Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Connection Design - Its Role in Steel Detailing
Încărcat de
Eduardo De Castro Cruz Jr.Descriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Connection Design - Its Role in Steel Detailing
Încărcat de
Eduardo De Castro Cruz Jr.Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
CONNECTION DESIGN: Its role in Steel Detailing
By: CSF Engineering Team
CSF Phils. Continuing Education Page 1
1.) Connection Components:
SSLN Short Slot Hole Normal to Load Direction
Hole Types:
SSLP Long Slot Hole Parallel to Load Direction
STD Standard Round Hole
OVS Oversized Hole
Note: Short Slot any or all of the plies is allowed
Long Slot only in one ply is allowed
a) Snug-tightened Joints Washers are not required
Washer (Ref: 2004 RCSC Specs Sec. 6):
Hex Bolts - Crystal Steel provides washer under the nut
Sloping surfaces
For slope not greater than 1/20, washer is not required; otherwise
provide ASTM F436 beveled washer
Generally, all channels and S-shape sections need to have ASTM F436
beveled washer
b) Pretensioned Joints and Slip-Critical Joints
Hex Bolts
Waiting for the inputs from Delmar to what method of
pretensioning is used.
TC Bolts
No additional washer is required for except when Long-
Slotted Hole and diameters greater than 1 A490 are used.
See also Table 6.1 for other washer requirements.
CONNECTION DESIGN: Its role in Steel Detailing
By: CSF Engineering Team
CSF Phils. Continuing Education Page 2
SC (Slip Critical)
Bolts:
Is not a type of Bolt. It is a connection type
TC and Hex Types of bolts commonly used. The use of TC
bolts is the easiest way to achieve SC connections.
Table 6.1. Washer Requirements for Bolted Joints with
Oversized and Slotted Holes in the Outer Ply
Hole Type in Outer Ply
ASTM
Designation
Nominal
Bolt
Diameter,
d
b
, in.
Oversized Short-Slotted Long-Slotted
A325 or
F1852
-1
1
AS TM F436
a
5/16-in. -thick plate
washer or
continuous bar
b, c
A490
> 1
AS TM F436 with 5/16 in.
thickness
b, d
AS TM F436 washer
with either a 3/8-in. -
thick structural
grade plate washer
or continuous bar
b
a
This requirement shall not apply to heads of round head tension-control bolt
assemblies that meet the requirements in S ection 2. 7 and provide a bearing circle
diameter that meets the requirements of AS TM F1852.
b
Multiple washers with a combined thickness of 5/16 in. or larger do not satisfy this
requirement.
c
The plate washer or bar shall be of structural-grade steel material, but need not be
hardened.
d
Alternatively, a 3/8-in. -thick plate washer and an ordinary thickness F436 washer
may be used. The plate washer need not be hardened.
CONNECTION DESIGN: Its role in Steel Detailing
By: CSF Engineering Team
CSF Phils. Continuing Education Page 3
Fillers for bolted connection equal to or less than in. may be used without
precaution.
Fillers (Ref: AISC 360-05 Specs Sec. J5):
2.)
Connections:
a) Generally, double angle connection has a greater capacity than Single Shear
plate connection
b) Rule of Thumb with a minimum of 3/8 plate/angle thickness
In ASD (Allowable Stress Design)
Shear Plate capacity = 10 x No. of Bolts
Double Angle capacity = 2 x 10 x No. of Bolts
Single Angle capacity = 10 x (No. of Bolts 1)
Note: For (SC) Slip Critical connections, multiply the above capacity by 0.6
In LRFD (Load and Resistance Factor Design)
To determine the strength of connection, multiply the above specified
strength by a factor 1.5
c) The maximum bolt gage for shear plate connection is 3 . Above this value,
the rule of thumb does not apply; the plate becomes an extended shear
plate.
d) Copes that are long and/or deep enough must be given attention.
Note that the connection plate/angle may encroach upon the fillet(s), as given
below (Ref: AISC 13
th
Edition Manual p 10-7).
k - - tf, in. encr. , in.
k
t
encr.
t
/
1
32 in.
w
f
Fillet Encroachment Chart
5/16
3/8
7/16
1/2
9/16
5/8
11/16
3/4
3/16
7/8
1
1/8
3/16
3/16
3/16
1/4
1/4
1/4
1/4
1/4
5/16
5/16
CONNECTION DESIGN: Its role in Steel Detailing
By: CSF Engineering Team
CSF Phils. Continuing Education Page 4
w
w
w 2w
w
Unless otherwise noted in the contract documents, angle legs shall be welded such
as shown below.
Welding of Connection Angles (Ref: AISC 13
th
Edition Manual p 10-8).:
Single Angle Welding:
Double Angle Welding:
Painting on Slip Critical Connection Interfaces (Ref: 2004 RCSC Specs. Sec.3.2.2
Commentary):
Unqualified paint on the faying surfaces
away from the edge of the bolt hole by shall
not be less than 1 in. nor the bolt diameter.
w 2w
w
CONNECTION DESIGN: Its role in Steel Detailing
By: CSF Engineering Team
CSF Phils. Continuing Education Page 5
Moment Connections:
Doubler Plate(s) (Ref: AISC Design Guide 13)
Unless otherwise noted in the contract documents, doubler plates shall be
welded as shown below.
For cases where stiffeners are not present, extend the doubler plate to the
distance of 2.5 times the column k-distance for directly welded flange or
flange-plated moment connection and 3 times the column k-distance plus the
end-plate thickness for an extended end-plate moment connection.
Column web
Transverse
stiffener
Web doubler
plate
(a) (c)
Fillet weld made
first, remaining
gap filled
(b) (d)
Figure 4-11 Common welded joint details at top and bottom edges with one
web doubler plate and a pair of transverse stiffeners.
CONNECTION DESIGN: Its role in Steel Detailing
By: CSF Engineering Team
CSF Phils. Continuing Education Page 6
If a complete-joint-penetration groove weld is used, this can be successfully
made with slight modification to the following AWS prequalified weld joint
designations:
(a) C-L1a or C-L1a-GF for web doubler plates that meet the thickness limitation
(1/4 to 3/8) and plate edges cut square
(b) TC-U4a (series) for plate thicknesses exceeding the qualifications of (a)
with beveled plate edges
Single-bevel-groove weld (4)
T-joint (T)
Corner joint (C)
Welding
Process
Joint
Desig-
nation
Base
Metal Thickness
(U = unlimited)
Groove Preparation
Permitted
Welding
Positions
Gas
Shielding
for
FCAW Notes
Root
Opening
Groove
Angle T
1
T
2
SMAW TC-U4a U U R =
1
4 = 45 All J, Q, V
R =
3
8 = 30 F, V, OH J, Q, V
GMAW
FCAW
TC-U4a-GF U U R =
3
16 = 30 All Required A, J, Q, V
R =
3
8 = 30 F Not req. A, J, Q, V
R =
1
4 = 45 All Not req. A, J, Q, V
SAW TC-U4a-S U U R =
3
8 = 30 F J, Q, V
R =
1
4 = 45
Tolerances
As Detailed As Fit Up
R = +
1
16, 0 +
1
4,
1
16
= +10 , 0 +10 , 5
Square-groove weld (1)
Butt joint (B)
Corner Joint (C)
Welding
Process
Joint
Desig-
nation
Base
Metal Thickness
(U = unlimited)
Groove Preparation
Permitted
Welding
Positions
Gas
Shielding
for
(FCAW) Notes
Root
Opening
Tolerances
T
1
T
2
As
Detailed
As Fit
Up
SMAW B-L1a
1
4 max R = T
1
+
1
16, 0 +
1
4,
1
16
All N
C-L1a
1
4 max U R = T
1
+
1
16, 0 +
1
4,
1
16
All
GMAW
FCAW
B-L1a-GF
3
8 max R = T
1
+
1
16, 0 +
1
4,
1
16
All Not
Required
A, N
CONNECTION DESIGN: Its role in Steel Detailing
By: CSF Engineering Team
CSF Phils. Continuing Education Page 7
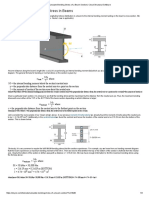
3.) Welding:
When load is applied perpendicular to the fillet weld, the strength of weld is
increased by a factor of 1.5. The factor decreases to 1.0 as the angle of load with
respect to the line of weld approaches to zero.
Fillet Welding
Fillet weld allowable root opening is 3/16 inch. (Ref: AISC 13
th
Edition Manual p 10-
151/AWS D.1.1 Sec. 2.2.5.2).
When connecting two plate elements, the minimum weld requirement is based
on the thinner part joined (Ref: AISC 360-05 Specs Table J2.4)
Minimum Weld Requirements
Fillet Weld Size + 1/4
Minimum Shelf Dimensions for Fillet Welds (Ref: AISC 13
th
Edition Manual p 8-18):
Use of Back gouge Waiting for Delmars input.
CJP Welding:
Use of Backing Bar
TABLE J2.4
Minimum Size of Fillet Welds
[b]
Material Thickness of Minimum Size of
Thicker Part Joined (in.) Fillet Weld[a] (in.)
To
1
inclusive
1
4
8
Over
1
4
to
1
3
2
16
Over
1
2
to
3
1
4
4
Over
3
5
4
16
[a] Leg dimension of fillet welds. Single pass welds must be used.
[b] See Section J2.2b for maximum size of fillet welds.
CONNECTION DESIGN: Its role in Steel Detailing
By: CSF Engineering Team
CSF Phils. Continuing Education Page 8
Permissible Offset in abutting member :
Note: An offset not exceeding 10% of the thickness of the thinner part joined, but in no case more than 1/8 in [3 mm], may be allowed as
a departure from the theoretical alignment.
Note: n correcting misalignment that exceeds the allowance, the parts shall not be drawn to a slope greater than 1/2 in [12 mm] in 12 in
[300 mm
].
CONNECTION DESIGN: Its role in Steel Detailing
By: CSF Engineering Team
CSF Phils. Continuing Education Page 9
4.) Brace and Beam Connections issues:
a) Moving Clips and Bolt
position along the
Beam Web in Shear
Connection
Clips and Bolts can be moved (deviate from the
design calcs) without any adverse effect on the
strength of the connection. This is also valid
for single plate shear connection.
b) Moving Clips and Bolts
position along the
Beam Web in Brace
Connection
To avoid connection constructability problem,
detailers, most of the time are forced to deviate
from the design calcs by moving or adjusting
clips and bolt positions. This has to be
confirmed with the design engineer: a re-calcs
maybe necessary.
Brace beam is designed for both Shear and
Axial forces. Slight change in Clips and Bolts
position affects stress distribution. Ideally, in
brace connection, the center of bolt group and
center of clips must coincide with the line of
force to eliminate moment due to eccentricity.
c) Changing the geometry
of gusset plates
If changing gusset plate geometry due to
constructability issue is inevitable, it has to be
verified with the design engineer for a possible
re-calcs. Gusset plate is shaped using Uniform
Force Method a method that determines the
location and distribution of forces such that no
moments are induced in column and beam
interfaces. Changing the dimension of gusset
plate in either interface creates eccentricity
and induces moment on the supporting
member (column or beam).
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Column Beam Seismic ConnectionDocument8 paginiColumn Beam Seismic ConnectionPrakash Singh RawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12 - AS - NZS 2327 COMPOSITE STRUCTURES - A NEW STANDARD FOR STEEL-CONCRETE COMPOSITE BUILDINGS - Hicks PDFDocument8 pagini12 - AS - NZS 2327 COMPOSITE STRUCTURES - A NEW STANDARD FOR STEEL-CONCRETE COMPOSITE BUILDINGS - Hicks PDFvodugu123Încă nu există evaluări
- Design Criteria and Structural Calculations - Service StationDocument32 paginiDesign Criteria and Structural Calculations - Service StationEduardo De Castro Cruz Jr.100% (2)
- Why 0.6W PDFDocument3 paginiWhy 0.6W PDFHyunkyoun JinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stiffner Design For Beam Column ConnectionsDocument84 paginiStiffner Design For Beam Column ConnectionsfabnameÎncă nu există evaluări
- ER-5861 SSDA Slotted Web Beam-To-Column Steel Moment Frame ConnectionDocument6 paginiER-5861 SSDA Slotted Web Beam-To-Column Steel Moment Frame Connectioncancery0707Încă nu există evaluări
- Design Slip-Critical Steel ConnectionDocument9 paginiDesign Slip-Critical Steel ConnectionKUROÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Drawing ManualDocument128 paginiEngineering Drawing Manualadnan100% (6)
- Solutions To Design of Weldments - BlodgettDocument80 paginiSolutions To Design of Weldments - Blodgettstudent_bl94% (17)
- Steel Connection DesignDocument16 paginiSteel Connection DesignHazza JumaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 7 BoltDocument38 paginiChapter 7 BoltRamesh P KoiralaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BookDocument814 paginiBookAboalmaail AlaminÎncă nu există evaluări
- All - Revised PDFDocument280 paginiAll - Revised PDFAbel MuluqenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Mechanics and Strength of Materials PDFDocument17 paginiEngineering Mechanics and Strength of Materials PDFAnu chavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factors Affecting Strength of Epoxy Repaired TimberDocument15 paginiFactors Affecting Strength of Epoxy Repaired TimberJosé PeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction in Steel DesignDocument18 paginiIntroduction in Steel DesignJade Carillo100% (1)
- Beam To Column ConnectionsDocument15 paginiBeam To Column ConnectionsKevinManuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aspects of Connection in Steel FramesDocument50 paginiAspects of Connection in Steel FramesChai Weng100% (2)
- ACI 318 08 Design of Retaining Wall With Counterfort Rev1Document4 paginiACI 318 08 Design of Retaining Wall With Counterfort Rev1KING ENG100% (2)
- Bolted Beam Column ConnectionsDocument16 paginiBolted Beam Column Connectionslael00Încă nu există evaluări
- Design of Steel BeamDocument19 paginiDesign of Steel BeamAnonymous tBhJoH5wgMÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2016 To 2010 Spec Comparison - Final PDFDocument42 pagini2016 To 2010 Spec Comparison - Final PDFFernando Alfredo Sepúlveda JiménezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basketball Court Design Final PresentaionDocument26 paginiBasketball Court Design Final PresentaionEduardo De Castro Cruz Jr.Încă nu există evaluări
- Steelwork Design Chapter 2 - Steelwork Connections HKCodeDocument49 paginiSteelwork Design Chapter 2 - Steelwork Connections HKCodeMa Man KinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wind Calculation Method 2 2015Document27 paginiWind Calculation Method 2 2015Eduardo De Castro Cruz Jr.71% (21)
- Introduction-Design-Guide 2Document16 paginiIntroduction-Design-Guide 2Sutha100% (1)
- Factors Designing Structural Joint ConnectionsDocument23 paginiFactors Designing Structural Joint ConnectionsCharlton CabagingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Joints in Steel Construction - Simple Connections - Part 15 PDFDocument5 paginiJoints in Steel Construction - Simple Connections - Part 15 PDFkakem61Încă nu există evaluări
- Friction Type Connections FullDocument64 paginiFriction Type Connections FullmohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bolted ConnectionsDocument17 paginiBolted ConnectionsNguyen KhoiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bolted Connections (Prying Force)Document16 paginiBolted Connections (Prying Force)Ivan Hadzi BoskovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.design of Steel StructuresDocument13 pagini3.design of Steel Structuresarju21Încă nu există evaluări
- Civil Structural Specifications - Rev 6 - EBHDocument160 paginiCivil Structural Specifications - Rev 6 - EBHEduardo De Castro Cruz Jr.Încă nu există evaluări
- Specific StepsDocument26 paginiSpecific StepsAbdul Hamid BhattiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plumbing Study GuideDocument43 paginiPlumbing Study GuidebillpetrrieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparison of Ansiaisc 360-05 To 1989 Asd SpecificationDocument32 paginiComparison of Ansiaisc 360-05 To 1989 Asd SpecificationH.Hamdan Neo100% (1)
- 6.design of Connections in Steel Building ConstructionDocument50 pagini6.design of Connections in Steel Building ConstructionNovember RainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flitch Plate BeamDocument1 paginăFlitch Plate Beamdnl_vicarsÎncă nu există evaluări
- SWD-CSA-A23.3-04 Shear Wall Design ManualDocument82 paginiSWD-CSA-A23.3-04 Shear Wall Design ManualYohan LimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Column Design Procedure PDFDocument26 paginiColumn Design Procedure PDFTamilÎncă nu există evaluări
- cp4 ConnectionDocument127 paginicp4 Connectionznyaphotmail.com100% (1)
- Welding Connection 2Document55 paginiWelding Connection 2dinu69inÎncă nu există evaluări
- Joints in Steel Construction - Simple Connections - Part 18 PDFDocument23 paginiJoints in Steel Construction - Simple Connections - Part 18 PDFkakem61Încă nu există evaluări
- ACI 530 QuestionsDocument3 paginiACI 530 QuestionsEduardo De Castro Cruz Jr.100% (1)
- Steel Design Project: Laterally Supported and Unsupported Beams, Columns, Column Base Plate, ConnectionsDocument24 paginiSteel Design Project: Laterally Supported and Unsupported Beams, Columns, Column Base Plate, Connectionsozzieastro96% (24)
- Chapter - 7 Part II STDDocument43 paginiChapter - 7 Part II STDBelkacem AchourÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 - Beam Column ConnectionDocument13 pagini8 - Beam Column Connectionhari1008108Încă nu există evaluări
- SlabsDocument29 paginiSlabsPimpa Mwiinga100% (2)
- Shear Walls - An OverviewDocument6 paginiShear Walls - An OverviewTabish IslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Galvanized Slip-Critical ConnectionsDocument2 paginiGalvanized Slip-Critical Connectionsaams_sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plumbing TerminologiesDocument24 paginiPlumbing TerminologiesEduardo De Castro Cruz Jr.Încă nu există evaluări
- Design of BoltsDocument18 paginiDesign of BoltsFunny & InformativeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bolt Is A Metal Pin With A Head Formed at One End and Shank Threaded at The Other EndDocument25 paginiBolt Is A Metal Pin With A Head Formed at One End and Shank Threaded at The Other Endgoutham sankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Model Analysis of Plane Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Structures and Solid Body Mechanics DivisionDe la EverandModel Analysis of Plane Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Structures and Solid Body Mechanics DivisionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laterally Loaded Piles PDFDocument16 paginiLaterally Loaded Piles PDFAnonymous Re62LKaAC100% (1)
- Structural analysis of 6-level modular accommodation unitDocument67 paginiStructural analysis of 6-level modular accommodation unitEduardo De Castro Cruz Jr.Încă nu există evaluări
- Concrete Design Excel SheetDocument16 paginiConcrete Design Excel SheetCleth Hiren Santos25% (4)
- Support of Deep Excavation in Soft Clay A Case History StudyDocument8 paginiSupport of Deep Excavation in Soft Clay A Case History StudyAlfredo A LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- SteelwiseDocument5 paginiSteelwiseΈνκινουαν Κόγκ ΑδάμουÎncă nu există evaluări
- E26.To2 Steel PDFDocument10 paginiE26.To2 Steel PDFAmolsingh100Încă nu există evaluări
- Cavity Wall Construction Guide: Insulation Methods, Advantages & DetailsDocument30 paginiCavity Wall Construction Guide: Insulation Methods, Advantages & DetailsTejas JoshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Weld Analysis For DummiesDocument6 paginiWeld Analysis For DummiesJosh SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- W14x43 To HSS6x6x1 - 2 Moment ConnDocument21 paginiW14x43 To HSS6x6x1 - 2 Moment ConnrajedmaglinteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Concrete Beam StructuresDocument26 paginiDesign of Concrete Beam StructuresVRKVRK10Încă nu există evaluări
- Design of Haunched Composite Connections For Long-Span Beam ConstructionDocument10 paginiDesign of Haunched Composite Connections For Long-Span Beam ConstructioncasanovavnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Limit state deflection and cracking in reinforced concrete structuresDocument17 paginiLimit state deflection and cracking in reinforced concrete structuresRadhikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Aluminum StructureDocument29 paginiDesign of Aluminum StructurerobcfuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seismic design loads and combinationsDocument15 paginiSeismic design loads and combinationsAmey Gudigar100% (1)
- Connection Types: Simple (Shear) ConnectionsDocument5 paginiConnection Types: Simple (Shear) Connectionsmahhor82_635643838Încă nu există evaluări
- Bondek I - Calculation Note - 1 Row of SupportDocument7 paginiBondek I - Calculation Note - 1 Row of Supporttrung1983Încă nu există evaluări
- Joint Penetration Groove Welds MemoDocument3 paginiJoint Penetration Groove Welds MemoRobertBostanÎncă nu există evaluări
- LX LyDocument3 paginiLX LyAnand AdkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- DOS Web Cleat ConnectionDocument31 paginiDOS Web Cleat ConnectionArfat PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Description: Welded Lifting LugDocument2 paginiDescription: Welded Lifting LugHomer SilvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 - Introduction To Steel DesignDocument19 pagini1 - Introduction To Steel DesignkrainajackaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Truss Problem 1Document2 paginiTruss Problem 1Eduardo De Castro Cruz Jr.Încă nu există evaluări
- RC Beam Problem - 102421Document3 paginiRC Beam Problem - 102421Eduardo De Castro Cruz Jr.Încă nu există evaluări
- Load cases defined for structural analysisDocument4 paginiLoad cases defined for structural analysisEduardo De Castro Cruz Jr.0% (1)
- Soil Stress Test PDFDocument1 paginăSoil Stress Test PDFEduardo De Castro Cruz Jr.Încă nu există evaluări
- Construction GuidelinesDocument20 paginiConstruction GuidelinesEduardo De Castro Cruz Jr.Încă nu există evaluări
- Analytical Geometry and Trigonometry QuestionsDocument4 paginiAnalytical Geometry and Trigonometry QuestionsEduardo De Castro Cruz Jr.Încă nu există evaluări
- Quantity Take-Off Sample ProblemDocument2 paginiQuantity Take-Off Sample ProblemEduardo De Castro Cruz Jr.Încă nu există evaluări
- Metal Roof Deck - VercoDocument87 paginiMetal Roof Deck - VercoEduardo De Castro Cruz Jr.Încă nu există evaluări
- Plumbing ToolsDocument13 paginiPlumbing ToolsEduardo De Castro Cruz Jr.Încă nu există evaluări
- Technical Specifications-Format (For Review)Document2 paginiTechnical Specifications-Format (For Review)Eduardo De Castro Cruz Jr.Încă nu există evaluări
- Structural Review ChecklistDocument4 paginiStructural Review ChecklistEduardo De Castro Cruz Jr.Încă nu există evaluări
- Metal Roofing FABRAL PDFDocument54 paginiMetal Roofing FABRAL PDFJuan100% (1)
- Mkii Soldiers: FormworkDocument2 paginiMkii Soldiers: FormworkHummadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fem Previous r07 Question PapersDocument9 paginiFem Previous r07 Question Papersyeswanthr100% (1)
- Re 1Document25 paginiRe 1kkklllyyyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1984 Malley - Popov - 1984 - Design Methodology (Continuation With Popov (1983) )Document21 pagini1984 Malley - Popov - 1984 - Design Methodology (Continuation With Popov (1983) )Saurabh TakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculate Bending Stress of A Beam Section - Cloud Structural SoftwareDocument3 paginiCalculate Bending Stress of A Beam Section - Cloud Structural SoftwaretereveÎncă nu există evaluări
- MTech Structural Engineering Question Bank on Advanced Steel StructuresDocument12 paginiMTech Structural Engineering Question Bank on Advanced Steel StructuresravirainbowÎncă nu există evaluări
- WC67K NC Hydraulic Plate Press Brake With E21 ControllerDocument6 paginiWC67K NC Hydraulic Plate Press Brake With E21 ControllerryneleeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.4. Stress StiffeningDocument12 pagini3.4. Stress StiffeningLe Anh TuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- FRP Strengthened RC Beam StudyDocument49 paginiFRP Strengthened RC Beam StudyCivil StructureÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Manual-RccDocument34 paginiLab Manual-RccRabin BhattaraiÎncă nu există evaluări
- American Wide Flange Beams - W BeamDocument8 paginiAmerican Wide Flange Beams - W BeamWicas SieteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deflection check calculations under 40 charsDocument1 paginăDeflection check calculations under 40 charsMyat Thu Zar KhineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study of Tension Field Beams (Wagner Beam) EquationsDocument5 paginiStudy of Tension Field Beams (Wagner Beam) EquationsRaj KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tips & More: For Economical DesignDocument4 paginiTips & More: For Economical DesignLuis Horacio Martínez MartínezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rollover Analysis of A Bus Using Beam and Nonlinear Spring ElementsDocument6 paginiRollover Analysis of A Bus Using Beam and Nonlinear Spring ElementsRamganesh TÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shear Retrofitting of RC Beams: February 2017Document9 paginiShear Retrofitting of RC Beams: February 2017kiranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Damping Coefficient CalculationDocument16 paginiDamping Coefficient CalculationVasile BrustureanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nov 2018 Ce Board Math Part 1 of 2 Pages 1 To 11 of 19 ChuaDocument12 paginiNov 2018 Ce Board Math Part 1 of 2 Pages 1 To 11 of 19 ChuaOwen Radaza Pirante100% (1)
- Analysis and Concrete Design of Structure With STAADDocument18 paginiAnalysis and Concrete Design of Structure With STAADGautam PaulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liceo de Cagayan University College of Engineering Prestressed Concrete Design Take Home ExamDocument1 paginăLiceo de Cagayan University College of Engineering Prestressed Concrete Design Take Home ExamdbircsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adam Christopulos Thesis (BRB Reference-BRB04)Document331 paginiAdam Christopulos Thesis (BRB Reference-BRB04)Anant ParghiÎncă nu există evaluări
- StaadProConnect PDS Letter 0218 HR FDocument2 paginiStaadProConnect PDS Letter 0218 HR FmikollimÎncă nu există evaluări