 1 Activity 3.3HYACINTH GALLENEROÎncă nu există evaluări
- YaalDocument25 paginiYaalruseenyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kravitz Et Al (2010)Document5 paginiKravitz Et Al (2010)hsayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Direct RetainerDocument186 paginiDirect RetainerAngkita KalitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AL Applied Mathematics 1989 Paper1+2 (E)Document7 paginiAL Applied Mathematics 1989 Paper1+2 (E)eltytanÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Aging Game Simulation Activity For Al PDFDocument13 paginiAn Aging Game Simulation Activity For Al PDFramzan aliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Men Orr HagiaDocument8 paginiMen Orr HagiaAtika Bashirati IlmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- مذكرة التأسيس الرائعة لغة انجليزية للمبتدئين?Document21 paginiمذكرة التأسيس الرائعة لغة انجليزية للمبتدئين?Manar SwaidanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Perception On The Impact of New Learning Tools in Humss StudentDocument6 paginiPerception On The Impact of New Learning Tools in Humss StudentElyza Marielle BiasonÎncă nu există evaluări
- VW Golf 2 Sam Naprawiam PDFDocument3 paginiVW Golf 2 Sam Naprawiam PDFScottÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Mathematical InvestigationDocument1 paginăWhat Is Mathematical Investigationbj mandia100% (1)
- P.E and Health: First Quarter - Week 1 Health-Related Fitness ComponentsDocument19 paginiP.E and Health: First Quarter - Week 1 Health-Related Fitness ComponentsNeil John ArmstrongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Info Cad Engb FestoDocument14 paginiInfo Cad Engb FestoBayu RahmansyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- BTCTL 17Document5 paginiBTCTL 17Alvin BenaventeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mindfulness: Presented by Joshua Green, M.S. Doctoral Intern at Umaine Counseling CenterDocument12 paginiMindfulness: Presented by Joshua Green, M.S. Doctoral Intern at Umaine Counseling CenterLawrence MbahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 18 Ex Parte Applic Shorten Time Consolidate 11/01/21Document13 pagini18 Ex Parte Applic Shorten Time Consolidate 11/01/21José DuarteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Merger of Bank of Karad Ltd. (BOK) With Bank of India (BOI)Document17 paginiMerger of Bank of Karad Ltd. (BOK) With Bank of India (BOI)Alexander DeckerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Correct Translation of 2-16Document19 paginiCorrect Translation of 2-16muhammad_zubair708110Încă nu există evaluări
- PM-KISAN: Details of Eligible and Ineligible FarmersDocument2 paginiPM-KISAN: Details of Eligible and Ineligible Farmerspoun kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- DBS AR 2019 Final Final PDFDocument371 paginiDBS AR 2019 Final Final PDFDevi Nurusr100% (1)
- Accounting Volume 1 Canadian 8th Edition Horngren Solutions ManualDocument25 paginiAccounting Volume 1 Canadian 8th Edition Horngren Solutions ManualElizabethBautistadazi100% (43)
- Prayer For Stages On The PathDocument6 paginiPrayer For Stages On The PathEijō JoshuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TestFunda - Puzzles 1Document39 paginiTestFunda - Puzzles 1Gerald KohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood Is A Body Fluid in Human and Other Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances Such AsDocument24 paginiBlood Is A Body Fluid in Human and Other Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances Such AsPaulo DanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Failure of Composite Materials PDFDocument2 paginiFailure of Composite Materials PDFPatrickÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 1 Course Objectives and OutlineDocument15 paginiWeek 1 Course Objectives and Outlinechrisbourque13Încă nu există evaluări