Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Basic Nutrition
Încărcat de
gilpogsDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Basic Nutrition
Încărcat de
gilpogsDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
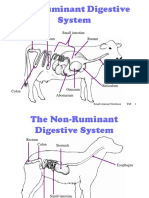
Basic Nutrition Nutrition comes from the latin word Nutrire, means to suckle or feed.
Nutrition- is the study of the food in relation to health of an individual, community or society and the process through which food is used to sustain life and growth. Nutrition- is the science of food the nutrients and other substances therein action, interaction and balance in relation to health and disease, and the process by which an organism ingest, digest, absorbs, transport, utilizes and excretes food substances. Types of Nutrition 1) Autotrophs (self, feed) Photosynthesis (Green plants) Chemosynthesis (Bacteria synthesis organic compounds by oxidising inorganic compounds ammonia) 2) Heterotrophs (cannot synthesise their own food) Holozoic (Herbivours, Carnivours & Omnivours) Saprophytic (Organisms fed on dead / decaying matter Parasitic (Organisms obtains nutrient by living on/ in the body of other living organisms
Food- is any substances organic or inorganic when ingested or eaten nourishes the body by building and repairing tissue supplying heat and energy and regulating body processes. Food- sustain life second to oxygen. Food Quality Ideally, food must have the following qualities. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. It is safe to eat. It is prepared under sanitary conditions, aesthetically and scientifically. It is nourishing or nutritious. Its palatability factors (color, aroma, flavour, texture, etc, etc.) satisfy the consumer. It has satiety value. It offers variety and planned within the socio-economic context, (e.g. within the budget and suitable to the lifestyle of the person, including cultural, religious practices and other aspects) 6. It is free from toxic agents or does not contain substances deemed deleterious to health. Nutrient- a chemical component needed by the body for one or more of these three general functions. 1. To built and repair tissues 2. To regulate life process 3. To provide energy Nutrient- are food chiefly in foods and normal nutrition necessitates the ingestion of nutrients from natural food sources. Some nutrients are manufacture in the body. Nutrient classification According to function 1. Body-Building nutrients- they form tissues or structural components of the body.
include water, protein, fat, carbohydrate and minerals. Water- is most abundant in the body, about 2/3 of body weight. Protein- constitutes about one-fifth or 20% of body weight Minerals- constituents about 4% of the body weight Carbohydrates- amount to less than one pound (about 1/3 kilogram) or 1% Vitamins- are not considered structural nutrients since the total concentration in the body is not even an ounce (less 28 gms.) 2. Regulatory nutrients-they maintain homeostasis of the body fluids and expedite metabolic process. include all the six groups of nutrients. 3. Furnish energy-they are sometimes referred to as the fuel nutrients they are carbohydrate, fat and protein. Water, minerals and vitamins do not yield energy or are non-caloric nutrients According to chemical nature 1. Organic- protein, fat, carbohydrate and vitamins 2. Inorganic- minerals and water According to essentiality/concentration 1. Macronutrients/ Essential-that provide energy and are classified as protein, fats, and CHOs, required for human life. 2. Micronutrients/ Non-Essential- nutrients that the body utilizes but are not required for human life. BALANCE DIET Balance diet: a diet which contains the right amounts of carbohydrate, proteins, fat, vitamins, mineral, water and fibers. Healthy diet: should provide the body with all the substances necessary to maintain growth, to keep good health and repair damage tissue.
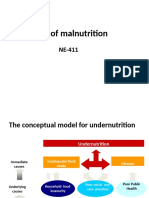
Enzymes- are organic catalysts that are protein in nature and produced by living cells. Hormones- are organic substances produced by special cells of the body which are discharged into the blood to be circulated and brought to specific organs or tissue that are remote from the source or point of manufacture. They regulate vital processes which are highly specific. Nutritional Status (Nurtriture) Categories and Defintions Nutritional status or Nurtriture- is the condition of the body resulting from the utilization of essential nutrients. Optimun or Good Nutrition- means that the body has adequate supply of essential nutrients that are efficiently utilized such that growth and good health are maintained at the highest possible level. Malnutrition- is the opposite of good nutrition. It is a condition of the body resulting from lack one or more essential nutrients (nutritional deficiency) or it may be due to an excessive nutrient supply to the point of creating toxic or harmful effects.
Factors affecting Nutritional Deficiencies 1. Primary factors refers to faulty diet. The nutrient intake is lacking in quality and/or quantity for given individual. Factors that brings faulty diet Poverty Ignorance Poor food Habits Limited supply of due to over population Poor distribution of food Cultural taboos 2. Secondary factors are multiple and include all conditions within the body that reduce the ultimate supply of nutrients to the cells after the food goes beyond the mouth. Factors affecting the normal digestion Gastrointestinal disorder Lack of appetite Poor teeth Lack of digestive enzymes Factors affecting the metabolism and utilization in the cells Liver diseases Malignancy Some drugs Alcoholism Toxins Diabetes mellitus Factors affecting the increase excretion and result in nutrient loss Polyuria Excessive perspiration Certain drugs Methods of evaluating Nutriture 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Dietary surveys Physical methods Anthropometry Clinical examination Biochemical test Functional assessment
Scope of Nutrition as a Science 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Basic/ Fundamental Nutrition Nutrition of Growth and development/ Child and Maternal Nutrition Medical Nutrition therapy Community Nutrition Comparative Nutrition Other areas of specialization
Calorie/Kcalorie- represents the energy measurement of nutrients that the foods provide. A. Protein X4 kcal/gram B. CHOs X4 kcal/gram
C. Fats X9 kcal/gram D. Alcohol x7 kcal/gram Nutrient Density- refers to the concentration of the nutrients in a given amount of food source relative to its caloric content. Considers calories CHO, Fats, protein, vitamins, and water, the higher the nutrients density the greater the nutritional value in a small amount of food. Signs Of Good Nutrition Healthy, shiny looking hair Clean skin and bright eyes A well-developed, healthy body An alert facial expression An even, pleasant disposition Restful sleep patterns Healthy appetite Regular elimination habits Appropriate body weight
Results of Poor Nutrition Hair and eyes appear dull Irregular bowel habits Weight changes Osteoporosis and other diseases Lack of interest - mental slowdown Skin color and appearance poor Anemia leading to: tired feeling shortness of breath increased pulse problems with digestion pale skin poor sleep patterns headaches
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Introduction To Nutrition 1Document4 paginiIntroduction To Nutrition 1Izzah SalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- NUTRITION AND DIET THERAPHY ModuleDocument11 paginiNUTRITION AND DIET THERAPHY ModuleDon Maur ValeteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition FinalDocument3 paginiNutrition Finalcassy SadieÎncă nu există evaluări
- THE Process of DigestionDocument39 paginiTHE Process of DigestionskaiiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic2 - MacronutrientsDocument28 paginiTopic2 - MacronutrientsBea Santos BarrozoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Life CycleDocument30 paginiLife Cycleapi-246570276100% (1)
- 5 Nutrition Care ProcessDocument10 pagini5 Nutrition Care ProcessMilagros ConstantinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition Powerpoint Week 2Document20 paginiNutrition Powerpoint Week 2Shaira Kheil TumolvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutritional AssessmentDocument7 paginiNutritional AssessmentCm MacaliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 7. 2 CHN-FNCPDocument51 paginiWeek 7. 2 CHN-FNCPPatrick Jumao-asÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beginning The Physical Examination: General Survey, Vital Signs, and PainDocument26 paginiBeginning The Physical Examination: General Survey, Vital Signs, and PainDoaa M AllanÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM 105 LEC Finals 1Document17 paginiNCM 105 LEC Finals 1Syed FlyntÎncă nu există evaluări
- Casestudy 1Document6 paginiCasestudy 1api-240055755Încă nu există evaluări
- Diet TherapyDocument82 paginiDiet TherapyElishah CaprichoÎncă nu există evaluări
- LAB Acitvity 1 NUTRITION AND DIET THERAPYDocument2 paginiLAB Acitvity 1 NUTRITION AND DIET THERAPYMarc Fres0% (1)
- Nutri LEC AssignmentDocument3 paginiNutri LEC AssignmentJohnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutri ExamDocument14 paginiNutri ExamVic Intia PaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MNT pt1Document5 paginiMNT pt1api-339312954Încă nu există evaluări
- LIFE CYCLE NUTRITION - Pregnancy and Lactation 2Document63 paginiLIFE CYCLE NUTRITION - Pregnancy and Lactation 2Ruby Ann David-DancelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laboratory No.2Document3 paginiLaboratory No.2Tricia Anne Sernicula RoqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physiologic Value of FoodDocument46 paginiPhysiologic Value of FoodMICHELLE FACTOÎncă nu există evaluări
- NUTRI LAB P1 ExamDocument7 paginiNUTRI LAB P1 ExamAllyza Jane SartigaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition Care ProcessDocument7 paginiNutrition Care ProcessALYSSA NICOLE GINESÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diet Lecture Notes JobertDocument9 paginiDiet Lecture Notes JobertMariel BernabeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Component of Energy ExpenditureDocument14 paginiComponent of Energy ExpenditureAnahgen RomeoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Exam Review NutritionDocument9 paginiFinal Exam Review Nutritionjenm1228Încă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition Guidelines - InsideDocument81 paginiNutrition Guidelines - Insideannaafia69969Încă nu există evaluări
- Notes On Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocument1 paginăNotes On Nutrition and Diet TherapyJaymee0% (1)
- The Changing Nutritional Needs Across The Life CycleDocument24 paginiThe Changing Nutritional Needs Across The Life CycleFrance Dave CantorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Six Essential Nutrients Powerpoint 2022Document10 paginiSix Essential Nutrients Powerpoint 2022Paul HernandezOchoaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Process: Claudette Mcgregor-Coombs, MSN, ArnpDocument63 paginiNursing Process: Claudette Mcgregor-Coombs, MSN, ArnpDanou_Bennett__828Încă nu există evaluări
- NCM101 Collection of Objective Data (Validation of Data)Document50 paginiNCM101 Collection of Objective Data (Validation of Data)Roland100% (1)
- Nutrition and DieteticsDocument3 paginiNutrition and DieteticsAryan RaykarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition Through The Lifespan and Diet and Disease BackupDocument67 paginiNutrition Through The Lifespan and Diet and Disease BackupJessica SnowÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM 105 LEC DISCUSS Tools-NCPDocument36 paginiNCM 105 LEC DISCUSS Tools-NCPPatt100% (1)
- Types of DietDocument2 paginiTypes of DietBhabykhrishÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1zlaboratory ProceduresDocument81 pagini1zlaboratory ProceduresJAYNE NICOLE M. MOTILLA (Warka)100% (1)
- Basics of Therapeutic DietsDocument12 paginiBasics of Therapeutic DietstiruchanurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition Care Process Briefer CP OrientationDocument37 paginiNutrition Care Process Briefer CP OrientationAnni SholihahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition and HIVDocument16 paginiNutrition and HIVShyr R PalmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutritional AssessmentDocument6 paginiNutritional AssessmentReyna Mee AhiyasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Nutrition and Diet Therapy PDFDocument16 paginiIntroduction To Nutrition and Diet Therapy PDFOfficially RandomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition Life CycleDocument24 paginiNutrition Life CycleJada Knights100% (1)
- Nutrition Throughout The LifespanDocument60 paginiNutrition Throughout The LifespanLloyd The UnicornÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mine Rals: Nutrition and Diet Therapy Lecture Notes On Minerals and WaterDocument7 paginiMine Rals: Nutrition and Diet Therapy Lecture Notes On Minerals and Watermildred alidonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition Final Exam QuestionsDocument1 paginăNutrition Final Exam Questionsroboat96Încă nu există evaluări
- WEEK 1 CU1 History of Health EducationDocument5 paginiWEEK 1 CU1 History of Health EducationDaichi100% (1)
- Unit 2 Nutritional Consideration in Infancy and Preschool Years, Educational PlatformDocument51 paginiUnit 2 Nutritional Consideration in Infancy and Preschool Years, Educational Platformzia ullah100% (1)
- c.2 Safety Security and Emergency PreparednessDocument49 paginic.2 Safety Security and Emergency PreparednessSunshine SaraspiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cancer Blood White Blood Cells BlastsDocument6 paginiCancer Blood White Blood Cells BlastsAsif NewazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition ReviewDocument23 paginiNutrition ReviewMonice Robinson Williams0% (2)
- MIDTERMS EXAM-NutriLECDocument9 paginiMIDTERMS EXAM-NutriLECNelia AlfonsoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition - Print - QuestionsDocument4 paginiNutrition - Print - QuestionsSuri BenggauÎncă nu există evaluări
- R E N I: Ecommended Nergy and Utrient Ntakes (2003)Document7 paginiR E N I: Ecommended Nergy and Utrient Ntakes (2003)Christian FarofaldaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study 3Document5 paginiCase Study 3api-644492588Încă nu există evaluări
- Chap 4 QuizDocument19 paginiChap 4 QuizKelly ZhaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH Components of Food AssignmentDocument3 paginiCH Components of Food AssignmentRuma GhoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition - Vitamins Part 2Document29 paginiNutrition - Vitamins Part 2jeshemaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition LecDocument14 paginiNutrition LecCheska jane Morales100% (1)
- Ethical Issues in Nursing Research by GilDocument2 paginiEthical Issues in Nursing Research by GilgilpogsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gathering and The Intelligent Use of Relevant DataDocument6 paginiGathering and The Intelligent Use of Relevant DatagilpogsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Powerpoint by GilDocument34 paginiResearch Powerpoint by GilgilpogsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ethical Isuues by GilDocument12 paginiEthical Isuues by GilgilpogsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Action in An EmergencyDocument6 paginiAction in An EmergencygilpogsÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Aid For PoisoningDocument5 paginiFirst Aid For Poisoninggilpogs100% (1)
- Fluid and Electrolyte TherapyDocument6 paginiFluid and Electrolyte Therapygilpogs100% (1)
- Cervical CancerDocument2 paginiCervical Cancergilpogs0% (1)
- Cleft Lip and PalateDocument20 paginiCleft Lip and Palatejapzee1988100% (1)
- Expended Program For ImmunizationDocument4 paginiExpended Program For ImmunizationgilpogsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Family StructureDocument1 paginăFamily StructuregilpogsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Community Health Nursing ReviewerDocument24 paginiCommunity Health Nursing ReviewergilpogsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Critical ThinkingDocument13 paginiCritical ThinkinggilpogsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 3rd Term Workbook (Class 4)Document32 paginiScience 3rd Term Workbook (Class 4)Masnoon MorshedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Full Download Nutrition From Science To 3rd Edition Blake Solutions ManualDocument36 paginiFull Download Nutrition From Science To 3rd Edition Blake Solutions Manualsteviehiraoz100% (26)
- Ngoh Et AlDocument12 paginiNgoh Et AlLawrence Mundene-timotheeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animal NutritionDocument10 paginiAnimal NutritionshivendraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biochemical and Organoleptic Study of The Mahua Flower and Mahua Flower Wine.Document8 paginiBiochemical and Organoleptic Study of The Mahua Flower and Mahua Flower Wine.IOSRjournalÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is NutritaionDocument24 paginiWhat Is NutritaionMrs RehanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fertilization of Vine by A 5 Aminolevulinic Acid Based Fertilizer and Its Profitability enDocument14 paginiFertilization of Vine by A 5 Aminolevulinic Acid Based Fertilizer and Its Profitability enfaiz hidayatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Read/ Study The Following Definitions and Explanations and Answer The Questions AccordinglyDocument41 paginiRead/ Study The Following Definitions and Explanations and Answer The Questions Accordinglyarsc123Încă nu există evaluări
- Marstall Katalog-English WEBDocument80 paginiMarstall Katalog-English WEBeovidiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Student Karate Manual 2016 PDFDocument55 paginiStudent Karate Manual 2016 PDFCavalera MaxÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Quarter:: Elements and CompoundsDocument11 paginiFirst Quarter:: Elements and CompoundsFrennyÎncă nu există evaluări
- DA AO 26 2007 Guidelines Waste Water Reuse For Irrigation AgricultureDocument37 paginiDA AO 26 2007 Guidelines Waste Water Reuse For Irrigation AgricultureBoni MagtibayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Dietary Modification and Overview of Routine and Therapeutic DietsDocument4 paginiPrinciples of Dietary Modification and Overview of Routine and Therapeutic Dietsmheo2004Încă nu există evaluări
- Health Benefits of Vitamin CDocument5 paginiHealth Benefits of Vitamin CZackÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jhonson ResearchDocument7 paginiJhonson ResearchJohn Charlie CadanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- UTS 101-Module3 v.2Document13 paginiUTS 101-Module3 v.2angel mintsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition Guide - Live Like Louise 1Document17 paginiNutrition Guide - Live Like Louise 1Florina MihailaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GPB 316 Plant Biotechnology (2+1) - Online Study MaterialDocument150 paginiGPB 316 Plant Biotechnology (2+1) - Online Study MaterialadityaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The DR Sebi Diet A Healing Journey 100 - DR Sebi Research CenterDocument159 paginiThe DR Sebi Diet A Healing Journey 100 - DR Sebi Research CenterDEEJAY NERVSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Micronutrient and MacronutrienttsDocument1 paginăMicronutrient and MacronutrienttsSuper heroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition Care ProcessDocument31 paginiNutrition Care ProcessMark Anthony CorpuzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research FinalDocument53 paginiResearch FinalJhon Paul MonesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animal Nutrition Study GuideDocument9 paginiAnimal Nutrition Study Guidebwade2_916499061Încă nu există evaluări
- Unicity Product CatalogDocument32 paginiUnicity Product Catalogwrightellis0% (1)
- Modifiable Risk Factor of Lifestyle DiseaseDocument11 paginiModifiable Risk Factor of Lifestyle DiseaseMae JeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Date Performed: August 18, 2015 Group No. and Section: Group 5 WCDE-A Date Submitted: September 1, 2015 Group MembersDocument28 paginiDate Performed: August 18, 2015 Group No. and Section: Group 5 WCDE-A Date Submitted: September 1, 2015 Group MembersCm MacaliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Science Questions and Answers - Standards MaintainedDocument7 paginiClinical Science Questions and Answers - Standards MaintainedManish JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Big Cunnie Energy Recipe BookDocument51 paginiBig Cunnie Energy Recipe Bookjoelle Fidler100% (1)
- Causes of MalnutritionDocument13 paginiCauses of MalnutritionEman ZahraÎncă nu există evaluări
- MANUSKRIP SKRIPSI - Image.MarkedDocument17 paginiMANUSKRIP SKRIPSI - Image.MarkedTitis Retno Sawitri SawitriÎncă nu există evaluări