Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Fluid Mechanics - Assignment I-2012-2013
Încărcat de
Robert WalusimbiDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Fluid Mechanics - Assignment I-2012-2013
Încărcat de
Robert WalusimbiDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
MAKERERE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, DESIGN, ART AND TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL AND ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING
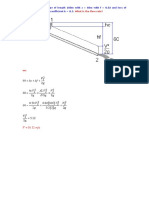
BSC (CIVIL ENG.) FIRST YEAR SEMESTER I 2012/13 CIV1202: FLUID MECHANICS ASSIGNMENT-I Question 1 (a) Water is flowing over a sharp-crested rectangular weir of width 50cm into a tank with crosssectional area 0.6 m2. After a period of 30s the depth of water in the tank is 1.4m. Assuming a discharge coefficient of 0.9, determine the height of the water above the weir. (b) If the rectangular weir is replaced by a 90o notch weir with the same head and a discharge coefficient of 0.8, calculate the depth increase of the water in the tank after 30s. Question 2 A 600mm diameter pipeline carries water under a head of 30m with a velocity of 3m/s. This water main is fitted with a horizontal bend which turns the axis of the pipeline through 75o (i.e. the internal angle at the bend is 105o). Calculate the resultant force on the bend and its angle to the horizontal. Question 3 A Venturimeter of throat diameter 0.076m is fitted in a 0.152m diameter vertical pipe in which liquid of relative density 0.8 flows downwards. Pressure gauges are fitted to the inlet and to the throat sections. The throat being 0.914m below the inlet. Taking the coefficient of the meter as 0.97, find the discharge; a) When the pressure gauges read the same b) When the inlet gauge reads 15,170 N/m2 higher than the throat gauge. Question 4 The figure below shows a smooth curved vane attached to a rigid foundation. The jet of water, rectangular in section, 75mm wide and 25mm thick, strike the vane with a velocity of 25m/s. Calculate the vertical and horizontal components of the force exerted on the vane and indicate in which direction these components act.
Due date: 30th April 2013
Question 5 A 45o reducing bend, 0.6m diameter upstream, 0.3m diameter downstream, has water flowing through it at the rate of 0.45m3/s under a pressure of 1.45 bar. Neglecting any loss in head for friction; calculate the force exerted by the water on the bend, and its direction of application. Question 6 A hydraulic jack is shown below. The area at A is 0.5 m2. The area at B is 2 m2. A 400 kg car sits on a platform at B. What force is required at A to lift the car?
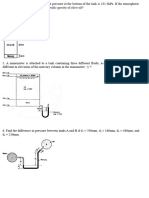
Question 7 A faucet on the 4th floor of a building is at a height of 12 meters, and fed by a pipe with a radius of 1 cm. Water enters the building at ground level through a pipe with has a radius of 4 cm. The pressure in the lower pipe is 230,000 Pa. (a) If the faucet is closed, what is the pressure at the faucet? (b) Once the faucet is opened, water begins to flow at a rate of 2 m/s at the faucet. i. What is the speed of the water in the lower pipe? ii. What is the pressure in the lower pipe? Question 8 A cylindrical tank containing water of density 1000kg/m3 is filled to a height of 0.70m and placed on a stand as shown in the cross-section above. A hole of radius 0.0010m in the bottom of the tank is opened. Water then flows through the hole and through an opening in the stand and is collected in a tray 0.30m below the hole. At the same time, water is added to the tank at an appropriate rate so that the water level in the tank remains constant. (a) Calculate the speed at which the water flows out from the hole (b) Calculate the volume rate at which water flows from the hole (c) Calculate the volume of water collected in the tray in t = 2.0minutes (d) Calculate the time it takes for a given droplet of water to fall 0.25m from the hole.
Due date: 30th April 2013
Question 9 A large tank, 25m in height and open at the top, is completely filled with saltwater (density 1025 kg/m3). A small drain plug with a cross-sectional area of 4.0 x 10-5 m2 is located 5.0m from the bottom of the tank. The plug breaks loose from the tank, and water flows from the drain. (a) Calculate the force exerted by the water on the plug before the plug breaks free (b) Calculate the speed of the water as it leaves the hole in the side of the tank (c) Calculate the volume flow rate of the water from the hole
Question 10
The Hoover Dam has a depth of 221 meters. A cross section of the dam is shown below
Dam Water
Due date: 30th April 2013
a) b) c) d) e)
Why does the dam get wider as you go down? If the dam is filled to the top with water, what is the pressure at the bottom of the dam? What is the average pressure over the whole face of the dam? If the surface area of the dam is 60,000 m2, what is the force on the dam? An engineer claims that if the water behind the dam were only 1 m wide, the dam could be made thinner. A second engineer says that this is not true; the dam would still have to be as thick. Which is right? Explain. Engineer 1 Engineer 2
W a t e r
W a t e r
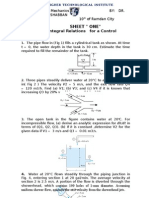
Question 11 (a) Derive the following expression for the actual discharge of a venturimeter.
(b)
A venturimeter has an area ratio of 9 to 1, the larger diameter being 30cm. During the flow, the recorded pressure head in the larger section is 6.5m and that at the throat 4.25m.If the meter coefficient C is 0.99, compute the discharge through the meter.
Question 12 Water is supplied from a tank into a canal through a rectangular sluice 1m wide and 1.75m high. The water level in the tank is 2m above the top edge of the opening and the canal water level is 30cm below the top edge. If the coefficient of discharge is 0.62 for the both free and the submerged portions, calculate the discharge.
Due date: 30th April 2013
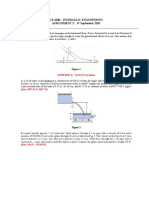
Question 13 In the figure below, the tank contains water and immiscible oil at 20oC. What is h in cm if the density of the oil is 898 kg/m3?
Question 14 Gate AB is 1.2 m long and 0.8 m into the paper (see figure below). Neglecting atmospheric pressure effects, compute the force F on the gate and its center of pressure position X from point A
Question 15 The tank shown below is 2 m wide into the paper. Neglecting atmospheric pressure, find the resultant hydrostatic force on panel BC.
Due date: 30th April 2013
Question 16 A constant pressure of 250 kPa, is available to push ethanol ( = 790 kg/m3, = 1.5 x 10-6 m2/s) through a pipe made of commercial steel (= 0.045 mm). The pipe has a length L = 25 m, and is inclined upwards at a 10 angle. The required minimum flowrate is 800 LPM. If pipes are available in 1-cm increments, what size pipe diameter should be used?
Due date: 30th April 2013
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Pipe Flow Rate CalculationDocument146 paginiPipe Flow Rate Calculationmalditaako66% (47)
- (1967) East Africa Law ReportsDocument1.115 pagini(1967) East Africa Law ReportsRobert Walusimbi85% (27)
- (1971) East Africa Law ReportsDocument750 pagini(1971) East Africa Law ReportsRobert Walusimbi100% (8)
- 1965 East African Law Reports Volume 1Document1.093 pagini1965 East African Law Reports Volume 1Robert Walusimbi82% (11)
- (1961) East Africa Law ReportsDocument991 pagini(1961) East Africa Law ReportsRobert Walusimbi71% (7)
- Module 2 HW4Document15 paginiModule 2 HW4hgfhfghfghgÎncă nu există evaluări
- (1968) East Africa Law ReportsDocument909 pagini(1968) East Africa Law ReportsRobert Walusimbi91% (22)
- EA Law Reports 1960 Volume 1Document1.299 paginiEA Law Reports 1960 Volume 1Robert Walusimbi75% (4)
- (1962) East Africa Law ReportsDocument1.061 pagini(1962) East Africa Law ReportsRobert Walusimbi100% (1)
- Hydraulics Geotech2Document101 paginiHydraulics Geotech2Sigue Ramel HinayasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1970 East African Court of Appeal CasesDocument882 pagini1970 East African Court of Appeal CasesRobert Walusimbi100% (8)
- 19 1 PDFDocument6 pagini19 1 PDFآكوجويÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bills of Quantities For Standard Residential House - 2 Bedroom-Type A PDFDocument13 paginiBills of Quantities For Standard Residential House - 2 Bedroom-Type A PDFHammad SalahuddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- (1964) East Africa Law ReportsDocument990 pagini(1964) East Africa Law ReportsRobert Walusimbi67% (9)
- (1966) East Africa Law ReportsDocument792 pagini(1966) East Africa Law ReportsRobert Walusimbi91% (11)
- EA Law Reports 1963 Volume 1Document941 paginiEA Law Reports 1963 Volume 1Robert Walusimbi100% (14)
- Hydraulics Practice ProblemsDocument19 paginiHydraulics Practice Problemsgoddowon100% (1)
- ESAL AASHTO Design for Flexible PavementDocument2 paginiESAL AASHTO Design for Flexible PavementRobert Walusimbi100% (1)
- (1972) East Africa Law ReportsDocument760 pagini(1972) East Africa Law ReportsRobert Walusimbi83% (18)
- Airbus Reference Language AbbreviationsDocument66 paginiAirbus Reference Language Abbreviations862405Încă nu există evaluări
- 797B Commissioning Guidebook 07 (Procesos)Document65 pagini797B Commissioning Guidebook 07 (Procesos)wilmerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment I SKPU1123 1213 2Document4 paginiAssignment I SKPU1123 1213 2Rajab AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mixed TopicDocument105 paginiMixed TopicSigue Ramel Hinayas50% (2)
- Hydrau Geo 1Document8 paginiHydrau Geo 1Marichu Davillo GarbilesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flow Rate Calculation for PipeDocument146 paginiFlow Rate Calculation for PipeKarl Anne DomingoÎncă nu există evaluări
- PipeFlow PracticeProblemsDocument23 paginiPipeFlow PracticeProblemsFawaz PartoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Mechanics 1Document8 paginiFluid Mechanics 1Rj Jocson100% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics Assignment SolutionsDocument7 paginiFluid Mechanics Assignment SolutionsPraveen SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE EVALUATION EXAM No. 5 - Buoyancy, Equilibrium, Fluid Flows (Answer Key)Document5 paginiCE EVALUATION EXAM No. 5 - Buoyancy, Equilibrium, Fluid Flows (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Mechanics ExamDocument6 paginiFluid Mechanics ExamMatthewÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 3 SW5Document13 paginiModule 3 SW5hgfhfghfghgÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8b-Fluids FR Practice ProblemsDocument11 pagini8b-Fluids FR Practice ProblemsdilsharakaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- FlowMaster Course - Assignments - 10Qs - 2023 PDFDocument3 paginiFlowMaster Course - Assignments - 10Qs - 2023 PDFRamil EnsarÎncă nu există evaluări
- CEBoard Geohyd Nov2021Document14 paginiCEBoard Geohyd Nov2021under fakerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compre Hydraulics PSDocument5 paginiCompre Hydraulics PSAlvin Lualhati0% (1)
- TCW3101200904 HydraulicsDocument3 paginiTCW3101200904 HydraulicsTinashe Mazokera100% (1)
- prac prob HGE 2Document8 paginiprac prob HGE 2jeannechoiashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid B SheetDocument7 paginiFluid B SheetmustafaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uniform Open Channel Flow Problems 2019 20Document2 paginiUniform Open Channel Flow Problems 2019 20RaghuÎncă nu există evaluări
- HydraulicsDocument4 paginiHydraulicsHakdog GieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter Six Orifices Weirs and Tubes Practice ProblemsDocument14 paginiChapter Six Orifices Weirs and Tubes Practice ProblemsJerle ParondoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dams QuizDocument3 paginiDams QuizErwin Jed RachoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uniform Open Channel Flow Problem Sheet 2017 18Document2 paginiUniform Open Channel Flow Problem Sheet 2017 18Karan GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- National University of Science and Technology Faculty of Industrial Technology Department of Civil and Water Engineering Hydraulics ExamDocument3 paginiNational University of Science and Technology Faculty of Industrial Technology Department of Civil and Water Engineering Hydraulics ExamTinashe MazokeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Open Channel Hydraulics WorksheetDocument5 paginiOpen Channel Hydraulics WorksheetLemi100% (3)
- Group Assignment IDocument5 paginiGroup Assignment Ilelisagetachew90Încă nu există evaluări
- CENG 197 Problem Set 1 PDFDocument18 paginiCENG 197 Problem Set 1 PDFChristian Acter0% (1)
- Assignment RVF HJ 1Document1 paginăAssignment RVF HJ 1Abdel Samie MuhyadinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Mechanics Tutorial on Bernoulli EquationDocument2 paginiFluid Mechanics Tutorial on Bernoulli EquationMohammadDawodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fayoum University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Department Fluid Mechanics (1), SheetDocument2 paginiFayoum University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Department Fluid Mechanics (1), SheetMo 16Încă nu există evaluări
- Fluid B SheetDocument7 paginiFluid B SheetAmr Mustafa MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- HW Hydraulics (SetII) Ch3Document4 paginiHW Hydraulics (SetII) Ch3Zairah FranciscoÎncă nu există evaluări
- HW Hydraulics (setII) Ch3Document4 paginiHW Hydraulics (setII) Ch3Zairah Francisco100% (1)
- Section 3Document5 paginiSection 3Aduchelab AdamsonuniversityÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uniform Open Channel Flow Problems 2017 18 PDFDocument2 paginiUniform Open Channel Flow Problems 2017 18 PDFAbhyuday SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PNG University of Technology CE322 Hydraulics II Assignment 1Document2 paginiPNG University of Technology CE322 Hydraulics II Assignment 1Nickson KomsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compri QuestionsDocument2 paginiCompri QuestionsCheryl ChaudhariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problems ؤا 5Document4 paginiProblems ؤا 5Abdalla MemeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q.3) Any three_20231224_195046_0000Document5 paginiQ.3) Any three_20231224_195046_0000Swapnali MatsagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercises - Ii 13-12-2022Document5 paginiExercises - Ii 13-12-2022Gãlväñ FôxÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE 2040 Hydraulic Engineering Assignment ProblemsDocument4 paginiCE 2040 Hydraulic Engineering Assignment ProblemsAsh0% (1)
- Module 3 HW5Document14 paginiModule 3 HW5hgfhfghfghgÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2002ENG Final-Exam 2010 NathanDocument9 pagini2002ENG Final-Exam 2010 NathanMatthewÎncă nu există evaluări
- SUEZ CANAL University Fluid Mechanics AssignmentDocument3 paginiSUEZ CANAL University Fluid Mechanics Assignmentmahmoud EissaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.5 Application of The Bernoulli EquationDocument5 pagini3.5 Application of The Bernoulli EquationbabissoulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydraulics Final Exam QuestionsDocument3 paginiHydraulics Final Exam QuestionsHenok AsmamawÎncă nu există evaluări
- OrificeDocument36 paginiOrificeCamille Joy CucioÎncă nu există evaluări
- VR 17 FM and HM HA Questions - Part 1Document5 paginiVR 17 FM and HM HA Questions - Part 1bhanu tejaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CVE 372 Exercise Problems - Open Channel FlowDocument7 paginiCVE 372 Exercise Problems - Open Channel FlowDorry Magdy100% (1)
- Unit Operations IIDocument2 paginiUnit Operations IIChristian Mercado PagsinohinÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2019 Hyd MayDocument13 pagini2019 Hyd MayChantal Faye GacusanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, Vol. LXX, Dec. 1910 A Concrete Water Tower, Paper No. 1173De la EverandTransactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, Vol. LXX, Dec. 1910 A Concrete Water Tower, Paper No. 1173Încă nu există evaluări
- Scientific American Supplement, No. 365, December 30, 1882De la EverandScientific American Supplement, No. 365, December 30, 1882Încă nu există evaluări
- Kaweeri Project PDFDocument1 paginăKaweeri Project PDFRobert WalusimbiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Badminton: A New Scoring SystemDocument1 paginăBadminton: A New Scoring SystemRobert WalusimbiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Best Evaluated Bidder for Paving Parking YardDocument1 paginăBest Evaluated Bidder for Paving Parking YardRobert WalusimbiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculation For PH SolutionsDocument1 paginăCalculation For PH SolutionsRobert WalusimbiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Convert The Volume Counts To Equivalent Pcu Using The Factors Presented in The Table Below For Each IntervalDocument1 paginăConvert The Volume Counts To Equivalent Pcu Using The Factors Presented in The Table Below For Each IntervalRobert WalusimbiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moisture Dry Density 4.3 1.819 6.1 1.849 8.5 2.072 10.3 2.017 11.8 1.931Document4 paginiMoisture Dry Density 4.3 1.819 6.1 1.849 8.5 2.072 10.3 2.017 11.8 1.931Robert WalusimbiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Piano ScalesDocument3 paginiPiano ScalesRobert WalusimbiÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Full Stop: Punctuation ExplainedDocument7 paginiThe Full Stop: Punctuation ExplainedRobert WalusimbiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Makerere RainfallDocument25 paginiMakerere RainfallRobert WalusimbiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Determine Lime Content for Soil StabilizationDocument2 paginiDetermine Lime Content for Soil StabilizationRobert WalusimbiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 23+000 24+000 8+000 1st Layer 2nd Layer 3rd Layer 4th Layer 5th Layer 6th Layer 7th Layer 8th Layer 9th LayerDocument1 pagină23+000 24+000 8+000 1st Layer 2nd Layer 3rd Layer 4th Layer 5th Layer 6th Layer 7th Layer 8th Layer 9th LayerRobert WalusimbiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rodney Kajjabwangu Job Application Janitorial Post Fame Lounge KampalaDocument1 paginăRodney Kajjabwangu Job Application Janitorial Post Fame Lounge KampalaRobert WalusimbiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Civil TranspDocument8 paginiCivil TranspSumit VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moisture Dry Density 4.3 1.819 6.1 1.849 8.5 2.072 10.3 2.017 11.8 1.931Document4 paginiMoisture Dry Density 4.3 1.819 6.1 1.849 8.5 2.072 10.3 2.017 11.8 1.931Robert WalusimbiÎncă nu există evaluări
- My Notes For Design SoftwaresDocument4 paginiMy Notes For Design SoftwaresRobert WalusimbiÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Belkhayate Timing Indicator?: Buying/selling (Moments To Enter The Market) and Possible Reversal PointsDocument2 paginiWhat Is Belkhayate Timing Indicator?: Buying/selling (Moments To Enter The Market) and Possible Reversal PointsRobert WalusimbiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arts and Culture An Introduction To The Humanities Combined Volume 4th Edition Benton Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument22 paginiArts and Culture An Introduction To The Humanities Combined Volume 4th Edition Benton Test Bank Full Chapter PDFoutscoutumbellar.2e8na100% (15)
- Pirates and Privateers of the Caribbean: A Guide to the GameDocument25 paginiPirates and Privateers of the Caribbean: A Guide to the GameLunargypsyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Canberra As A Planned CityDocument12 paginiCanberra As A Planned Citybrumbies15100% (1)
- Gr.10 Music History ModuleDocument45 paginiGr.10 Music History ModuleKyle du PreezÎncă nu există evaluări
- As 91435Document3 paginiAs 91435api-271057641Încă nu există evaluări
- Ajwin Handbuch enDocument84 paginiAjwin Handbuch enEnzo AguilarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 63 Standard Integration: EXERCISE 256 Page 707Document9 paginiChapter 63 Standard Integration: EXERCISE 256 Page 707Khaerul UmamÎncă nu există evaluări
- ms360c Manual PDFDocument130 paginims360c Manual PDFEdgardoCadaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Admission Notice 2023-24Document2 paginiAdmission Notice 2023-24Galav PareekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bylaw 16232 High Park RezoningDocument9 paginiBylaw 16232 High Park RezoningJamie_PostÎncă nu există evaluări
- Texas LS Notes 19-20Document2 paginiTexas LS Notes 19-20Jesus del CampoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ut ProcedureDocument2 paginiUt ProcedureJJ WeldingÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2-STM Answers SokhaDocument6 pagini2-STM Answers SokhamenghokcÎncă nu există evaluări
- CVCITC Smoke-Free Workplace Policy & ProgramDocument2 paginiCVCITC Smoke-Free Workplace Policy & ProgramKristine Joy CabujatÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Psychotropic Drugs Under International ControlDocument32 paginiList of Psychotropic Drugs Under International ControlRadhakrishana DuddellaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Candida by Shaw, George Bernard, 1856-1950Document61 paginiCandida by Shaw, George Bernard, 1856-1950Gutenberg.orgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kamera Basler Aca2500-20gmDocument20 paginiKamera Basler Aca2500-20gmJan KubalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Building MassingDocument6 paginiBuilding MassingJohn AmirÎncă nu există evaluări
- CM - Scope of ServicesDocument3 paginiCM - Scope of ServicesMelvin MagbanuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subtracting-Fractions-Unlike DenominatorsDocument2 paginiSubtracting-Fractions-Unlike Denominatorsapi-3953531900% (1)
- Fundamental of Computer MCQ: 1. A. 2. A. 3. A. 4. A. 5. A. 6. ADocument17 paginiFundamental of Computer MCQ: 1. A. 2. A. 3. A. 4. A. 5. A. 6. AacercÎncă nu există evaluări
- India's 1991 Economic ReformsDocument5 paginiIndia's 1991 Economic ReformsLive AspireÎncă nu există evaluări
- EHT For Athletes For Brain HealthDocument2 paginiEHT For Athletes For Brain HealthTracey Jorg RollisonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Smartrac - Iolineug - r5Document66 paginiSmartrac - Iolineug - r5Darwin Elvis Giron HurtadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- AE3212 I 2 Static Stab 1 AcDocument23 paginiAE3212 I 2 Static Stab 1 AcRadj90Încă nu există evaluări
- Inventory of Vacant Units in Elan Miracle Sector-84 GurgaonDocument2 paginiInventory of Vacant Units in Elan Miracle Sector-84 GurgaonBharat SadanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- WFP-Remote Household Food Security Survey Brief-Sri Lanka Aug 2022Document18 paginiWFP-Remote Household Food Security Survey Brief-Sri Lanka Aug 2022Adaderana OnlineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laptop repair messageDocument3 paginiLaptop repair messagePonpes Manbaul MaarifÎncă nu există evaluări