Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Aromatic Hydrocarbons
Încărcat de
Tarunesh PandeyDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Aromatic Hydrocarbons
Încărcat de
Tarunesh PandeyDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
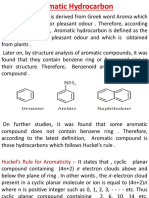
Benzene is the parent member of Aromatic compounds.
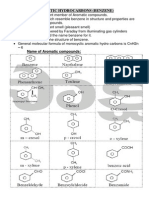
The compounds which resemble benzene in structure and properties are called aromatic compounds. Aroma means fragrant smell (pleasant smell) Benzene was discovered by Faraday from illuminating gas cylinders Mitcherlich proposed the name benzene for it. Kekule discovered the structure of benzene. General molecular formula of monocyclic aromatic hydro carbons is CnH2n 6 Name of Aromatic compounds:
AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS (BENZENE)
Methods of preparation of benzene : 1. Decarboxylation of sodium salt of benzoic acid :
2. Reduction of phenol :
3. Hydrolysis of benzene sulphonic acid C6H5 SO3H + HOH C6H6 + H2SO4 4. Polymerisation of Acetylene :
In the trimerisation of benzene, three pi bonds are broken and 3 sigma bonds are formed. 5. Commercial preparation of Benzene : Benzene is prepared on large scale from coal. Coal on destructive distillation gives 1. Coal gas 2. Coal tar 3. Ammoniacal liquor 4. Solid coke Coal tar is black, viscous, oily liquid with unpleasant smell. Coal tar is separated from other 3 fractions and subjected to fractional distillation.
The fractions collected at different temperatures and the aromatic compounds present in the respective fractions are Light oil or crude naptha upto 1700C Benzene, Toulene, xylene 0 Middle oil or carbolic oil 170 - 230 C Napthalene, Phenol, Pyridine 0 Heavy oil or cresote oil 230 270 C Napthalene, Cresol 0 Anthracene oil or green oil 270 400 C Anthracene, Phenanthrene Residue left is called pitch and it is used in road making and varnishes. Light oil fraction is treated with H2SO4 to remove basic impurities like pyridine and then with NaOH to remove acidic impurities like phenol, cresol etc. Light oil fraction on further fractional distillation gives 1) 1st fraction at 1100C 2) 2nd fraction upto 1400C These two fractions are remixed and further distilled to give benzene between 800C 810C. Physical properties of benzene: It is colorless liquid with pleasant smell Its B.P. is 800C It is lighter than water. It is insoluble in water but soluble in alcohol, ether etc. It burns with sooty flame due to high percentage of carbon. Chemical Reactions of benzene : Benzene is highly unsaturated, but it is less reactive because the benzene ring is stabilised by resonance. Benzene is expected to give normal addition reaction due to unsaturation. Because of unusual stability caused by resonance, it normally gives substitution reactions rather than addition reactions. Due to the presence of - electron cloud, benzene ring easily attracts electrophilies. Thus, benzene normally gives electrophilic substitution reactions and under special conditions it also gives certain addition reactions. Electrophilic substitution reactions: In these reactions, benzene acts as nucleophile. Electrophile can attack any of six positions of Benzene. Mechanism of electrophilic substitution:
When, electrophile attacks the benzene, positive charge is developed at ortho position and then delocalises to para position thus, ortho and para positions carry the charge in case of electrophilic attack.
In the nitration of benzene, nitration mixture is con. HNO3 and con.H2SO4 in 1:1 ratio . con.HNO3 acts as base in the nitration reaction. II. Addition reactions : Under special conditions, benzene gives certain addition reactions.
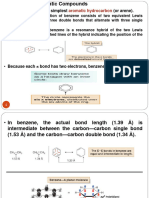
Structure of benzene : Its molecular formula is C6H6 and empirical formula is CH. The ratio of carbon to hydrogen indicates, it is highly unsaturated. But the behaviour of benzene resembles saturated compounds.
Thus benzene looks like unsaturated but behaves like saturated. Resonance : If the properties and structure of a compound can not be explained by a single structure but can be explained by two or more possible structures, it is called resonance and the different possible structures are called resonance structures or canonical forms. Chemically, resonance involves delocalisation (oscillation) of - electrons or lone pairs of electrons. Delocalisation is possible only if the - electron pairs, lone pairs or charge are at alternate positions. Because of resonance, some energy is lost by the compound and it is called resonance energy. Greater the number of resonance forms, more is the resonance energy and greater is the stability. Resonance structures are hypothetical and the real structure lies somewhere in between them. Kekules structures of benzene :
Dewars structures of benzene :
Kekules structures will contribute about 80% and Dewars structures will contribute about 20% towards the real structure of benzene. Benzene is stable because of resonance and greater resonance energy i.e. 150.48 KJ/mol. In benzene each carbon is sp2 hybridised. Due to resonance, all the six carbons are identical and all C C bond lengths are identical the C C bond length is 1.39 A which is intermediate to that of C C (single) and C = C (double), bond lengths. Number of sigma bonds :12 Number of - bonds: 3 Number of C C bonds: 6 Number of C H bonds: 6 Number of bonds involving sp2 sp2 overlapping: 6 Number of bonds involving sp2s overlapping : 6 Number of bonds involving sp2p overlapping : 0 Number of bonds involving P P overlapping : 3 C C bond order is 3/2.C H bond order is 1. The number of hybrid orbitals involved in the formation of benzene molecule is 18. The number of all types of orbitals (hybrid and pure) involved in the formation of benzene molecule is 30. The ratio of s character to p character of all the orbitals together, involved in the formation of benzene molecule is 2 : 3. The number of mono substituted isomers of benzene : 1 The number of di-substituted isomers of benzene: 3 The number of tri-substituted isomers of benzene : 3 Aromaticity or aromatic character: Aromatic compounds must possess the following properties. 1. They must be cyclic and planar. 2. All Carbons must be sp2 hybridised. 3. Alternate single and double bonds should be present. i.e. conjugation of electrons. 4. Delocalisation of electrons (Resonance) is required. 5. Normally they must undergo electrophilic substitutions. 6. They must obey Huckels rule : According to which aromatic compounds must contain (4n+2) etc.
Aromatic hydrocarbon
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- BenzeneDocument14 paginiBenzeneJueeli More100% (1)
- Aromatic Hydrocarbons Unit For SuccessDocument54 paginiAromatic Hydrocarbons Unit For SuccessN210084 CHOULA MANIKANTAÎncă nu există evaluări
- BenzeneDocument21 paginiBenzeneosamakhan8967Încă nu există evaluări
- Corrected Fundamentals of Organic ChemistryDocument71 paginiCorrected Fundamentals of Organic ChemistryDAM2120Încă nu există evaluări
- Benzene Aromatic CompoundsDocument14 paginiBenzene Aromatic CompoundsBook of Life fgfhfghfghfghÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 BenzeneDocument41 pagini1 Benzeneraj royelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aromatic HydrocarbonDocument45 paginiAromatic HydrocarbonPrashantÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15 CH242 Benzene & AromaticityDocument68 pagini15 CH242 Benzene & Aromaticityali mu'adÎncă nu există evaluări
- Benzene and Aromaticity: Based On Mcmurry'S Organic Chemistry, 9 EditionDocument68 paginiBenzene and Aromaticity: Based On Mcmurry'S Organic Chemistry, 9 Edition張湧浩Încă nu există evaluări
- STK 1233 Organic Chemistry 1: LU 5.1: Aromatic CompoundsDocument37 paginiSTK 1233 Organic Chemistry 1: LU 5.1: Aromatic CompoundsArllen Joy AlbertÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organic Chemistry - Chapter 15 Benzene & Aromatic CompoundsDocument9 paginiOrganic Chemistry - Chapter 15 Benzene & Aromatic CompoundsSairille ManejaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Benzene and Aromaticity: Based On Mcmurry'S Organic Chemistry, 6 EditionDocument72 paginiBenzene and Aromaticity: Based On Mcmurry'S Organic Chemistry, 6 EditionAdzimahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aromatic CompoundsDocument36 paginiAromatic CompoundsMaria Ruela Agodera SumogÎncă nu există evaluări
- OCR Chemistry NotesDocument10 paginiOCR Chemistry NotesJack WoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- BP301T Poc Unit IDocument34 paginiBP301T Poc Unit ISUBHASISH DASHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edited 2022 - Aromatic CompoundsDocument73 paginiEdited 2022 - Aromatic CompoundsedinapetermugaduiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrocarbon NotesDocument4 paginiHydrocarbon NotesSaumiaDevadasÎncă nu există evaluări
- AromaticsDocument70 paginiAromaticsEceDiril100% (1)
- Dienes & Aromatic Compounds, FNDocument60 paginiDienes & Aromatic Compounds, FNMuzahidul IslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 1Document26 paginiChapter 4 1Izzat Rafiq Mohamad MastamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aromatic CpdsDocument48 paginiAromatic CpdsDe- YoungÎncă nu există evaluări
- ARENES AND PHENOLS (Autosaved)Document85 paginiARENES AND PHENOLS (Autosaved)dodoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bab 10a Benzene and AromaticityDocument41 paginiBab 10a Benzene and AromaticityAl KahfiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aromatic Compounds: Y Y Y YDocument9 paginiAromatic Compounds: Y Y Y YCamille AdleÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Organic Chemistry - BenzeneDocument39 pagini3 Organic Chemistry - BenzeneIsuriy AdasuriyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aromatic CompoundsDocument25 paginiAromatic CompoundsElizabeth Vivar100% (1)
- Hydrocarbons PDFDocument19 paginiHydrocarbons PDFNeha ChaudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 11Document30 paginiChapter 11kanilkadianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aromatic ChemistryDocument16 paginiAromatic ChemistrysimbaleoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aromatic HydrocarbonsDocument50 paginiAromatic HydrocarbonsEdan Balao-asÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geometrical Isomerism: It is known that a carbon-carbon double bond is made up of one σ bond and one π-bond. The π-bond presents free rotation about the double bond.ThisDocument3 paginiGeometrical Isomerism: It is known that a carbon-carbon double bond is made up of one σ bond and one π-bond. The π-bond presents free rotation about the double bond.ThisKisha KhuranaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arenes and Aromaticity: Example: Alkyl BenzenesDocument24 paginiArenes and Aromaticity: Example: Alkyl BenzenesSteveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2.5 Aromatic CompoundDocument38 paginiChapter 2.5 Aromatic Compound0JTINGÎncă nu există evaluări
- Benzene and Aromaticity (2nd Year Ndaweni)Document54 paginiBenzene and Aromaticity (2nd Year Ndaweni)Mbali MazongweÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry II NotesDocument59 paginiPharmaceutical Organic Chemistry II NotesSayyeda SumaiyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aromatic Hydrocarbon NoteDocument41 paginiAromatic Hydrocarbon NoteBichitra GautamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Benzene: Milton Biswas Student Madhav University, Abu RoadDocument23 paginiBenzene: Milton Biswas Student Madhav University, Abu RoadMilton BiswasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aromatic Compounds - Chapter 14 Is Mostly Descriptive and Does NotDocument9 paginiAromatic Compounds - Chapter 14 Is Mostly Descriptive and Does NotRafid InamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thah The &tion: SeumdaryDocument28 paginiThah The &tion: SeumdaryMd HajjulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aromaticity PPT NotesDocument19 paginiAromaticity PPT NotesMadhurjya DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 05 АрениDocument42 pagini05 АрениМария МановаÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aromatic CompoundsDocument56 paginiAromatic CompoundsSeth Andrew Salih100% (2)
- Organic Chemistry For USTH Students Benzene and Aromatic SystemsDocument69 paginiOrganic Chemistry For USTH Students Benzene and Aromatic SystemsHoàng Hiệp100% (1)
- Part 3 HydrocarbonDocument25 paginiPart 3 Hydrocarbonaleenashaji.abraham1Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 Aromatic HydrocarbonsDocument34 paginiChapter 4 Aromatic HydrocarbonsAbdirashid Adam IsakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King: H C CH H C CHDocument12 paginiLecture Notes Chem 51B S. King: H C CH H C CHshivanna shivanna mÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aromatic CompoundsDocument30 paginiAromatic CompoundsMA Masum HossainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4Document51 paginiChapter 4Wai Kwong ChiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5.4 - Organic Independat OtesDocument5 pagini5.4 - Organic Independat Otesvarda9877Încă nu există evaluări
- CH 16Document42 paginiCH 16Kishore KishoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aromatic HydrocarbonsDocument8 paginiAromatic HydrocarbonsEbookGeekRNÎncă nu există evaluări
- O14 AromaticDocument11 paginiO14 AromaticDottie Landreth BaileyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aromatic Hydrocarbons - 1620192910Document40 paginiAromatic Hydrocarbons - 1620192910Sahisa MahatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organic Chemistry,: Benzene & AromaticsDocument41 paginiOrganic Chemistry,: Benzene & AromaticsRIZKI ALDINO AHMAD 1506723912Încă nu există evaluări
- Aromatic CompoundsDocument76 paginiAromatic CompoundsefatÎncă nu există evaluări
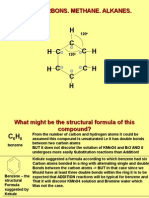
- C H H H H H: Hydrocarbons. Methane. AlkanesDocument14 paginiC H H H H H: Hydrocarbons. Methane. AlkanesDavidDavidovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 7-8 Term 3, AY 22-23Document31 paginiLecture 7-8 Term 3, AY 22-23LujainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aromatic Compound Theory - EDocument23 paginiAromatic Compound Theory - Ethinkiit100% (1)
- An Introduction to the Chemistry of Benzenoid CompoundsDe la EverandAn Introduction to the Chemistry of Benzenoid CompoundsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic Chemistry with AnswersDe la EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic Chemistry with AnswersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sheet ChemistryDocument3 paginiSheet ChemistryTarunesh PandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Inorganic Nomenclature FOR IIT-JEE ENTRANCE TEST by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atDocument5 paginiBasic Inorganic Nomenclature FOR IIT-JEE ENTRANCE TEST by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atmyiitchemistry88% (17)
- Aromatic Hydrocarbons (Benzene) : Name of Aromatic CompoundsDocument23 paginiAromatic Hydrocarbons (Benzene) : Name of Aromatic CompoundsTarunesh PandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 - Electro Chemistry (Level)Document16 pagini01 - Electro Chemistry (Level)Tarunesh PandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lect2 - 2009 1 API MFCDocument22 paginiLect2 - 2009 1 API MFCvarunpandeyenggÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE200 Exp 11Document6 paginiEE200 Exp 11Tarunesh PandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE200 Exp 10 PDFDocument8 paginiEE200 Exp 10 PDFTarunesh PandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alkyl HalidesDocument6 paginiAlkyl HalidesTarunesh PandeyÎncă nu există evaluări