Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Denmark (: Danmark
Încărcat de
EJ Henz SahagunDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Denmark (: Danmark
Încărcat de
EJ Henz SahagunDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Denmark (
i
/dnmrk/; Danish: Danmark, pronounced [d nmg ] ( listen)),
officially the Kingdom of Denmark (Danish: Kongeriget
Danmark, [koqeuie d nmg ] ( listen)), is a sovereign
state inNorthern Europe, located south-west of Sweden,
south of Norway, and bordered to the south byGermany.
The Kingdom has two autonomous constituent countries in
the north Atlantic Ocean, theFaroe Islands and Greenland.
At 43,094 square kilometres (16,638.69 sq mi),
[10]
and a
population of around 5.6 million inhabitants, Denmark
consists of a peninsula, Jutland, and the Danish archipelago
of 407 islands,
[11]
of which around 70 are inhabited, are
characterised by flat, arable land and sandy coasts with little
elevation and a temperate climate. The national
language, Danish, is closely related to and mutually
intelligible with Swedish and Norwegian.
The Kingdom of Denmark is a unitary constitutional
monarchy with Margrethe II as queen regnant, organised in
a parliamentary democracy. Ending absolute
monarchy introduced in 1660, theConstitution of
Denmark was signed on 5 June 1849, only to be rewritten
four times; the latest revisionin 1953. The unicameral
parliament, the Folketing, resides in the capital
of Copenhagen, together withjudicial, executive,
and legislative powers.
Denmark
[b]
exercises hegemonic influence in the Danish
Realm, devolving political powers to handle internal affairs
to the Faroe Islands and Greenland. Denmark became a
member of the European Union in 1973, maintaining four
opt-outs from European Union policies, as outlined in the
1992 Edinburgh Agreement. Both the Faroe
Islands and Greenlandremain outside the Union.
Home of the Vikings, the unified kingdom of
Denmark emerged in the 8th century as a proficient
seafaring nation in the struggle for control of the Baltic Sea.
The establishment of the personal Kalmar Union under
Danish rule in 1397 ended with Swedish secession in 1523;
one year later, Denmark entered union with Norway until its
dissolution in 1814. Several cessions of Danish territory that
had begun in the 17th century caused a surge of nationalist
movements that gained momentum in the 1830s and
concluded with a defeat in the 1864 Second Schleswig War.
A new European outlook was sought after the war, resulting
in adjustment and cooperation.
Denmark remained neutral during World War I and
the German invasion in April 1940 saw brief military
skirmishes while the Danish resistance movement was
active from 1943 until the German surrender in May 1945.
Denmark abandoned its traditional neutrality by
joining NATO in 1949. The post-war period generated an
increase of wealth and brought closer European integration.
Denmark has been an active participant in international
peacekeeping missions. It took part in the UN peacekeeping
mission in the Balkans in the 1990s. More recently, it has
participated in military engagements in the Middle East at
the turn of the 21st century.
[12]
An industrialized exporter of agricultural produce in the
second half of the 19th century, Denmark introduced social
and labour-market reforms in the early decades of the 20th
century, making the basis for the present welfare state with
a highly developed mixed market economy. The Danish
krone has been pegged to the euro since 1 January 1999.
Denmark has close cultural, economic, and historical ties
with its neighbours, resulting in the Danish-
Swedish resund Bridge and the planned Danish-
German Fehmarn Belt Fixed Link.
Denmark is frequently ranked as the happiest country in the
world in cross-national studies
ofhappiness.
[13][14][15][16][17]
Denmark ranks as having the
world's highest social mobility,
[18]
a high level of income
equality,
[19]
has one of the world's highest per capita
income, and has one of the worlds highest personal income
tax rates.
[20]
For 2013, Denmark is listed 15th on the Human
Development Index
[21]
and 9th on the inequality-adjusted
HDI. Denmark ranks highly positive on theCorruption
Perceptions Index and the Legatum Prosperity Index, and
as a full democracy on theDemocracy
Index.
[22][23][24]
Denmark is among the founding members of
the NATO, Nordic Council,OECD, OSCE, and the United
Nations. There are three Danish heritage sites inscribed on
theUNESCO World Heritage list in Northern Europe.
Greenland, which is part of the Kingdom of Denmark, has
one of the highest suicide rates in the world.
[25][26][27]
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- DenmarkDocument2 paginiDenmarkMaximos ManiatisÎncă nu există evaluări
- DENAMRKDocument2 paginiDENAMRKȘova AngelicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Denmark (: ProperDocument2 paginiDenmark (: ProperddalexandruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Denmark: This Article Is About The European Country. For Other Uses, SeeDocument4 paginiDenmark: This Article Is About The European Country. For Other Uses, Seemegawhat115Încă nu există evaluări
- Denmark (: PronouncedDocument1 paginăDenmark (: PronouncedMaximos ManiatisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kingdom of Denmark: History & CultureDocument7 paginiKingdom of Denmark: History & CultureAli SaleemÎncă nu există evaluări
- DEN2Document1 paginăDEN2qevwÎncă nu există evaluări
- DenmarlDocument4 paginiDenmarlJeremy CookÎncă nu există evaluări
- Danish RealmDocument13 paginiDanish RealmJorge AlamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- COMUN SSUC ResearchDocument23 paginiCOMUN SSUC ResearchAadhya HarugeriÎncă nu există evaluări
- DenmarkDocument2 paginiDenmarkVirat GadhviÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Beauty of DenmarkDocument8 paginiThe Beauty of DenmarkJoshua DaarolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Support 5Document7 paginiSupport 5muezzaislami23Încă nu există evaluări
- Government System 1Document1 paginăGovernment System 1api-308499386Încă nu există evaluări
- Denmark Business CultureDocument7 paginiDenmark Business CultureKarthikSelvakumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- GreenlandDocument31 paginiGreenlandJorge AlamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- DEN1Document1 paginăDEN1qevwÎncă nu există evaluări
- Denmark County ProfileDocument4 paginiDenmark County ProfileAroosa A. ChapalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Denmark ProjectDocument1 paginăDenmark ProjectNadia BahlovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Norway (: Norge NoregDocument1 paginăNorway (: Norge NoregAbrudan GabrielÎncă nu există evaluări
- DenmarkDocument4 paginiDenmarkNicola DudanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Task Performance Research Paper Outline I. BackgroundDocument6 paginiTask Performance Research Paper Outline I. BackgroundmichaelabatraloÎncă nu există evaluări
- International Relations and StrategiesDocument40 paginiInternational Relations and StrategiesRoshni VinodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Celand (: LandnámabókDocument1 paginăCeland (: LandnámabókAngelo R RobertÎncă nu există evaluări
- SwedenDocument2 paginiSwedenMaximos ManiatisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Country of ICELANDDocument31 paginiCountry of ICELANDprecauteÎncă nu există evaluări
- IcelandDocument37 paginiIcelandyairherreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coins of DenmarkDocument111 paginiCoins of DenmarkHasdrubalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Smilla S Sense of Snow Research ReportDocument13 paginiSmilla S Sense of Snow Research Reportdavid_wolf300Încă nu există evaluări
- Alestalo 1986Document39 paginiAlestalo 1986I'm an OrbitzencleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Denmark: BackgroundDocument7 paginiDenmark: BackgroundTina PascualÎncă nu există evaluări
- DenmarkDocument6 paginiDenmarkDj BuliusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Norway DescriptionDocument2 paginiNorway Descriptioncamilo sierraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Netherlands: Location of The - in - in TheDocument25 paginiNetherlands: Location of The - in - in ThenomitekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Greenland (: Lavrador (Later Applied ToDocument2 paginiGreenland (: Lavrador (Later Applied ToAngelo R RobertÎncă nu există evaluări
- DenmarkDocument41 paginiDenmarkMozartÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Guide to Denmark and the Happy People #hygge #happiest People # DenmarkDe la EverandA Guide to Denmark and the Happy People #hygge #happiest People # DenmarkEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (1)
- Greenland!Document3 paginiGreenland!mia.secovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pronounced Danish PronunciationDocument1 paginăPronounced Danish PronunciationAlexandra MarinÎncă nu există evaluări
- DenmarkforkidsDocument28 paginiDenmarkforkidsodassostefanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iceland (: LandnámabókDocument3 paginiIceland (: LandnámabókrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iceland: Universitatea Babeș-Bolyai Cluj Napoca, Facultatea de Științe Economice Și Gestiunea AfacerilorDocument10 paginiIceland: Universitatea Babeș-Bolyai Cluj Napoca, Facultatea de Științe Economice Și Gestiunea AfacerilordexterkeÎncă nu există evaluări
- DEN11Document1 paginăDEN11qevwÎncă nu există evaluări
- Denmark PortfolioDocument4 paginiDenmark PortfoliothepavlomalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cursuri 1-6 PDFDocument37 paginiCursuri 1-6 PDFfrozenglxÎncă nu există evaluări
- DenmarkDocument40 paginiDenmarkGrigore VieruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Norway V Denmark CaseDocument3 paginiNorway V Denmark CaseMae ParsomalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lars JANSEN - Postcolonial Denmark Beyond The Rot of ColonialismDocument14 paginiLars JANSEN - Postcolonial Denmark Beyond The Rot of ColonialismJorge MaloneÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Brief History of Norway - Fjord ToursDocument6 paginiA Brief History of Norway - Fjord ToursRear BaueltazarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Description of Denmark by Bagas Indra AnggitaDocument5 paginiDescription of Denmark by Bagas Indra AnggitabagasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4270 Overview of DenmarkDocument3 pagini4270 Overview of DenmarkNhật Minh Nguyễn ĐỗÎncă nu există evaluări
- World HisDocument3 paginiWorld Hisapi-420665496Încă nu există evaluări
- A Profile of Laws, Governance and Economics of DenmarkDocument16 paginiA Profile of Laws, Governance and Economics of Denmarkbilly momanyiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scandinavia: The Saylor Foundation Page 1 of 2Document2 paginiScandinavia: The Saylor Foundation Page 1 of 2oierulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tema 5. ReeDocument19 paginiTema 5. ReeJuana Muñoz RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- DEN7Document1 paginăDEN7qevwÎncă nu există evaluări
- DenmarkDocument1 paginăDenmarkschool stuffÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nordic Paths to ModernityDe la EverandNordic Paths to ModernityJóhann Páll ÁrnasonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Greenlandic Independence:: Historical BackgroundDocument2 paginiGreenlandic Independence:: Historical BackgroundIbrahim JumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finals Essay (Sahagun, Jerolet) (Sec C-grp1)Document11 paginiFinals Essay (Sahagun, Jerolet) (Sec C-grp1)EJ Henz SahagunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Land Use Planning: Key To Disaster Risk Management: AgricultureDocument4 paginiLand Use Planning: Key To Disaster Risk Management: AgricultureEJ Henz SahagunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antique AntiqDocument5 paginiAntique AntiqEJ Henz SahagunÎncă nu există evaluări
- PECs Self-Rating QuestionnaireDocument2 paginiPECs Self-Rating QuestionnaireEJ Henz Sahagun100% (1)
- NPK FertilizerDocument6 paginiNPK FertilizerEJ Henz SahagunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Participatory Rural Communication AppraisalDocument10 paginiParticipatory Rural Communication AppraisalEJ Henz SahagunÎncă nu există evaluări
- CLUP Bacolod CityDocument11 paginiCLUP Bacolod CityEJ Henz Sahagun67% (3)
- Pest Control OperatorsDocument2 paginiPest Control OperatorsEJ Henz SahagunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chrono Events Syn Bt11Document2 paginiChrono Events Syn Bt11EJ Henz SahagunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary Evaluation FPA BCTDocument3 paginiSummary Evaluation FPA BCTEJ Henz SahagunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sem Solubilization TechnologyDocument1 paginăSem Solubilization TechnologyEJ Henz SahagunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application Form PIP RegsnDocument1 paginăApplication Form PIP RegsnEJ Henz SahagunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tox PIPDocument1 paginăTox PIPEJ Henz SahagunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Memorandum Order Fpabiocore TeamDocument2 paginiMemorandum Order Fpabiocore TeamEJ Henz SahagunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enhancing Institutional Mechanism Forum 1: Changing The Context by Jerolet SahagunDocument2 paginiEnhancing Institutional Mechanism Forum 1: Changing The Context by Jerolet SahagunEJ Henz SahagunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fpa Biocoreteam DutiesDocument1 paginăFpa Biocoreteam DutiesEJ Henz SahagunÎncă nu există evaluări
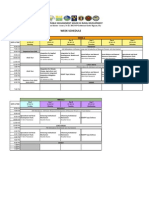
- Week Schedule: Master in Public Management Major in Rural DevelopmentDocument1 paginăWeek Schedule: Master in Public Management Major in Rural DevelopmentEJ Henz SahagunÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 - LESSON 4 - To Kill A Mockingbird.Document22 pagini4 - LESSON 4 - To Kill A Mockingbird.Aenna SaludÎncă nu există evaluări
- Allan R. Millett, Williamson Murray-Military Effectiveness, in WW2 2 Edition (Volume 3) - Cambridge University Press (2010)Document16 paginiAllan R. Millett, Williamson Murray-Military Effectiveness, in WW2 2 Edition (Volume 3) - Cambridge University Press (2010)Costea CatalinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trundy v. Strumsky, 1st Cir. (1992)Document13 paginiTrundy v. Strumsky, 1st Cir. (1992)Scribd Government DocsÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Functional Approach To World Organization - MitranyDocument15 paginiThe Functional Approach To World Organization - MitranySamuel KramerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bribery & Corruption PolicyDocument4 paginiBribery & Corruption Policykashifbutty2kÎncă nu există evaluări
- Administrative Reform Carried Out by The Malaysian Government Paper Public AdminDocument6 paginiAdministrative Reform Carried Out by The Malaysian Government Paper Public AdminctrockÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15646Document6 pagini15646ncwazzy100% (1)
- Essay About The Drug War in The PhilippinesDocument3 paginiEssay About The Drug War in The PhilippinesKavin GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Social JusticeDocument351 paginiPrinciples of Social JusticeAnamica SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Section 188 IPCDocument2 paginiWhat Is Section 188 IPCKishor SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Executive Order Road ClearingDocument3 paginiExecutive Order Road ClearingDILG STA MARIA63% (8)
- Unit 5 Labour LawDocument22 paginiUnit 5 Labour LawANkit JAinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evictions Procedendo and Mandamus Complaint FINAL THIRDDocument18 paginiEvictions Procedendo and Mandamus Complaint FINAL THIRDFinney Law Firm, LLCÎncă nu există evaluări
- GlobalizationDocument3 paginiGlobalizationAnnie Jane SamarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 Summary - Catharina ChrisidaputriDocument3 paginiChapter 5 Summary - Catharina ChrisidaputriCatharina CBÎncă nu există evaluări
- ERDULFO C BOISER Vs CA and PLDTDocument3 paginiERDULFO C BOISER Vs CA and PLDTfermo ii ramos100% (1)
- Theories of International Regimes - Stephan Haggard and Beth A. SimmonsDocument9 paginiTheories of International Regimes - Stephan Haggard and Beth A. SimmonsTANIA FERREÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arrest and Detention FlowchartDocument1 paginăArrest and Detention FlowchartAliÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1st and 3rd World CountryDocument9 pagini1st and 3rd World CountryJullien CeladaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Act 193 National Emblems Control of Display Act 1949Document9 paginiAct 193 National Emblems Control of Display Act 1949Adam Haida & CoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form No. 10GDocument3 paginiForm No. 10GAravind KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Consti-Midterm ReviewerDocument29 paginiConsti-Midterm ReviewerrusselsithliÎncă nu există evaluări
- The EnlightenmentDocument3 paginiThe EnlightenmentIan RoderickÎncă nu există evaluări
- Temporary Environmental Protection OrderDocument1 paginăTemporary Environmental Protection OrderR.A. GregorioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cudia VS PmaDocument2 paginiCudia VS PmaMarian's PreloveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marx Communist ManifestoDocument50 paginiMarx Communist ManifestoyjohnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gaventa and Barrett 2012 - Mapping The Outcomes of Citizen EngagementDocument12 paginiGaventa and Barrett 2012 - Mapping The Outcomes of Citizen EngagementStephen ThorpeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Court Deposition of Drew DeBerryDocument73 paginiCourt Deposition of Drew DeBerryHank GilbertÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rem Rev 1 Digests - Mejia (Sept 10)Document5 paginiRem Rev 1 Digests - Mejia (Sept 10)melaniem_1Încă nu există evaluări
- Essay On Corruption in in IndiaDocument1 paginăEssay On Corruption in in IndiaGaurav ThakurÎncă nu există evaluări