Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
T25 - VFD Cable Guide
Încărcat de
kapernikovDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
T25 - VFD Cable Guide
Încărcat de
kapernikovDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Cabling for Variable Frequency Drives
Brian Shuman, RCDD
Senior Product Development Engineer
November 3-4, 2010
Agenda
VFD's and their impact on your design
VFD Technology requires Cable Solutions
Noise ssues, Cable Longevity, System Longevity
VFD Cable installation considerations
General Recommendations and Conclusion
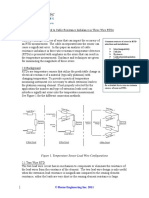
VFD Schematic
VariabIe Frequency Drives' Impact on
Your Design
VFDs have a significant affect on your installation
VFDs pull power off your source line in chunks and
produce very high frequency outputs
Source for harmonics
They can create significant EM and RF
They can affect other parts of the system and
neighboring systems
CabIe's RoIe in Drive System
ts Ability to Withstand the Operating
Conditions Caused by the Drive System
How it Affects Other Drive System
Components & Surrounding Equipment
CriticaI CabIe Characteristics
Ability to provide 20+ year service life
Voltage withstand capability
Sizing for currents present in Drive Systems
Environmental survival
Reduce Standing Waves
mpacts motor life, cable life, and noise levels
Cable is one of several factors in overall reflected
wave picture
Reduce radiated/coupled noise from Drive System
VFD Operation Issues
Reflected Waves
Cable Charging
Corona Discharge
Radiated Noise
Conducted Noise
RefIected Wave
Impedance Mismatch
CabIe Type ( Test
Frequency of 60Hz)
Impedance
(Ohms)
Voltage at
Motor
Terminals
Length of
CabIe
SampIe
Foil/Braid 78 1220 V 132 ft
Shielded PVC-
Nylon/PVC
38 1260 V 120 ft
Un-Shielded PVC-
Nylon/PVC
58 1220 V 106 ft
Cu - Tape Shield 58 1230 V 128 ft
Impedance vs. Peak VoItage
CabIe Charging
XLPE,
RHW-2
Focus Cable
XLPE,
XHHW-2
Standard Wire
Thickness
PVC 15 mil -
Nylon 4 mil,
THHN
Capacitance:
30pf/ft
Capacitance:
40pf/ft
Capacitance:
80pf/ft
Corona Effect - BottIing FaciIity
Copper
Conductor
1 5 miI PVC
InsuIation
1 5 miI PVC
InsuIation
Copper
Conductor
High E fieId in
1 miI air gap
Based on ~ 30% humidity exacerbated by high moisture
environments, longer runs, or smaller air gaps
InsuIation MateriaIs Comparison
Thermoplastic insulations are not recommended
Shorter life expectancy under long-term voltage stress
Less resistant to temperature extremes caused by corona
discharge sometimes present in drive applications
Thin insulations increase likelihood for corona inception
Thermoset materials (XLPE) are recommended
Exhibit ideal durability qualities for both temperature
extremes and aging characteristics under long-term
voltage stress
Due to their required thickness to meet TC standards, it
will further enhance cable longevity by reducing likelihood
of corona discharge
Radiated Emissions
Radiated Emissions
Radiated (coupled) Noise to nearby cables
High frequency, high amplitude noise
corresponding to leading-edge of PWM carrier
signal and reflected wave can be coupled to
adjacent cables (and components)
Noise on adjacent cables and components may
cause other systems to malfunction
Other susceptible equipment often affected:
encoders, capacitive sensors, thermocouples,
proximity sensors, network communications.
Radiated Noise from Motor
Source for common-mode noise
Motor frame (shell) acts like a shield to
capture radiated noise
This captured noise has two paths to
ground
Through the motor frame to the
ground grid back to the drive
Through the cable back to the
Drive
SOLUTON:
Contain the noise on the cable and
keep the noise off your ground grid
Motor Frame
acts like a
shield
Drains the
noise to
ground
Radiated Emissions
Radiated SignaI
without ShieId
Radiated SignaI
with Braid ShieId
Measured with a voltage pick-up antenna set-up using a
Cable with an 85% braid-only vs. an unshielded cable
CoupIed Noise - AII CabIes Compared
Noise CoupIed on UnshId Comm. CabIe
-16
-12
-8
-4
0
4
8
12
16
Time
V
o
I
t
s
Foil/Braid
Cu Tape
Armored
Foil
Conducted Noise
Conducted Noise
Conducted (common mode) noise from the motor affects
nearby equipment
High levels of noise couples between the windings of
the motor to building ground through the frame of the
motor
Unshielded motor leads in a conduit couple VFD output
to ground via conduit fasteners
Digital systems and proper grounding are effective at
isolating most low-frequency current
Drive square wave output couples noise that resembles
square digital communication pulses (ie 24V and 5V
systems)
Common Mode Noise (Termination)
Common Mode noise takes
path of least resistance
Factors affecting this are
infinite humidity, distance,
design, load, source, etc.
Following graph indicates
impedance across multiple
frequencies for each cable
Reduced shield and ground
impedance results in reduced
common-mode noise outside
the cable
DRVE FRAME
MOTOR
WNDNGS
MOTOR
FRAME
LTTLE HF
CURRENT
PVC
ARMOR
OR
SHELD
PE GRD
PE TE N
USER #1
PE TE N
USER #2
PE TE N
USER #n
SOLUTON: SHELD CONTROLS HF NOSE CURRENT PATH
A+
A-
+
-
PE
I
ao
Courtesy of Rockwell Automation
ShieId Resistance Comparison
* Lower resistance = improved common-mode performance
ShieId Impedance High Freq
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
5 10 100 200 300 400 500 600 800 1000
Frequency (kHz)
I
m
p
e
d
a
n
c
e
(
O
h
m
s
)
Foil/Braid
Cu Tape
Armored
Foil
VFD CabIe Advantages
CIassic VFD CabIe Features
.045 XLPE nsulation (NEC TYPE XHHW-2/RHW-2)
Full Size, nsulated Ground Wire
Shielding
85% TC Braid for EM (Low Frequencies)
100% Alum/Mylar Tape for RF (High Frequencies)
Full Size, Uninsulated Drain Wire
ndustrial Grade PVC Jacket Sunlight Resistant.
TC-ER Exposed Runs
Dual Rated 1000V/600V
MSHA Approved
Available w/ #16PR
for signals in small sizes
Large-size VFD CabIe Features
XHHW-2 nsulation
Full Size, sectioned, un-insulated
ground wires
Two, contra helically applied
copper tape shields
Each shield is 2 mils thick, with a
20-25% overlap for superior shield
coverage and low-impedance path
to ground even after installation
ndustrial Grade PVC Jacket
Sunlight Resistant.
TC-ER Exposed Runs
Dual Rated 1000V/600V
MSHA approved
New VFD CabIe Designs
Small and Large Gauge Cables available
with 2000 volt rating
Small and Large Gauge Cables available
in Low Smoke Zero Halogen designs
Environmentally friendly
Small and Large Gauge Cables available
in MC listed designs
Aluminum or steel interlocked armor
VFD CabIe Advantages
Thick, wet rated insulation = lower capacitance.
Foil + Braid / Cu Tape = better noise protection.
Full Size Drain wire + Ground = easier
termination.
TC-ER rating = no conduit required
Small OD = Small bend radius for tight enclosures
VFD FIex Life
29501
3 cond #14 XLPE + 1 #14 gnd PVC foil + braid PVC
Flexed 1.98 million flexes at 6 radius
29502
3 cond #12 XLPE + 1 #12 gnd PVC foil + braid PVC
flexed 1.82 million flexes at 6 radius
Both were tested on the Belden C-track tester
Single axis, continuous DCR monitoring
VFD CabIe InstaIIation & Termination
InstaIIation of VFD CabIe
Flexible stranding and smaller diameter allow for
bends 50% tighter than comparable VFD cables
Glands required are much less expensive and
simpler to use
Type TC ER listing allows for reduced cost and
installation flexibility
InstaIIation of VFD CabIe
Multipoint grounding is recommended,
reducing common-mode noise while harmonic
noise is drained off by the "supersized neutral
(ground)
Terminate ground (and drain if present) with a
lug or terminal strip on each end
Termination kits are available
InstaIIation of VFD CabIe (cont)
Avoid sharp bends with the conductors
Cable glands with a conductive gasket should be
used to connect the shield to the motor junction
box and drive enclosure
This avoids a gap in the shield coverage
The jacket should also be inserted into the
gland
Avoid loose conductors!
InstaIIation of VFD CabIe (cont)
Use parallel runs for high horsepower
drives/motors
Terminal strips or lugs typically required
Cable must be adequately supported
Follow local, regional and national codes, laws
and standards
VFD CabIe Termination
OptionaI
Taping
Motor Frame Housing
Tinned
Drain
Wire
Frame PE GND
Stud or Screw
Tinned
Drain
Wire
METAL or PLASTIC connector
into drive paneI or cabinet
100%
AI/MyIar
foiI
85%
tinned
Cu
braid
System PE GND
OptionaI
Taping
Motor Junction Box Housing
Motor Frame Housing
Tinned
Drain
Wire
Frame PE GND
Stud or Screw
Tinned
Drain
Wire
METAL or PLASTIC connector
into drive paneI or cabinet
100%
AI/MyIar
foiI
85%
tinned
Cu
braid
System PE GND
Motor Frame
Housing
85
tinned
Cu
braid
Foil
Shield
Ground
Wire
Drain
Wire
Frame PE GND
Stud or Screw
Optional taping
OI Ioil and braid
ConcIusion & Questions
Unshielded motor leads, unshielded cable, AL foil-only
shielded cable, and thermoplastic insulated cables are
not recommended for VFD/VSD applications
At a minimum, 30 mils of XLPE or similar insulation
should be used
Shields should be a heavy wall 100% coverage
system
Ground conductors should be oversized to handle
harmonic currents
Run lengths should be minimized and special care
must be given to proximity of the drive, motor, and
cable to susceptible components
Questions
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Cisco DA and AMI v01Document45 paginiCisco DA and AMI v01kapernikovÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Rockwell Automation - Psug Educ Alarm MGMT Final1Document55 paginiRockwell Automation - Psug Educ Alarm MGMT Final1kapernikovÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5795)
- Tp21 - Bec - DT - 0458 Fat Procedure PLC - Scada System Rev - 1Document33 paginiTp21 - Bec - DT - 0458 Fat Procedure PLC - Scada System Rev - 1kapernikovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- R6521e KitzDocument10 paginiR6521e KitzkapernikovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- U R T For A Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) Process Control SystemDocument65 paginiU R T For A Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) Process Control Systemkapernikov50% (2)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- PublicationDocument52 paginiPublicationkapernikovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Type 2 Surge Arrester - VAL-MS-EE-T2-1+0-320 - 2910577: Key Commercial DataDocument6 paginiType 2 Surge Arrester - VAL-MS-EE-T2-1+0-320 - 2910577: Key Commercial Datavardaan industriesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lyle 2022 J. Electrochem. Soc. 169 060527Document9 paginiLyle 2022 J. Electrochem. Soc. 169 060527Emre KAÇANERÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- RS232 Pin Out - Connector Reference GuideDocument6 paginiRS232 Pin Out - Connector Reference GuideDaj NemojÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- 48V, 120AH, 6KW Lifepo4 Battery For Solar EnergyDocument1 pagină48V, 120AH, 6KW Lifepo4 Battery For Solar EnergyJosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Effectron II Manual PDFDocument32 paginiEffectron II Manual PDFtelengard_t100% (2)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- IEE Current Ratings Regulations Table 4E1ADocument3 paginiIEE Current Ratings Regulations Table 4E1AsanjaigÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Agitadores de Laboratorio Barnstead Maximix II ManualDocument16 paginiAgitadores de Laboratorio Barnstead Maximix II ManualJair Jesús Cazares RojasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Speed Sensors: Product Range GuideDocument12 paginiSpeed Sensors: Product Range GuideRafael Angel Valencia GutierrezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polycab Pricelist PDFDocument7 paginiPolycab Pricelist PDFyesukannanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Testing & Commissioning Method StatementDocument3 paginiTesting & Commissioning Method StatementanfalapÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Fluid Capacitance Logging - PetroWikiDocument3 paginiFluid Capacitance Logging - PetroWikiSamba Koukouare ProsperÎncă nu există evaluări
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Motor m42sp 6nkDocument2 paginiMotor m42sp 6nkWil WiltmarÎncă nu există evaluări
- NEC ALM Battery 12V7s DatasheetDocument4 paginiNEC ALM Battery 12V7s DatasheetkiymhfghfÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Wire RTD Accuracy AssessmentDocument6 pagini3 Wire RTD Accuracy AssessmentHirokÎncă nu există evaluări
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Mettu Science and Technology UniversityDocument44 paginiMettu Science and Technology UniversityYared WendaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1091)
- 3-Phase VoltDocument14 pagini3-Phase VoltBibah GeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- GU3310 & GU3311 Controller Brief Operation Manual: 1. Main Buttons' InstructionDocument6 paginiGU3310 & GU3311 Controller Brief Operation Manual: 1. Main Buttons' InstructiongutierkÎncă nu există evaluări
- CB Band Frequency Chart PDFDocument2 paginiCB Band Frequency Chart PDFdeyede2003Încă nu există evaluări
- OPTO-4 Datasheet Issue 1.00Document2 paginiOPTO-4 Datasheet Issue 1.00tariktunadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tunnel DiodeDocument15 paginiTunnel Diodesoumyadeepctry04Încă nu există evaluări
- Ceragon 3200T Installation - GuideDocument99 paginiCeragon 3200T Installation - GuideFabricio VilelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- JM Electro - Persamaan TransistorDocument4 paginiJM Electro - Persamaan TransistorAndi KaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- 1073R PDFDocument10 pagini1073R PDFElhindi hatimÎncă nu există evaluări
- EI2203 - Electronic Devices and Circuits - 2 Marks With AnswersDocument16 paginiEI2203 - Electronic Devices and Circuits - 2 Marks With AnswersASPCN 2017Încă nu există evaluări
- Matlab Simulink BasedDocument9 paginiMatlab Simulink BasedFarshid FaghihiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2016 - Obi e Bass - Trends and Challenges of Grid-ConnectedDocument13 pagini2016 - Obi e Bass - Trends and Challenges of Grid-ConnectedFabricio HigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Woodward Zastitni RelejiDocument8 paginiWoodward Zastitni RelejiRusty AllenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical (Sample)Document14 paginiElectrical (Sample)Alaa ShawkyÎncă nu există evaluări
- p203 PDFDocument7 paginip203 PDFMehmood Khan MarwatÎncă nu există evaluări
- JN TechDocument21 paginiJN Techsami ullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)