Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Salivary Function
Încărcat de
newmexicoomfsDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Salivary Function
Încărcat de
newmexicoomfsDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Physiology Exam 5
Salivary Function Function of GI Tract o Propulsion of food & mixing of GI contents o Digestion & !sorption Secretions that promote digestion Ingest " #$day of %ater Secrete & #$day of saliva Secrete " #$day of gastric secretions 'ther secretions( o )ile * 5++ m#$day o Pancreatic * &,-5+ m#$day o Intestinal * " #$day Total excreted into GI tract * . # Small intestine rea!sor!s * /,-5+ m# 5++ m# enters colon 0++ m# rea!sor!ed !y colon &++ m#$day excreted 1utrient upta2e Sugars are a!sor!ed !y secondary active transport 3SG#T 4 sodium$glucose transporter5
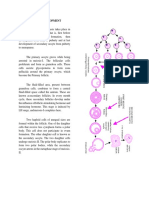
Salivary Glands 6a7or Functions of Saliva o #u!rication o Digestion o Solvent action o nti!acterial action o )uffering action o 8e9minerali:ation o Temperature regulation o Production of gro%th factors Salivary Glands o Parotid Gland o Su!mandi!ular Gland o Su!lingual Gland 8esting ;onditions vs< Stimulated ;onditions Gland =istologic Secretion > of total Type secretion 3!asal5 @ rest Parotid Serous ?atery + Submandibula 6ixed 6oderatel /+ r y viscous Sublingual 6ucous Biscous "+$+
> of total secretion %hen stimulated @+ A+ "$/
Innervation o )oth sympathetic & parasympathetic salivary flo% Sympathetic * viscous saliva Parasympathetic * %atery saliva 3from parotid gland5 o Sensory afferents 3taste & smell5 4 trigger saliva flo%
Physiology Exam 5
Parasympathetic
Primary cell !ody Inferior Salivatory 1ucleus Dorsal vagal 1ucleus & 1ucleus m!iguus
1erve Glossopharyngeal 3;1 IC5
Ganglion 'tic
Gland Parotid 6ucous glands of oral cavity )ronchi, lungs =eart GI 3esophagus descending colon5 #iver, gall !ladder, pancreas Didneys #acrimal Palatal, pharyngeal, & nasal mucous glands Su!mandi!ular & su!lingual 6ucous glands of oral cavity Parotid Su!mandi!ular Su!lingual
Bagus 3;1 C5
Terminal Ganglia
#acrimal & superior salivatory nucleus Sympathetic
Pterygopalatine Facial 3;1 BII5 Su!mandi!ular Superior cervical ganglion
Secretory Path%ay o Initially, you can have salivary flo% %$out !lood flo% o Salivary secretion is 1'T a filtration process 4 it is due to active & passive ion transport o Path%ay( primary secretion in acinar cells intercalated ducts granular tu!ule striated duct excretory duct oral cavity o 6yoepithelial cells #ocated around acinar cells & intercalated duct ;ontractile 4 force saliva into striate duct o Striated Ducts 1aE$DE exchange as saliva moves thru striated duct 1aE is rea!sor!ed DE is excreted Secretion of various glycoproteins & proteins Ex( gro%th factors, immunoglo!ins )oth processes %or2 !etter %ith slo%er saliva flo% 3processes ta2e time5 Slo% flo% * F1aEG & FDEG in saliva Fast flo% * FDEG & F1aEG in saliva o Total salivary secretion is -5+9&+++ m#$day ;omposition of Saliva o 6ain ;omponents ?ater Electrolytes 4 1aE, ;l9, DE, =;'A9 6ucous 4 made of glycoprotein Slippery & stic2y 4 allo%s for lu!rication Protects GI tract from acid Gro%th factors 1umerous proteins$glycoproteins o Electrolyte ;omposition
Physiology Exam 5
Dependant on Flo% rate Slo% * more hypotonic 3/@ m'sm5 Fast * slightly hypotonic 3&A" m'sm5H more !icar!onic acid 3due to ;'"5
'rganic ;omponents Proteins of acinar cell origin( digestive en:ymes 3amylase & lipase5, mucous glycoproteins mylase 4 starts car! digestion #ingual #ipase 4 not that important under normal conditions 6ucous Secretion o 6ucous is pac2aged into glo!ules Glo!ules fuse %$ mem!rane mucous released into lumen o 6ucin glycoprotein & 4 high 6? 4 coat hard & soft tissues o 6ucin glycoprotein " 4 lo% 6? 4 clump !acteria together so they can !e removed from oral cavity 1on9acinar cell origin( gro%th factors, regulatory peptides 1erve Gro%th Factor 31GF5 o Found in salivary secretion of the su!mandi!ular salivary gland 3also produced !y other !ody organs5 o Function in saliva is un2no%n 4 it does stimulate the gro%th of sympathetic 1S o Giving ne%!orns anti!ody to 1GF %ill inhi!it 1GFIs systemic action, creating immunosympathetomy Salivary Gland Epidermal Gro%th Factor o ?ound healing in saliva 3ex( animals lic2 %ounds5 o Gets into general circulation & has trophic effects( 6aintains ileal mucosa ids in healing ulcers 8ole in liver regeneration 3regenerate hepatocytes5 Salivary Gland Dalli2rein o Protease found in saliva o Ta2es a precursory molecule to !rady2inin o )rady2inin is a potent vasodilator Immunoglo!ins 6a7ority is Ig 3->5 Ig J Ig6 J IgG J IgD 'ther Salivary constituents P'A 6g"E ;ortisol, estrogens, progesterone, testosterone, & aldosterone ;oncentrations close to those in plasma DonIt have to dra% !lood to do testing
;ontrol of Salivary Secretion 'vervie% o Small !asal secretion 3small amount secreted even %$out stimulation5 o 6ost secretion caused !y afferent sensory input Taste triggers secretion( acid J s%eet & salty J !itter 3almost no secretionH !itter su!stances usu< toxic5 6astication( saliva triggered !y mechanoreceptors
Physiology Exam 5
'lfactory 3smell5 Tactile & temperature receptors o 6echanical irritation of oral mucosa 3ex( mastication5 * salivation Ex( patients %$ ne% dentures or ortho appliances salivary flo% is usu< temporary 1ervous system factors o " nuclei control salivary glands( superior salivatory nucleus 4 Facial nerve 3BII5 su!mandi!ular & su!lingual glands inferior salivatory nucleus 4 glossopharyngeal 3IC5 parotid glands o 1S ;ontol 3controls ho% much saliva & composition5 1S is the most important factor in control of saliva Parasympathetic Increase !lood flo% to%ards salivary glands ="' & electrolytes #arge in %atery secretion * volume " mechanisms for parasympathetic neurons to secretion o 6uscarinic receptors 4 ;h !inds to 6A receptor on salivary gland ctivates phospholipase ; converts phosphatidylinositol90,59!isphosphate into( IPA F;a"EG opens ;l9 channels ="' secretion into lumen 3="' follo%s ;l9 into lumen5 D G protein 2inase ; protein secretion into lumen o ;otransmitter BIP 3vasoactive intestinal polypeptide5 is released %$ ;h 1' 3nitric oxide5 is released vasodilation of salivary gland !lood vessels Sympathetic Small increase in secretion * volume Secretion is rich in protein * more viscous " receptors used !y sympathetic neurons to secretion( o receptors 3same activity as muscarinic receptor5 fe%er availa!le compared to receptors activates phospolipase ; converts phosphatidylinositol90,59!isphosphate into( IPA F;a"EG opens ;l9 channels ="' secretion into lumen 3="' follo%s ;l9 into lumen5 D G protein 2inase ; protein secretion into lumen 8esults in small secretion 3only "+> of that caused !y parasympathetic stimulation5 o & receptors activates adenylyl cylase c 6P rich protein secretion 'ther factors involved in Salivary Secretion o =ormones Trophic effects =elps maintain salivary glands Does 1'T cause change in rate of flo%
Physiology Exam 5
o o o o
Psychic 3cephalic5 stimulation 3ex( sight & smell5 4 via salivary center in medulla Fright * salivary secretion nxiety * salivary secretion ;ircadian rhythm 6ost secretion occurs in the afternoon Secretion K lo%est levels during sleep 3only L&+ m#5 Seasonal factors 'nly occurs in temperate :ones 3%here it is %arm all year5 =ighest secretion in %inter 4 lo%est in summer 6ay !e due to hydration
Electrolyte & Protein Secretion o cinar ;ell ;l9 & 1aE Secretion Solution is hypertonic as it first is secreted !y acinar cells ;o9transporter moves A 1aE9@ ;lMA DE I1 3electrically neutral5 Pump moves A 1aE 'NT & " DE I1 5 DE lea2 'NT @ ;l9 move thru ion channel 'NT 4 %ater follo%s ;l9 'NT o cinar ;ell =;'A9 Secretion ;'" & ="' 3%hen more active5 =";'A =E E =;'A9 exchanger moves =E 'NT %hile moving 1aE I1 =;'A9 moves thru ;l9 anion channel 3non9selective anion channel5 Due to !icar! ion moving 'NT 4 p= increases as flo% rate increases o Striated Duct 1aE$DE Exchange DE$=E exchanger moves DE 'NT 3into lumen5 & =E I1 3into cell5 1aE is !eing rea!sor!ed I1 3out of lumen5 do%n its concentration gradient thru 1a9selective ion channel o Fluoride ;oncentration is saliva is the same as in plasma ;oncentration is raised !y exogenous sources ;ities in NS put & ppm fluoride in drin2ing %ater ?or2s to sta!ili:e ;a"E in enamel & prevent caries
Physiological Functions of Saliva Taste 4 dissolves particles so the can !ind to taste !uds Digestion o 9amylase 4 dissociates all 9&,0 !onds, cannot !rea2 9&,@ !onds 3K !ranch points5 o lingual lipase 4 not very active under normal conditions S%allo%ing 4 coats oral cavity & esophagus Speech Pathological states 4 ex( fever * in salivary flo% 3can result in fever !listers5 Esophageal secretion 4 mucous secreted into esophagus 4 facilitates movement of !olus
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Obturation of The Root Canal: Capital EndodonticsDocument36 paginiObturation of The Root Canal: Capital EndodonticsnewmexicoomfsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Index Fund Investing 101Document100 paginiIndex Fund Investing 101newmexicoomfs100% (8)
- Metallurgy & File Classification: Capital EndodonticsDocument26 paginiMetallurgy & File Classification: Capital EndodonticsnewmexicoomfsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Locator Root AttachmentDocument8 paginiLocator Root AttachmentnewmexicoomfsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trushape Instrumentation: Capital EndodonticsDocument5 paginiTrushape Instrumentation: Capital EndodonticsnewmexicoomfsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vortex Blue Instrumentation: Capital EndodonticsDocument16 paginiVortex Blue Instrumentation: Capital EndodonticsnewmexicoomfsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Entry Point I Entry Point II Entry Point IIIDocument1 paginăEntry Point I Entry Point II Entry Point IIInewmexicoomfsÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Practice Checklist: Business Office QTY Model # Unit Cost Total Cost Comments EquipmentDocument10 paginiNew Practice Checklist: Business Office QTY Model # Unit Cost Total Cost Comments EquipmentnewmexicoomfsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Valplast PDFDocument4 paginiValplast PDFnewmexicoomfs100% (1)
- Dental SchoolDocument5 paginiDental SchoolnewmexicoomfsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Useful Medications For Oral Conditions: AnalgesicsDocument8 paginiUseful Medications For Oral Conditions: AnalgesicsnewmexicoomfsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monitors at A GlanceDocument8 paginiMonitors at A GlancenewmexicoomfsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Periodontal Reevaluation 2Document11 paginiPeriodontal Reevaluation 2newmexicoomfsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vascular Pathology Vasculitis BasicsDocument6 paginiVascular Pathology Vasculitis BasicsnewmexicoomfsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skin Pathology OutlineDocument4 paginiSkin Pathology OutlinenewmexicoomfsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2015 WREB ClinicalCandidateGuideDocument86 pagini2015 WREB ClinicalCandidateGuidenewmexicoomfsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Musculoskeletal Pathology OutlineDocument4 paginiMusculoskeletal Pathology OutlinenewmexicoomfsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Kuliah 10 Antitiroid 2014Document32 paginiKuliah 10 Antitiroid 2014cccccÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fpfl2 Training Manual CompleteDocument111 paginiFpfl2 Training Manual CompleteLobito Solitario67% (3)
- Thyroid Disease in PregnancyDocument24 paginiThyroid Disease in PregnancyKai XinÎncă nu există evaluări
- ProlactinomasDocument9 paginiProlactinomastvleeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Good HormoneDocument22 paginiGood Hormonemaxwell amponsahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine SystemDocument24 paginiEndocrine Systemapi-290318217Încă nu există evaluări
- Management of Hypothyroidism and Hypothyroxinemia During Pregnancy-AaceDocument8 paginiManagement of Hypothyroidism and Hypothyroxinemia During Pregnancy-Aacegu mailÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Levothyroxine SodiumDocument2 paginiDrug Levothyroxine SodiumSrkocher0% (1)
- Hyperthyroidism CaseDocument52 paginiHyperthyroidism CaseEncee Mian100% (2)
- Nodular Nontoxic GoiterDocument4 paginiNodular Nontoxic GoiterEjay Jacob RicamaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine System Lab WorksheetDocument7 paginiEndocrine System Lab WorksheetedwardÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine SystemDocument3 paginiEndocrine Systemyessii_rahmawatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inserto T3Document2 paginiInserto T3cesiahdez0% (2)
- CRETENISMDocument2 paginiCRETENISMPhilip Gene II MalacasÎncă nu există evaluări
- HipertiroidismDocument131 paginiHipertiroidismElena Borş MorariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sonography of Normal and Abnormal Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands PDFDocument15 paginiSonography of Normal and Abnormal Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands PDFJheyson Javier Barrios PereiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Developmental Biology - Oogenesis (Reviewer)Document2 paginiDevelopmental Biology - Oogenesis (Reviewer)shizuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sex Book Urdu PDFDocument124 paginiSex Book Urdu PDFKhalid Almas71% (7)
- THYROID Nodules PPT June 2013Document56 paginiTHYROID Nodules PPT June 2013GaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- MRI of The Pituitary Gland - Jean-Francois Bonneville, Fabrice Bonneville, Francoise Cattin, Sonia Nagi - 2016 PDFDocument382 paginiMRI of The Pituitary Gland - Jean-Francois Bonneville, Fabrice Bonneville, Francoise Cattin, Sonia Nagi - 2016 PDFoprea82Încă nu există evaluări
- B11.5 Interpreting The Menstrual CycleDocument7 paginiB11.5 Interpreting The Menstrual CycleBenjamin WatsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCN 313 1HDocument4 paginiMCN 313 1HJon EricÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thyroid Function TestsDocument2 paginiThyroid Function TestsBassem HafezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine System Function and AssessmentDocument3 paginiEndocrine System Function and Assessmentbomoore79Încă nu există evaluări
- Sem 4 MCQ Week 4 Jan 2014 CTL McqsDocument15 paginiSem 4 MCQ Week 4 Jan 2014 CTL McqsFlowerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine SystemDocument40 paginiEndocrine SystemTaaka Constance100% (1)
- Endocrine SystemDocument5 paginiEndocrine SystemMelissa630100% (1)
- 1 PPT Endocrine SystemDocument30 pagini1 PPT Endocrine SystemBianca ManimtimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thyroid Disease in PregnancyDocument70 paginiThyroid Disease in PregnancyRajeev Sood100% (1)
- The Wolff-Chaikoff Effect Crying WolfDocument7 paginiThe Wolff-Chaikoff Effect Crying WolfMo'men El-MassryÎncă nu există evaluări