Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Authorization Objects
Încărcat de
rvk386Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Authorization Objects
Încărcat de
rvk386Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
SDN Contribution Authorization Objects A Simple Guide Applies to: Netweaver 2004s Web Application Server SPS7 Summary
This guide is intended to demonstrate how to create and use the Authorization Co ncept in the most simplest of conditions. It is based on the Netweaver Web Appli cation Server, and will utilize a table available in all R/3 systems. Author(s): Glen Spalding Company: gingle Ltd Created on: 24th May 2006 Author Bio There did not appear to be any simple guide and explanation on how to create aut horizations in the most simplest manner. Therefore, I thought I would create thi s basic guide that, I hope, explains the main principles and tasks needed for th e beginner. This Authorization Object method should only be utilized in the most basic of us es. 2006 SAP AG 1 Table of Contents Introduction.................................................................... ..................................................................3 Scenario........................................................................ ...................................................................4 Create Authorization Field...................................................... .........................................................5 Create Authorization Class & Object............................................. ..................................................6 Create Role, Profile & Authorization............................................ ....................................................9 Assign Role to User............................................................. ..........................................................12 Code the Authorization Check.................................................... ...................................................13 Testing......................................................................... ..................................................................14 Copyright....................................................................... .................................................................15 2006 SAP AG 2 Introduction The Authorization Object mechanism is used to inspect the current user s privilege s for specific data selection and activities from within a program. An Object Class contains one or more Authorization Objects. The Authorization Object is where Permitted Activity configurations are performe d against specific fields. E.g. Change (being the activity) the material s text MA KTX (being the specific field), or Read (being the activity) a certain Customer (using Customer Number KUNNR, as the specific field). Before a User can be granted permission by the Authorization Object, the User s Ma ster Record is assigned a Role, which includes a Profile. The Profile contains what is simply called the Authorization and is where the sp ecific data for the Authorization Object s field is assigned to the configured Per mitted Activity. E.g. Allow changes to any Material Text, or read Customers betw een the ranges AA100 & BB999 . Finally the calling of the Authorization Object can me performed in code. User M aster Record Role Authorization Object Object ClassAuthorization Object Authoriz ation Object Role Role Authorization Profile 2006 SAP AG 3 Scenario We will be using table TSTC Transaction Codes, which should exist in any R/3 versi
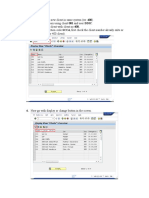
on. The screen shots are taken from the SAP Netweaver 2004s Release 7. We will demonstrate the selection of a record from this table, and due to the pr ivileges revoked from the user, via an Authorization Object, the selection will be denied. We will create a specific Authorization Field for which the check will be made a gainst. Then the Authorization Class and Authorization Object, in which the Field previo usly mentioned is added. A new Role and Profile will contain the actual Authorization for data. The Role will be assigned to the User Master Data. Finally the Authorization Object will be called in Code. 2006 SAP AG 4 Create Authorization Field Transaction SU20 Create a new Authorization Field by clicking on the Create button. Enter ZTCODE and TCODE in the Field Name and Data Element, then Enter. Notice the Use in Authorization Objects area at the bottom of the display. Naturally, as we have just created this Field, it is not yet utilized in any Aut horization Object. Save, a Local Object will suffice. The Field has now been created for use in any Authorization Object. 2006 SAP AG 5 Create Authorization Class & Object Transaction SU21 Create a new Authorization Class (Object Class) by clicking on the Create button s drop down icon, then select Object C description and Save. Authorization Object. Object Class, and performsimilar action to before. Click on the Create buttodrop down, this time selecting AuthorizatioObject . 2006 SAP AG 6 In the Authorization Object s create screen, enter a Name, and description. Under the section Authorization fields enter two Field names. One being ACTVT , this is going to be responsible for the activities that will be permissible, and the other ZTCODE which is the Authorization Field, created earlier. Note: If a suitable Authorization Field already exists, it is possible to re-use it. However, for this example, we are assuming it did not, to give exposure to all necessary tasks involved when dealing with Authorization Objects. Be careful when navigating this screen, as it is a bit buggy. Now press the Permitted activities button, at the bottom of the Create Authorizati on Object screen, to begin configuring what actions can be taken against our new field ZTCODE. Save when prompted. At the next popup, simply press the tick, button to continue. Now we should be at the Define Values for the ACTVT field, where we will select 01, 02, and 03. Save and exit. All out Authorization Objects have now been created. Back out ALL THE WAY and ch eck the creation and configuration in display mode. 2006 SAP AG 7 Having assigned the Authorization Field to the Authorization Object just created . Return back to the Authorization Field SU20, and check that the Field is actua lly assigned. Double click in the ZTCODE Authorization Field line On the next screen in the Use in Authorization Objects section, see the assignment . 2006 SAP AG 8 Create Role, Profile & Authorization Transaction PFCG We now have to create a Role, in which a new Profile will be added, and also an Authorization will be added that is responsible for permitting activities agains
t specific data(fields) in the database the actual authorization. Enter a Role name and press the create Role button, then supply a description an d Save. On the Authorizations tab, in the Maintain Authorization Data and Generate Profil es area, press the Change Authorization Data button. On the next popup screen Choose Template , select the Do not select templates option. 2006 SAP AG 9 We are now in the Authorizations area where we will add specific activities to f ield data. Press the button Manually , ( Ctrl + Shift + F9 ) and enter the Authorization Objec t Z_TCODE created earlier. Select the Tick button to continue. Expand all nodes. Press the edit i Select all thre S No a 2006 SAP AG 10 This current Authorization will permit a Create, C w Generate the Authorization using the generation A w R screen, and notice that we now have a Profile assigned to our Role, in the zatio n Profile area. 2006 SAP AG 11 Assign Role to User Transaction SU01 Note: It is not in scope to explain how to create a user, so either, create a su itable user now, or select an appropriate one, so that the Role can be assigned. Also, make sure the user is able to execute a program in SE38, as this is how t he Authorization will be tested and demonstrated. Choose the User, and in Edit mode, select the Roles tab. Assign the Role recently created, press Enter and Save. Note: If the User is currently logged on, the User will have to log off and on a gain before the new Role assignment can be utilized. 2006 SAP AG 12 Code the Authorization Check Create the program as seen below to test the Authorization. Note the Authorization check with the syntax beginning AUTHORITY-CHECK and the c hecking of the sy-subrc. Also, the 03 literal that is being passed into the Object check field ACTVT which denotes a read , and the p_tcode parameter being passed into the Object check field ZTCODE which represents the actual data, wishing to read . REPORT zauth_check_demo. DATA: wa_tstc TYPE tstc. PARAMETERS: p_tcode TYPE tcode. AUTHORITY-CHECK OBJECT 'Z_TCODE' ID 'ACTVT' FIELD '03' " read access ID 'ZTCODE' FIELD p_tcode. " actual value IF sy-subrc EQ 0. " check authorization * fetch record SELECT SINGLE * FROM tstc INTO wa_tstc WHERE tcode EQ p_tcode. WRITE:/ wa_tstc-tcode, wa_tstc-pgmna, wa_tstc-dypno, wa_tstc-menue,
wa_tstc-cinfo, wa_tstc-arbgb. ELSE. * bad authorization WRITE:/ 'Bad Authorization'. ENDIF. 2006 SAP AG 13 Testing Transaction SE38 with appropriate Test User, that has been given the Role previo usly created. Execute the program above, in this case ZAUTH_CHECK_DEMO. Enter an permitted value and run the program. Result Now enter any other value, and see the difference Result 2006 SAP AG 14 Copyright Copyright 2006 SAP AG. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or for any purpose without the express permission of SAP AG. The information contained herein may be changed without prior notice. Some software products marketed by SAP AG and its distributors contain proprieta ry software components of other software vendors. Microsoft, Windows, Outlook, and PowerPoint are registered trademarks of Microso ft Corporation. IBM, DB2, DB2 Universal Database, OS/2, Parallel Sysplex, MVS/ESA, AIX, S/390, A S/400, OS/390, OS/400, iSeries, pSeries, xSeries, zSeries, z/OS, AFP, Intelligen t Miner, WebSphere, Netfinity, Tivoli, Informix, i5/OS, POWER, POWER5, OpenPower and PowerPC are trademarks or registered trademarks of IBM Corporation. Adobe, the Adobe logo, Acrobat, PostScript, and Reader are either trademarks or registered trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated in the United States and/or other countries. Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation. UNIX, X/Open, OSF/1, and Motif are registered trademarks of the Open Group. Citrix, ICA, Program Neighborhood, MetaFrame, WinFrame, VideoFrame, and MultiWin are trademarks or registered trademarks of Citrix Systems, Inc. HTML, XML, XHTML and W3C are trademarks or registered trademarks of W3C, World Wi de Web Consortium, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Java is a registered trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc. JavaScript is a registered trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc., used under licen se for technology invented and implemented by Netscape. MaxDB is a trademark of MySQL AB, Sweden. SAP, R/3, mySAP, mySAP.com, xApps, xApp, SAP NetWeaver, and other SAP products a nd services mentioned herein as well as their respective logos are trademarks or registered trademarks of SAP AG in Germany and in several other countries all o ver the world. All other product and service names mentioned are the trademarks of their respective companies. Data contained in this document serves informatio nal purposes only. National product specifications may vary. These materials are subject to change without notice. These materials are provid ed by SAP AG and its affiliated companies ("SAP Group") for informational purpos es only, without representation or warranty of any kind, and SAP Group shall not be liable for errors or omissions with respect to the materials. The only warra nties for SAP Group products and services are those that are set forth in the ex press warranty statements accompanying such products and services, if any. Nothi ng herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. These materials are provided as is without a warranty of any kind, either express or implied, including but not limited to, the implied warranties of merchantabil ity, fitness for a particular purpose, or non-infringement. SAP shall not be liable for damages of any kind including without limitation dir ect, special, indirect, or consequential damages that may result from the use of
these materials. SAP does not warrant the accuracy or completeness of the information, text, grap hics, links or other items contained within these materials. SAP has no control over the information that you may access through the use of hot links contained in these materials and does not endorse your use of third party web pages nor pr ovide any warranty whatsoever relating to third party web pages. Any software coding and/or code lines/strings ( Code ) included in this documentatio n are only examples and are not intended to be used in a productive system envir onment. The Code is only intended better explain and visualize the syntax and ph rasing rules of certain coding. SAP does not warrant the correctness and complet eness of the Code given herein, and SAP shall not be liable for errors or damage s caused by the usage of the Code, except if such damages were caused by SAP int entionally or grossly negligent. 2006 SAP AG 15
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- MaxDB Admin DBStudio LCM263 PDFDocument57 paginiMaxDB Admin DBStudio LCM263 PDFrvk386Încă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- SupportDocument1 paginăSupportrvk386Încă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- TcodesDocument3 paginiTcodesrvk386Încă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- SAP NetWeaver 7.4Document1 paginăSAP NetWeaver 7.4rvk386Încă nu există evaluări
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (894)
- TcodesDocument3 paginiTcodesrvk386Încă nu există evaluări
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- SCC4 Client Change OptionsDocument3 paginiSCC4 Client Change Optionsrvk386Încă nu există evaluări
- Sap Maxdb Database Studio Installation: SymptomDocument6 paginiSap Maxdb Database Studio Installation: Symptomrvk386Încă nu există evaluări
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Sap Maxdb Database Studio Installation: SymptomDocument6 paginiSap Maxdb Database Studio Installation: Symptomrvk386Încă nu există evaluări
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Procedure for creating a new client in same system (ex: 400Document6 paginiProcedure for creating a new client in same system (ex: 400rvk386Încă nu există evaluări
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Phases of The Support Package ManagerDocument3 paginiPhases of The Support Package Managerrvk386Încă nu există evaluări
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- Andhrapradesh Telugu Calendar 2015 June PDFDocument1 paginăAndhrapradesh Telugu Calendar 2015 June PDFbvbrahmamÎncă nu există evaluări
- After LifeDocument6 paginiAfter Lifervk386Încă nu există evaluări
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- After LifeDocument6 paginiAfter Lifervk386Încă nu există evaluări
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Early Watch ConfigDocument7 paginiEarly Watch Configrvk386Încă nu există evaluări
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- STORY2Document1 paginăSTORY2rvk386Încă nu există evaluări
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Story 6Document1 paginăStory 6rvk386Încă nu există evaluări
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- What Is An Instance of An SAP System?Document1 paginăWhat Is An Instance of An SAP System?rvk386Încă nu există evaluări
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- Batch Determination PPDocument13 paginiBatch Determination PPrvk386Încă nu există evaluări
- What Is An Instance of An SAP System?Document1 paginăWhat Is An Instance of An SAP System?rvk386Încă nu există evaluări
- RubikDocument45 paginiRubikrvk386Încă nu există evaluări
- Basis TipsDocument9 paginiBasis Tipsrvk386Încă nu există evaluări
- Memory ManagementDocument1 paginăMemory Managementrvk386Încă nu există evaluări
- Basic Sap PPDocument1 paginăBasic Sap PPrvk386Încă nu există evaluări
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Kernel Upgrade ECC6Document8 paginiKernel Upgrade ECC6triminikÎncă nu există evaluări
- REM e T eDocument22 paginiREM e T ervk386Încă nu există evaluări
- Inspection With Material Specification-QMDocument8 paginiInspection With Material Specification-QMrvk3860% (1)
- QM Quality Management Overview FunctionsDocument16 paginiQM Quality Management Overview Functionsrvk386Încă nu există evaluări
- Direct Production Process in SAPDocument26 paginiDirect Production Process in SAPrvk386Încă nu există evaluări
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Production StrategyDocument3 paginiProduction Strategyrvk386Încă nu există evaluări
- SAP HCM Organizational ManagementDocument135 paginiSAP HCM Organizational ManagementVaishnavi MakamÎncă nu există evaluări
- FT C++ PDFDocument123 paginiFT C++ PDFkavyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Object Oriented DesignDocument27 paginiObject Oriented DesignSuman KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual2 UpdatedDocument128 paginiManual2 UpdatedsimÎncă nu există evaluări
- EncapsultaionDocument10 paginiEncapsultaionpriyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Static KeywordDocument2 paginiThe Static Keywordmallikarjun1630Încă nu există evaluări
- Object Oriented Paradigm (Java)Document43 paginiObject Oriented Paradigm (Java)Sivaramakrishna Markandeya GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ibm Websphere Application Server V7 Properties-File-Based ConfigurationDocument25 paginiIbm Websphere Application Server V7 Properties-File-Based ConfigurationmickyscribdÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPP OOPS Module 4Document145 paginiCPP OOPS Module 4Tanisha SinghalÎncă nu există evaluări
- pkcs-15v1 2Document85 paginipkcs-15v1 2Pedro LopesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 189-Oop Java BiyaniDocument28 pagini189-Oop Java BiyaniAnupam MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Ju It Syllabus Pmit 2015Document42 paginiJu It Syllabus Pmit 2015asreetoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CS6502 Unit 5 OOADDocument19 paginiCS6502 Unit 5 OOADUdhaya SankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Workshop on Multimedia and Internet Technologies Content and StructureDocument12 paginiWorkshop on Multimedia and Internet Technologies Content and StructurelesocrateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adobe Print Base FormsDocument74 paginiAdobe Print Base FormsGaurav BansalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Mining NotesDocument21 paginiData Mining NotesaryanÎncă nu există evaluări
- IfDocument38 paginiIfapi-236544093Încă nu există evaluări
- The Visual LISP Developers Bible - 2011 EditionDocument304 paginiThe Visual LISP Developers Bible - 2011 EditionEmanuel Ocampo100% (5)
- Callum Dempsey Leach's CV highlights skills and experienceDocument2 paginiCallum Dempsey Leach's CV highlights skills and experienceM KÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Patterns Elements of Reusable Object-Oriented SoftwareDocument21 paginiDesign Patterns Elements of Reusable Object-Oriented SoftwareSamin YeaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- Object Oriented Programming in DelphiDocument31 paginiObject Oriented Programming in Delphidisist14354Încă nu există evaluări
- Ide PDFDocument402 paginiIde PDFnathan_allgrenÎncă nu există evaluări
- ADO ConnectionDocument3 paginiADO ConnectionMehtaz ShirinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pertemuan 1. Introduction ZA YADocument20 paginiPertemuan 1. Introduction ZA YAMeisyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual B30Document336 paginiManual B30Juan PavezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cognos Impromptu by GopiDocument14 paginiCognos Impromptu by Gopipsaravanan1985Încă nu există evaluări
- OOP Lab Manual - W01Document17 paginiOOP Lab Manual - W01Radish KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- EMPLOYEE'S WORKPROGRESS MANAGEMENT SOFTWAREDocument95 paginiEMPLOYEE'S WORKPROGRESS MANAGEMENT SOFTWAREDrMohamed MustaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adobe Forms - Using AlternativeDocument265 paginiAdobe Forms - Using AlternativeMunnur Pandari100% (1)