Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Cogeneration Power Plant
Încărcat de
Ganvendra Singh ChaharDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Cogeneration Power Plant
Încărcat de
Ganvendra Singh ChaharDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Assignment 5
Cogeneration System
10/18/2013 MEL342 Ganvendra Singh Chahar Ujjawal Gupta Dhruv Jain Deependra Mehlawat
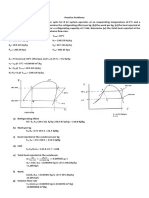
Schematic
Assumptions
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. SSSF process. Make-up water added in the hot well is at ambient conditions (T = 40 oC). The steam extracted in the gland seal extraction is minimal and neglected. Piping and frictional losses are minimal. The condenser is ideal and cools down the water to saturated liquid level at condenser pressure.
Heat balance for turbine:
Inlet of Turbine At first extraction At second extraction At third extraction At exit from other processes
Enthalpy Mass flow (kJ/kg) rate (kg/s) 3272 2826.6 6.67 2810.9 10 2748.67 5.56 2568.64 5.56
Energy produced from steam expansion from the three extractions = = 6.67 (3272 - 2826.6) + 10 (3272 - 2810.9) + 5.56 (3272 - 2748.67) + 5.56 (3272 - 2568.64) = 14.402 MW Total energy requirement = 23 MW => Mass flow rate at the exit of turbine: = (23 - 14.402 ) / (3272 - 2568.64) = 12.22 kg/s => Total inlet mass flow rate = 40.01 kg/s
Heat balance for Extraction 1:
It's an open ended system and all the inlet flow is lost in the process A. Mass flow rate = 6.67 kg/s Enthalpy = 2828.6 kJ/kg 1 = 18.87 MW
Heat balance for extraction 2:
Inlet flow rate = 10 kg/s h1 = 2810.9 kJ/kg Outlet flow recovered = 5 kg/s h2 = 798.64kJ/kg 2 = 24.11 MW
Heat balance for extraction 3:
Inlet mass flow rate = 5.56 kg/s Outlet mass flow rate = 5.56 kg/s h1 = 2748.67 kJ/kg h2 = 640.21 kJ/kg 3 = 11.72 MW
Typical COP of a VAM = 0.6 to 0.7 Taking COP of VAM = 0.65 (say) COP = Heat load in evaporator / Heat input in generator Heat input in generator = 11.72 MW Maximum capacity for refrigeration system = 7.618 MW
Make-up water requirement:
Total Inlet mass flow to the turbine = 40.01 kg/s => Total flow recovered at the inlet of condenser = 5 + 5.56 + 2.78 + 12.22 = 25.56 kg/s => Make-up water = 40.01 - 25.56 = 14.45 kg/s
Mass balance for Condenser:
Mass flow (Kg/s) Flow from Extraction 2 Flow from VAM Flow from Turbine exit Flow from sec. processes Make up water Outlet mass flow rate = 40.01 kg/s 5 5.56 12.22 2.78 14.45 Enthalpy (kJ/kg) 798.33 640.09 2568.3 417.5 167.62
Heat balance for deaerator:
Inlet Mass from CEP= 40.01 kg/s Inlet Mass from extraction 2 = 1.53 kg/s Outlet Mass From the deaerator = 41.54 kg/s Enthalpy= 417.94 kJ/kg Enthalpy= 2748.1 kJ/kg Enthalpy= 504.02 kJ/kg
Efficiency of Cogeneration power plant:
= (out + 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 - BFP) / heat input in boiler out = 23.80 MW 1 = 18.87 MW 2 = 24.11 MW 3 = 11.72 MW 4 = 13.11 MW BFP = 0.33 MW Heat Input in boiler = 114.706 MW = 80.15 % (j) To meet the required power output from turbine, the fluctuations in mass flow rate in various other systems will be accounted in the outlet mass flow rate of turbine which directly goes into condenser. The Governing system of the turbine will regulate the output mass flow rate to the condenser as per the situation and hence will maintain the balance.
Carbon Footprint calculation:
Heat requirement as per system in 5.1 = 114.4 MJ/s Calorific value of natural gas = 43000 kJ/m3 CO2 emissions of natural gas = 3142 kg/tonne Density of natural gas = 0.717 kg/m3
=>
CO2 emissions per hour = 20837.56 kg
For the alternative system: Vapour compression refrigeration: Refrigeration Effect = 7.618 MW Efficiency of the cycle = 0.65 Power taken from grid = 11.72 MW DG Set: Power produced = 23 + 11.72 = 34.72 MW Diesel Consumption for 1MW power generation = 250 l/h Diesel consumption = 8680 l/h Boiler: Energy required to meet the steam requirement = 215.488 * 10^6 kJ/h Density of diesel = 0.832 kg/l Diesel Consumption = 5781.25 l/h Total Diesel Consumption = 14461.25 l/h CO2 emissions of diesel = 2.68 kg/l => CO2 emissions per hour = 38756.15 kg
The carbon footprint for the alternate system is roughly 2 times that of the system of cogeneration. Thus, it can be seen co-generation leads to a much cleaner was of energy production.
References:
1) COP of a VAM machine, Website: <http://www.cibse.org/content/documents/Groups/CHP/Datasheet%207%20%20Absorption%20Cooling.pdf> 15-Oct-13, 8:15 pm 2)Carbon footprint calculation. Website: http://people.exeter.ac.uk/TWDavies/energy_conversion/Calculation%20of%20CO2%20emissions%20fr om%20fuels.htm Date: 15 August 2013 Time: 5:30pm 3)Natural gas Calorific Value. Website: http://www.marcopower.com/fuel.html Date: 16 August 2013 Time: 11:30am 4)Properties of fuel. Website: http://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/gas-density-d_158.html Date: 16 August 2013 Time: 6:00pm
Engineering Packages used:
1) TKSolver 2) EDraw CAD software
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Noo Xii Ch01 Solid StateDocument51 paginiNoo Xii Ch01 Solid StateG boiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Project FinalDocument18 paginiPhysics Project Finalatharvatanksale25% (4)
- Energy BalanceDocument11 paginiEnergy BalanceBharat VaajÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1Document6 pagini1Jake ArbutanteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formulas RefrigerationDocument2 paginiFormulas RefrigerationZac Ryan CasteloÎncă nu există evaluări
- SUMMARY: This Experiment Demonstrates A Rankine Cycle by Use of A Model SteamDocument9 paginiSUMMARY: This Experiment Demonstrates A Rankine Cycle by Use of A Model SteamCharlotte BÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applications of Infrared SpectrometryDocument32 paginiApplications of Infrared SpectrometryNgurah MahasviraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solved Multiple Choice Questions IE by NKB - PDF 116788864Document15 paginiSolved Multiple Choice Questions IE by NKB - PDF 116788864Pranav SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mass and Energy BalanceDocument15 paginiMass and Energy BalanceSam Low83% (6)
- HW 5 SolnDocument7 paginiHW 5 SolnNik Hafiy HafiziÎncă nu există evaluări
- OTECDocument6 paginiOTECibong tiriritÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sepinov™ Emt 10: New "2-In-1" Powder PolymerDocument31 paginiSepinov™ Emt 10: New "2-In-1" Powder Polymerrafaeldelperu1982Încă nu există evaluări
- 27 36 and 84 87Document34 pagini27 36 and 84 87Aub EnriquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refrigeration ProblemsDocument7 paginiRefrigeration ProblemsAkash Bhange100% (1)
- Evap Cond F F G G Sat SatDocument17 paginiEvap Cond F F G G Sat SatAlexis CarpenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chem 31 NotesDocument4 paginiChem 31 NotesEvernim OmpacanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steam Power Board ProblemsDocument6 paginiSteam Power Board ProblemsCaguioa Mark Anthony G.100% (4)
- Heat BalanceDocument18 paginiHeat BalanceVinish Shankar100% (1)
- Calculation of Boiler EfficiencyDocument14 paginiCalculation of Boiler EfficiencyBharat Choksi100% (1)
- Chapter 4: Absorbers Rules of Thumb For Chemical Engineers, 5th Edition by Stephen HallDocument11 paginiChapter 4: Absorbers Rules of Thumb For Chemical Engineers, 5th Edition by Stephen HallBaskar KannaiahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Thermodynamics Production of Power From HeatDocument27 paginiAdvanced Thermodynamics Production of Power From HeatPappuRamaSubramaniam100% (1)
- CH 12Document30 paginiCH 12hirenpatel_universal0% (3)
- Tutorium Refrigeration SolutionDocument20 paginiTutorium Refrigeration SolutionwanpudinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geothermal Power PlantDocument22 paginiGeothermal Power PlantLily CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 5 E BalanceDocument3 paginiTutorial 5 E BalanceYi Ying Hannie100% (1)
- Sustainable Energy Conversion for Electricity and Coproducts: Principles, Technologies, and EquipmentDe la EverandSustainable Energy Conversion for Electricity and Coproducts: Principles, Technologies, and EquipmentÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energy Balance: Hydrogen ProductionDocument7 paginiEnergy Balance: Hydrogen ProductionMohit MangalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energy Balance:: ReactionDocument7 paginiEnergy Balance:: ReactionHarsh ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- CalculationsDocument14 paginiCalculationsPratyush BadrinarayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steam Generation Calculations of BoilerDocument5 paginiSteam Generation Calculations of BoilerRaza Un Nabi100% (1)
- Energy BalanceDocument10 paginiEnergy BalanceAadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Itaconic Acid 2 ReviewDocument65 paginiItaconic Acid 2 ReviewVanitha EÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 12 (Vapor Power Systems) : Ideal Rankine CycleDocument14 paginiChapter 12 (Vapor Power Systems) : Ideal Rankine CycleNagham MuradÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHPC PDFDocument6 paginiCHPC PDFsaliyarumesh2292Încă nu există evaluări
- Hydrogen Energy 2520balance.Document6 paginiHydrogen Energy 2520balance.sahilchemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample ProblemsDocument2 paginiSample ProblemsLul LolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emma MangarooDocument17 paginiEmma MangarooCharlotte BÎncă nu există evaluări
- H S S X S S HDocument4 paginiH S S X S S HahmadskhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 12 (Vapor Power Systems) : Actual Rankine CycleDocument8 paginiChapter 12 (Vapor Power Systems) : Actual Rankine CycleNagham MuradÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 3 ThermoDocument27 paginiTutorial 3 ThermoHaiqal AzizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Feedwater Heater - Regeneration Analysis - HandbookDocument19 paginiFeedwater Heater - Regeneration Analysis - HandbookAnonymous wIPMQ5rhÎncă nu există evaluări
- A7 - 20-SEP-2016 - RM001 - POCE5 - Module-4-Energy Balance-NumericalsDocument17 paginiA7 - 20-SEP-2016 - RM001 - POCE5 - Module-4-Energy Balance-NumericalssantoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Utility Cost Estimate: Associate Professor Dr. Deacha Chatsiriwech Chemical Engineering, Chulalongkorn UniversityDocument16 paginiUtility Cost Estimate: Associate Professor Dr. Deacha Chatsiriwech Chemical Engineering, Chulalongkorn UniversitySitiMursidahÎncă nu există evaluări
- UntitledDocument25 paginiUntitledAshutosh TiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermodynamics Cycle:: 1. Power Generation 2. Refrigeration 1. Power Cycles (Engines)Document16 paginiThermodynamics Cycle:: 1. Power Generation 2. Refrigeration 1. Power Cycles (Engines)saketbajaj123Încă nu există evaluări
- DMX9208 - CAT - 2021 With AnswersDocument14 paginiDMX9208 - CAT - 2021 With AnswersSampath WeeratungeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chloroalkali Process: Membrane Cell: Process Synthesis Term ProjectDocument14 paginiChloroalkali Process: Membrane Cell: Process Synthesis Term ProjectAndrés Camilo Regino RamirezÎncă nu există evaluări
- THERMO PROJECT DR KhawarDocument14 paginiTHERMO PROJECT DR KhawarHamza AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 06Document15 paginiCH 06hirenpatel_universalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power PlantDocument12 paginiPower PlantCharlotte BÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculations 2Document3 paginiCalculations 2LeoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alarzar Refrigeration Act 4Document6 paginiAlarzar Refrigeration Act 4Aldrin TamayoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mebs6006 0708 Exercise PDFDocument5 paginiMebs6006 0708 Exercise PDFbilal almelegyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 14Document11 paginiCH 14hirenpatel_universalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shantanu DasDocument10 paginiShantanu DasarunkdevassyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ejercicio para CompararDocument4 paginiEjercicio para CompararCamila SarabiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ATD Tutorial Sheet 01Document2 paginiATD Tutorial Sheet 01Aditya raj sachdevÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module Title: Plant & Process Design Module Code:: +417.5 KJ/KG)Document4 paginiModule Title: Plant & Process Design Module Code:: +417.5 KJ/KG)doniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- RAC Tute Unit 2vcdfesdDocument2 paginiRAC Tute Unit 2vcdfesdSushant MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Production of 20,000 LPD Biodiesel From Chicken Fat Waste: Project SupervisorDocument36 paginiProduction of 20,000 LPD Biodiesel From Chicken Fat Waste: Project Supervisorsaqib sulmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applied Thermodynamics D201 Self Assessment Solutions Tutorial 5 Self Assessment Exercise No. 1Document4 paginiApplied Thermodynamics D201 Self Assessment Solutions Tutorial 5 Self Assessment Exercise No. 1Alexander MugabeÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 05Document14 paginiCH 05hirenpatel_universalÎncă nu există evaluări
- University of The West Indies, St. Augustine.: FacultyDocument8 paginiUniversity of The West Indies, St. Augustine.: FacultyCharlotte BÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat Loss Throughthe Exhaustin Internal Combustion EngineDocument8 paginiHeat Loss Throughthe Exhaustin Internal Combustion Engineanon_961539748Încă nu există evaluări
- Paper 4 - Set A Key 14 National Certification Examination FOR Energy Auditors - August, 2013Document14 paginiPaper 4 - Set A Key 14 National Certification Examination FOR Energy Auditors - August, 2013Muthiah Chidambaram MuthiahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 (B) Energy Balance: 3.9 AssumptionsDocument21 paginiChapter 3 (B) Energy Balance: 3.9 Assumptionssaur1Încă nu există evaluări
- Effortlessly Easy Oven and BBQ Cleaner HCHS75Document1 paginăEffortlessly Easy Oven and BBQ Cleaner HCHS75Gurinder SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sas7 STM-005Document6 paginiSas7 STM-005mayasÎncă nu există evaluări
- FTFS Chap21 P001Document33 paginiFTFS Chap21 P001AbdulAbdulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lynch - 2012 - Hydrogen Embrittlement Phenomena and MechanismsDocument19 paginiLynch - 2012 - Hydrogen Embrittlement Phenomena and MechanismsIgor FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Annotated-Acid-base EquilibriaDocument11 paginiAnnotated-Acid-base EquilibriaVECNAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alternative Cycles Based On Carbon Dioxide For Central Receiver Solar Power PlantsDocument13 paginiAlternative Cycles Based On Carbon Dioxide For Central Receiver Solar Power PlantsfaizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics Compressor CalculationDocument12 paginiBasics Compressor CalculationOthman MansoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment No.: TITLE HERE: Department of Chemical EngineeringDocument10 paginiExperiment No.: TITLE HERE: Department of Chemical EngineeringCARLO CASTILLOÎncă nu există evaluări
- SKF3013 - Manual Amali PDFDocument26 paginiSKF3013 - Manual Amali PDFhazwani safuraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Periodic Classification Revision QuestionsDocument6 paginiPeriodic Classification Revision QuestionsSumiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 06-Measurement of TemperatureDocument16 pagini06-Measurement of TemperatureChidiebere Samuel OkogwuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapterwise Important QuestionsDocument11 paginiChapterwise Important QuestionsrevamanianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Paper HMT EME504Document1 paginăSample Paper HMT EME504manidev25% (4)
- Maintenance and Cleaning of Thermal OilDocument6 paginiMaintenance and Cleaning of Thermal OiligorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat 4e Chap02 LectureDocument48 paginiHeat 4e Chap02 LectureSubho Samanta100% (4)
- S.# Answer Option (A) Answer Option (B) Answer Option (C) Answer Option (D)Document2 paginiS.# Answer Option (A) Answer Option (B) Answer Option (C) Answer Option (D)geologistlakhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nano and Micro PTFEDocument22 paginiNano and Micro PTFERazvan ScarlatÎncă nu există evaluări
- VL2022230501086 DaDocument2 paginiVL2022230501086 DabihbugvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preparation of DEETDocument4 paginiPreparation of DEETdevbones18Încă nu există evaluări
- Skripsi Tanpa Bab PembahasanDocument56 paginiSkripsi Tanpa Bab PembahasanromaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Govpub C13Document54 paginiGovpub C13Matty WrobelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural and Defect Properties of The Lapo and Lap O - Based Proton ConductorsDocument7 paginiStructural and Defect Properties of The Lapo and Lap O - Based Proton ConductorsEstudiante2346Încă nu există evaluări