Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Orifice Sizing Calculation
Încărcat de
jamestppTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Orifice Sizing Calculation
Încărcat de
jamestppDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
No.
DATE
REVISION SHEET NO. ISSUE DATE:
REV.
Citgo Petroleum Corporation 135th Street & New Avenue Lemont, IL 60439
MANUFACTURER: P.O. No.:
INSTRUMENT SPECIFICATION Flange-type Restrictive Orifices
ALL ITEMS SHALL COMPLY WITH GENERAL SPECIFICATION SHEETS
ISSUED:
CHECK:
Installation notes: 1. Orifice dia. As specified to suit required conditions. 2. Gaskets furnished by vendor.
MATERIAL: Monel
REV. QTY. TAG. NO. PIPE SIZE (IN.) SCH. ORIFICE (IN.) FLOW QUANTITY (SCFH) UPSTREAM PRESSURE (PSIG) 60 DP (PSI) M S W G a TEMP. (F) FLANGE RATING ITEM SERVICE
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
20FO-057
###
80
0.084
250
57
17.00
100
300
Pilot gas to acid relief header.
1. The actual flow of 20FO-057 is about 110 SCFH for a bore diameter of 0.084.
1 of 24
204569257.xls.ms_office/Current Flange Spec Sheet_Monel
No. DATE
REVISION SHEET NO. REV. ISSUE DATE:
Citgo Petroleum Corporation 135th Street & New Avenue Lemont, IL 60439
MANUFACTURER: P.O. No.:
Union Restrictive Orifices
ISSUED:
CHECK:
INSTRUMENT SPECIFICATION
ALL ITEMS SHALL COMPLY WITH GENERAL SPECIFICATION SHEETS
MATERIAL: 316SS
ITEM REV. QTY. TAG. NO.
Installation notes: 1. Unless otherwise specified, the only markings on the orifice tab shall be the orfice diameter indicated by a decimal fraction as shown on the drawing with 1/16-in. figure stamping hand dies. 2. Where lines are to be insulated, the insulated material covering the union shall be applied in such a manner that the markings on the tab will be fully exposed. 3. No asbestos-bearing material is acceptable; vendor to provide TFE gaskets.
UPSTREAM PRESSURE (PSIG) 60
PIPE SIZE (IN.)
SCH.
ORIFICE (IN.)
FLOW QUANTITY (SCFH)
DP (PSI)
M S W G a 0.586
TEMP. (F)
FLANGE RATING
SERVICE
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
20FO-184
1-1/2 80
0.285
57
100
3000
Acid pump vent header purge.
1. Item 1 is made of monel.
2 of 24
204569257.xls.ms_office/Current Union Spec Sheet
No. DATE
REVISION SHEET NO. REV. ISSUE DATE:
Citgo Petroleum Corporation 135th Street & New Avenue Lemont, IL 60439
MANUFACTURER: P.O. No.:
INSTRUMENT SPECIFICATION
Flange-type Restrictive Orifices
ISSUED:
CHECK:
ALL ITEMS SHALL COMPLY WITH GENERAL SPECIFICATION SHEETS
Installation notes: 1. Orifice dia. As specified to suit required conditions. 2. Gaskets furnished by vendor.
MATERIAL: 316SS
REV. QTY. TAG. NO. PIPE SIZE (IN.) SCH. ORIFICE (IN.) FLOW QUANTITY (SCFH) UPSTREAM PRESSURE (PSIG) 60 DP (PSI) M S W G 55 a TEMP. (F) FLANGE RATING ITEM SERVICE
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
20FO-175
###
80
0.135
17.00
100
150
Pilot gas to 20F-527.
3 of 24
204569257.xls.ms_office/Current Flange Spec Sh_SS
No. DATE
REVISION SHEET NO. REV. ISSUE DATE:
Citgo Petroleum Corporation 135th Street & New Avenue Lemont, IL 60439
MANUFACTURER: P.O. No.:
Union Restrictive Orifices
ISSUED:
CHECK:
INSTRUMENT SPECIFICATION
ALL ITEMS SHALL COMPLY WITH GENERAL SPECIFICATION SHEETS
MATERIAL: 316SS
ITEM REV. QTY. TAG. NO.
Installation notes: 1. Unless otherwise specified, the only markings on the orifice tab shall be the orfice diameter indicated by a decimal fraction as shown on the drawing with 1/16-in. figure stamping hand dies. 2. Where lines are to be insulated, the insulated material covering the union shall be applied in such a manner that the markings on the tab will be fully exposed. 3. No asbestos-bearing material is acceptable; vendor to provide TFE gaskets.
UPSTREAM PRESSURE (PSIG)
PIPE SIZE (IN.)
SCH.
ORIFICE (IN.)
FLOW QUANTITY (SCFH)
DP (PSI)
M S W G a
TEMP. (F)
FLANGE RATING
SERVICE
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
###
80
100
4 of 24
204569257.xls.ms_office/New Union Spec Sheet
Yellow is an input cell: P1: 60 psig
Green is a calculation: W= 11.12 PPH
Underline is value actually used: Green in grey is a look-up value: 0.603 tp = 2.50 0.607 White in black is a final answer: D2 = 0.106 in. Important reference information about a cell is in violet: From Fluor table Cell for iteration with goal seek: [1st Cell] 4.87 Target (To) cell for goal seek: [2nd Cell] 4.93 Changing cell for goal seek: [3rd Cell] 0.084
ell for goal seek:
No. DATE
REVISION SHEET NO. REV. ISSUE DATE:
Citgo Petroleum Corporation 135th Street & New Avenue Lemont, IL 60439
MANUFACTURER: P.O. No.:
INSTRUMENT SPECIFICATION
Flange-type Restrictive Orifices
ISSUED:
CHECK:
ALL ITEMS SHALL COMPLY WITH GENERAL SPECIFICATION SHEETS
Installation notes: 1. Orifice dia. As specified to suit required conditions. 2. Gaskets furnished by vendor.
MATERIAL: 316SS
REV. QTY. TAG. NO. PIPE SIZE (IN.) SCH. ORIFICE (IN.) FLOW QUANTITY (SCFH) UPSTREAM PRESSURE (PSIG) DP (PSI) M S W G a TEMP. (F) FLANGE RATING ITEM SERVICE
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
###
80
100
7 of 24
204569257.xls.ms_office/New Flange Spec Sheet_SS
No. DATE
REVISION SHEET NO. ISSUE DATE:
REV.
Citgo Petroleum Corporation 135th Street & New Avenue Lemont, IL 60439
MANUFACTURER: P.O. No.:
INSTRUMENT SPECIFICATION Flange-type Restrictive Orifices
ALL ITEMS SHALL COMPLY WITH GENERAL SPECIFICATION SHEETS
ISSUED:
CHECK:
Installation notes: 1. Orifice dia. As specified to suit required conditions. 2. Gaskets furnished by vendor.
MATERIAL: Monel
REV. QTY. TAG. NO. PIPE SIZE (IN.) SCH. ORIFICE (IN.) FLOW QUANTITY (SCFH) UPSTREAM PRESSURE (PSIG) DP (PSI) M S W G a TEMP. (F) FLANGE RATING ITEM SERVICE
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
###
80
100
8 of 24
204569257.xls.ms_office/New Flange Spec Sheet_Monel
Caution: this sheet calculates properties based on yellow-highlighted cells. The viscosities will change and pressure and temperature, however, the NIST values for pure components will change so if T or P change NIST. Gas Properties Vc, cm3/molProperties using coresponding states y Tc, K Pc, atm 1 Zc w Hydrogen 0 33.20 12.80 65.00 0.31 -0.22 Methane 0.94 190.60 45.40 99.00 0.29 0.01 Ethane 0.05 305.40 48.17 148.00 0.29 0.10 Propane 0.01 369.80 41.95 203.00 0.28 0.15 Propylene 0 365.00 45.60 181.00 0.28 0.15 Butane Average, Mixture: 1.0000 198.13 45.65 102.49 0.29 0.01 k=
R, atm-cm^3/(K-gmole): Temperature, F: Pressure, psig.: Viscosity, cP:
Methane Ethane Propane Propylene Butane
8.21E+01 100 311 90 Use initial (1) properties. From VISC Sheet - manual entry-- use NIST website for 0.01151 individual m , then use Wilke's method in spreadsheet to calculate mixture m . m, cP @ 78 psig m, cP @ 90 psig 100 120 100 120 0.011661 0.012008 0.011659 0.012006 0.00986 0.010179 0.009882 0.010201 0.00853 0.008836 0.008547 0.008853 0.009013 0.009347 0.009039 0.009372 0.009254 0.012779
scosities will change and are a function of ange so if T or P change update with Cpo, cal/gmolK 6.91 8.66 12.98 18.30 15.78 8.98 1.28
M 2.02 16.04 30.07 44.10 42.08 17.02
m, cP 0.00919 0.01167 0.00988 0.00855 0.00904
use NIST website for hod in spreadsheet to
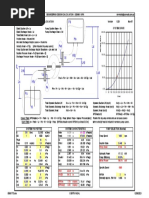
RESTRICTIVE ORIFICE ---- Method 1
Thin plate orifice Low-Moderate DP
Rough method provided originally in an article in Chemical Engineering magazine tb/bore diameter = 0.93 P2/P1 = 0.05 Thin plate, no choked flow. Calculation not applicable: refer to Kirk-Cunningham method.
D1:
P1: D2: P2:
D =
7 X 8
Qg/SQRT( DP(P1 +P2)/(2SgT1) 5440
1/5 X (tp/0.125)
Method assumes, implicitly, that gas is ideal gas mixture or perfect gas. Flow through a thin plate is never choked flow. For this to apply, the ratio of tb/bore diameter must be < 6. (Reference: pg. 13.22, Richard Miller's "Flow Measurement Engineering Handbook," 3rd ed., McGraw Hill, 1996. Page 13-22 refers to the work of Cunningham (1951) and Ward-Smith (1979). Kirk-Cunningham applies when P2<0.63P1. Cunningham showed that choked flow (critical, i.e., M =1 @ throat) does not occur for thin orifice plates.
D, inches; Qg, gas flow in SCFH (60 F, 1 atm); DP, P1, P2, psia; Sg = Mg/Mair T1, R; tp, plate thickness. Qg: DP = P1: P2: Mw: Sg = T: Plate Rate tp = Z: D1, nom: 250 57.00 60 3 17 0.59 100 300 2.50 1.00 2.00 SCFH @ 60 F, 1 atm psig psi Complete Property Sheet Tr = 2.51 from sheet Pr = 0.11
Using initial properties @ P1, T1
Line Size 0.5 0.75 1 1.5 2 3 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 24
tp,mm 1.5 1.5 1.5 2 2.5 3 3 3 6 6 6 9 9 12 12 16
manual allowed deg. F k = 1.28 300, 600# ANSI mm From Fluor table 0.98 Calculated using virial equations in. Sch.: 80 0.749 0.433 0.135 -0.014 psig Test: OK Saturated Area Pr/Tr = 0.044 Abbott Equations are acceptable Z = 1.00
Using table from Fluor specification: "Flange Type Restrictive Orifice"
Sat. Curve Test: Hot Gas Test: B1 = B0 = Pcf = 40.98
Choked Flow - for thick plate
D2 =
0.106 in.
Beta =
0.055
11 of 24
Lemont, Illinois
204569257.xls.ms_office/RO1
RESTRICTIVE ORIFICE ---- Method 2
Thick plate orifice or flow nozzle, Choked Flow psig
tb/db = 7.41 Thick plate method applies: choked flow. Min. Pressure is: 40.98 Choked Flow: eq. 4-40, pg. 100, Daniel Crowl, Joseph Louvar, "Chemical Process Safety Fundamentals with Applications, Prentice-Hall, 1990. P1:
W Co P1 k gc M RT1 X
2 k+1 4-40 Crowl & Louvar assume a thick orifice plate, or flow nozzle, not a thin plate.
A =
(k+1)/(k-1)
Also found in Perry's 6th edition of "Chemical Engineering Handbook," pg. 5-14, equation 5.27. Assumes Beta < 0.2. (Ideal gas also assumed and implicite in solution using isentropic expansion).
A: throat cross-sectional area, sq. ft; W: #/s; Co = 0.72; P1: inlet pressure, psf; gc = 32.174 T1: inlet temperature, F; R = 1545.3 ft-#f/#mole-R. This sheet is most useful in estimating flow from nozzles and holes in vessels or Qg: W= r= D1: P1: Mw: T: A= D= Beta = tp = 250 11.22 0.04 1.939 60 17.02 100 0.004 0.067 0.0348 0.50 SCFH @ 60 F, 1 atm PPH lbs./cf in. psig Property Sheet Pcf = 40.98 deg. F sq. in. in. in. Complete Property Sheet Tr = 2.51 Pr = 0.11 Sat. Curve Test: Hot Gas Test: Test: B1 = B0 = Pr/Tr = psig Choked Flow St. T = Co: 60 14.696 0.72 F psia Crowl/Louvar recommends 1.0 for Co with sharp-edged orifices with Re 1 >30,000; seldom does this occur. Property Sheet
k = 1.28 exp. = 8.03
Using initial properties @ P1, T1 0.749 0.433 OK 0.135 -0.014 0.044 Below: use charts Saturated Area Abbott Equations are acceptable
12 of 24
Lemont, Illinois
204569257.xls.ms_office/RO2
Z = 1.00
13 of 24
Lemont, Illinois
204569257.xls.ms_office/RO2
1/16/2014
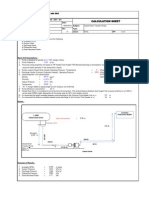
Calculation for North American Mfg. Co. Combustion Air FE
ORIFICE DATA SHEET
Type of Orifice Plate: Drain Hole (for Condensate):
MAXIMUM (URV-Ranged) DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE MAXIMUM FLOW RATE REQUIRED = =
DP (Required ) AT REQUIRED MAX. FLOW RATE = CALCULATED MAXIMUM FLOW RATE (At URV) = PERMANENT PRESSURE LOSS AT MAX. RATE (At URV) = ORIFICE INLET MAX. CALC. REYNOLDS NUMBER = NOMINAL DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE NOMINAL FLOW RATE MINIMUM DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE MINIMUM (Practical) FLOW RATE = = = = =
Standard None 40 10,000 131,510 29.78 11,589 152,400 1.35 37.53 1,050,626 7.45 5,000 65,750 0.30 1,000 13,150 10,000
IWC PPH SCFH IWC PPH SCFH PSIG IWC
Pipe Diameter?
Y-Equation? hw-O.K. Turndown O.K. Y-O.K.
0.895
IWC PPH SCFH IWC PPH SCFH
Orifice Re? Re--tubulent--O.K. Safe Min. Rate? Min.---O.K. Mach No. OK? Gas Orifice velocity is O.K. Change in Physical Properties? Change in properties --O.K
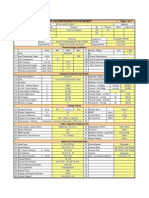
MINIMUM ORIFICE INLET REYNOLDS NUMBER FLUID: INITIAL GAS TEMPERATURE INITIAL GAS PRESSURE GAS SPECIFIC HEAT RATIO, k, GAS VISCOSITY @ FLOW CONDITIONS BASE TEMPERATURE BASE PRESSURE BASE COMPRESSIBILITY FACTOR, Z, NOMINAL PIPE DIAMETER, INCHES PIPE INTERNAL DIAMETER, INCHES = = = = = = = = =
GAS COMPRESSIBILITY COEFFICIENT, Z, =
70 F 30 psig 1.000 1.39817842 0.01634555 cP 60 F 14.696 psig 1.000 24" CS Pipe 23.5 Inches 4.262225274 Inches 0.1814 SS 0.0000097 1/F 0.0000089 1/F -0.94% -4.9 0.126
FLANGE ORIFICE DIAMETER, do, INCHES , = ORIFICE BETA PLATE MATERIAL PLATE BASE THERMAL EXPANSION PLATE THERMAL EXPANSION CHANGE IN GAS DENSITY OVER PLATE CHANGE IN GAS TEMPERATURE = = = = = =
DISCHARGE MACH NO., M=1 IS CRITICAL, =
For Maximum Flow Calculation
C' (PPH) = 274.091 Ftb = 1.003 Fm = 1.000 Fa = 1.000 Flowing conditions were used to calculate the discharge rate of the orifice. K= C' (SCFH) = FG = FTf = 0.5972 3604.474 0.99857 0.9896 Y1 = Fpv = FPb = Fl = 0.9905 1.0000 1.0000 0.9998
D. Willard
International Steel Services, Inc.
204569257.xls.ms_office
This method is more general.
RESTRICTIVE ORIFICE ---- Method 3
Crane TP 410, "Flow of Fluids Through Valves, Fittings, and Pipe," 23rd printing. P2/P1 = 0.016667
Thin plate orifice All flow conditions tb/bore diameter = 0.67 Thin plate, no choked flow.
ASME calculation not practical --- P2/P1 too low ---Kirk-Cunningham method.
D1:
P1: Do: P2:
2 DP r W = 1891 Y C d 0 Equation 2-24, Crane TP 410,
Flow through a thin plate is never choked flow. For this to apply, the ratio of tb/bore diameter must be < 6. (Reference: pg. 13.22, Richard Miller's "Flow Measurement Engineering Handbook," 3rd ed., McGraw Hill, 1996. Page 13-22 refers to the work of Cunningham (1951) and Ward-Smith (1979). In 2005, Kirk explored the limits of Cunningham's work. He found that ASME formulas worked fine with adjustment of Y; C could be defined using ASME and other methods. Kirk-Cunningham applies when P2<0.63P1. Cunningham showed that choked flow (critical, i.e., M =1 @ throat) does not occur for thin orifice plates.
W: lbs./hr; Y: dimensionless; C: 1/ft; do: inches; DP: psi; r: #mass/cf Standard Conditions: P, psia = 14.696 T, F = 60 Complete Property Sheet Qg: 86 r, #/cf = 0.06 DP = 59.00 P1: 60 P2: 1 Mw: 24 r, #/cf = 0.01 T: 120 Plate Rate 300 tp = 1.50 Z: D1, nom: 0.75 mg, cP= 0.01151 DPp = 56 SCFH
@ 14.696 psia & 1 atm.
Flange taps Y= 0.72 Kirk-Cunningham k= 1.28 C, ft-1 = 0.607 0.607 0.607 ASME, Crane 410 Cunningham manual allowed
Tr = 1.43 Pr = 0.11
Using initial properties @ P1, T1
from sheet
psig psi
manual allowed deg. F 300, 600# ANSI mm From Fluor table 0.99 manual allowed in. manual allowed psig PPH PPH psig Wcalc = 5.47 PPH
Sat. Curve Test: 0.749 Test: Hot Gas Test: 0.433 OK Pr/Tr = 0.078 Saturated B1 = 0.100 Area B0 = -0.156 Abbott Equations are acceptable Z = 0.99
Sch.: Re1 =
160 4,874
Wd = 5.44 Match Qg: 4.93 Pcf = 40.98
Problem solved with goal seek 0.088 in. Beta = 0.144
Choked Flow - for thick plate
Do =
15 of 24
Lemont, Illinois
204569257.xls.ms_office/RO3
This method is more general.
RESTRICTIVE ORIFICE ---- Method 4
Crane TP 410, "Flow of Fluids Through Valves, Fittings, and Pipe," 23rd printing. P2/P1 = 0.033333
Thin plate orifice All flow conditions tb/bore diameter = Thin plate, no choked flow.
ASME calculation not practical --- P2/P1 too low ---Kirk-Cunningham method.
P1: D1:
P2: Do: P2:
W =
338.178 rb K d2 Y1 FPb FTb FTf1 FPvGr FGr
Dh Pf1
Adapted from equation 9.68, "The AGA equation," in Richard Miller's Flow Measurement Engineering Handbook, 3rd ed., McGraw Hill , CR 1996 (This equation was adapted originally from equation 2-24, Crane TP 410.)
Flow through a thin plate is never choked flow. For this to apply, the ratio of tb/bore diameter must be < 6. (Reference: pg. 13.22, Richard Miller's "Flow Measurement Engineering Handbook," 3rd ed., McGraw Hill, 1996. Page 13 refers to the work of Cunningham (1951) and Ward-Smith (1979). In 2005, Kirk explored the limits of Cunningham's work. He found that ASME formulas worked fine with adjustment of Y; C could be defined using ASME and other methods. Kirk-Cunningham applies when P2<0.63P1. Cunningham showed that choked flow (critical, i.e., M =1 @ throat) does not occur for thin orifice plates.
Complete Property Sheet W: lbs./hr; Y: dimensionless; C: 1/ft; do: inches; DP: psi; r: #mass/cf Standard Conditions: P, psia = 14.696 T, F = 60
Choose Cunningham ( 1 ),Miller ( 2 ), or Fluor ( 3 ) for Y1:
For (b): 1
Cunningham
Estimated Compressibility Factor (Z) for Base and Inlet Conditions Trb = 1.46 Sat. Curve Test: 0.714 Test: Prb = 0.04 Zb = 0.980 0.980 Hot Gas Test: 0.400 OK Pr/Tr = 0.030 Saturated Area B1 = 0.104 B0 = -0.148 Abbott Equations are acceptable Zf = 0.980 Sat. Curve Test= 0.772 Hot Gas Test= 0.455 Test: OK
Qg: rb, #/cf = DP = P1: P2: Mw: r1, #/cf =
250 0.05 87.0 90 3 17 0.02
SCFH
Flange taps Y1 = 0.66 k= 1.28 0.595 0.607
Cunningham recommended
OK
manual ASME, Crane 410 Cunningham manual allowed
psig psi
C, ft-1 =
For (1):
manual allowed deg. F 300, 600# ANSI mm From Fluor table manual allowed in. manual allowed psig PPH PPH psig Wcalc = Qcalc = 11.31 247 PPH SCFH Do = Problem solved with goal seek 0.054 in.
Tr1 = 1.57 Pr1 = 0.16
T: 100 Plate Rate 300 tp = 2.50 Z1: 0.991 D1, nom: 2.00 mg, cP= 0.01151 DPp = 86
Sch.: Re1 =
80 3,233
Pr/Tr = 0.100 Saturated Area B1 = 0.113 B0 = -0.122 Abbott Equations are acceptable Zf = 0.991
Wd = 11.43 Match Qg: Pcf = 57.43
Choked Flow - for thick plate
Beta =
0.028
16 of 24
Lemont, Illinois
204569257.xls.ms_office/R04
This method is more general.
Thin plate orifice All flow conditions 1.82 Thin plate, no choked flow.
ASME calculation not practical --- P2/P1 too low ---Kirk-Cunningham method.
Flow through a thin plate is never choked flow. For this to apply, the ratio of tb/bore diameter must be < 6. (Reference: pg. 13.22, Richard Miller's "Flow Measurement Engineering Handbook," 3rd ed., McGraw Hill, 1996. Page 13 -22 Smith (1979). In 2005, Kirk explored the limits of Cunningham's work. He found that ASME formulas worked fine with adjustment of Y; C could be defined using ASME and other
. Cunningham showed that choked flow (critical, i.e., M =1 @ throat) does
Estimated Compressibility Factor (Z) for Base and Inlet Conditions
Saturated Area
Abbott Equations are acceptable
Saturated Area Abbott Equations are acceptable
17 of 24
Lemont, Illinois
204569257.xls.ms_office/R04
VISC
GAS
This sheet talks with the Properties Sheet. Enter values in "Yellow." Temperature 38
MIXTURE
VISCOSITY
Manual input values are in "Green."
100 F
Calculated values in "Light Green".
Program assumes that gases are perfect and form an ideal vapor solution. Program will deviate slightly for high pressure (>150 psig & presence of wet gas. Wilke method shows some deviations where molecular weights are significantly different, i.e., Mi>>Mj.
Wilke Gas Mixture Viscosity Calculation for Ideal Gases or Real Gases @ Low-Moderate Pressures hi F i1 F i2 F i3 F i4 F i5 F i6 F i7 M
Component
Hydrogen Methane Ethane Propane Propylene Gas 6 Gas 7 Gas 8 Gas 9 Gas 10
yi 0.00 0.94 0.05 0.01 0.00 1.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 2.00
Man Manual hi
F i8
0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000
F i9
0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000
F i10
0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000
Sum F ij 0.000 1.033 0.689 0.524 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 mm =
Sum yihi 0.000 0.011 0.001 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000
N 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
0.009189 0.011672 0.009882 0.008547 0.009039 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000
0.0117 0.0099 0.0085 -
2.02 16.04 30.07 44.10 42.08 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
0.000 0.000 0.000 0.506 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000
0.000 1.000 0.665 0.506 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000
0.000 1.473 1.000 0.766 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000
0.000 1.899 1.300 1.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000
0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000
0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000
0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000
Total
0.0115
Gas AlCl2 AlCl3 Carbon Dioxide Carbon Monoxide Chlorine Hydrogen Sulfide Nitrogen Oxygen HCl Sulfur Dioxide TiCl4 Water
m = a + b(T) + c(T) +d(T) a b -0.0006 0.00187 0.00628 0.00215 ####### 0.00344 0.00624 0.00177 ####### 0.0071 -0.001
c -7.11E-10 -1.27E-09 -1.70E-09 2.33E-09 -3.40E-10 7.15E-09 -2.71E-09 3.95E-09 -1.44E-09 1.16E-08 -3.84E-09
1.365E-05 2.39E-05 2.16E-05 2.014E-05 2.40E-05 4.28E-05 2.59E-05 2.26E-05 2.12E-05 0.000073 1.97E-05
Mwt. 97.89 133.34 44.009 28.01 70.9 33.068 28.013 31.998 36.461 64.058 189.69 18.015
Cp = a + b(T) + c(T) + d(T) + e(T) + f(T) a b c d e f 9.04015 8.68E-03 ####### 1.72E-09 ####### 0 12.25740 2.40E-02 ####### 4.81E-08 ####### 5.57E-15 6.21415 5.12E-03 ####### 0 0 0 6.42043 8.88E-04 ####### 0 0 0 6.02127 6.56E-03 ####### 3.01E-09 0.00000 0 6.66150 2.85E-03 ####### 0 0 0 6.89500 7.62E-04 ####### 0 0 0 6.44284 1.25E-03 ####### 0 0 0 6.51457 ####### 0 0 0 0 7.11595 5.93E-03 1.08E-06 0 0 0 13.31361 2.92E-02 ####### 1.32E-08 ####### 2.62E-16 7.08976 1.55E-03 0 0 0 0 Cp = a + b(T) + c(T)2 + d(T)3 + e(T)4 + f(T)5 a b c d e #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A
Information Alligned for MBAL & VISC for auto entries. a(m) b (m) c (m) MAT-MATRIX #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A
Mwt #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A
f #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A
D. Willard 1/16/2014
Plant I
RELSIZE.XLS(VISC)
b .v.s. Q for sq.-edged orifice plates
0.120 0.110 0.100 0.090 0.080 b , (bore dia./pipe ID) 0.070 0.060 0.050 0.040 0.030
k = 1.2; M = 30
T1 = 100oF, DP = 87 psig, P1 = 90 psig, Using Cunningham calculation for Y1, as yielding the highest Q. The pressure drop is not "hw;" the drop is the permanent pressure loss.
0.020 0.010 0.000 0 500 1,000 1,500 2,000 2,500 W = Q(PM/RT) = QM/408.67 PPH: pounds per hour Q = W(408.66/M)
k=1.3; M = 17 k = 1.4; M = 2
3,000
3,500
Q, SCFH (60 F, 14.7 psia)
T1 = 100oF, DP = 87 psig, P1 = 90 psig, Using Cunningham ko 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.4 1.4 1.4 1.4 1.4 1.4 1.4 1.4 1.4 Q, SCFH 50 250 500 1,000 1,500 2,000 3,000 4,000 5,000 50 250 500 1,000 1,500 2,000 3,000 4,000 5,000 50 250 500 1,000 1,500 2,000 3,000 4,000 5,000 b, 2" 0.0144 0.0322 0.0455 0.0643 0.0788 0.0910 0.1114 0.1298 0.1451 0.0126 0.0281 0.0397 0.0561 0.0688 0.0794 0.0973 0.1317 0.1472 0.0072 0.0163 0.0230 0.0325 0.0398 0.0460 0.0563 0.0660 0.0737 b, 1" 0.0144 0.0322 0.0455 0.0643 0.0788 0.0910 0.1114 0.1298 0.1451 0.0126 0.0281 0.0397 0.0561 0.0688 0.0794 0.0973 0.1317 0.1472 0.0072 0.0163 0.0230 0.0325 0.0398 0.0460 0.0563 0.0660 0.0737 M 30
17 0.0279
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Citgo Petroleum Corporation Orifice Specification SheetsDocument25 paginiCitgo Petroleum Corporation Orifice Specification SheetseshraghianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Orifice Calc: LiquidDocument1 paginăOrifice Calc: LiquidJames R. Lawrence Sr.100% (2)
- Valve Sizing CalculationDocument10 paginiValve Sizing CalculationJayesh Chandran100% (1)
- Valve SizingDocument6 paginiValve Sizingcarlosiq37Încă nu există evaluări
- Pressure Drop and Pipeline Flow CalculatorDocument1 paginăPressure Drop and Pipeline Flow CalculatorgrabettyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pipe Size CalcDocument19 paginiPipe Size Calcnitin_bir100% (1)
- PSV SizingDocument6 paginiPSV SizingBui Khoi Nguyen100% (1)
- Control Valve Sizing - LiquidDocument4 paginiControl Valve Sizing - Liquidbrazili2010100% (1)
- Orifice Plate CalculationDocument10 paginiOrifice Plate CalculationkswaghmareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Orifice CalculationsDocument4 paginiOrifice CalculationsTsouki TsoukiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPF-010 Process Line Sizing Attachment - 0Document38 paginiCPF-010 Process Line Sizing Attachment - 0goodspeed_ph100% (1)
- Orifice Calc: GasDocument4 paginiOrifice Calc: GasJames R. Lawrence Sr.100% (6)
- Line Sizing ProgramDocument14 paginiLine Sizing ProgramYakubuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pipe Sizing Calculation DumaiDocument39 paginiPipe Sizing Calculation DumaiKemas Muhandis M.100% (3)
- Calculate Flow Rate From Differential PressureDocument27 paginiCalculate Flow Rate From Differential PressureThang Hoang Anh100% (1)
- Restrictive Orifice - Method 1: Rough Method Provided Originally in An Article in Chemical Engineering MagazineDocument1 paginăRestrictive Orifice - Method 1: Rough Method Provided Originally in An Article in Chemical Engineering MagazinealvinchuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- OrificeDocument13 paginiOrificexjaf01Încă nu există evaluări
- Pressure Drop Caln - 1Document390 paginiPressure Drop Caln - 1Prashant SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control Valve CalcDocument7 paginiControl Valve Calcartneves100% (1)
- Orifice SizingDocument1 paginăOrifice SizingMarco D'OnofrioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blowdown of A Gas VolumeDocument41 paginiBlowdown of A Gas VolumeJames R. Lawrence Sr.20% (5)
- Weymouth Gas Flow CalculationsDocument44 paginiWeymouth Gas Flow CalculationsPierre GermaineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculation of Orifice CoefficientDocument18 paginiCalculation of Orifice Coefficientvinayjoshi270586Încă nu există evaluări
- Gas Line Pressure LossesDocument4 paginiGas Line Pressure Lossesyash saragiyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Orifice Plate Calculator Pressure Drop CalculationsDocument4 paginiOrifice Plate Calculator Pressure Drop CalculationsAnderson Pioner100% (1)
- Air Receiver SizingDocument4 paginiAir Receiver SizingAnonymous a4Jwz14WÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pipe Heat Loss CalculationDocument10 paginiPipe Heat Loss Calculationingemarquintero67% (3)
- Compressed Air PipingDocument3 paginiCompressed Air PipingManoranjan Kumar Choudhary100% (1)
- Engineering Design Calculation - Dennis Kirk Single Stage Centrifugal Pump Calculation (Clean Water Use) System CurveDocument1 paginăEngineering Design Calculation - Dennis Kirk Single Stage Centrifugal Pump Calculation (Clean Water Use) System Curvebuntimehta007Încă nu există evaluări
- PUMP SIZING SPREADSHEET FOR KEROSENE TRANSFERDocument30 paginiPUMP SIZING SPREADSHEET FOR KEROSENE TRANSFEREbby Onyekwe100% (1)
- Pipe Sizing CalculationsDocument8 paginiPipe Sizing CalculationsRajat SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CALCULATION Characteristic Pump2Document16 paginiCALCULATION Characteristic Pump2Ahlan Haryo PambudiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Line SizingDocument18 paginiLine SizingNathaniel Thomas100% (1)
- Info Calculation Pipe Line SizingDocument8 paginiInfo Calculation Pipe Line Sizingrasnowmah2012Încă nu există evaluări
- Calculation Acc. To Calame A. Hengst: Only For Gases Only For Low Pressure Regulator ZM-R, ZM-B and LPR, LPSDocument6 paginiCalculation Acc. To Calame A. Hengst: Only For Gases Only For Low Pressure Regulator ZM-R, ZM-B and LPR, LPSkarthipetro100% (2)
- Restriction Orifice Calculation SheetDocument2 paginiRestriction Orifice Calculation Sheetparykoochak50% (2)
- PIPE SIZING CALCULATIONSDocument17 paginiPIPE SIZING CALCULATIONSJaykumar100% (6)
- Liquid Orifice SizingDocument4 paginiLiquid Orifice SizingrmaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pressure Drop Calculation Equations For PIPING and PIPELINEDocument3 paginiPressure Drop Calculation Equations For PIPING and PIPELINETiano BaLajadia100% (4)
- Siemens Valve SizingDocument32 paginiSiemens Valve SizingSteven Wei100% (2)
- AGA Gas CalculationDocument5 paginiAGA Gas CalculationgopaltryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volume3A MechDocument321 paginiVolume3A MechAdeel JamilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hookup LibraryDocument221 paginiHookup Librarykapilarora123100% (6)
- 145B9973 - Off Base Piping List of Lines PDFDocument4 pagini145B9973 - Off Base Piping List of Lines PDFHumayun NawazÎncă nu există evaluări
- CW Pump CalculationDocument22 paginiCW Pump Calculationzamijaka100% (1)
- APNEA-J-DSH-0002 Rev. 1Document3 paginiAPNEA-J-DSH-0002 Rev. 1Michelle MartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optimize for gas separator test skid control valve documentDocument1 paginăOptimize for gas separator test skid control valve documentelias2505Încă nu există evaluări
- Si 83 - ENDocument52 paginiSi 83 - ENBabis PapadopoulosÎncă nu există evaluări
- PSV Sizing Psv-414 UpdateDocument7 paginiPSV Sizing Psv-414 UpdateBui Khoi NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inputs From Client: 1. bfp132401 1 0 (G.A. Drawing For SWS Gas KO Drum)Document3 paginiInputs From Client: 1. bfp132401 1 0 (G.A. Drawing For SWS Gas KO Drum)SIVAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steam Pressure DropDocument8 paginiSteam Pressure DropDavid Muñoz CastroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air Cooler - DesignDocument7 paginiAir Cooler - Designkarthipetro100% (1)
- RNZ Integrated (M) SDN BHD: Calculation SheetDocument14 paginiRNZ Integrated (M) SDN BHD: Calculation SheetNhantran VanÎncă nu există evaluări
- FO14-104 Vacuum Deaerator Datasheet - Rev ADocument3 paginiFO14-104 Vacuum Deaerator Datasheet - Rev AHuzefa Calcuttawala100% (2)
- Typical Flare PackageDocument5 paginiTypical Flare PackageRahmat RiskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- PSV Sizing Psv-402 Update PsetDocument7 paginiPSV Sizing Psv-402 Update PsetBui Khoi NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- JIS G3464 Steel Heat Exchanger TubesDocument14 paginiJIS G3464 Steel Heat Exchanger TubeshbookÎncă nu există evaluări
- Memorial PSVDocument1 paginăMemorial PSVRicardo TsuyamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 13205-PPE-DS-V-003-1 - DataSheet - CVDocument7 pagini13205-PPE-DS-V-003-1 - DataSheet - CVAnggun RushÎncă nu există evaluări
- ORF1Document25 paginiORF1Mokez JittasopawadeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Real Time Optimization With Multivariable Control Is Required To Maximize ProfitsDocument5 paginiReal Time Optimization With Multivariable Control Is Required To Maximize ProfitsjamestppÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multi-Variable Predictive Controller For Bauxite MillingDocument4 paginiMulti-Variable Predictive Controller For Bauxite MillingjamestppÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aspen Manufacturing Suite Advanced Process Control: Release NotesDocument35 paginiAspen Manufacturing Suite Advanced Process Control: Release NotesjamestppÎncă nu există evaluări
- OPC and DCOM Configuration - Windows Server 2008Document24 paginiOPC and DCOM Configuration - Windows Server 2008jamestppÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handbook of Commercial Catalysts: Heterogeneous Catalysts: by Howard F. Rase Pag 462 and 463Document1 paginăHandbook of Commercial Catalysts: Heterogeneous Catalysts: by Howard F. Rase Pag 462 and 463jamestppÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solving first order linear differential equationsDocument2 paginiSolving first order linear differential equationsjamestppÎncă nu există evaluări
- IsoclinesDocument2 paginiIsoclinesErnani LezierÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conda Cheatsheet PDFDocument2 paginiConda Cheatsheet PDFDeeptiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simulacao Dinamica e o Engenheiro de ProcessosDocument16 paginiSimulacao Dinamica e o Engenheiro de ProcessosAlancássio EulálioÎncă nu există evaluări
- MPC AspenDocument4 paginiMPC AspenjamestppÎncă nu există evaluări
- EXASOCDocument7 paginiEXASOCjamestppÎncă nu există evaluări
- Decentralized Model Predictive Control of Cooperating Uavs: Arthur Richards and Jonathan HowDocument6 paginiDecentralized Model Predictive Control of Cooperating Uavs: Arthur Richards and Jonathan HowjamestppÎncă nu există evaluări
- MPC Aspen PDFDocument5 paginiMPC Aspen PDFjamestppÎncă nu există evaluări
- Source - DCOM Event ID - 10021 (Windows Operating System 5Document1 paginăSource - DCOM Event ID - 10021 (Windows Operating System 5jamestppÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To ODEDocument1 paginăIntroduction To ODEjamestppÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handbook of Commercial Catalysts: Heterogeneous Catalysts: by Howard F. Rase Pag 462 and 463Document1 paginăHandbook of Commercial Catalysts: Heterogeneous Catalysts: by Howard F. Rase Pag 462 and 463jamestppÎncă nu există evaluări
- Decentralized Model Predictive Control of Cooperating Uavs: Arthur Richards and Jonathan HowDocument6 paginiDecentralized Model Predictive Control of Cooperating Uavs: Arthur Richards and Jonathan HowjamestppÎncă nu există evaluări
- Decentralized Model Predictive Control of Cooperating Uavs: Arthur Richards and Jonathan HowDocument6 paginiDecentralized Model Predictive Control of Cooperating Uavs: Arthur Richards and Jonathan HowjamestppÎncă nu există evaluări
- AmmoniaDocument17 paginiAmmoniajamestppÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aspen InfoPlus.21 Mobile V7.3Document8 paginiAspen InfoPlus.21 Mobile V7.3jamestppÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comp Gas Flow FormulaDocument10 paginiComp Gas Flow FormulajamestppÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exchanger Selection & Design in An LPG Recovery UnitDocument27 paginiExchanger Selection & Design in An LPG Recovery UnitjamestppÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reduce Gas Entrainment in Pipe FlowDocument3 paginiReduce Gas Entrainment in Pipe FlowjamestppÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vapor Phase Pressure Drop MethodsDocument32 paginiVapor Phase Pressure Drop MethodsjamestppÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control Structure Design For Complete Chemical PlantsDocument16 paginiControl Structure Design For Complete Chemical PlantsjamestppÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slurry Line SizingDocument147 paginiSlurry Line Sizingjamestpp0% (1)
- Solving Vessel EquationsDocument5 paginiSolving Vessel EquationsjamestppÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tecnicas para Cartas de Amor U OdioDocument4 paginiTecnicas para Cartas de Amor U OdioChristian Gabriel Stampacchio100% (16)
- Sizing Air ReceiverDocument3 paginiSizing Air ReceiverAnkon Mukherjee100% (3)
- CH 12Document29 paginiCH 12Aljebre MohmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 20160969Document7 pagini20160969Dr.AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- DPR1Document286 paginiDPR1Tenders TGSPLÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHEMCAD reactor design tutorialDocument4 paginiCHEMCAD reactor design tutorialErich EscobarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deep Shaft ProcessDocument12 paginiDeep Shaft ProcessDevendra Sharma100% (1)
- Az Proced e Distillation Report 157Document3 paginiAz Proced e Distillation Report 157Crezl MontebonÎncă nu există evaluări
- ThermoMax Steam Systems BrochureDocument4 paginiThermoMax Steam Systems Brochureandersonmipa12Încă nu există evaluări
- FlowMeasurement OilGasIndustryThapa16Document34 paginiFlowMeasurement OilGasIndustryThapa16tsiftiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 10Document63 paginiChapter 10Hosam Abd Elkhalek100% (1)
- A New Automotive Air Conditioning System Simulation Tool Developed in MATLAB/SimulinkDocument15 paginiA New Automotive Air Conditioning System Simulation Tool Developed in MATLAB/SimulinkPrashant IngaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Journal BearingsDocument45 paginiDesign of Journal BearingsVELMURUGAN MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Methods of Measurement and Estimation of Discharges at Hydraulic StructuresDocument46 paginiMethods of Measurement and Estimation of Discharges at Hydraulic StructuresJea Escabal MosenabreÎncă nu există evaluări
- EXPERIMENT and Latest EquipmentDocument10 paginiEXPERIMENT and Latest EquipmentMaria Cecille Sarmiento GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CIVE 4307 Tutorial #2 2021 SolnDocument4 paginiCIVE 4307 Tutorial #2 2021 Solnrizwan ghafoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Listado de Partes Bomba FLOMAX 30 Mesas de CargaDocument1 paginăListado de Partes Bomba FLOMAX 30 Mesas de CargaLibardo GonzalezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preguntas Norma API 675Document3 paginiPreguntas Norma API 675Diego Rodriguez0% (1)
- 248 CMR - Ma PlumbingDocument136 pagini248 CMR - Ma PlumbingSalvatore Canciello100% (1)
- HRSG Valve Tag AuditDocument66 paginiHRSG Valve Tag AuditKasthuri CoimbatoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- GT Load Effect On HRSGDocument3 paginiGT Load Effect On HRSGsatishchemeng100% (1)
- International Journal of Mechanical Sciences: G. Paniagua, M.C. Iorio, N. Vinha, J. SousaDocument13 paginiInternational Journal of Mechanical Sciences: G. Paniagua, M.C. Iorio, N. Vinha, J. SousaDEEPESH KUMARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Master Plumbing Reviewer 2Document24 paginiMaster Plumbing Reviewer 2mcpayodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Separator SizingDocument11 paginiSeparator Sizingmusaveer50% (2)
- Curva Bomba 3K8X6-16 ARV M3ST Con 100Hp Imp. 13.0 inDocument5 paginiCurva Bomba 3K8X6-16 ARV M3ST Con 100Hp Imp. 13.0 ineduinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air Fin Cooler Optimisation For Offshore & Onshore Application PDFDocument3 paginiAir Fin Cooler Optimisation For Offshore & Onshore Application PDFDHAVAL PANCHALÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beneficiation of Rungta SlimeDocument32 paginiBeneficiation of Rungta SlimesssadangiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air-side heat transfer and pressure drop analysis of spiral wire-on-tube condensersDocument13 paginiAir-side heat transfer and pressure drop analysis of spiral wire-on-tube condensersAndresInforBJÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wastewater Treatment Plant Design in Metehara Sugar FactoryDocument91 paginiWastewater Treatment Plant Design in Metehara Sugar FactoryTeddy Ekubay GÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fuel Valve Test Device Model: Vtu-1100nDocument11 paginiFuel Valve Test Device Model: Vtu-1100njohn smith75% (4)
- Air Fin Cooler CatalougeDocument14 paginiAir Fin Cooler Catalougesammar_10Încă nu există evaluări
- CHE463 Heat TransferDocument2 paginiCHE463 Heat TransferEitrah Tasnim Mohamat KasimÎncă nu există evaluări