Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
MR Sharil Physic 1 Y10
Încărcat de
Dee MohanTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
MR Sharil Physic 1 Y10
Încărcat de
Dee MohanDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
EKHLASS INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL
LOT 4779, Taman Kijal Meraga
24100 Kijal, Kemaman,
Terengganu.
Malaysia
SECOND TERM EXAMINATION 2013
PHYSICS YEAR 10
PAPER 1
DURATION: 1 HOUR 15 MINUTES
Name:
Date :
=====================================================================
=================
DO NOT OPEN THIS QUESTION PAPER UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO
1.
2.
3.
4.
This question paper contains 20 printed pages included front cover.
Answer all questions.
Circle only one answer either A, B, C or D.
This question paper must be submitted as soon as the time is over.
Paper
MARKS
Paper 1
/ 50
Paper 2
/ 140
Carry marks
TOTAL
Percentage and Grade
/ 10
/ 200
PHYSICS YEAR 10
EIS- 2nd TERM EXAM 2013
PAPER 1
_________________________________________________________________________________
SECOND TERM EXAMINATION 2013
PHYSICS YEAR 10 PAPER 1
Answer all questions
1. Read the statements below. Which one gives the correct description of the
e.m.f. of a cell?
a. The difference in energy between that needed to drive a unit charge through
the load resistors and through the cell.
b. The energy used to drive a unit charge through all the resistors in the circuit.
c. The total energy used to drive a unit charge around the complete circuit.
d. The energy used to drive a unit charge through the resistance of the cell.
2. A cell has an e.m.f. of 2.0 V. This means that the cell supplies.
a.
b.
c.
d.
2.0 coulombs of charge per second.
2.0 amperes per second.
2.0 Newtons per coulomb of charge it delivers.
2.0 joules of electrical energy per coulomb of charge it delivers.
3. A battery drives 60 C of charge round a circuit. The total work done is 900 J.
what is the electromotive force of the battery?
a. 0.07 V
c. 700 V
b. 15 V
d. 800 V
_____________________________________________________________________________-
Marks
PHYSICS YEAR 10
EIS- 2nd TERM EXAM 2013
PAPER 1
_________________________________________________________________________________
4. Study the circuit below. Which one can be used to find the resistance of the
lamp?
5. Study the following diagrams. Which one correctly shows the V-I characteristic
graph for a conductor that obeys Ohms law?
6. The four diagrams below show the voltage-current graphs for four electrical
devices. Which of the graphs shows the resistance increasing as the current
increases?
_____________________________________________________________________________-
Marks
PHYSICS YEAR 10
EIS- 2nd TERM EXAM 2013
PAPER 1
_________________________________________________________________________________
7. Figure below shows how the current in the filament of a lamp depends on
the potential difference across it.
Calculate the resistance of the filament when the current is 0.25 A.
a. 35
c. 350
b. 0.25
d. 55
Question 8, 9 and 10 based on the diagram below.
8. Calculate the current l1 flowing through the 4 resistor.
_____________________________________________________________________________-
Marks
PHYSICS YEAR 10
EIS- 2nd TERM EXAM 2013
PAPER 1
_________________________________________________________________________________
a. 2 A
b. 3 A
c. 22 A
d. 33 A
9. Calculate the current l2 flowing through the 2 resistor.
a. 2 A
c. 4 A
b. 3 A
d. 5 A
10. Hence or otherwise, find the ammeter reading.
a. 3 A
c. 5 A
b. 4 A
d. 6 A
11. Figure below shows an electric circuit. How will the readings on the ammeters A 1
and A2 be affected when the switch S is closed?
a.
b.
c.
d.
Reading on A1
Increase
Decrease
Increase
Decrease
Reading on A2
Increase
Increase
Decrease
Decrease
_____________________________________________________________________________-
Marks
PHYSICS YEAR 10
EIS- 2nd TERM EXAM 2013
PAPER 1
_________________________________________________________________________________
12. The circuit in figure below shows two resistors R1, R2 and a lamp L connected to
a 24 V supply with their respective current values in table below. The lamp L has
a resistance of 2.0 . What are the resistances of R 1 and R2?
R1
3
2
1
6
a.
b.
c.
d.
R2
6
4
3
9
13. In the figure below, resistors X and Y act as a potential divider to control the
speed of a motor. What is the reason for using the potential divider?
a.
b.
c.
d.
To vary
To vary
To vary
To vary
the
the
the
the
current through X.
e.m.f. of the battery.
potential difference across the motor.
resistance of the motor.
_____________________________________________________________________________-
Marks
PHYSICS YEAR 10
EIS- 2nd TERM EXAM 2013
PAPER 1
_________________________________________________________________________________
14. Figure below shows a light-dependent resistor (LDR) in a circuit. This circuit can
be used for
a.
b.
c.
d.
Switching on the lamp when daylight begins.
Switching on the lamp when it begins to get dark.
Making the battery charge up in sunlight.
Making the lamp flash on and off.
15. Why is a thermistor useful as an input transducer?
a.
b.
c.
d.
Its resistance
Its resistance
Its resistance
Its resistance
decreases as the light on it increases.
decreases as its temperature increases.
increases as the light on it increases.
increases as its temperature increases.
16. A battery of e.m.f. 3.0 V is connected in series with a 200 resistor and a
thermistor ( figure below ). The graph shows how the resistance of the
thermister varies with temperature.
_____________________________________________________________________________-
Marks
PHYSICS YEAR 10
EIS- 2nd TERM EXAM 2013
PAPER 1
_________________________________________________________________________________
What are the ammeter and voltmeter readings when the temperature of the
thermistor is 300C?
a.
b.
c.
d.
Ammeter reading
0.005 A
0.05 A
0.5 A
0.0005 A
Voltmeter reading
2.0 V
1.0 V
0.5 V
0.1 V
17. In the circuit shown in figure below, a 4700 resistor is connected in series
with a 12 V power supply and a light-dependent resistors (LDR), which has a
resistance of 3300 .
Calculate the current through the LDR and the voltage across the LDR.
a.
b.
c.
Current
0.15 A
0.015 A
0.051 A
Voltage
4.59 V
4.95 V
4.59 V
_____________________________________________________________________________-
Marks
PHYSICS YEAR 10
EIS- 2nd TERM EXAM 2013
PAPER 1
_________________________________________________________________________________
d.
0.0015 A
4.95 V
18. An electric heater uses 60 kJ of electrical energy in five minutes. What is the
power rating of the heater?
a. 720 kW
c. 1.2 kW
b. 12 kW
d. 200 W
Question 19,and 20 based on diagram question 19.
19. The lamps in a house are connected in parallel to the mains supply.
Each lamp is labelled 240 V, 30 W. Calculate the current in one lamp when it is
operating correctly.
a. 0.125 A
c. 0.1 A
b. 0.12 A
d. 125 A
20.State the current from the mains supply when the three lamps are switched on.
a. 0.375 A
c. 0.37 A
b. 0.3 A
d. 375 A
21. Which of the following is the most suitable fuse rating for a 240 V, 3 000 W
electric water heater?
_____________________________________________________________________________-
Marks
PHYSICS YEAR 10
EIS- 2nd TERM EXAM 2013
PAPER 1
_________________________________________________________________________________
a. 3 A
b. 5 A
c. 10 A
d. 13 A
22.The outer casing of an electrical appliance is often earthed. Which of the
following statements is not true?
a.
b.
c.
d.
It
It
It
It
allows current to pass through when the appliance is in use.
prevents the user from getting an electric shock.
allows the current to flow to the earth.
is ineffective if the wire is not connected to the metal casing.
23.Figure below shows a household circuit which consists of an air conditioner ( 200
V, 2 000 W) and lighting circuit (200 V, 400 W) connected in parallel to the 200
V mains supply.
Calculate the total fuse rating can be used in the circuit an above?
a. 10 A
c. 12 A
b. 2 A
d. 12 mA
Question 24 and 25 based on diagram question 24.
24. Figure below shows how the current through the filament of a lamp varies as
the potential difference across it is altered.
_____________________________________________________________________________-
10
Marks
PHYSICS YEAR 10
EIS- 2nd TERM EXAM 2013
PAPER 1
_________________________________________________________________________________
For a potential difference of 12 V across the filament, calculate the resistance
of the filament.
a. 2
c. 6
b. 4
d. 8
25.Calculate the electrical power supplied to it.
a. 12 V
c. 12 W
b. 24 V
d. 24 W
26.Which of the following are magnetic materials?
a. Alloy
c. Copper
b. Brass
d. Wood
27.Which of the following are non-magnetic materials?
a. Cobalt
c. Steel
b. Nickel
d. Plastics
28.It can be deduced that a piece of metal is already a magnet if
_____________________________________________________________________________-
11
Marks
PHYSICS YEAR 10
EIS- 2nd TERM EXAM 2013
PAPER 1
_________________________________________________________________________________
a.
b.
c.
d.
Copper wire is attracted to it.
Both ends of a compass needle are attracted to it.
A magnet is attracted to it.
One end of a compass needle is repelled by it.
29.Which of the following statements describes an example of induced magnetism?
a.
b.
c.
d.
Two North poles repel each other, but a North pole attracts a South pole.
A bar magnet, swinging freely, comes to rest pointing North-South.
A bar magnet loses its magnetism if it is repeatedly dropped.
A bar magnet attracts a piece of soft iron.
30.Figure below shows a magnet picking up a steel needle. The north pole of the
magnet is brought near the centre Y of the needle.
What are the poles induced in the needle at X, Y and Z?
a.
b.
c.
d.
Pole induced at X
N
N
S
S
Pole induced at Y
S
N
S
N
Pole induced at Z
N
N
S
S
31. What are the polarities labelled C, D, E and F of the induced magnets in metals
X and Y in a diagram below.
_____________________________________________________________________________-
12
Marks
PHYSICS YEAR 10
EIS- 2nd TERM EXAM 2013
PAPER 1
_________________________________________________________________________________
a.
b.
c.
d.
C
North
North
North
North
D
South
South
North
North
E
South
North
South
North
F
North
South
South
South
32.A piece of metal can be magnetised by stroking it with a magnet as shown in
figure below. When the magnet moves in the direction indicated, which poles are
produced at X and at Y?
a.
b.
c.
d.
X
North
North
South
South
Y
North
South
North
South
33.Three plotting compasses are placed close to a solenoid carrying a current.
_____________________________________________________________________________-
13
Marks
PHYSICS YEAR 10
EIS- 2nd TERM EXAM 2013
PAPER 1
_________________________________________________________________________________
How many compass needles will stay unchanged if the current through the
solenoid is reversed?
a. 0
c. 2
b. 1
d. 3
34.Figure below shows a round container which has a magnet hidden inside it.
Compasses are placed around the outside and their needles point as shown.
What is the position of the magnet inside the round container?
_____________________________________________________________________________-
14
Marks
PHYSICS YEAR 10
EIS- 2nd TERM EXAM 2013
PAPER 1
_________________________________________________________________________________
35.A magnet was used in an experiment to distinguish between three metal
specimens A, B and C which could be iron, steel or brass. Identify the three
different metal specimens A, B, and C.
a.
b.
c.
d.
Metal A
Brass
Brass
Iron
Iron
Metal B
Iron
Steel
Steel
Brass
Metal C
Steel
Iron
Brass
Steel
36.Figure below shows a locking device. When the current is switched off, the
spring pulls the bar to the right. Which materials should the coil and bar made
from?
a.
b.
c.
d.
Coil
Copper
Copper
Iron
Steel
Bar
Iron
Copper
Copper
Nylon
_____________________________________________________________________________-
15
Marks
PHYSICS YEAR 10
EIS- 2nd TERM EXAM 2013
PAPER 1
_________________________________________________________________________________
37.In figure below, a plug is wrongly wired. It is connected to an old vacuum cleaner
which has a metal case. What will happen when using the plug as wired in figure
below.
a.
b.
c.
d.
The
The
The
The
fuse in the plug would blow.
metal case would be live.
neutral wire would melt.
vacuum cleaner would catch fire.
38.A heater used on a 220 V mains circuit has a 8 A fuse in its plug. Which is the
highest power rating for this heater?
a. 50 W
c. 1 000 W
b. 250 W
d. 1 500 W
39.Figure below shows a circuit with a lamp, variable resistor and battery. The
brightness of the lamp can be adjusted by varying the resistance of the variable
resistor, R. this is because varying the resistance of R changes.
a. The current flowing in the circuit.
_____________________________________________________________________________-
16
Marks
PHYSICS YEAR 10
EIS- 2nd TERM EXAM 2013
PAPER 1
_________________________________________________________________________________
b. The electromotive force (e.m.f.) of the battery.
c. The resistance of the bulb.
d. The temperature of the battery.
Question 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, and 46 based on diagram below.
40.Which of the letters indicates the live terminal?
a. B
b. D
c. A
d. C
41. Which terminal is connected to the earth wire?
a. B
c. A
b. D
d. C
42.What is the colour of wire connected to the neutral terminal?
a. Blue
c. Yellow
b. Brown
d. Green
43.What is the colour of the wire connected to the live terminal?
a. Brown
b. Blue
c. Yellow
d. Green
_____________________________________________________________________________-
17
Marks
PHYSICS YEAR 10
EIS- 2nd TERM EXAM 2013
PAPER 1
_________________________________________________________________________________
44.What is the colour of the wire connected to the earth terminal?
a. Green
c. White
b. Brown
d. Blue
45.What is connected between X and Y?
a. Cord
c. Plug
b. Resistor
d. Fuse
46.Name the part labelled Z?
a. Fuse
c. Plug
b. Cord grip
d. Wire
47.Which are the correct match the poles A and poles B of the first magnet.
a.
b.
c.
d.
Pole A
South
North
North
South
Pole B
South
North
South
North
48.Figures below show the l-V characteristics of ohmic and non-ohmic conductors.
_____________________________________________________________________________-
18
Marks
PHYSICS YEAR 10
EIS- 2nd TERM EXAM 2013
PAPER 1
_________________________________________________________________________________
Which of the graphs below shows conductor of filament lamp in a current
electricity.
a.
b.
c.
d.
49.Figures below show the l-V characteristics of ohmic and non-ohmic conductors.
Which of the graphs below shows conductor of pure metal at constant
temperature in a current electricity.
a.
b.
c.
d.
_____________________________________________________________________________-
19
Marks
PHYSICS YEAR 10
EIS- 2nd TERM EXAM 2013
PAPER 1
_________________________________________________________________________________
50.Figures below show the l-V characteristics of ohmic and non-ohmic conductors.
Which of the graphs below shows conductor of semiconductor diode in current
electricity?
a.
b.
c.
d.
_____________________________________________________________________________-
20
Marks
PHYSICS YEAR 10
EIS- 2nd TERM EXAM 2013
PAPER 1
_________________________________________________________________________________
End of papers
_____________________________________________________________________________-
21
Marks
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Diagrama de Circuito DURABRAND ChinoDocument1 paginăDiagrama de Circuito DURABRAND ChinoArkadium ElectronicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antennas and Radar For Environmental Scientists and EngineersDocument400 paginiAntennas and Radar For Environmental Scientists and EngineersNabil Dakhli100% (1)
- Tender of ResignationDocument1 paginăTender of ResignationDee MohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology TransportationDocument13 paginiBiology TransportationDee MohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Paper 2 N 3Document16 paginiBiology Paper 2 N 3Dee MohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physic 1 Y9Document21 paginiPhysic 1 Y9Dee MohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mini Project: Topic: Design of A Solar Powered Lawn MowerDocument25 paginiMini Project: Topic: Design of A Solar Powered Lawn MowerchituÎncă nu există evaluări
- Question BankDocument7 paginiQuestion BankAvinash ChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3100 Paralleling QST30 Service ManualDocument214 pagini3100 Paralleling QST30 Service ManualVictor Julian Ortiz Porras0% (1)
- Design and Construct A 3 KVA Micro Controller Based Pure Sine Wave Inverter With Controlled OutputDocument70 paginiDesign and Construct A 3 KVA Micro Controller Based Pure Sine Wave Inverter With Controlled OutputMcCurtis Akpojaro100% (1)
- Instrumentation (Chapter 2)Document7 paginiInstrumentation (Chapter 2)Yab TadÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Multi-Functional In-Memory Inference Processor Using A Standard 6T SRAM ArrayDocument14 paginiA Multi-Functional In-Memory Inference Processor Using A Standard 6T SRAM ArrayNavritaBeniwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15KW-18.5KW InverterDocument1 pagină15KW-18.5KW InverterMAROC INVESTISSEMENTÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2N7002K, 2V7002K Small Signal MOSFETDocument7 pagini2N7002K, 2V7002K Small Signal MOSFETsindhu adhiwijayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catalogue SGF Eng PDFDocument8 paginiCatalogue SGF Eng PDFrimce77Încă nu există evaluări
- ListOf PHD Students OngoingDocument5 paginiListOf PHD Students OngoingBiswajit DebnathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coupled Mode Theory of WaveguidesDocument18 paginiCoupled Mode Theory of WaveguidesKartikay5Încă nu există evaluări
- Energies: Design and Implementation of A Low-Power Low-Cost Digital Current-Sink Electronic LoadDocument14 paginiEnergies: Design and Implementation of A Low-Power Low-Cost Digital Current-Sink Electronic LoadciccioÎncă nu există evaluări
- DIAL's RequirementsDocument57 paginiDIAL's RequirementsShaikh Saeed AlamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review of Modern Field Effect Transistor Technologie1Document8 paginiReview of Modern Field Effect Transistor Technologie1G ManÎncă nu există evaluări
- TP of AutomobileDocument20 paginiTP of AutomobileHicham Salahdine100% (1)
- 09 Nov 2017 Catálogos Atlas CopcoDocument52 pagini09 Nov 2017 Catálogos Atlas CopcoAlvaro RJÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oppo Ecno Buds 2Document2 paginiOppo Ecno Buds 2patelsingh638Încă nu există evaluări
- Laboratory Exercise No. 2Document34 paginiLaboratory Exercise No. 2Darren Ezra AliagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Survey & Mitigation: Who We Are & What We DoDocument5 paginiSurvey & Mitigation: Who We Are & What We DorustyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quality Function DeploymentDocument8 paginiQuality Function DeploymentShivangi GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
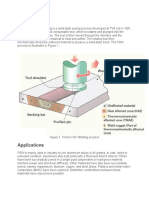
- Figure 1. Friction Stir Welding ProcessDocument4 paginiFigure 1. Friction Stir Welding ProcessINfo WTCSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Turbidimetry: I. PurposeDocument14 paginiTurbidimetry: I. PurposeMiftahul Jannah0% (1)
- EOBDII Fault Code Reader: With CAN Protocol. For Petrol Engines From 2001 Onwards and From 2004 For Diesel EnginesDocument78 paginiEOBDII Fault Code Reader: With CAN Protocol. For Petrol Engines From 2001 Onwards and From 2004 For Diesel EnginesAliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brocade Bottel Neck CMDDocument32 paginiBrocade Bottel Neck CMDragservÎncă nu există evaluări
- Feynman Path-Integral: Andreas ToppDocument80 paginiFeynman Path-Integral: Andreas ToppVigneshwaran KannanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matlab DSPDocument0 paginiMatlab DSPNaim Maktumbi NesaragiÎncă nu există evaluări
- T460 304BDocument56 paginiT460 304BRedbeard RocknRollÎncă nu există evaluări